Diseases of the oral mucosa include not only those familiar to every dentist, but also diseases such as candidiasis, cheilitis, and stomatitis. The oral mucosa is also important for assessing the general condition of the patient and his immunity. Indeed, often the oral mucosa is almost the first place of manifestation of infectious diseases, such as syphilis, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, diphtheria, and gonorrhea. And here the dentist should not only accurately diagnose the infectious disease in order to help the person, but also warn himself so that cross-infection does not occur.
Organization of treatment
With the development of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity, treatment has two directions - general and local.
General treatment
General treatment of the oral mucosa is carried out in case of severe disease. Patients are prescribed drugs for oral administration in the following groups:
- antibiotics – Amoxiclav, Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole;
- antiviral drugs - Zovirax, Acyclovir;
- vitamins – vitamin complexes or monovitamins in injections;
- means for normalizing blood microcirculation - Trental, Pentoxifylline;
- immunostimulants – Levamisole.
General therapy aimed at restoring the throat mucosa necessarily involves correction of the primary disease. In accordance with the diagnosis, antihistamines, chemotherapy drugs, etc. may be indicated. General treatment to restore the condition of the mucous membrane is prescribed on an individual basis.
Local treatment
The inflammatory process in the mouth requires treatment of the lesions. The ulcers are washed with a soda solution; infusion solutions of sodium bicarbonate can also be used, which can be bought in pharmacies in 200 ml glass containers. It is forbidden to use cotton wool to treat ulcerations, as its fluff may remain in the wound, causing increased inflammation.
After treatment with solutions, the ulcers are washed with antiseptics - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, and a slightly diluted solution of potassium permanganate. Antiseptics help reduce the intensity of inflammation and quickly achieve the onset of regeneration.
After antiseptics, the ulcers are treated with healing preparations that soften and moisturize the lesions. This is Solcoseryl, sea buckthorn oil. In case of severe pain, anesthetics - Kamistad or Lidocaine - can be used for recovery. For viral stomatitis, the use of Acyclovir is indicated.
How to restore lost teeth
The loss of one tooth in old age provokes the loss of the rest. After the loss of one tooth, the dentition closes and shifts, the teeth and bite become crooked, and this gradually leads to the loss of the remaining teeth. Lack of teeth affects the appearance, health of the entire oral cavity, food intake, and psychological comfort of a person. This problem needs to be solved - the sooner the better. If teeth have been extracted or fallen out, their deficiency can be filled with dentures or implants.
Let's look at their types:
• Removable denture. Replaces missing teeth, imitating real ones. It can be complete (used when there is a complete absence of teeth on one or both jaws) or partial (used when several teeth are missing). • Prosthesis on implants. Dental implants are inserted into the jawbone to provide greater stability. • A permanent restoration implant solves the problem by using individual crowns or bridges that support natural teeth.
Main reasons
The reasons why the mucous membrane in the mouth hurts and focal inflammation forms in the mouth include:
- Caries and other pathologies of the gums and teeth in the absence of timely treatment.
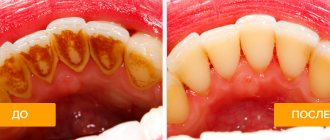
- Tartar.
- Diabetes.
- Wearing incorrectly fitted dentures that injure the mucous membranes.
- Reaction to the use of certain medications.
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Smoking.
- Alcohol abuse, since alcohol greatly irritates the mucous membrane of the mouth with constant contact.
- Chronic lesions of the stomach.
- Problems in the functioning of the immune system associated with overwork, constant stressful situations in life, lack of sleep or past illnesses.
- Hormonal problems.
- Damage to the oral mucosa by bacteria or viruses - laryngitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, etc.;
- Frequent surface injury. For example, when actively brushing your teeth with a hard brush or consuming very hard foods.
- Lack of nutrients in the body.
- Symptoms of anemia.
- HIV.
- Insufficient washing of products, after which pathogenic microbes can enter the oral cavity.
- Leakage of dental crowns, which provokes the constant proliferation of bacteria in the mouth.
- Self-medication with drugs that enhance saliva production.
- Dehydration due to large blood loss due to vomiting or diarrhea.
- Influenza, scarlet fever or herpes.
- Lack of iron, vitamin B and zinc in the diet.
- Chemical burn of the oral cavity.
- Toothpaste containing sodium lauryl sulfate. This substance irritates the mucous membranes.
- Oncology of the neck, pharynx, throat, larynx.
Toothbrush
An important requirement is its compliance with the anatomy of the oral cavity. A slightly curved and narrow toothbrush head is considered the most suitable option. As for its bristles, it is better if it is presented in the form of sparsely spaced tufts, because too thick bristles, on the contrary, make it difficult to care for your teeth, reducing the effectiveness of cleansing. Don’t forget about the hygiene of the brush itself: after each use, it should be rinsed under running water and stored in a separate glass with the bristles facing up. To maintain high cleaning power and prevent the accumulation of microorganisms, you should change the brush once a month.
