Home / Teeth whitening
Back
Published: 07/12/2020
Reading time: 9 min
0
7
- 1 What are the advantages of electrophoresis
- 2 Types of electrodes for electrophoresis
- 3 Intrachannel electrophoresis
- 4 Gels
- 5 Drugs used
- 6 How is the procedure carried out?
- 7 Therapeutic effects of electrophoresis
- 8 Methods of electrophoresis
- 9 Non-carious lesions of teeth (before eruption)
- 10 Indications for the procedure
- 11 Carrying out the procedure
- 12 Remineralization of teeth in childhood
- 13 Symptoms of dental mineralization disorders
- 14 Methods of electrophoresis
- 15 The essence of the treatment method
- 16 Electrical anesthesia with direct electric current
Physiotherapy in dentistry
Physiotherapy is a field of medicine that studies the characteristics and healing properties of physical factors, develops methods of their use for treatment, disease prevention and medical rehabilitation.
Recently, physical treatment methods have been increasingly introduced into dental practice, which, in combination with other treatment methods, make it possible to quickly stop various problems. processes in the jaw. Physical factors are used mainly in the treatment of many dental diseases in the phase of incipient or complete remission with inflammatory, dystrophic and functional changes, they are used in organizing dispensary observation of patients, and in the rehabilitation of patients after traumatic injuries of the maxillofacial area. Physical factors allow for more accurate diagnosis of diseases and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment. General contraindications to physiotherapeutic procedures: severe body conditions, severe exhaustion, malignant neoplasms, tendency to bleeding, blood diseases, severe cardiovascular and respiratory failure, impaired renal and liver function.
In the treatment of dental diseases, natural artificial physical factors are used: direct electric current, pulsed current of low voltage and frequency, alternating electric currents and electric fields of high, ultra-high and ultra-high frequencies. Magnetic therapy, phototherapy, constant high-voltage electric field, aerotherapy, aerosol therapy, ultrasound therapy, cryotherapy are used. In dental practice, hypothermia, paraffin, ozokerite and mud therapy are used, hydrotherapy, vacuum therapy and massage are also used. It is necessary to prescribe no more than 2 procedures, provided that one of them has a predominantly local effect, and physical factors of the opposite effect (sedative and stimulating procedures) are not prescribed simultaneously. In dental practice, physiotherapy is used in combination with other treatment methods, it occupies a worthy place and has great prospects.
Electrotherapy is used in dental practice:
• Direct low voltage electric current (galvanization, medicinal electrophoresis, electrical anesthesia);
• Pulsed currents of low frequency and low voltage (treatment with diadynamic, sinusoidal, modulated, fluctuating currents, pulsed low voltage current used for electrodiagnostics and EDI);
• High frequency alternating electric currents (darsonvalization, diathermocoagulation);
• Electric, magnetic, electromagnetic field (electric field of ultra-high frequency - EG-UHF, alternating magnetic field of ultra-high frequency - MP-UHF, microwave therapy, magnetic therapy).
The essence of the treatment method
Electrophoresis is a physiotherapeutic procedure. During the session, the patient's body is exposed to electrical impulses in order to obtain a lasting therapeutic effect.
Drug electrophoresis is also used to administer medications through the skin and mucous membranes.
We can say that this method is complex, since there is simultaneous exposure to current and medication.
Which drug to choose for the procedure, what the percentage and polarity of administration are, is determined only by the attending physician, taking into account the patient’s condition and the severity of the disease.
The essence of electrophoresis is that drugs enter tissues in the form of charged particles through the intercellular spaces, ducts of the sweat and sebaceous glands. As a result of exposure to electric current, the effectiveness of the drugs increases significantly, as tissue sensitivity increases.
All medications are administered taking into account their polarity; if they are cations, then they are introduced from the anode, and anions from the cathode. Distilled water is considered the best solvent, but for poorly soluble compounds, alcohol or Dimexide is used.
Galvanization and electrophoresis
Galvanization
This is the use for therapeutic purposes of continuous direct current of low strength (up to 50mA), and low voltage (30-80V), which are passed through certain areas of the body.
