.
Teething in a child is an important stage in the development of the body and at the same time a very difficult period.
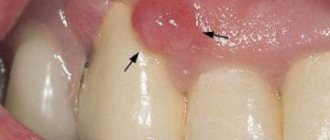
Swollen gums during teething in a child
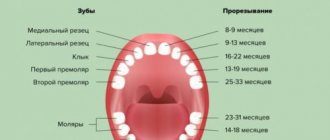
The first symptoms of teething appear at about four months. The lower incisors usually appear at 7–12 months. At 16 months, the child's lateral incisors should emerge. The canines and first molars will grow when the baby is 1.5–2 years old. By the age of two, all baby teeth will appear. Parents should consult a doctor if at the age of 6 months the child does not have a single tooth.
Complications of hematoma during eruption
The tumor in the form of a lump when erupting has a soft consistency, usually located above the teeth that are most actively involved in the chewing process - molars and premolars. When it appears, the gums turn blue throughout, and the cyst itself forms locally. Most often, pathology above the crown of the tooth does not require treatment. However, there are situations when a child needs help:
- addition of infection;
- the beginning of the inflammatory process;
- cone suppuration;
- bleeding;
- pain and discomfort while eating.
Inflammation of the cyst is observed in weakened children whose immunity is reduced. If left untreated, the process can spread to neighboring areas, which will provoke widespread inflammation.
You should consult a doctor if you have a hematoma in the following situations:
- education does not go away within 3 days;
- the baby has a fever;
- there is pain in the affected area (the child cries when the mother tries to touch the lump);
- deterioration in the general condition of the baby.
Treatment depends on the characteristics and size of the pathology, as well as the reason why the area above the crown turned blue. For large hematomas, an incision is made in the gum and the contents are cleared of pus. Abscesses are also removed surgically. In other cases, after a preventive examination, the doctor will tell the mother how to help the baby at home and take the baby under observation.
Symptoms of hematomas in the mouth, appearance, photo
The main symptom characteristic of bruises in the mouth is compaction in problem areas and darkening. The surrounding tissues swell, and the pain radiates to the jaw or cheek area. Possible high temperature, purulent inflammation, signs of poisoning. Experts divide the manifestations of this problem into two groups:
- The accumulation of blood in the gum gives it a bluish tint. The tissues increase in volume, the person feels uncomfortable and cannot close his mouth completely. There are problems with chewing and speech. These manifestations are typical for damage to dental pockets.
- If blood pours into the gum pockets, a round swelling is formed that spreads to the cheek from the inside. Such symptoms are often confused with gumboil: patients report severe pain, irritability, and abnormal facial shape. The gums tighten, fever and impairment are possible.
During the course of treatment, the disturbing symptoms are erased, and the cyanosis of the gums gradually disappears. A hematoma on the gum resolves in the same way as on other parts of the body. Usually the defect is corrected within a few weeks.
Causes of hematoma formation on the gums
When a hematoma is detected promptly, it can be treated with the help of a qualified dentist. Before starting therapy, it is necessary to identify the causes of the tumor. In adults, a hematoma is often the result of a cyst, mechanical trauma, flux and fistula. As for children, there are not so many reasons; a hematoma on a child’s gum can form due to teething or caries. But each individual cause has its own nuances and treatment methods.
When a baby is teething
At 6 months of age, the child begins the physiological process of teething. In children, this period usually passes calmly and practically painlessly, but there are also complications - blue gums during teething are one of them. Parents do not need to worry about the course of this physiological process, but they need to know what to do if complications arise. Most moms and dads are confused when they discover blackened tissue when their baby's baby teeth erupt.
At the time of teething, the baby becomes excessively capricious or lethargic, pulls various objects into his mouth, and loses appetite. The mouth begins to produce copious amounts of saliva, and the tissues swell slightly. A bruise on a baby’s gum can come in different sizes, shapes and shades:
- if the mucous membrane turns blue and a light and transparent ball appears on the gum, this is an indicator that a tooth will appear in the near future,
- blue tissue may be a result of injury, it is a kind of bruise or hematoma,
- when the formation has a red tint, this indicates the passage of the active stage of the inflammatory process, which requires appropriate treatment.
