In this article you will find answers to questions such as:
- why does caries appear between teeth?
- how is interdental caries treated?
- photos of the main stages of treatment.
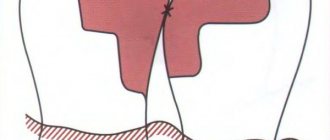
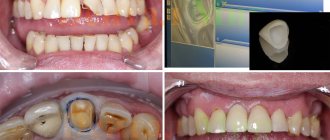
Caries between teeth is a carious lesion that is localized on the lateral surfaces of the teeth (in the interdental spaces). It must be said that this zone is the most favorite for the occurrence of dental caries, which is explained by two reasons. Firstly, after eating, food debris constantly accumulates in the interdental spaces, and secondly, very few people use dental floss every time after eating to clean the interdental spaces.
As a result, carious lesions of tooth enamel occur in the interdental space, which is accompanied by minor pain when eating sour/sweet foods, as well as thermal irritants (cold or hot). As the carious defect deepens, these symptoms then disappear. It should be noted that interdental caries can be difficult to diagnose in time, because this area is difficult to visually observe, and patients usually do not see a dentist in the early stages of caries.
Caries between teeth: photo
In dentistry, the treatment of interdental caries is not a simple task, because... here, in addition to restoring the side wall of the tooth, it is necessary to restore the contact point between the teeth. This last task is quite difficult for most dentists. Filling a tooth without creating good contact between the teeth in the interdental space leads to the fact that food will actively get stuck in it, and this, in turn, will provoke the development of secondary caries near the filling, as well as periodontal pockets.
Who is susceptible to developing interdental caries?
Carious lesions on the lateral surfaces of adjacent teeth can occur in anyone, including children. But the following categories of people are especially susceptible to the formation of interdental caries:
- those who eat poorly: consume a lot of sweet foods and drinks, few solid vegetables, fruits and foods rich in fluoride, calcium, phosphorus;
- those who have problems with oral hygiene (do not brush or brush their teeth poorly, do not use dental floss or irrigator to clean the interdental spaces);
- those whose normal salivation process is disrupted;
- when there is a gap between the teeth that is too narrow or closed at the bottom and widened at the top, into which food easily gets clogged.
How to detect caries in interdental spaces?
One of the specific features of interdental caries is that it is difficult to diagnose. Since enamel damage is located at the junctions of teeth, it can be quite difficult to detect it yourself. Therefore, caries between teeth is rarely diagnosed at an early stage, when it is possible to manage with conservative methods and not prepare the tooth. Much more often it is detected already in the presence of symptoms in the form of pain or a reaction to cold/hot.
The dentist diagnoses interdental caries using several basic methods:
- External visual inspection using a mirror and probe. Only an experienced dentist can detect areas affected by caries and dark spots on the enamel in hard-to-reach areas.
- If the teeth are very closely spaced, a diagnostic examination may be difficult, and then the dentist will order an x-ray, which will show the presence of a carious cavity in the tooth.
- Sometimes, as an alternative to x-rays, a modern sound diagnostic method is used.
After making a diagnosis, the question arises of how caries between teeth is treated.
Diagnostics
- visual inspection
. It is performed using special instruments to assess the condition of the oral cavity. A dental mirror makes it possible to carefully examine the distal surfaces: detect spots, stripes/dots of black, brown color, carious lesions. The probe helps differentiate the depth of the cavity; - percussion method
. Intended for identifying pathological segments by tapping. The diseased unit reacts with a muffled sound, the patient experiences pain and severe discomfort; - radiography
. The x-ray image shows the distance of the lesion from the pulp, the level of prevalence of the process; - transluminescence
. Luminescence (transmission through a filter with an ultraviolet beam) and fiber optic exposure (transmission with a light beam) are practiced. Damaged areas appear darker than healthy areas; - coloring
. Application of staining markers (potassium iodide/methylene blue solution). Allows you to identify pathology and distinguish it from fluorosis/hypoplasia.
In difficult cases, fissurotomy (opening the grooves on the surface of the molars) and electroodontometry are used to determine the degree of pulp damage.
Features of the treatment of interdental caries
Treatment tactics depend on several factors:
- stages of the carious process;
- localization of caries.