In dental practice, galvanization is used in the collar area. Galvanic current is a factor that stimulates blood circulation, improves tissue trophism, promotes the removal of metabolic products from the source of inflammation, the resorption of infiltrates and scars at the site of exposure, helps restore the conductivity of nerve elements, increases tissue metabolism, which is associated with increased blood and lymph circulation in the skin, mucous membranes, tissues due to vasodilation, the appearance of hyperemia, with an increase in the permeability of the vascular wall, with an increase in local temperature. This promotes the absorption of medicinal substances introduced into the skin using direct current.
Galvanic effect on the salivary glands:
Galvanization for periodontal disease:
Location of electrodes when affecting the TMJ:
Drug electrophoresis
Drug electrophoresis is the introduction of medicinal substances (DS) into the body through the skin or mucous membranes using direct current.
Advantages of electrophoresis:
♦ Combined action of direct electric current and drug;
♦ Absence of general toxic effect of drugs;
♦ The ability to selectively introduce one or another ion depending on its polarity into tissues that are inaccessible to other methods of drug administration.
Devices for galvanization and medicinal electrophoresis:
Indications for the use of galvanization and electrophoresis:
- Chronic inflammatory processes.
- Gingivitis.
- Periodontitis.
- Periodontal disease.
- Arthrosis, arthritis (trismus).
- Scarring.
- Post-traumatic conditions.
- Glossalgia.
- Neuralgia and neuritis.
- Dental diseases.
- Diseases of the salivary glands.
Contraindications for the use of galvanization and electrophoresis:
- Acute inflammatory (purulent) processes.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Cardiac decompensation, blood diseases.
- Severe sclerosis of cerebral vessels.
- Epilepsy.
- Acute skin diseases.
- Tuberculosis in the active phase.
- Toxic condition, cachexia.
- Individual intolerance.
- Second half of pregnancy.
- Feverish condition.
Galvanization and electrophoresis in childhood
Galvanization and electrophoresis can also be used in childhood. When carrying out the procedure, electrodes with wires soldered to them are used, rather than clamps. Electrodes must be secured with bandages. Since the sensitivity of children's skin to direct current is increased, the current strength is increased slowly, bringing it within 3-4 minutes to the value prescribed by the doctor. The current density depends on the age of the child - in the range of 0.03-0.08 mA per 1 cm2 of area. Physiotherapy pads for children are carried out with less power, until a slight tingling sensation appears, for 5-10 minutes.
Galvanic collar according to A.E. Shcherbak:
Galvanization and electrophoresis of the facial area (“Bergonier half mask”):
Methods of electrophoresis
To increase the effectiveness of this procedure, methods of drug electrophoresis are constantly being developed and improved. The following are currently used:
- Prolonged galvanization. A low-intensity electric current is used, but the exposure time is long. The Krona battery is a source of current. The course of treatment procedures is usually 20-30 sessions. Electrophoresis is very calming and has an analgesic effect.
- Labile galvanization. During the procedure, one electrode is fixed motionless, and the second is in motion and moves at a speed of 3-5 cm per second along the surface of the skin. To eliminate current fluctuations, a stabilizing device is introduced into the device. The procedure well increases metabolism, improves blood supply to organs and tissues and neuromuscular conduction.
- Interstitial electrophoresis. Carrying out the procedure of medicinal electrophoresis using this technique comes down to the introduction of a drug or mixture of substances through a cannula subcutaneously or intramuscularly. The medicine can be administered by stream or drip. Electrodes are applied across the lesion to increase the concentration of the drug. If the medicine is administered in a stream, then the current is turned on simultaneously, and when administered by drip, after administration.
In neurological practice, electrophoresis is used for many diseases of the nervous system. The following methods are used:
1. Vacuum electrophoresis. A special device EVAC-1 is used, which has a vacuum pump and cuvettes. During the procedure, the cuvettes are applied to the skin or mucous membrane, and the pad is impregnated with the drug.