READ ALSO: why can a ball appear on the gum, and what does it mean?
When a baby tooth develops a crown and root, it begins to erupt. As the tooth passes from the bone to the surface, it passes through a layer of soft tissue. During such movement, the crown can press, rupture and injure blood vessels. By looking at how the gums become inflamed during teething in the photo, you can make a diagnosis yourself (for more details, see the article: photo of inflamed gums during teething in babies). If the lateral teeth are pressed down by the blood capillaries, then the tumor may be much larger than in the case of teeth in the frontal plane.
READ ALSO: treatment of gumboil in children
The consequences of such an injury may be the following:
- on the surface of the gums, a few weeks before teething begins, small bruises may form,
- the size of the blue discoloration directly depends on how large the blood capillary was damaged,
- when capillary vessels are damaged, small swellings can form, the color of which varies, ranging from bright red to dark blue.
READ ALSO: What should you apply to your gums when teething?
In an adult
Why does the gum above the crown turn blue in an adult? There can be many reasons for the color change. And it’s not a fact that the blue discoloration occurred due to an incorrectly installed crown. If purple gum occurs, then no toothpastes, solutions, powders, bleaches or mouth rinses will help. The only right decision would be to see a dentist. This disease is especially noticeable with lightened teeth, after the whitening procedure.
Experts in this field identify the following reasons why an adult’s gums begin to turn blue:
- Violation of prosthetic technology, due to which blood in the gums begins to stagnate. The consequence of this is a change in the color of the gums and the formation of bumps or hematomas. In this case, there is a significant lack of oxygen in the blood.
- After installing a metal-ceramic crown, the tissues surrounding the tooth may change color - purple spots are caused by oxidation of the metal. The patient probably received a low-quality metal-ceramic crown.
- Gingivitis. This is a complex inflammatory process in which the periodontal attachment remains in a stable position and is not disturbed, and the blueness of the gums occurs due to an increase in the active stage of the inflammatory process.
Atypical manifestation of tooth growth
Blue gums during teething are one of the unpleasant and painful symptoms. The tooth presses on the gum and then breaks through it. White or red and blue spots may appear on the gum, near the area where the tooth is emerging. The color of the spots will differ in different situations:
- White formations are observed shortly before the tooth appears. They look like small balls or compactions.
- Redness is accompanied by swelling and indicates that the tooth will erupt soon. The capillaries are damaged, and blood flows more actively to the gums. If the areas of redness are small, then the teething process is proceeding normally, but if the child’s entire mouth is red, then you should consult a dentist. This is a symptom of gum inflammation.
- Darkening of the gums also accompanies ruptured capillaries. If there are many vessels, then a hematoma is formed - this is a subcutaneous hemorrhage, an accumulation of blood in an area of the human body with closed injuries. A general swelling may appear on the child's face. Often it resolves on its own and does not require intervention. There are cases when there are so many breaks that the area turns black.
Blue gums during teething in a child
This dark or red spot is called an unerupted tooth cyst or eruption cyst. Changing gum color while teething is completely normal, but if the color has changed away from the new tooth, then there is cause for concern. Hurry to see a pediatric dentist if the bruise does not go away for a long time. It usually disappears within 3 weeks.
When a child is teething and blue or blackened lesions appear, parents often resort to home treatment and cover the gums with cooling and pain-relieving medicinal ointments. This is allowed, but only with the permission of a doctor.
The appearance of a hematoma
- The formation may be white in the shape of a ball, have a red tint or darken.
- Usually the bruise is located at the site of the new tooth. Size up to 2 cm.
- A hematoma appears before the tooth erupts and resolves within 3 weeks.
Pay attention if:
- dark spots appear throughout the child’s mucous membranes;
- there is inflammation, suppuration or infection in the affected areas;
- itching and bleeding gums;
- general painful condition of the child.
In this case, immediately go to a specialist to avoid disastrous consequences. Do not use traditional methods and remedies. They are ineffective and will cause more problems.