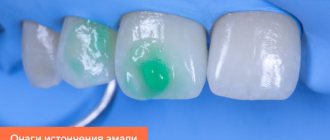
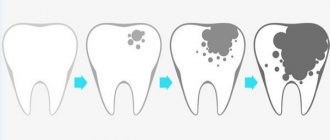
In terms of the depth of damage, interdental caries can vary from the spot stage, when there is no carious cavity yet, but only a section of demineralized enamel is found, to medium and deep caries, when a large carious cavity forms in the dentin and there may be a risk of pulpitis and other complications.
At the stain stage, it is possible to treat teeth using conservative methods, without preparation. As a rule, this is remineralization by simple or deep fluoridation, infiltration method or ozone therapy. These methods strengthen tooth enamel, increase its protective functions and resistance to external influences.
At the stages of superficial, medium and deep caries, the disease will have to be treated surgically - through tooth preparation, removal of affected tissue and further filling of the affected areas.
At the same time, the main difference between interdental caries and other types is that it is necessary to treat not one, but two teeth at once in the area of contact surfaces.
Possible complications
Tooth decay should be treated as early as possible. Otherwise, the disease will penetrate deeper and affect the tooth even more. When caries reaches the nerve, the tooth will begin to hurt and become inflamed. In addition, untimely treatment leads to complications such as:
- Inflammation of internal dental tissues (pulpitis, periodontitis);
- The occurrence and rapid spread of an infection that will extend beyond the tooth and require treatment with antibiotics or surgical intervention;
- Development of chronic infection;
- Removal of a tooth.
Interdental caries of the anterior teeth: what should be done?
The most unpleasant and “ugly” caries occurs between the front teeth. If the disease is not detected at the spot stage, then treatment will be carried out approximately according to the following scheme:
- a drug with an anesthetic effect is applied to the affected area;
- clean areas affected by caries from dental plaque and other deposits to prevent the spread of pathology to neighboring areas;
- isolate the affected teeth using a latex napkin (rubber dam) to prevent saliva from getting into them or being injured during dental treatment;
- carious cavities are prepared, the affected tissue is removed on the contact surfaces between the two front teeth using a drill;
- treat the interdental areas with antiseptic solutions (for example, chlorhexidine), and then with adhesive compounds, which improves the fixation of the filling to the tooth walls;
- teeth are filled, and then polished and ground in such a way as to restore their natural anatomical shape and the contours of the interdental spaces as much as possible;
- in case of severe damage, when it is not possible to restore the aesthetics of the front teeth with a filling, they are restored using crowns or veneers.
Both upper and lower teeth are treated in this way.
Kinds
Various types of fillings are used to repair holes and cracks. Their composition, purpose and service life differ.
By material
Patients of modern dental clinics can independently choose the compositions that the doctor will use for treatment or restoration. Filling material differs in strength, consistency, and hardening time. Which one to choose depends on the problem the person is addressing.
Cement
Just a few decades ago, this material had no alternative competitors. It was possible to place a cement filling on a tooth in any clinic, and its cost was minimal. They were made on the basis of phosphate and silicate powders, which hardened under the influence of a chemical reaction when mixed with liquid.
The dentist needs to work with such material quickly, and after filling the patient should not consume food or water for 2 hours. Advanced clinics refuse cement fillings - the material is characterized by low adhesion, even under a technically correctly installed filling, food debris can get in, and carious processes can continue to develop underneath it.
Plastic
A damaged tooth without a filling continues to rapidly deteriorate, posing a danger to neighboring units and the oral cavity. Some dentists suggest using plastic to eliminate the problem. Such fillings are characterized by rapid hardening, excellent strength, and chemical resistance.
However, it is worth noting the disadvantages of the material. Over time, the plastic filling decreases in size and sags, and may be irreversibly stained by bright drinks. This will lead to the need to quickly replace the insert, which is associated with additional financial expenses.
Note! Plastic fillings are slightly toxic.
Composite light-curing
Photopolymer fillings are ideal for dental treatment. It has a paste-like consistency, is easy for a doctor to work with, and the material hardens under the influence of a special ultraviolet lamp. A variety of shades allows you to choose the one that will best match the tone of your native enamel. Thanks to this, it is from photopolymer that fillings are placed on the front teeth. To add shine, the composite is sanded with fine abrasive attachments after installation.
Ceramic
In terms of its properties, ceramics are closest to natural enamel. It is not surprising that this material is often used for fillings. Dentists make special ceramic inlays based on an impression of a pre-treated molar. They completely replicate the anatomical features of the tooth, and after installation, the chewing load will be evenly distributed over the entire surface. Over time, ceramics do not change color, do not wear off, and do not shrink. The only disadvantage for the patient is how much a filling costs for a bad tooth.