After a discharged pressure is created, the skin rises and comes into close contact with the drug. The duration of the procedure is only 5-10 minutes; 5-10 must be done per course, depending on the patient’s condition and the severity of his illness.
This electrophoresis method allows for a larger amount of medication to be injected much deeper.
2. Microelectrophoresis. To carry out the procedure, use a cotton pad into which a wick soaked in a medicinal product is inserted. An electrode is located on top to create contact between the metal tip and the cotton wool. The use of medicinal electrophoresis using this technique is often used for hypertension, sleep disorders, and pathologies of the nervous system.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Gummy Smile | Children's and family dental clinic "White Bear" | Saint Petersburg
3. Electrophonophoresis is a combination of ultrasound and electrophoresis. There is a special device that consists of an alternating current source that has a therapeutic effect, a sensor that converts ultrasound, a stabilized current source, an electric nozzle and an electrode.
During the procedure, the electrode is fixed on the skin, the electric nozzle is filled with the drug, secured to the ultrasonic sensor and connected to the other pole of the current source. The current strength increases gradually, and then the ultrasound turns on.
The procedures are done daily, maybe every other day, for 10-15 minutes.
Methods of medicinal electrophoresis are different, but which one to use is decided by the attending physician.
Electrical anesthesia with direct electric current
The analgesic effect of direct electric current is used when opening a tooth cavity, in the treatment of pulpitis, during injections, when treating a tooth for a crown. For electrical anesthesia, direct current is used from the positive pole, but it is also possible from the negative pole. The cathode anesthetizes better than the anode (Rubin L.R., 1967). It is necessary to select a current strength that can block the pain impulse. The optimal current parameters for direct action on the nerve receptor are from 109 to 20 µA. For different groups of teeth, an electric current of a certain strength is selected: in the front teeth the average is 5-10 µA, in molars - 10-16 µA. An electric current of more than 30 μA leads to pulp damage and subsequent necrosis.
Physiotherapy of diseases of hard tissues of temporary and permanent teeth
Physical methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention are used at various stages of the carious process. For caries in the stain stage, remineralization of tooth tissue is used using calcium and fluoride electrophoresis. For children, use a 5% solution of calcium gluconate, for adults, a 10% solution of calcium gluconate. The exposure time is 10-15 minutes, then an application is carried out with a 2% sodium fluoride solution for 2-3 minutes. The course of treatment is 10-15 sessions. The procedure is carried out every day. Simultaneously with electrophoresis of microelements, general irradiation with UV rays is prescribed for multiple caries. They recommend 2-3 courses of UV irradiation, 20 procedures every other day. For superficial, medium and deep caries, electrical anesthesia and electroodontodiagnosis can be used during preparation.
Physioprophylaxis of dental caries
Physioprophylaxis of dental caries occupies a prominent place among other methods of preventing dental caries. Prevention of caries in children begins from the prenatal period of the child's development. For this purpose, the pregnant woman is prescribed general UV irradiation, aimed at strengthening the woman’s body and stimulating phosphorus-calcium metabolism, improving the formation and absorption of vitamins.
It is possible to prescribe aeronization to normalize the autonomic nervous system. During the neonatal period (up to 1 month), daily walks and exposure of the child to reflected sunlight are important. In the summer, children should be exposed to sunlight for sufficient time. In the northern regions, children need to undergo artificial general irradiation with ultraviolet rays.
To prevent caries in children, irradiation of the gums and oral mucosa can be carried out, starting with l/3 biodoses and increasing by 1/3 biodoses, the duration of each subsequent irradiation, bringing up to 2-3 biodoses. There are 2 courses of radiation per year, preferably in winter and spring. The same procedures can be performed on adults prone to dental caries.
Non-carious lesions of teeth (before eruption)
Enamel hypoplasia
In the treatment of enamel hypoplasia with pronounced forms and large foci of impaired mineralization, which is accompanied by hyperesthesia, medicinal electrophoresis of calcium, phosphorus, fluorine and B vitamins is used in combination with novocaine. To do this, calcium electrophoresis is carried out from a 2.5% solution of glycerophosphate or a 2-4% solution of calcium chloride in alternation with vitamins B and a 6% solution with 2% novocaine. The course of treatment is 10-15 procedures, 20 minutes each. To treat systemic enamel hypoplasia, UV irradiation is prescribed according to the generally accepted method during the period of low insolation of the body (November-April). You can apply galvanization of the cervical sympathetic nodes - 10-15 procedures.