Causes and associated symptoms
A bruise on a child’s gums in most cases is a hematoma - hemorrhage in the tissue of the mucous membrane. This can only happen when the walls of the blood vessels are damaged and blood escapes beyond them. But the circumstances under which the walls of blood vessels are destroyed may be different:
| Cause of hematoma formation | Symptoms | Circumstances indicating the cause of hematoma formation |
| Teething | The gum in the area of the bruise is swollen, but looks healthy - its surface is smooth, shiny, there are no films, plaque, etc. There is a single bruise - no changes are observed in other areas. The boundaries of the hematoma are clear, the bruise does not “blur”. | Age of the child (5-24 months - the age of eruption of baby teeth, or 5-12 years - the age of changing teeth to permanent ones); increased secretion of saliva; the child's need to gnaw or chew inappropriate things or objects. |
| Gum injury | The gums are noticeably swollen, external damage may be visible on it - abrasions, scratches, dents, etc. The boundaries of the hematoma are unclear, it can increase in size after some time. When you press on the gum, blood or ichor may leak between it and the tooth. The gums (and often the tooth) are painful, become sensitive to mechanical and chemical irritants (injuries are characterized by increased pain when the mucous membrane comes into contact with sour or salty foods and drinks). Swelling of the gums and other injured areas intensifies after some time (usually the greatest degree of swelling reach the morning after the injury). | The appearance of a bruise is preceded by a fall, a blow (perhaps there was something on the child’s menu that he could try to chew or crack); child's complaints of pain in the gums; if a tooth was damaged at the time of injury, a chip or crack may be observed on its surface, a decrease in the height of the injured tooth compared to neighboring ones, its excessive mobility, unnatural position (rotation along a vertical axis, tilting inward or outward); on the side of the injured gum, there may be “mirror” injuries on the mucous membrane of the cheek or lip. |
| Bleeding disorders | Hematomas, as a rule, are multiple, of different sizes and shapes, and are not “attached” to any one area of the oral cavity. Most often observed in the area that is subject to the greatest mechanical stress (in front, in the area of the teeth that take part in biting food, and in areas at the end of the dentition - that take part in chewing food). Pain is not observed or is very mild. | diagnosed diseases and conditions in which blood clotting function is impaired; test results confirm a low platelet count; the child is undergoing treatment with drugs that have an anticoagulant effect; any disease accompanied by a strong increase in body temperature; taking NSAIDs as painkillers and antipyretics. |
In addition to the reasons listed, blue gums in a child may be an “optical illusion” due to a disease such as pulp necrosis. In this case, the dying and blackening of the pulp causes the entire tooth to change color. This process occurs in the direction from root to crown.
At the stage of necrosis when the neck of the tooth has blackened, the adjacent gum may look blue or gray due to the fact that the dark color of the neck is visible through it. As the necrotic lesions extend coronally, this effect disappears and it becomes apparent that the gingival color is normal.
Symptoms of teething in young children
The rudiments of future teeth are formed during intrauterine development at approximately 7 weeks of pregnancy. The time of their eruption is completely individual. Some babies start teething at 5 months, while others start teething at almost a year. The lower incisors are the first to erupt, this occurs at approximately 6-9 months. After which the upper incisors erupt almost immediately (7-9 months). The full “set” is assembled at 2-2.5 years.
As a rule, parents begin to look for the first signs in their newborn baby for 4 months. Moodiness and excessive salivation are immediately attributed to teeth. Symptoms of teething in infants:
- Swollen gums. During teething, the gums swell and increase in size (what can you apply to the gums when a child is teething?). This means that the crown is already coming out of the bone and heading upward. The baby begins to pull fingers and any foreign objects into his mouth. In the photo below you can see what swelling and swelling looks like.
- Excessive salivation in a child from 3 months. Increased secretion of saliva is aimed at softening and soothing the inflamed mucous membrane.
- Sleep disturbance and poor appetite. The cutting process is painful and therefore affects the child’s behavior. Constant discomfort prevents you from sleeping and eating peacefully.
- Temperature rises to 38-39 degrees. This is a kind of response of the body to a stressful situation. The temperature is brought down by children's antipyretics (syrups or suppositories); consultation with a pediatrician is required. Parents often confuse “dental fever” with infectious diseases, since these processes can occur simultaneously.