Organization of diagnostics
If a person goes to the hospital with complaints of discomfort and pain in the oral cavity, the doctor first conducts a survey to diagnose associated lesions. Then tests are prescribed:
- allergy test;
- bacterial culture from the site of inflammation to identify the type of infection - viral, fungal or bacterial.
A general blood test and blood serum test are required. If necessary, a referral for diagnostics from specialists of a different profile is issued.
Only after a full examination, identification of the etiology and type of the disease is it prescribed how to treat inflammation in the mouth. Independent actions will only aggravate the condition and provoke complications.
- Inflammation of the oral mucosa: causes and treatment
Dental irrigators
Externally, they look like an electric toothbrush, which is equipped with a special tip that performs a kind of hydromassage. Water supplied through it under pressure cleanses the tooth surface and hard-to-reach places, including performing cleansing procedures on the cheeks, tongue and gums.
It should be remembered that taking all preventive measures does not relieve you of the need for regular monitoring by a dentist.
Symptoms of the problem
In almost any form of stomatitis, despite the difference in causes, the symptoms remain similar. The clinic for inflammation of the oral mucosa is as follows:
- severe pain and formation of suppuration;
- discomfort, pain in the gums, preventing you from chewing food or taking a sip;
- swelling, swelling, irritation of the mucous membranes of the lips and cheeks;
- rise in body temperature;
- discomfort that occurs when drinking hot food;
- foci of redness and purulent plaque;
- ulcers and inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa;
- itching;
- persistent dry mouth, microflora disturbance;
- profuse drooling;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- loss of taste perception;
- pain and discomfort while speaking.
When inflammation in the oral cavity occurs due to poisoning, pigment spots appear on the gums, and a metallic taste is present. Symptoms of general malaise may also develop: weakness, digestive problems, apathy, numbness of the tongue.
With mechanical injuries, inflammation is always accompanied by hematomas.
What does burning and tingling of the tongue indicate?
Burning, tingling of the tongue may indicate developing glossalgia. The causes are usually injuries to the tongue or mucous membranes in the mouth, improper placement of fillings or dentures.
Glossalgia is a functional disorder of the nervous system. Usually the disease develops against the background of problems with the gastrointestinal tract or liver.
Similar symptoms accompany another pathology – leukoplakia. These are lesions of the mucous membranes in the mouth, caused by smoking and alcoholism. This is how mucous surfaces react to toxins in cigarettes and alcoholic drinks. Leukoplakia also occurs in case of a lack of vitamin A, with a genetic predisposition. As a rule, the pathology has a chronic course.
Inflammation due to smoking
This pathological condition should be considered separately. It often occurs in heavy smokers with extensive experience. Despite treatment, it will not be possible to completely get rid of the disease if you continue the bad habit. Nicotine is much stronger and kills all the beneficial components entering the body.
Smokers are diagnosed with stomatitis several times more often than non-smokers. Therapy involves regular rinsing and treating the oral mucosa with special products. Treatment will not give results if you do not give up the bad habit.
How to brush your teeth
Good hygiene is of great importance for older people. Retirees who have good oral care experience fewer dental problems. If necessary, teach your elderly relative how to care for their teeth and select suitable hygiene products for them.
Brushing your teeth should be done in the morning and evening. Cleansing lasts at least 3 minutes. It is better to choose a fluoride toothpaste: it restores the balance of minerals in teeth and reduces the risk of developing caries.
It is necessary to follow the correct technique for brushing teeth - from the gums to the cutting edges, to clean both the outer and inner surfaces. Hard-to-reach places and the space between teeth should be thoroughly cleaned.
It is important to take into account age-related characteristics: the gums shift, the necks of the teeth become exposed, and the distance between the teeth increases. For these reasons, teeth must be brushed carefully to avoid damage.
After cleaning, it is useful to use a rinse aid. Rinsing will prevent the development of caries and other dental problems, and eliminate bad breath. The mouthwash should be pleasant and not too spicy. You can choose the right one at a pharmacy or store (“Forest Balsam” and others).
In addition to brushing your teeth twice a day, it is recommended to use dental floss or a special brush at least once a day. These products will help you get rid of pieces of food between your teeth. Rinsing is also recommended after each meal.
Even if a person has no teeth, he needs to wash his mouth regularly to prevent dental problems. If you don’t have a rinse aid, you can use regular warm water with a small amount of salt dissolved in it. It is important to rinse your mouth thoroughly. The procedure can be performed before bed after brushing your teeth.
Healthy eating in old age
The diet of an elderly person should be varied and healthy. The need for minerals and vitamins increases with age. Vitamin complexes can be used. Calcium is especially needed, which accumulates poorly and is lost from the period of maturity. Due to its deficiency, teeth and bones become fragile. Vitamins A, C, D and others are important.