Endemic fluorosis
It is recommended to carry out local saturation of tooth tissues with calcium, phosphorus, vitamins C, P, PP, group B. A 10% solution of calcium gluconate is used for electrophoresis and a 6% solution of novocaine. A course of treatment requires 10 procedures with calcium and 10 procedures with vitamin B1. Calcium electrophoresis in a course of 10-12 is prescribed after bleaching pigmented areas of enamel with a 30% solution of hydrochloric acid - 5 minutes and 33% solution of hydrogen peroxide - 10 minutes.
Non-carious lesions of teeth (after eruption)
Increased abrasion of hard dental tissues
This pathology is accompanied by increased sensitivity of the tooth to physical and chemical irritants, so electrophoresis of calcium, phosphorus, vitamins C, P, PP and group B is prescribed. To improve metabolic processes and vitamin formation, general UV irradiation is prescribed.
Wedge effect
Among the clinical symptoms of the disease, demineralization of enamel and hyperesthesia when exposed to physical and mechanical stimuli predominate.
Therefore, the complex of treatment measures includes:
• electrophoresis of calcium, phosphorus, fluorine;
• electrophoresis of vitamin B1 with trimecaine;
• general UV irradiation 2-3 courses per year, with a break of 3-4 months;
• UV irradiation of the collar zone, course of 5-6 exposures every 11-2 days;
• UV irradiation of gums (5-6 exposures every other day, every day).
Tooth injury
When a tooth is injured, the neurovascular bundle ruptures or is compressed. It is necessary to conduct electroodontic diagnostics. A drop in electrical excitability from 7 to 200 μA is an indication for the administration of a UHF electric field or microwave therapy with pulsed currents. Course - 3-5 impacts. Electroodontic diagnostics must be repeated after 2 weeks. If the indicators improve, then calcium electrophoresis is prescribed. In the worst case, the tooth is trepanned after 3-4 weeks.
Tooth erosion
Tooth erosion is the progressive loss of enamel and dentin. To remineralize tooth enamel, electrophoresis is introduced with a 10% calcium solution, then an application is carried out with a 2% sodium fluoride solution for 2-3 minutes. The course of treatment is 10-15 procedures. Repeat course in a year. UV irradiation is also prescribed.
Hyperesthesia
Hyperesthesia is a symptom that accompanies many dental diseases: non-carious lesions, dental caries, periodontal disease, etc. Since the appearance of hyperesthesia is associated with impaired mineral metabolism, electrophoresis with calcium, phosphorus, and fluorine is prescribed. To eliminate hyperesthesia, electrophoresis of vitamin B1 is used in combination with novocaine. In case of pronounced hyperesthesia, electrophoresis of anesthetics alone is used. To quickly relieve hyperesthesia, electrophoresis of a 1% sodium fluoride solution is indicated. The course of treatment is 7-10 procedures, the duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. Electrophoresis with a 10% calcium gluconate solution is carried out followed by the application of a 1% sodium fluoride solution. The course of treatment is 10-15 procedures. Calcium glycerophosphate electrophoresis is recommended. The procedure ends with the application of “Sensodyne” or “Pearl” pastes to the teeth. To stimulate the autonomic nervous system, electric sound is applied to the upper spine. The course of treatment is 12 procedures daily, duration of exposure is 5-8 minutes, intensity is 0.05-0.2 W/cm2. For pain relief, you can use the ELOZ-1 device, and UV irradiation to stimulate metabolism.
Treatment of pulpitis
Physical factors are used at all stages of treatment of pulpitis. Electroodontodiagnosis is used to correctly diagnose and select a specific treatment method. Electrical anesthesia using the ELOZ-1 apparatus is effective in many cases. For pain relief, you can use electrophoresis of anesthetics and diadynomophoresis. After opening the tooth cavity, diathermocoagulation is widely used to necrotize the dental pulp. This method can be carried out in well-passable canals; in poorly passable canals, the inflamed pulp is necrotic by electrophoresis of a saturated iodine solution.
