The tooth hurts badly. Each of us has had to deal with this unpleasant situation more than once or twice. Many regular patients of the dental clinic already independently differentiate pain due to caries from pain due to pulpitis.
If pain occurs spontaneously, intensely, and worsens at night, they will rush to the dentist the next morning, and if pain arises from external irritants and indicates the development of deep caries, they will allow themselves to postpone treatment for a couple of days. But what to do when all your teeth hurt at once? First, let's figure out why we feel toothache in the first place.
Diagnosing the problem at home
Sometimes, to understand which tooth hurts, it is enough to look into your mouth. You need to go to the mirror and conduct a visual inspection. The diseased element may be damaged, with dark spots and depressions. There are also signs that indicate a problem: chipped, worn, cracked or transparent enamel, the presence of pustules and seals on the mucous membrane, inflamed, swollen or bleeding gums.
It also happens that a visual inspection reveals nothing. For example, when the problem develops under an artificial crown or filling. In this case, light pressure on the crowns or gently tapping them with the tip of a teaspoon will help determine the source of the pain.
How else can you find out which tooth hurts? During eating, pieces of food can become lodged in an element destroyed by dental diseases; it is difficult not to feel it. Hard tissues in the area of the pathological process can react to food temperature and mechanical stress during hygiene procedures.
On a note! If you want to understand which tooth hurts, then take the diagnostic question seriously. Before examination, remove soft plaque and food debris from your mouth. The room where the inspection is being carried out should have good lighting. Carefully examine every visible surface of the tooth using a mirror, and also check your gums for inflammation.
Treatment methods for pulpitis
Elena Bobkova , a dental therapist at the Dental Hi-Tech clinic, spoke about how pulpitis is treated in a conversation with the Federal News Agency . According to her, the dentist’s manipulations are aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the pulp. She noted that there are two methods of treating pulpitis - biological (conservative) and surgical.
“The biological method is used quite rarely. It is mainly used for treatment of tooth injuries or accidental opening of the pulp during the treatment of deep caries. It is also worth paying attention to age - the patient should be no more than 25 years old.”
During treatment, the exposed pulp is treated with non-aggressive antiseptic agents, a special calcium hydroxide gasket is applied to it, and then the whole thing is closed with a temporary filling. If the inflammatory process has been stopped and the tooth no longer bothers you, then a permanent filling is placed.
If we talk about the surgical method, it is divided into vital and non-vital. With the vital method of treatment, a tooth is prepared under local anesthesia: all softened carious tissues are removed, then the tooth cavity is opened, the pulp is removed, the root canals are treated with special instruments, they are expanded and washed with special antiseptics.
“Very often such treatment is divided into several visits. On the first visit, the doctor fills the canals with a temporary filling, and only after the tooth stops bothering the patient, the doctor fills the root canals - either by vertical or lateral condensation of gutta-percha, or by the condensation method of hot gutta-percha. And only on the patient’s next visit, the doctor restores the crown part of the tooth.”
The devitalizing method is the treatment of pulpitis using devitalizing agents. Previously, arsenic paste was used in dentistry; now doctors use more modern and safe means. They are applied for several days to influence the pulp, after which the “killed” nerve is removed and the root canals are again treated and filled, as with the vital method.
Thus, for each patient who is awaiting treatment for pulpitis, there is approximately the following work plan:
• local anesthesia - you cannot do without it, because the pulp is a nerve, touching which will cause sharp pain. However, we advise you to warn the doctor in advance about the presence of allergies to medications, since the doctor should be aware of the possible risks; • elimination of carious cavity. The previously listed treatment methods are used here, depending on the clinical picture; • pulp removal. This is done with a special tool - a pulp extractor; • channel measurement; • treatment of canals and teeth; • installation of fillings in the canals and on the crown of the tooth.
pexels.com/
We determine the cause of pain by the nature of the sensations and accompanying symptoms
In most cases, checking which tooth hurts on your own is not difficult. It is more difficult to establish why the discomfort and discomfort appeared. It all depends on the accompanying symptoms.