- Runny nose. Snot appears almost always (how can parents distinguish snot on their teeth from a cold?). The condition of the mucous membranes in the mouth and nasopharynx is interconnected. Swelling, swelling and inflammation of the oral mucosa indicates the possible presence of infection. A runny nose appears as a protective reaction of the body.
- Cough. It occurs when there is excess saliva in the mouth and throat, making it difficult to breathe freely. The child simply chokes on excess fluid. Dental cough is short-term in nature - no more than 2 days.
- Diarrhea or vomiting ( Teething Diarrhea: Treatment Options ). The child swallows more saliva than usual. Its chemical composition affects the functioning of the intestines, which causes loose stools.
- Excitability, moodiness. During this period, the baby becomes capricious, sleeps poorly, does not eat, and cries a lot. The deterioration of the emotional state is explained by pain, other discomfort, fatigue (the child does not sleep) and other unpleasant symptoms.
Teething is accompanied by lethargy and moodiness of the baby
It is important to remember that teething symptoms can easily be confused with an infectious disease. If fever, runny nose, cough or diarrhea persist for more than 2 days, you should immediately contact your pediatrician
Sleep disturbance
As you know, any pain is especially acute during sleep; this problem is not spared during the teething period. At night or during daytime sleep, the baby begins to be capricious, often wake up, cry, and sob.
Many parents have had to go through sleepless nights, because in this case it is extremely difficult to calm their child down, he refuses to eat, and is not soothed by rocking or lullabies.
In this case, pain-relieving gels, tablets or a chilled teether can help, which will temporarily soothe the pain and itching, giving the baby the opportunity to sleep peacefully for a while.
In rare cases, teething in babies is accompanied by the appearance of small hematomas on the gums - bluish-colored tubercles.
Doing anything to eliminate this symptom is highly undesirable; doctors do not recommend touching the tubercles or lubricating them with ointments.
The only effective way to speed up the process of hematoma resorption and reduce discomfort is to apply a cold compress to the inflamed area.
Another extremely unpleasant symptom is pain in the gums.
A small child is unlikely to be able to tell his parents that something hurts, so it’s worth paying attention to the baby’s behavior. The main feature of teething toothache is its direct connection with other organs and parts of the body: ears, chin, cheeks
The main feature of teething toothache is its direct connection with other organs and parts of the body: ears, chin, cheeks.
As soon as a sharp tooth comes as close to the gum as possible, nerve impulses spread and radiate to the ears and cheeks. The baby may begin to constantly rub his cheeks, pull his ears, or scratch his chin - this indicates that he is in severe pain.
As a result, the child becomes more irritable and restless. If such symptoms continue for a week or longer, but there are still no hints of a tooth, then parents should consult a pediatrician, because similar signs occur with otitis media.
If a child is cutting his first teeth, it is difficult to imagine this process without increased salivation.
The baby has not yet learned to quickly swallow the saliva accumulated in the mouth or spit it out, which leads to mucus running down the back of the throat. This may cause a frequent cough that coughs up.
Children especially often cough in their sleep, when snot and saliva caused by teething flow into the throat.
In this case, you can help the child by turning him on his side for better removal of mucus or by picking him up in an upright position.
Another way to understand that your baby is teething is to observe the discharge from the baby's nose.
A runny nose during teething occurs due to the fact that the baby’s immunity decreases, and saliva often gets into the nasopharynx.
To get rid of a runny nose, just rinse your nose with saline solution, sea salt-based drops, or use an aspirator.
If the baby still gets sick with a respiratory disease due to teething, then you should contact a pediatrician who will prescribe a good medicine for nasal congestion.
Treatment options
The choice of one or another treatment method is made by the attending dentist based on the diagnosis and visual examination of the small patient.
Treatment of a bruise from an injury on the gum
If you are sure that the bruise on the child’s gum is the result of an injury, you can try to provide the child with first aid, which consists of using the following methods:
- applying cold compresses to the injured half of the jaw;
- rinsing the mouth with decoctions of chamomile, calendula and sage.