The most common complication after filling a tooth canal is pain, which intensifies when biting on the tooth (acute apical periodontitis).
In such cases, physiotherapy is prescribed:
• UHF electric field - up to 5-6 procedures for 10 minutes each.
• fluctuating currents (ASB-2 device) - up to 5 procedures (the first three procedures are carried out in weak doses with an analgesic effect, then medium doses with an anti-inflammatory effect are used). The first three procedures are carried out every day, then every other day. Weak doses are given from 5 to 8 minutes, medium doses - 8-10 minutes. The number of procedures is determined by the doctor.
• microwave therapy - 2-3 procedures daily, procedure time - 6 minutes.
To accelerate the epithelization of the oral mucosa after its treatment with an antidote, UV and UV irradiation are prescribed. The course of treatment is 3-10 procedures.
Treatment of acute periodontitis
To quickly relieve acute serous inflammation in the complex treatment of acute periodontal disease, physical factors are used:
• UHF electric field - athermal dose up to 6 procedures of 10 minutes each;
• fluctuating currents of the first form, with an average dose of up to 6 procedures 1-2 μA - 8-10 min;
• microwave therapy - 2-3 procedures, 5-6 minutes;
• thermal procedures - rinsing with warm solutions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, etc.);
• diathermocoagulation of root canals;
• darsonvalization (for pain without pronounced inflammation) - spark technique (time 3-4 minutes from the vestibular side along the root up and down, 3-4 minutes from the oral side). Course of up to 6 procedures, daily or every other day;
• intrachannel iodine electrophoresis - 2-3 procedures to influence the microflora of macro- and microchannels. If there is purulent discharge in 1 channel, electrophoresis with a 1% trypsin solution is prescribed. Electrophoresis is carried out after acute symptoms have subsided;
• UV irradiation along the transitional fold during periostitis. A course of 3 to 10 impacts daily or every other day;
• irradiation with a Solux lamp to accelerate the maturation focus - 3-5 times, exposure time 3-5 minutes.
Treatment of chronic periodontitis
In the treatment of periodontitis, physical treatment methods are used independently or as part of complex therapy.
The goal of physiotherapeutic procedures is to eliminate the source of inflammation in the periodontium and accelerate the regeneration of bone tissue. In the treatment of chronic forms of periodontal disease, the following are used:
• electrophoresis of medicinal substances in the root canal and periodontium. The most widely used is electrophoresis of iodine and trypsin 0.5% in a buffer solution. For chronic fibrous periodontitis, 2 treatments are sufficient. For granulating and granulomatous periodontitis - 3-4 exposures, if the focus of the discharge is 5 mm. Electrophoresis can be performed with antibiotics. Electrophoresis with 10% calcium chloride can be performed periodontally after root therapy and canal obturation. The course of treatment is up to 10 procedures. They recommend (L.I. Furmanov) electrophoresis with a 5-10% solution of KU in the tooth cavity, and 5-10% solution of CaCl2 in the area of the fistula. Electrophoresis cannot be performed if there is a broken metal instrument in the root canal that extends beyond the apex of the tooth, and if there is living pulp in the canal. Iodine phonophoresis is more effective;
• microwave therapy in the fistula area 1-3-5 procedures for 5 minutes, power 3-7 W. Before carrying out electrophoresis with 5-10% potassium iodide into the tooth cavity and electrophoresis with 5-10% calcium chloride solution into the fistula area, L.I. Furmanov recommends applying a vacuum over the fistula to aspirate the pus and create a 1 cm hematoma in the area of the fistula to intensify the blood supply. Microwave therapy is carried out after electrophoresis with 5-10% potassium iodide and 5-10% calcium chloride;
• laser therapy can be used to achieve an anti-inflammatory effect and stimulate the healing process. Doses of 50-100 mW/cm2 are used, exposure is 1-2 minutes per field, up to 15 procedures per course of treatment.
