Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Endodontic treatment, affecting the internal parts of the tooth and, first of all, the roots, is one of the most important sections of modern dentistry. The effectiveness of all treatment procedures for such serious and dangerous diseases as pulpitis, periodontitis, purulent abscess, etc. often depends on the quality of tooth root canal treatment.
Being a very important part of the tooth, the roots provide its fixation in the jaw, nutrition and blood supply. However, the root can also easily cause pain; Many diseases associated with untimely or incorrect root canal treatment lead to severe consequences, including tooth loss. Infection can penetrate into the root canal either as a result of a pathological process (for example, caries) or as a result of errors made when performing certain dental procedures. There are cases when pathogenic microflora penetrates inside the canal as a result of a tooth injury that violates the integrity of its structure, the outer shell.
Root canal filling takes a central place in the treatment of pulpitis, periodontitis and similar diseases. Effective root canal treatment is impossible without solving this problem. If the canal is sealed in violation of the technology, or not tightly enough, then a focus of infection and inflammation is likely to form in its cavities. Sometimes pain occurs after root canal filling, caused by the same infection, mechanical, thermal or chemical damage to the tooth tissue during treatment. To avoid these and other adverse consequences, the dentist must follow technology at every stage of root canal filling, starting with the preparatory stage.
Indications
The cavity located inside the tooth, where the nerve endings and blood vessels are located, is called the pulp. If the caries lesion is not treated in a timely manner, the pathology reaches the pulp, which leads to the occurrence of an inflammatory process called pulpitis. The process does not go away on its own; the pain that inevitably arises is removed by painkillers in the initial stages. Over time, they also stop working. In advanced cases, inflammation spreads to the bone, which leads to periodontitis and, as a consequence, osteomyelitis. The main indication for root canal filling is pulpitis caused by caries.
What is root canal filling?
If endodontic treatment is of poor quality, the canals will have to be unsealed (disobturated) and sealed again. This process is called refilling.
It is prescribed if:
- the sealer has dissolved;
- the filling material was brought beyond the apex;
- the pulp was not completely removed;
- the canals were not hermetically sealed;
- the root canals were not obturated to the apex;
- Secondary inflammation has developed - periodontitis, granuloma, cyst.
The purpose of disobturation is to remove the old filling material and carry out subsequent sanitation and filling of the canals. You can remove the root filling in 2 ways:
- Using drugs (solvents) that soften the sealer. They are applied for a few minutes (if the canals were previously filled with gutta-percha and ordinary pastes) or left for 2-3 days (in teeth obturated with resorcinol-formalin or cement). Afterwards, the remaining filling materials are removed using files and reamers: they are gradually rotated in the canal, each time advancing the needle tip by 2-3 mm.
- Ultrasonic installations. For this I use ultrasonic endodontic motors. Ultrasound destroys the sealer, and files rotating at high speeds clean the canal cavity from paste residues.
Unsealing is a complex process. Dentists do not like to do it and, as a rule, do not provide guarantees for the treatment of such teeth. The chances of success are higher if endodontic therapy is carried out using endomotors and under a dental microscope.
If endodontic treatment is of poor quality, the canals will have to be unfilled.
The latter displays an image of the root canals enlarged up to 30 times, which allows you to examine all the anatomical features and carry out desobturation with microscopic precision.
Filling methods
Until recently, the procedure was carried out using pastes, which are inexpensive and do not require complex technologies. Now professional dentists have abandoned them due to insufficient fluidity, which leads to the formation of cavities. Voids lead to depressurization and relapse of inflammation.
At the moment, doctors choose progressive methods:
- Thermophile system. The filling is performed with hot gutta-percha, which hardens as it cools. It is characterized by high plasticity. There is no pain after treatment. The risk of complications is minimal;
- depophoresis. It is used for filling difficult, curved canals, as well as for restoring elements from which it is difficult to remove old fillings and where fragments of ostomy instruments remain in the cavities. Efficiency - no less than 95%;
- E&Q Plus. The latest generation method, which provides various methods of filling the roots of one tooth. The injection gun heats the gutta-percha directly inside the cavity. The doctor can control the temperature of the material using the information display.
Another common method is filling the canals with cold gutta-percha, which is used in several ways:
- lateral condensation;
- softening due to chemical action;
- with one pin. To give the shape, a pin is installed in the canal. Sealing is ensured through the use of paste.
There are other technologies that are selected depending on the location of the channels, the condition of the tissues and the experience of the doctor.
Clinical researches
As a result of clinical experiments using the Asepta series of products, conducted at the Kazan State Medical Academy, the complex use of anti-inflammatory drugs from the Asepta line contributed to faster relief of inflammation, the combined use of balm, gel, rinse, toothpaste and vitamin-mineral complex mutually enhanced the therapeutic effect did not require daily visits to the dentist.