If the bruise does not resolve for a long time (more than 5 days), and the main symptom is accompanied by severe pain and a rise in temperature, then most likely an inflammatory process has begun deep in the gums. In this case, medical assistance is necessary, which may include both the use of medications and surgical intervention.
Treatment of a cyst on the gum of a child
Treatment of the cyst is prescribed by the dentist after examining the child. There are two ways to do this:
- if the cyst formed during teething. In this case, experts recommend using special teething toys that help break the tissue and speed up the process of tooth extraction. If this technique does not help, and temperature is added to the main symptoms, it is possible to use the technique of dissecting the upper layer of the mucosa;
- if the cyst is large and accompanied by pain. In this case, the surface of the “blue bump” is usually dissected and the bloody or purulent contents are removed. After which the wound is treated and washed. In some cases, complete healing may require several visits to the dentist.
Medicines are usually not prescribed for blue gums. The only exceptions are those cases when the hematoma is accompanied by the formation of an abscess and an increase in body temperature.
Teether toy
Treatment of gingivitis
In this case, experts recommend resorting to plaque removal and prescribing anti-inflammatory rinses. In some cases, antibiotics are used as a rinse solution.
Painkillers
If the blueness is accompanied by severe pain, the child can be given painkillers. The most popular are “Ibuklin”, “Ibufen”, “Nurofen” and many others. In addition, you can use analgesics in the form of suppositories, for example “Viferon” - suppositories that, in addition to pain relief, have an antiviral effect. In addition, you can use special dental gels:
- "Holisal";
- "Kamistad";
- "Baby Doctor"
Treatment at home
It is worth understanding that any home therapy must be fully agreed with the attending dentist. In addition, sometimes experts themselves recommend supplementing the basic treatment with some folk recipes.
Mouth rinses
If the child is already quite independent and knows how to rinse his mouth, then this method will help to significantly speed up the process of relieving swelling and pain. The best options for preparing infusions are chamomile and calendula, which have an antibacterial effect.
To prepare the mixture you need:
- take 1 tablespoon of dried chamomile or calendula flowers;
- pour a glass of boiling water and leave for about an hour;
- Cool the infusion and strain.
You can rinse your mouth 4-5 times a day or after each meal.
Infusion of chamomile.
Teether toys
Such toys are sold in all pharmacies and children's stores. The teether contains distilled water inside, which allows you to significantly cool the toy by putting it in the refrigerator for a few minutes. This teether not only speeds up the process of teeth appearing, but also relieves swelling due to the cooling effect.
Applying compresses
Cold compresses help relieve swelling and inflammation. They have a special effect in the case of hematoma formation during dental surgery. To do this, you can take several lud cubes wrapped in a clean cloth and apply them for a while to the cheek or lip located above the injury.
How to reduce discomfort?
Methods to reduce discomfort during teething are different and their effect is individual. Often used:
- special anesthetic gels containing various local anesthetics (Dentinox, Kalgel, Bobodent and others);
- teethers (various models made of soft plastic, filled with water), which reduce discomfort but do not injure the mucous membrane;
- in case of severe anxiety and pain, the use of painkillers with ibuprofen and paracetamol (suppositories or syrup) in an age-appropriate dosage is allowed;
- the use of anti-inflammatory decoctions of medicinal herbs - treating the gums with a soda solution, a decoction of sage, chamomile or oak bark.
Why do gums become inflamed in children?
The cause of inflammation in a child’s mouth is improper hygiene. If you brush your teeth haphazardly, over time, bacterial plaque begins to accumulate on the enamel and in the gum area.
Pathogenic bacteria (Porphyromonas gingivalis) produce toxins and provoke an inflammatory process.
Factors contributing to gum inflammation in children:
- a sharp decrease in immunity, for example, during a cold;
- injury to the oral mucosa from hard or hot food;
- infection due to poor personal hygiene (children constantly put toys or dirty fingers in their mouths);
- malocclusion, crowding of the front teeth (while the gum tissues experience increased mechanical stress);
- vitamin deficiency (lack of vitamins C, E and B);
- hormonal imbalances (usually observed in adolescents).
In addition, childhood gingivitis can be a consequence of chronic illnesses, for example, diabetes, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or cardiovascular system.