| Possible reason | Associated symptoms |
| Increased sensitivity of enamel | Thin, transparent enamel, with cracks and chips. Reaction to cold and hot, sour, sweet. Discomfort due to mechanical impact. Often pain occurs not in one, but in several teeth at once or along an entire row |
| Caries | Reaction to food temperature and mechanical stress. The discomfort goes away almost immediately after the irritating factor is eliminated, but as the disease progresses, the pain persists longer. First, white chalky spots appear on the enamel, then black dots, depressions and pits into which food easily gets clogged. |
| Pulpitis | The pain is acute and prolonged, persists for a long time after the removal of the stimulus, can occur involuntarily, and “spread” to all parts of the face and head. Unpleasant sensations intensify at night. With pulpitis, the enamel of the diseased tooth may darken |
| Periodontitis | May occur under a filling or crown. Sharp pain appears when pressing or chewing solid food. With this disease, there is a feeling of fullness and pressure in the inflamed area. The root of the diseased unit may begin to wobble |
| Flux, abscess, cyst | The gums around the diseased element become inflamed, and ulcers, pimples, and lumps may appear on the mucous membrane. In acute and advanced stages, swelling of the soft tissues of the face occurs. Unpleasant sensations intensify during tapping and pressure on the sore area |
| Fistula | An ulcer or pimple on the gum that may ooze fluid or pus. Unpleasant taste and odor in the mouth |
| Root fracture, crack, trauma | Sharp and acute pain, the tooth becomes mobile, it is impossible to chew food on it |
| Periodontal inflammation | If it is not clear which tooth hurts, then it may not be about the tooth at all, but about the periodontal tissues. So, with gingivitis or periodontitis, the mucous membrane itches and becomes inflamed, and also bleeds, and this process is most often generalized (applies to the entire jaw). At advanced stages of periodontitis, the roots become exposed and the teeth become mobile and begin to respond to thermal and mechanical stress. |
| Previously performed poor-quality treatment | If you just recently visited the dentist, and after that the treated tooth began to ache, then in the first 2-4 days this situation can be considered normal. In most cases, this indicates a tissue reaction to various medications and surgical intervention. With each subsequent day, the discomfort should decrease, but if it becomes stronger, this may indicate medical errors made during treatment. |
“I don’t advise anyone to guess on the coffee grounds and independently identify various diseases. In general, I never know which tooth hurts me, because the sensations are always ambiguous. The other day, there was a situation: my upper jaw was aching, and I was sure that the problem was there, although visually everything was normal everywhere. Even when I went to the doctor, I indicated a specific area, but the dentist looked and said that this was not so. As a result, the lower filled molar turned out to be problematic, under which secondary caries developed, and it was treated.”
Katerina, review from the dental portal gidpozubam.ru
TOP 10 reasons why a tooth may hurt
Sometimes a person who is faced with toothache is perplexed - why does this happen, because the teeth are apparently completely healthy? In this case, you should not put off going to the dentist. It is the doctor who will be able to determine what caused the pain - it could be due to increased sensitivity, or due to caries under an old filling, or due to many other factors. Conventionally, they can be divided into several types: caused by bacteria (caries, pulpitis, gum disease, etc.), mechanical damage or provoked by general diseases of the body.
Let's look at the 10 most common causes of toothache:
Reason 1. Caries and its consequences
These diseases are caused by bacterial microflora, which destroys teeth both from the inside (pulpitis) and from the outside (caries). But first things first.
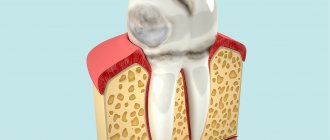
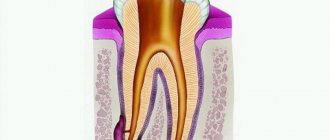
Caries occurs in almost every person. Appears as dark spots on the enamel. Interestingly, the initial stage of caries appears not as dark, but as white spots. In these places, the pathogenic process has just begun, and the waste products of bacteria little by little destroy the minerals that make tooth enamel hard. Gradually, the microbes penetrate deeper and the lesion becomes larger in size. The disease can spread to neighboring elements. If caries has reached the dentin, the process accelerates, because this layer is softer and more porous. If caries is not treated in time, the infection will penetrate into the pulp - i.e. the process of inflammation of the nervous and vascular tissue will begin. Pulpitis can be cured without “killing” the nerve, but not always. Typically, the inflamed contents of the pulp and root canals are cleaned out, disinfected and filled.
Painful sensations during caries and pulpitis are of a different nature. If caries causes mild pain, accompanied by a reaction to hot and cold drinks, food and air. The pain with pulpitis is often very strong and sudden (you can get sick at night, so much so that you “climb the wall”). The damaged element is painful when pressed and tapped. Unpleasant sensations can radiate to the nose, cheeks, temples (if the upper tooth is affected) and to the neck, ear (if the inflammation is in the lower row).