Sources:
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
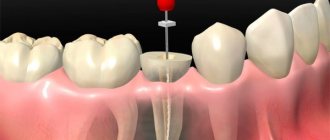
Stages of canal filling
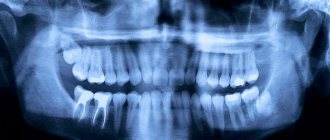
First of all, the doctor carries out an examination and the necessary diagnostic operations, which may include, for example, an X-ray examination of the oral cavity.
If suspicions about the need to fill the canal are confirmed, the dentist carries out preparatory manipulations. First of all, adequate anesthesia. After it has taken effect, the caries-affected tissue is removed using a burr. The dental nerve is then removed. Next, the doctor is engaged in mechanical processing of the endodont - a complex of dental tissues, including pulp and dentin.
Upon completion of the preparatory stage, the empty root canal is filled, then a permanent filling or crown is installed.
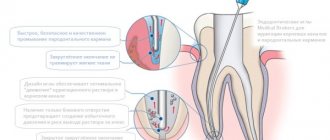
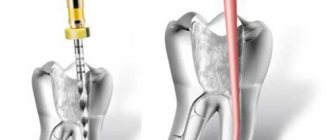
What is root canal obturation?
Obturation is the scientific name for filling. By it we mean the complete filling of the channels with sealing masses. The procedure is needed to strengthen the roots, eliminate the voids formed after depulpation (removal of the pulp - nerve) and, thereby, protect the tooth cavity from the penetration of aggressive substances, pathogenic microorganisms and subsequent inflammation.
Sealants in canals are called root fillings.
Preventing infectious processes is the main goal of filling. To prevent them from developing, the canals must be obturated to the root apex (apex), without bringing the filling material into the periapical space.
Obturation is the scientific name for filling
Unfortunately, bad fillings are common - in 60-70% of cases (according to the medical portal “24Stoma” https://24stoma.ru/plombirovanie-kanalov.html). It appears as a result of poor mechanical and medicinal treatment of the cavity, incorrect measurement of their length, the use of an inappropriate obturation method or cheap materials.
Description of the procedure
- Local snapshot. X-ray allows you to see the condition of all channels, their number, location. In difficult cases, a 3D image is taken.
- Anesthesia.
- Drilling of diseased tooth tissues.
- Removal of nerve and blood vessels.
- Determining the depth of the canal using an apexolator.
- Widening the passage to place the drug and install the pin (if required).
- Filling.
- Control photo.
After treatment, it is not recommended to consume hot drinks and food for 1 – 2 hours.
Temporary filling
In some cases, medicine is introduced into the canals for a certain period of time. Manipulation is carried out for:
- elimination of pathological microflora;
- stopping the inflammatory process;
- isolation of the canal, when it is impossible to carry out treatment in one visit.
Indications for temporary installation of a filling are injuries, perforation of walls, periodontitis in acute or chronic form.
The main active components of medicinal non-hardening pastes are antibiotics.
Cost of services
Consultation with an implant surgeon 0 rub.
1-canal tooth (canal filling with gutta-percha pins) 750 rub.
2-canal tooth (canal filling with gutta-percha pins) 980 rub.
3-canal tooth (canal filling with gutta-percha pins) RUB 1,300.
Placing a temporary filling costs 200 rubles.
Compomer filling for permanent teeth RUB 1,000.
Filling for permanent teeth made of gypsum resin, cotton RUB 1,200.
Filling for permanent teeth made of photocomposite RUB 1,800.
Placement of a light-curing filling for non-carious lesions RUB 2,000.
Placement of a light-curing filling for average caries RUB 2,500.
Placement of a light-curing filling for deep caries RUB 3,000.
Placement of a light polymerization filling for periodontitis (taking into account the formation of a cavity and the application of a lining) RUB 2,350.
Placement of a light polymerization filling for pulpitis (taking into account the formation of a cavity and the application of a gasket) RUB 2,370.
Restoration of the crown part of a tooth using light polymerization materials (caries) RUB 3,050.
Restoration (caries, pulpitis) RUB 4,650.
Possible complications after canal filling
In the absence of complications, the process can take about one to one and a half hours. But in severe and advanced cases, it may require several visits to the dentist.
The most common type of complications after filling a tooth canal is the neglect of the inflammatory process, accompanied by focal tissue destruction. In this situation, a temporary filling is installed from a non-hardening paste containing medications. The time of wearing it and the composition of medications is determined by the doctor during an individual consultation. This treatment shows high effectiveness for diagnoses of cystogranuloma and periodontitis.