How to distinguish cyanosis during teething from a symptom of the disease?
Often blue gums in infants indicate pathologies, including:
- Gingivitis. Inflammation of the gums occurs when the baby’s oral hygiene is insufficient and bacteria penetrate into the soft tissues. It differs from teething by bleeding, pain, and reaction to hot and cold stimuli.
- Stomatitis. With an infectious lesion of the oral mucosa, the gums only slightly change shade against the background of general redness. Additionally, there may be a coating or rash on the tongue, pain in the mouth, due to which the baby refuses to eat.
- Anemia. When hemoglobin in a child’s blood decreases to less than 110 g/l, a change in the tone of the skin and mucous membranes occurs. At the same time, pallor and a bluish tint are noticeable not only on the gums, but also on the skin, nails, and whites of the eyes. Additionally, with anemia, lethargy, brittle hair, loss of appetite, drowsiness, and peeling of the skin are observed.
- Cyst. Develops on the gum tissue above the crown of a baby tooth during eruption due to injury or careless medical examination. Initially, a hematoma is formed, around which a sheath of connective tissue is formed. The cyst looks like a blue bulge or purple bump (as in the photo). During its formation, the gum tissue peels off from the bone and a pocket is formed filled with purulent exudate and blood. If a pathology is detected, you should consult a dentist or pediatrician.
Possible pathologies
If a child’s gums turn blue or black, this may be a consequence of anemia, gingivitis and stomatitis, and not the actual eruption of baby teeth.
If the black or blue areas of the gums are more than 2 cm, you need to see a doctor. A black hematoma indicates stagnant blood. A bruise this large can cause high fever and pain. Treatment in this case will be an incision in the blue gum, from which the blood is released. It is necessary to ensure that it does not become infected and suppuration begins.
Causes and symptoms of gum discoloration independent of tooth growth:
- A symptom of anemia is a change in the color of mucous membranes. This disease is caused by a decrease in hemoglobin levels. Other signs: decreased appetite and cold extremities. A bluish tint will appear near the lips, eyes and nose. This condition occurs in children due to a lack of iron in the body.
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of a child. Usually manifests itself with poor oral hygiene. The gums turn blue, bleed and itch. When teeth come in, the gums are injured, and the wound can fester.
- With stomatitis, not only the gums are blue, but also the entire oral cavity. Stomatitis is similar to gingivitis and develops against the background of a child’s weakened immune system. Ulcers may appear.
Blue gums during teething
The physiological process of teething in children begins on average at 6 months. For some, teeth appear unnoticed and painlessly, while for others, various symptoms and complications arise, for example, blue gums when teeth erupt.
Young parents should not be afraid of the appearance of their first teeth, but they need to know what to do correctly if complications arise.
During the eruption of baby teeth, the child becomes restless, lethargic, loses appetite, and puts various objects into his mouth.
Salivation in the mouth increases, gums become swollen and inflamed. Blue, red or white formations may appear on the mucous membrane:
- A light ball that shines through the gum is a tooth and indicates the immediate appearance of a tooth.
- Red gum indicates acute inflammation and requires anti-inflammatory treatment.
- Blue formations are a complication - a hematoma or bruise.
The hematoma can be round or oval, inside the gum or protruding above its level, and have a purple, blue, burgundy and even black color.
Why do gums turn blue when teething?
One of the complications during teething is the occurrence of a hematoma due to injury to a blood vessel.
Baby teeth begin to erupt after the crown has formed and the root of the tooth begins to grow. During the movement of the tooth from the bone tissue to the surface of the gum, the tooth passes through the thickness of the soft tissue and during this it can press, injure or rupture small blood vessels. As a result, the following clinical picture may occur in the oral cavity:
- 2-3 weeks before a tooth erupts, a bruise may appear from the mucous membrane on the baby’s gum.
- The size of the submucosal hemorrhage will depend on the size of the damaged vessel: the larger the capillary, the larger the bruise.
- When pressure is applied to a blood vessel, mucous swellings of various colors from bright red to dark blue can occur.
When lateral teeth (molars) appear, the bruise on the baby’s gums will be more massive than in the frontal area.