You should limit your consumption of sweets. A good alternative is a glass of water with a tablespoon of honey. This drink can replace morning or evening tea. It will prevent dental diseases and help treat existing problems.
Before drinking a cup of coffee or tea in the morning, eat a small piece of solid food.
Do not mix very cold and hot foods.
Special attention should be paid to the nutrition of people without teeth. The oral cavity of such pensioners is vulnerable, so the food must be suitable.
When creating a menu and preparing food for elderly people without teeth, you need to follow these rules:
• Eat soft foods. Examples: cream soup, fresh bread, bananas. Rough food and large pieces can be chopped, include more drinking food in the diet, or choose recipes with soft dishes. • Food for older people without teeth should be healthy and balanced. Proteins, fats and carbohydrates are important in the diet. You should not replace healthy foods with only easy-to-digest ones. Yogurt will not be able to nourish you in the same way as meat - both products are healthy and necessary, only in the second case careful processing and grinding is important. • Consult your doctor when planning your diet. He will help you choose a menu and create a diet, tell you what to include in your diet and what to exclude from it. A nutritionist will select a suitable diet and create a nutrition plan. • Planning will help you create a varied and healthy diet. Make a list of groceries and dishes for your relative for the week, select suitable recipes. For example, you can plan oatmeal for breakfast, stew and soup for lunch, and a vegetable salad for dinner. A good snack option is healthy smoothies. • Use suitable kitchen equipment. A food processor will help grind various solid foods, a blender will help create purees and liquid smoothies.
It is very important for an elderly person to monitor the condition of the oral cavity. Maintaining hygiene, regular visits to the dentist, timely treatment of diseases and prevention of dental problems will help maintain oral health for life.
Features of the structure of the organ
The palate is the upper wall of the oral cavity, which acts as a kind of partition separating it from the nasal cavity. It consists of a hard and soft part. The hard or anterior part occupies 2/3 of the total area of the organ, so when they say that the palate hurts, they most often mean this section.
The palate takes an active part in chewing food. In addition, it is an important part of the articulatory apparatus. The surface of this organ is covered with thin mucous membrane with a large number of nerve endings. For this reason, when the palate of the mouth hurts, the discomfort is quite intense.
Aphthous stomatitis: symptoms
If you suspect you have aphthous stomatitis, the symptoms are quite similar. A day or two before the onset of ulcers, patients usually notice a slight burning sensation in some areas of the oral mucosa. A little later, one or 2-3 clearly defined ulcers (aphthae) appear, covered with a necrotic coating of a gray or yellowish tint. The ulcers are round in shape and their diameter is usually no more than 1 cm, and along the perimeter they are surrounded by an inflammatory red halo.
Ulcers of this size usually heal within 10 to 14 days without scarring. However, in 10-15% of patients, the diameter of the ulcers may exceed 1 cm, and sometimes they can even reach 2-3 cm in diameter. Ulcers of this size are usually deeper than ulcers smaller than 1 cm (which may cause the ulcer border to appear raised). Healing of such ulcers usually lasts up to 6 weeks, and most often with the formation of scar tissue.
Important: the typical localization of ulcers is on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and the inside of the lips, on the soft palate (Fig. 7-8), tonsils, as well as the lower and lateral surfaces of the tongue. This localization is due to the fact that ulcers in aphthous stomatitis occur primarily on “non-keratinized” areas of the oral mucosa, i.e. where keratinization of the mucosal epithelium does not occur.
Less commonly, ulcers can occur on the keratinized mucous membrane (hard palate, dorsum of the tongue, tightly attached alveolar gum around the teeth) - this may be a signal of autoimmune diseases or HIV infection. In contrast to aphthous stomatitis, keratinized gums are affected precisely in herpetic stomatitis, which can also be a distinguishing feature of these two main forms of stomatitis from each other.
Foci of aphthous stomatitis on the soft palate: photo
→ Symptoms of herpetic stomatitis
How to care for dentures
Dentures require regular careful care. Elderly people are advised to remove dentures after eating, clean off food debris and plaque with a toothbrush, then rinse thoroughly with water.
Cleaning tablets and denture powders can be used once a week. They are good at removing stains that regular toothpaste cannot deal with, and also disinfect dentures. You can use a special antiseptic, which must be dissolved in water for use. You can purchase a ready-made solution.
For additional care, you can use antibacterial tablets that will fight bacteria and get rid of bad breath. Such tablets are dissolved in a glass of water (one at a time) and the prosthesis is immersed in the solution for 15 minutes.
At night, dentures are stored in a suitable container with cold water.
If removable dentures move when chewing food, they need to be fixed with special glue. If possible, dentures should be removed for a short time to give the gums a rest, but no more than a day.
Dentures should be protected from shock and heat. Damage to them can injure the gums and mucous membranes.
If salivation increases while wearing dentures, you can cope with this by sucking on sugar-free lollipops or drinking water.
Dentures need to be replaced every five years.