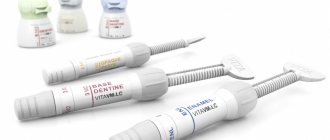
Materials for canal filling
Unfortunately, situations are common in which pain continues to torment the patient even after all medical procedures have been completed, and after the period adequate for rehabilitation has expired. The reason for this reaction of the body may be an error in choosing the filling material. There is still no universal substance that would suit everyone. Consequently, dentists, based on their knowledge and the results of examining patients, each time make a choice in favor of one material or another.
Today the following substances are used for canal filling:
- fillers. They are represented by gutta-percha, silver and titanium pins;
- sealers. These are different types of cements, including polymer, natural, glass ionomer or containing calcium hydroxide, as well as polydimethylsiloxanes.
Gutta-percha can be called perhaps the most popular material due to the complex of its properties:
- leaves the tooth color unchanged;
- copes with absolute sealing;
- not subject to dissolution;
- not subject to deformation.
Methods for removing fillings
In modern dentistry, two methods are used to remove fillings during repeated treatment. The first, mechanical, involves the use of specialized equipment. The filling is crushed or drilled, after which its remains are removed using other equipment or rinsing.
The second method is more common - chemical, it involves the use of special substances. These can be pastes, gels, solutions, which, when they come into contact with a filling, begin to dissolve it and thereby soften it. Further cleaning is done using endodontic instruments.
Chemical unsealing technique
| Click to sign up for a FREE consultation |
The choice of technology and the level of complexity of removing filling material depends on several factors. It is imperative to take into account the material used as a filling. The location of the channels and their features are important. And the dentist must pay attention to what treatment is necessary for repeated intervention.
Chemical deobturation is divided into cases with medium and high complexity. The former require only one visit and are distinguished by the use of hardening paste during the initial filling. Such material is easily exposed to solvents and quickly softens for further cleaning with tools.
Removing a filling in difficult cases requires cleaning in two steps and is used in the presence of fillings made of cement material or resocin-formalin. The second filling option has practically no application. However, patients with old fillings may contact the dentist. When pulling out material, an instrument is inserted into the channel and scrolled first clockwise, then counterclockwise and pulled out with a portion of soft material.
Tooth canal treatment methods
Along with canal filling, other techniques are common in modern dentistry that allow you to preserve both the appearance and functional load of teeth.
These include:
- depophoresis method - designed to increase the efficiency of cleaning the canal from pulp tissue. It is based on the effect of copper-calcium hydroxide and a weak electric field on tissue.
- The method of obturation with the Thermofil system allows you to introduce thermoplasticized gutta-percha into the prepared root canal with high precision.
- Treatment with cold or heated gutta-percha allows you to achieve perfectly accurate filling of all tooth cavities after treatment.
It is important that the dentist strictly follows all ISO standards when selecting the instruments required for endodontic treatment. The caliber, diameter and even color of the instrument play an important role.
Medical errors in endodontic treatment
According to some data, Russian specialists achieve success with endodontic treatment in only 30% of cases.
The most common mistakes include:
- incomplete obturation (when filling the prepared dental cavity with filling material, air bubbles remain; the material does not adhere tightly to the tooth tissue);
- insufficiency, low quality of antiseptic treatment (threatens the occurrence of an inflammatory process);
- deformation, breakage of the pin or tool.
Can an ordinary patient who does not have a medical education determine the degree of qualification of the endodontist he sees? Yes. The first, main sign of a low qualification of a doctor or insufficient technical equipment of the clinic is the lack of an X-ray examination at the beginning of therapy.
If inflammation occurs or if pain lasts for an inadequate duration after filling a tooth canal, you should immediately consult a doctor. Delay may result in tooth loss.
Author:
Lozinskaya Alla Nikolaevna
Pediatric dentist, general dentist.
You may also be interested in:
Treatment of a fistula on the gum Treatment of pulpitis Increased sensitivity of teeth: causes and methods of treatment
How to check the quality of canal filling?
Quality control of fillings is an integral part of the treatment process and is performed at every stage. X-ray control is especially important after filling. It allows you to identify areas of insufficiently dense obturation, detect pins or sealer residues protruding beyond the root apex, identify fragments of files and other defects. All this can lead to severe pain after treatment, as well as to the development of complications.
The x-ray image should clearly show the canal cavities, densely filled with filling material. There should be no enlightenment. The filling material should reach the very top of the canal.
Following simple rules of prevention also helps to avoid complications. Pain after treatment can last from several days to a month and does not always indicate ineffectiveness or low quality of treatment. However, if they appear, you should consult your dentist. Also, after treatment, it is recommended to abstain for some time from physical activity, drinking alcohol, and eating hot and spicy foods.
To prevent pulpitis, carefully monitor your oral hygiene. Use only professional products. If during the day you do not have the opportunity to brush your teeth after eating, use Asepta Fresh mouthwash. It disinfects the oral cavity, effectively fights caries, and normalizes acidity.