With caries, the pain subsides if the irritant is removed. For example, we ate something sweet, it got on our tooth, and it hurt. With pulpitis, the pain will last for a very long time.
Pain syndrome also occurs as a result of neglected or poorly treated caries, or rather even pulpitis - for example, with gumboil (periostitis), with periodontitis or even cysts. With gumboil, an additional purulent blister appears on the gum; with periodontitis, pain is often absent, but swelling of the mucous membranes and even parts of the face occurs. The insidiousness of cysts and granulomas is that, again, there may be no pain, but they appear as the tumors grow.
Reason 2. A new tooth grows and pericoronitis occurs
Pain during teething can occur in both children and adults. It is not uncommon for people at 70 and 80 years old to have “eights” - wisdom teeth. They are the ones that cause a lot of problems and are often painful.
Mostly the sensations are pulling and aching in nature. The head and neighboring elements may hurt. Their growth is often complicated by insufficient space on the jaw, so teething is accompanied by painful inflammation of the gums (called pericoronitis). Also, “sages” can grow incorrectly and damage the roots of “sevens”. In these cases, the “eight” must be “sacrificed” and removed.
Reason 3. Gum inflammation
Diseases such as periodontitis and periodontal disease affect the gums. There is pain and bleeding of the gums, pain when clenching the jaws and chewing food. Many patients are often confused and do not understand what exactly hurts – the gums or the tooth. At the same time, these pathologies lead to the fact that the roots of the teeth are exposed, which causes their increased sensitivity. If the infection is advanced or rapid, it can penetrate into the dental pulp through the apexes of the roots - this can result in the loss of one tooth, several, or even all of them in a row.
Reason 4. ARVI, sinusitis, sinusitis
Sinusitis and sinusitis are bacterial or viral inflammations of the mucous membranes of the nasal sinuses. Because Since the paranasal sinuses are located in close proximity to the upper jaw, their diseases can be reflected in the pain of those teeth that are in close proximity to the nasal sinuses. Often the lower dentition also reacts, for example, with sore throat and pharyngitis, since with these pathologies soreness of the lymph nodes often occurs.
Reason 5. Injuries, root fracture, cracks and chips
Chipped fillings, cracks in the enamel, and a fractured root tip can be caused by injuries due to bruises or chewing/biting very hard foods. Here, the pain from the injury itself may be joined by soreness due to inflammation (when the infection enters the pulp through microcracks). The sensations can be very different - strong, weak, sharp and dull. For a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an x-ray or an orthopantomogram (OPTG).
Reason 6. Whitening procedures and pastes with abrasive particles
In pursuit of a Hollywood smile, some patients notice that they have increased tooth sensitivity (hyperesthesia). This means that, along with the removed bacterial plaque, the mineralization of the hard tooth covering - enamel - is disrupted. In this case, all teeth may suffer at once, but most often the front teeth suffer from sharp and sudden “shots” - after all, they are located in the visible zone of the smile and during whitening they are given special attention.
Reason 7. Hard toothbrush and strong pressure while brushing
Everyone knows that you need to brush your teeth twice a day for two minutes. But not everyone knows how to choose the right toothbrush with the required hardness and how hard you can press on the tooth surface. Meanwhile, this is very important for oral health. Brushing too harshly can damage the enamel, rewarding a person with aching toothache and increased sensitivity to hot/cold.
Reason 8. Hypothermia and inflammation of the facial nerves
Fun winter games and walks are undoubtedly good for health and maintaining immunity. But a long stay in 20-degree frost, wind, or being outside without a hat can cause a very unpleasant disease - inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. This pathology almost always entails aching pain in the teeth.
Reason 9. General diseases of the body
The modern world sets a fast pace of life, but this is not suitable for every person. Therefore, various neurological conditions, stress and chronic fatigue arise. With such pathologies, the brain can receive and send incorrect signals to the nerve endings. They, in turn, can manifest themselves as a dull toothache that bothers a person for a long time. All these conditions are treated not by a dentist, but by a neurologist or psychotherapist.
Cervical chondrosis can appear due to being at the computer when a person’s head is turned to one side for a long time. In this case, there is an incorrect position of the spine, which contributes to the compression of blood vessels and nerves. The latter condition may cause pain in the lower jaw, lower molars and premolars.