Treatment of bruises on the gums during teething
The appearance of a bruise on the gum when teeth are cutting in 90% of cases does not require treatment. The coloring of the gums can last up to 2-3 weeks until the tooth appears. In most cases, the hematoma or hemorrhage resolves over time. You should consult a doctor in the following cases:
- the presence of a large hematoma more than 2 cm in diameter;
- long-term existence of blue gums (more than 3 weeks);
- hematoma suppuration;
- in case of acute pain;
- The baby's body temperature is more than 38 degrees.
To eliminate pain and speed up the appearance of teeth, use:
- anesthetic gels (for example, Cholisal);
- teethers;
- massage;
- medications;
- traditional medicine.
If there are formations on the gums, do not try to open them or burst them yourself, as there is a high probability of introducing microbes and developing further complications.
How to relieve a baby’s condition if his gums are swollen and painful?
When the gums are swollen and unpleasant symptoms appear, many pharmacological innovations come to the aid of children and parents that relieve pain and discomfort. You can use traditional medicine recipes that also helped our mothers and grandmothers.
First of all, you need to get a teething toy. It is first placed in the refrigerator or freezer - the cold rubber toy dulls the pain and safely scratches the gums.
If symptoms are intense, especially when the child does not sleep at all and cries a lot, a variety of gels, suppositories or suspensions are suitable.
Homeopathic medicines are popular and should reduce general symptoms.
Medicines
Medicines for children are divided into the following groups:
- local painkillers;
- complex homeopathy;
- painkillers for oral administration.
Local analgesics are presented in gels; almost all modern parents have them in their medicine cabinet. The advantages of such gels include convenient application to the gums, quick effect and antiseptic properties. During the first minute, the mucous membrane “freezes” and becomes insensitive. Among the disadvantages are the short duration of the effect and unpleasant sensations in the mouth. However, the pain relief effect is sufficient until the child falls asleep.
The most famous gels:
- Kamistad Gel (Baby);
- Kalgel;
- Dentinox Gel-N;
- Holisal.
Homeopathic medicines act comprehensively. They affect the entire process as a whole, speed it up and alleviate the baby’s condition. Such products contain only natural and safe ingredients, so they are suitable even for the smallest children. They must be used strictly according to the instructions.
Homeopathic medicines:
- Viburkol - candles;
- Dantinorm Baby - drops (composition of Dantinorm Baby and instructions for use);
- Dentokind - tablets (instructions for use of the drug Dentokind);
- Pansoral - gel, etc.
Analgesics and antihistamines intended for internal use are prescribed only by a doctor. Unlike the first two groups, taking these medications is indicated in the presence of serious symptoms or complications:
- Fenistil drops (from birth) and Parlazin (after 1 year) are antihistamines. They are prescribed to relieve and reduce swelling of the mucous membranes in the mouth and nasopharynx, and eliminate itching or burning of the gums. Antihistamines help reduce runny nose and inflammation.
- For severe pain or fever, taking antipyretic drugs (they also act as painkillers) is recommended. Children's (necessarily age-appropriate) suspensions or suppositories based on ibuprofen or paracetamol (Nurofen, Panadol, etc.) are suitable. Before starting to take the medicine, you should consult your pediatrician. He will assess the need for its use and also select the most suitable product.
Folk remedies
- Tea based on chamomile, lemon balm, lavender and catnip will calm the baby and reduce pain. Dry ingredients must be mixed in equal proportions. Pour a tablespoon of the prepared mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave for 10-15 minutes, then strain. You can drink this tea throughout the day.
- Wipe your mouth with a strong decoction of chamomile or make compresses. If the decoction is diluted with water, it can be drunk as tea.
- Clove oil helps children and adults in dentistry. It disinfects and relieves pain. Pure clove oil will burn, so it needs to be diluted with olive or almond oil in a 1.5:1 ratio. Treat the inflamed area with the resulting solution.
- For rubbing or compresses, a decoction of sage, calendula, and oak bark is used. You can use one component or prepare a mixture. The ingredients relieve inflammation, disinfect, reduce pain and itching.
Chamomile tea is a very effective teething soothing remedy.