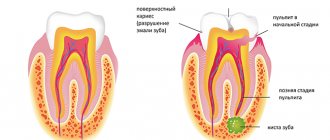
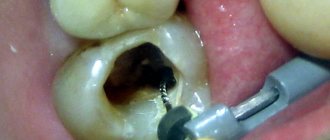
Pulp is a soft connective tissue that is found in the body of the tooth and contains many nerves and nerve endings. Patients remember her when they are overcome by toothache. Without this neurovascular bundle, tissue nutrition stops, and the hard dentin shells gradually become unusable. After some time, the enamel is destroyed. If the root system has been preserved, then it is possible to install a crown on a pulpless tooth.
But the depulpation procedure is not always provoked by pain and is carried out involuntarily. It is often carried out to install a bridge, clasp and other types of dentures that require the presence of supporting teeth. In rare cases, it is possible to perform prosthetics without removing the pulp , but this increases the risk of developing pulpitis, for the treatment of which it will be necessary to dismantle the working structure.
About the procedure
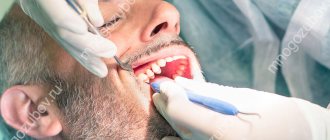
The decision on the need for tooth depulpation is made by the dentist. It takes into account the individual characteristics of the patient and his age. Before the manipulation, a complete sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out. It is advisable to have your teeth professionally cleaned to remove plaque. All these measures help reduce the risk of possible complications, because the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the mouth is fraught with their entry into open canals.
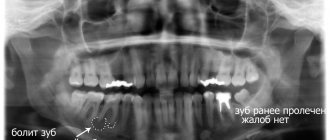
An x-ray of the problem tooth is first taken. This is required so that the doctor gets an idea of the level of complexity of the intervention, the width and depth of the canals.
In order for the manipulation to be painless for the patient, the dentist must perform preliminary anesthesia with drugs (Ultracaine, Lidocaine). The drug begins to act 15 minutes after injection.
There are two methods of depulpation:
- vital (with partial preservation of the pulp clot);
- Devital (with complete elimination of the living core of the tooth).
Vital
This method has priority. Includes the following steps:
- the affected dentin and pulp are drilled;
- bleeding stops;
- treatment is carried out with antiseptic agents, the formed cavity is dried;
- medications are prescribed (to relieve inflammation);
- an insulating pad is applied and a temporary filling is installed.
At a second visit after 10-14 days, if there are no complaints from the patient, the doctor installs a permanent filling.
Devital
Removal of the nerve takes place in several stages.
- Using a bur, a cavity is opened that is affected by caries. Destroyed enamel and dentin are removed and antiseptic treatment is carried out.
- The nerve is removed. For this, a pulp extractor is used - a long needle with a thick handle. Infection is not possible since this is a disposable instrument.
- The channels are cleaned and expanded.
- The canals are filled. First, a temporary filling is placed, a little later it is replaced with a permanent one (after 2-3 days in the absence of pathological symptoms). It is important to ensure that no air bubbles form during filling. Otherwise, the patient will experience discomfort every time he eats.
It is recommended that pulpless teeth be periodically whitened by a dentist. They quickly darken and lose their external aesthetics. This procedure is called endobleaching. Special preparations are introduced into the tooth cavity. This is a painless and safe manipulation that can be done once every few years.
List of indications for endobleaching:
- darkening of the enamel;
- damaged pulp with hemorrhages;
- penetration of dyes into microcracks in teeth.
Why does a tooth hurt when pressed after nerve removal?
Many people are afraid to visit dental centers and therefore, when any dental problems arise, they limit themselves to taking painkillers. However, it should be understood that toothache indicates an infectious lesion of the dental pulp, in which the nerve endings responsible for this symptomatology are located. Deep caries, pulpitis and periodontitis cannot be cured at home. And the longer a visit to the doctor is postponed, the more painful and longer the recovery period will be after depulpation - root canal treatment.
After removing the nerve, the tooth should hurt, but not severely and not for long. This pain is called post-filling pain and is associated with the body’s reaction to surgery. The depulpation procedure is painful because during it soft and hard dental tissues are injured and sensitive nerve endings are removed. For the same reason, almost all patients experience pain upon completion of canal cleaning. However, in order to accurately determine why a pulpless tooth hurts, you need to seek help from a dental center.
Upon completion of the depulpation procedure, you can:
- sensitivity of the enamel to hot, cold, sweets will appear;
- jaw hurts when closing;
- throbbing toothache becomes more frequent in the evening;
- general health worsens (headaches, weakness, fever).
If the acute pain in the tooth that arose after it was depulped did not go away within 7 days, most likely, re-inflammation has begun. In this case, you cannot do without the help of a specialist.
The main causes of toothache associated with root canal cleaning
Why a tooth may hurt after removing the nerve and cleaning the canals:
- The doctor performed the procedure poorly - particles of the dental nerve remained in the canals, which led to severe pain and increased body temperature.
- Poor quality antiseptic treatment of dental canals or infection after the procedure due to poor oral care.
- The appearance of voids under the filling is accompanied by pain when pressed and the formation of abscesses and fistulas.
- The doctor did not take an x-ray and did not notice one of the canals (their number can be up to 6), as a result of which the infected tissue remaining in them began to rot, and a toothache occurred.
Causes of toothache associated with root canal filling
Why can a tooth hurt after removing the nerve and filling the canals:
- Dentin burn. Occurs when a dentist drills into a tooth root for a long period of time and does not use cooling. In this case, the tooth hurts severely.