Also dangerous are stomach diseases, frequent heartburn - when stomach acid refluxes into the oral cavity. Enamel is destroyed by acids, dentin is exposed - sensitivity and pain increase.
Reason 10. Lack or improper intake of vitamins, dietary disorders
People with weak enamel (as well as children and the elderly) should avoid products with vinegar and citric acid, and vitamin C should be taken only with meals. Why? Because acids destroy enamel and cause hyperesthesia - this causes pain. The best source of vitamin C can be rosehip decoction - it is not sour, but it contains several times more useful vitamin than lemons.
Poor nutrition negatively affects the mineralization of enamel and the condition of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. And, again, beneficial substances are washed out of the enamel, it becomes fragile and sensitive to irritants. The diet of a healthy person should include greens, fresh vegetables, berries, nuts, eggs, legumes and cottage cheese (not low-fat! - calcium is almost not absorbed from it).
Interesting fact! Acute imaginary toothache is not an invention of overly sensitive people. This condition may appear at the site of the tooth after its removal and last 1-2 weeks. Experts explain phantom soreness as a feature of the restoration of nerve endings in the gums.
The whole jaw aches: what does this mean?
Many patients, when visiting a doctor, complain that their entire jaw ache, but after examination it turns out that one tooth is to blame. Why is this happening? With some pathologies, pain can radiate (give) to different parts of the face and head: jaw, temple, ear, eyes. This often happens with pulpitis, eruption of wisdom teeth, the presence of impacted and dystopic elements in the jawbone that grow in the wrong direction, put pressure on their neighbors or do not break out at all. Pain can radiate to different areas if the disease is in an acute stage or the patient has advanced pathology.
On a note! Does your entire jaw ache after tooth extraction? This situation is also not uncommon, especially if the extraction was difficult and traumatic, or occurred against the background of a cyst or abscess. To ensure that the discomfort quickly disappears, strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations. If improvements do not occur after 5-7 days, and alarming signs intensify, then contact your dentist immediately.
The entire jaw may ache if the patient has a malocclusion, since against the background of this problem the maxillofacial apparatus or its individual areas are overloaded, and teeth wear out, wear out and are destroyed ahead of schedule. Discomfortable sensations radiating throughout the entire jaw can also occur during bite correction with orthodontic devices, but many patients admit that these are temporary difficulties, because after a period of adaptation to braces or trainers, the situation normalizes.
Prevention of aching teeth
The best way to prevent an unpleasant symptom is to follow preventive measures. Despite the fact that the enamel itself is very strong, improper lifestyle and exposure to the external environment gradually weaken and destroy it. If you have sensitive enamel, you need to carefully choose hygiene products. In particular, it is recommended to avoid hard toothbrushes and use toothpastes with calcium and fluoride. An equally important point is the right diet. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of spicy, sour and sweet foods to a minimum, and give preference to fermented milk products and foods high in vitamins A and B. Temperature changes are a big stress for sensitive enamel, so the best solution is to drink drinks at room temperature.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Author of the material: Yaroslav Ikonnikov
If teeth have nothing to do with it
Sometimes it is not clear which tooth hurts. It may even seem like everything hurts at once. But dental disease is not always the cause. Similar symptoms may indicate other problems:
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve,
- cancerous tumors in the oral cavity,
- ENT diseases: sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis media,
- hypothermia,
- salivary stone disease,
- dysfunction of the temporal mandibular joint,
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system: for example, angina pectoris,
- intervertebral hernia, pinched cervical nerve,
- psychosomatic state of a person: it may simply seem to you that your teeth are aching, especially if you have recently suffered stress,
- Jaw Fracture: Discomfort may occur even years after you have been treated. Some people note that in this way the body and the bones that have grown together after injury react to changing weather.
It is important to understand that internal diseases of the body can aggravate dental problems or contribute to their occurrence, just as, conversely, diseased teeth can cause other pathologies, such as sinusitis. This occurs due to the fact that infections from the source of inflammation can freely penetrate into all adjacent areas.
Additional symptoms
In dentistry, a condition in which teeth ache or ache is called hyperesthesia. In this case, there is an increase in the sensitivity of the enamel due to the action of various predisposing factors.