Glass ionomer
This type of cement is often used in complex therapy against caries in children. They contain fluoride, which prevents recurrent caries. Since the material is quite fragile, a composite is usually applied on top of it - it is more aesthetically pleasing, resistant to abrasion and not subject to shrinkage.
By service life
Depending on the problem with the tooth, dentists offer the installation of 2 types of fillings.
Temporary
It is used for diagnostic purposes when the dentist needs to observe how a tooth responds to treatment. Installing a temporary tooth filling prevents medications from escaping and moisture and pieces of food from entering the open cavity. After a couple of days or months, the material is removed and the teeth are treated further.
Constant
This is a permanent element of the tooth. Installed for several years, good fillings made from quality materials can last up to 10 years without the need for replacement.
How teeth are filled
If caries has appeared, a piece of enamel has broken off, or an old filling has fallen out of a tooth, then a trip to the dentist is mandatory! The availability of modern equipment, fast-acting anesthetics and good materials makes the treatment completely painless and comfortable for the patient. Before filling, the doctor will assess the condition of the oral cavity, remove carious stains, and, if necessary, carry out additional treatment for pulpitis or periodontitis.
The filling is placed according to a single scheme:
- the cavity is disinfected;
- the cleaned cavity is dried;
- Antimicrobial pads are placed inside if necessary;
- the prepared cavity is filled with a filling mixture, it is formed and illuminated with a polymerization lamp;
- the frozen mass is polished.
Important! If the filling is placed correctly, then the patient can comfortably close his jaws.
The nuances of treating anterior teeth
Restoration of anterior teeth requires a special approach. There are special requirements for the material that is used to restore the surface of the visible part of the dentition. It must be immune to temperature changes, biocompatible with native enamel, durable, and able to withstand constant chewing loads. After cosmetic repairs with photopolymer or light fillings, the front teeth will look beautiful and healthy.
What to do with a wisdom tooth?
Eights today are considered to be a rudiment. If holes appear in these molars, then not every doctor undertakes to save the dental unit. Most often, they resort to extraction because it is unknown how the tooth will behave after treatment. Wisdom teeth are filled only in certain cases:
- if the nearest tooth is destroyed and the figure eight can be used to install a prosthesis;
- in the presence of an antagonist;
- with severe damage to the integrity of the dentition.
The procedure for treating wisdom teeth is no different from the standard one.
How is caries between teeth treated when molars and premolars are affected?
The algorithm is like this:
- First, anesthesia is performed. If the lesion is shallow, sometimes topical anesthesia is sufficient; for deeper stages, an anesthetic injection is given with a drug to which the patient is not allergic.
- The affected areas are cleaned of plaque and tartar, and a rubber dam is applied.
- Carious cavities are prepared; in most cases, not only the affected tissue is removed from the chewing teeth, but also some of the healthy tissue to provide the necessary access;
- The cavities are treated with disinfectants and treated with adhesives.
- The tooth is filled with modern photocomposite materials, which are illuminated with special lamps. To restore the side walls of the chewing teeth and ensure tight contact between them, the dentist uses special wedges and matrices.
- At the final stage, the restored surfaces are polished.
Prevention of interdental caries
Interdental caries is difficult to diagnose and treat; it affects the contact surfaces of several teeth at once. Therefore, it is much easier to prevent its occurrence than to treat it.
The following preventive measures will help reduce the risk of developing caries between teeth:
- brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpastes (unless your dentist recommends a different toothpaste);
- After each brushing of your teeth, clean the interdental spaces with a special floss;
- use an irrigator: with a powerful stream of water it cleans not only the interdental spaces, but also gum pockets, areas under crowns and braces and other hard-to-reach areas where food debris can accumulate;
- It is recommended to reduce the consumption of foods rich in simple carbohydrates and sugars, because this is what promotes the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity;
- do not snack between meals, especially sweet and sticky foods;
- visit the dentist once every six months for a preventive examination and for professional teeth cleaning using special equipment;
- on the recommendation of a doctor, promptly remineralize the enamel with fluoride and calcium preparations in order to stop the process of carious lesions at an early stage.
Following these simple rules will help reduce the risk of developing caries between teeth several times and maintain a healthy and beautiful smile for a long time.