- Depressurization of the seal after installation. Most often occurs due to mechanical trauma, in which the material is torn from the dental tissues.
- Allergic reaction. Allergies occur to medications and materials used in the treatment of pulpitis.
- Bite modification. If the filling is too high, it will prevent the jaws from closing, which will cause pain when biting on the tooth.
- Shrinkage of the filling. Any filling material hardens when exposed to light and can shrink. In this case, the filling begins to put pressure on the tooth walls. As a result, cracks appear in the dentin through which air penetrates. If you put pressure on such a tooth, it will begin to ache.
Why does a tooth hurt after root canal treatment - medical errors
The doctor may be to blame for the inflammatory process that occurs after root canal treatment. It is necessary to contact the dentist again so that he can eliminate the errors and heal the tooth correctly. Most likely, a decision will be made to install a temporary filling.
Medical errors that lead to toothache after depulpation include:
- Incorrect therapeutic treatment of pulpitis - the doctor poorly cleaned the dental canals, as a result of which the nerve was not completely removed, which began to decompose naturally.
- Root puncture - the doctor introduced a filling material beyond the root, which provoked the development of an inflammatory process.
- Poor application of filling material – the canals are not filled tightly enough with the material, which is why infection has penetrated into them.
- Violation of the canal filling technique - the tooth may hurt when touched after treatment of pulpitis if the doctor placed the filling beyond the apex of the root.
- Inattentiveness of the doctor - while cleaning the canals, part of the instrument broke off and remained in the gum, which led to discomfort and the development of inflammation.
A tooth may hurt after the pulp has been removed from it, due to trigeminal neuralgia. The disease progresses in different ways: pain can torment a person constantly or in attacks. Only a neurologist can identify and cure it.
Why could a long-healed tooth without a nerve with a filling get sick?
A long-healed tooth without a nerve with a filling may hurt for the following reasons:
- the doctor was unable to thoroughly clean the root system, which led to the development of low-grade chronic inflammation;
- the dentist who filled the tooth introduced the filling material beyond the apex of its root;
- during depulpation, the dental canals were poorly washed with an antiseptic;
- the canals are not completely filled with filling material - in this case, acute pain occurs when biting hard foods.
Contraindications
The nerve cannot be removed if there are contraindications. Here is their list:
- first and last trimester of pregnancy;
- the presence of foci of suppuration in the oral cavity;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- acute respiratory infections;
- mental disorders;
- epilepsy;
- some pathologies of the heart and blood vessels (post-infarction state, hypertensive crises);
- leukemia;
- stomatitis;
- hepatitis of an infectious nature.
In such cases, the procedure is not advisable. Doctors offer alternative treatments.
Complications
After tooth depulpation, pain may continue for some time. To alleviate the patient's condition, doctors prescribe analgesics to relieve pain. If suddenly unpleasant sensations persist for more than two weeks and signs of inflammation appear, then you should be wary. It is necessary to urgently seek medical help to prevent the development of complications (for example, periodontal abscess, cystic formation, granuloma).
They develop due to the following reasons:
- the affected nerves were not completely removed;
- areas left affected by caries;
- dental canals are cleaned incorrectly or incompletely;
- open channels are incorrectly or incompletely sealed;
- After the manipulation, the patient did not follow the recommendations for oral care.
Treatment
When a pulpless tooth hurts when pressed, treatment begins in most cases with medication. In this case, the patient is recommended to take painkillers, for example, Baralgin, Ketorol, etc. Anti-inflammatory drugs also have a good effect when such pathological phenomena occur. One of these remedies is “Nise”, which not only helps reduce pain, but also effectively relieves the inflammatory process.
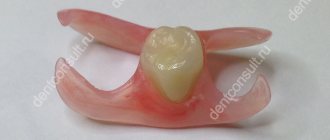
Features of the procedure for prosthetics
After depulpation, the tooth loses its natural internal nutrition, becomes fragile and may collapse over time. To prevent this from happening, experts advise using prosthetics. After this, the resistance of dental tissues to stress increases significantly.
Other indications:
- teeth too small;
- severe curvature of teeth;
- darkening of the enamel;
- increased sensitivity to hot and cold foods, sweet foods.
Pain under the denture after depulpation
Painful sensations in such a case almost always occur when mistakes are made during the intervention process. If they are moderate and appear when biting hard foods or applying pressure, then this may be normal. For some time after the procedure, the tissues are still being restored and pulpless teeth may hurt. If the pain is severe and is accompanied by other alarming signs (swelling of the gums, reaction to hot and cold), then this is a pathology.
The reasons may be:
- the finished prosthesis does not correspond in size to the original measurements;
- a piece of instrument is stuck in the cavity;
- the channels were not completely cleaned before the procedure;
- the integrity of the root walls is compromised.
If drug treatment is ineffective, the prosthesis is removed, the existing defects are corrected, and a new implant or crown is installed.
If you monitor the health of your teeth, do not neglect the rules of personal hygiene, regularly visit the dentist and promptly treat caries, you can minimize the need to remove dental nerves.
Category: Tooth extraction Published by Mister stomatolog
What is pulp and does it need to be removed?
The pulp, or dental nerve, is the connective tissue that fills the tooth cavity. It consists of fibers, nerve endings, lymphatic and blood vessels. The dental nerve supplies bone tissue with nutrients, is responsible for the proper development of the tooth and protects it from infection.
If the pulp is damaged, an inflammatory process begins, and the person experiences severe pain. After removal of the nerve, the tooth becomes “dead,” but with professional manipulation by a doctor, it fully retains its functions.