Additional signs of hyperesthesia:
- the appearance of characteristic pain after eating sweet, sour, cold or hot foods and drinks;
- teeth begin to ache when inhaling cold air;
- pain can spread to several teeth and the entire jaw, increases when trying to knock on the teeth;
- during a painful attack, salivation increases, it becomes difficult to talk, especially on the street, as the teeth suddenly begin to ache;
- Due to constant pain, appetite decreases; people are forced to eat only semi-liquid food, since chewing causes discomfort.
When teeth begin to ache, a person takes a forced position, tries to place warm palms on his face and have as little contact with irritating factors as possible. It is impossible to endure such pain for a long time. And in order to understand why teeth hurt and what can be done about it at home, it is necessary to understand what irritants cause hyperesthesia.
Methods for diagnosing problems in dentistry
Regardless of whether it is clear or unclear to you which tooth hurts, the first thing to do when an alarming symptom occurs is, of course, to consult a doctor. The specialist will not only accurately diagnose, but also cure the disease that caused the problem. Otherwise, after a short period of time you will notice that not just one, but several nearby units are aching, as the infection has spread further.
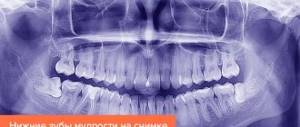
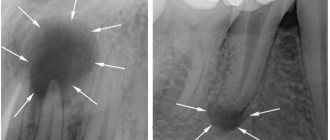
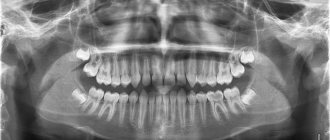
Today in dentistry there are many diagnostic methods, one of the informative ones is x-ray examination. To determine the condition of the entire jaw system, roots, root canals and bone tissue, as well as to identify hidden problems, for example, fractures and cracks of the root, cysts and granulomas, the presence of dystopic and impacted teeth, doctors prescribe a two-dimensional panoramic image of the jaw or CT (computed tomography) . The second type of examination - computed tomography - is more accurate, as it allows you to obtain three-dimensional 3D images and examine all processes in great detail.
In addition to X-rays, the doctor will definitely conduct a visual examination using a mirror, percussion1 (tapping on the crown) and examination of the oral cavity using special instruments (dental probe). Additionally, electroodontodiagnosis may be prescribed to determine the viability of the pulp, color and thermal tests to identify various non-carious (hypoplasia, wedge-shaped defect) and carious pathologies.
Diagnosis and complications of toothache
In order to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment, the dentist examines the oral cavity, clarifies complaints, recent diseases and injuries, and the nature of pain.
The doctor may perform the following manipulations during a visual examination:
- tapping on the dental crown: to determine how it hurts and where exactly,
- exposure to heat: to identify a reaction to hot,
- illumination with a special lamp or laser: carried out to identify areas of damage to the enamel,
- checking dentures (if any),
- X-ray: with this type of diagnosis you can “see” hidden inflammations, root fractures and other similar problems.
For any type of pain in the teeth - strong, weak, aching, acute, whether it hurts for a long time or not, you need to make an appointment with a dentist. And come to it, even if the pain has stopped bothering you. Tangible manifestations of some dangerous diseases can subside for a while (for example, pulpitis). But this does not mean that the destructive process has stopped.
Important! Before visiting the dentist, you should never take painkillers (neither tablets nor injections). The doctor will not be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe proper treatment if the symptoms are dulled by their action.
Failure to seek help in a timely manner is fraught with a number of unpleasant complications:
- purulent pulpitis,
- formation of a purulent sac under the gum: cysts, granulomas, abscesses. The latter are extremely dangerous, because can lead to blood poisoning and even death,
- loss of a tooth or even several.
I have a toothache: what to do?
If you have any kind of pain in your teeth, you should definitely make an appointment with a dentist as soon as possible. In addition, many clinics have a doctor on duty 24 hours a day to see patients with acute pain. He will conduct an examination, find out the exact cause of dentalgia, provide first aid and prescribe further treatment.
Before your visit, you can rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions or take your usual painkillers. Under no circumstances should you apply a heating pad to the sore cheek, or crushed garlic, onion or propolis tincture to the gum. This can speed up the course of the disease and additionally cause a burn to the mucous membrane.
Sometimes after taking medication or sleeping, the pain decreases greatly or disappears completely. Relief also comes if pus breaks out on the side of the gum during gumboil. But this relief is temporary: caries or pulpitis, and especially periodontitis, cannot be cured on their own. Most likely, the disease has become chronic and tissue destruction continues.