Chronic periodontitis in the acute stage
In the modern classification, this disease is classified as a separate nosological unit. Physiotherapy is prescribed after ensuring the outflow of exudate from the source of inflammation, opening the tooth cavity. The phenomena of exacerbation of chronic periodontitis are stopped by the same physical factors as in acute apical periodontitis.
Complications after filling a tooth canal
When filling canals with pulpitis, complications manifest themselves as signs of acute periodontitis, and with periodontitis - in the form of exacerbation of chronic periodontitis. If the pain symptom predominates, then darsonvalization, diadynamic sinusoidal modulated currents, fluctuarization are prescribed in the same way as for acute apical periodontitis, up to three effects. When severe inflammation predominates, fluctuarization, UHF electric field, and microwave therapy are used according to generally accepted methods. To prevent exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, fluctuarization is prescribed on the day of root canal filling if an excess of filling material is detected on the x-ray behind the apex of the tooth.
Source: stomat.org
Symptoms of dental mineralization disorders
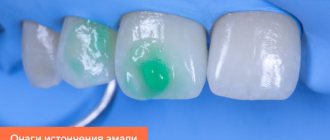
How can one suspect that a person has begun the process of demineralization?
The earliest manifestation of demineralization is focal damage to the enamel. In this case, white spots become noticeable on the tooth enamel, which are located on the tooth base or at the junction of two teeth.
The stains can be barely noticeable or occupy an entire tooth. Initially, the patient has one or two teeth affected. This pathology occurs especially often in children under 11 years of age. It also occurs in adults, but much less frequently.
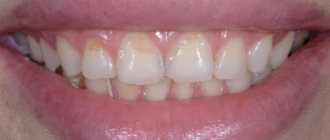
At the initial stage, when demineralization is just beginning to break down, it is very difficult to detect.
The main manifestations of enamel pathology at an early stage are:
- decreased shine of teeth;
- acquisition of dullness by teeth.
Then the pathological process intensifies and becomes more pronounced, which is manifested by symptoms:
- streaks or chalky spots on the enamel;
- porosity, roughness and deformation of enamel;
- darkening of white spots on the enamel, subsequently turning brown.
Thinning tooth enamel begins to darken and decay, forming carious lesions on the teeth. And this process cannot end on its own. Therefore, even with minimal suspicion of the onset of enamel destruction, it is important to consult a dentist as soon as possible.
About the procedure
The procedure is performed painlessly and makes it possible to quickly relieve inflammation inside the dental canal and in the tissues surrounding the apex of the tooth, and also has a bactericidal effect on the tissue, eliminating foci of infection. In difficult cases, dentists prescribe electrophoresis of teeth, because this is a treatment method that allows you to accumulate drugs in the very source of inflammation and significantly increase their effectiveness. Medicines administered by electrophoresis are eliminated more slowly and retain their therapeutic effect for several weeks, while the risk of developing allergic reactions is minimal.
The only drawback of the method is the presence of a number of contraindications. Electrophoresis of teeth cannot be prescribed to everyone, since for some diseases and conditions of the patient the procedure is strictly contraindicated:
- Acute diseases of the cardiovascular system
- Presence of a pacemaker
- Bronchial asthma
- Allergy to injected drugs
- Oncological diseases
- Inflammatory diseases and purulent processes in the body
This is what the dental electrophoresis procedure looks like in practice: a special pad is soaked in the medicine, then it is fixed on the sore spot. If treatment of pulpitis is necessary, the canals are processed and the drug is injected into the tooth. Next, using a special device, a weak current is applied to the tissues of the oral cavity through a patch with medicine.
The entire procedure lasts 10-30 minutes, and the course of treatment takes from 10 to 20 procedures, performed daily or every other day.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
Drugs used
Most often, dentists use the following substances to restore the mineral balance of enamel:
- Complex products - “Remodent”, “GC Tooth Mousse”, “Ftorodent”. Applications with a 3% solution of these products saturate the enamel with essential elements such as phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, manganese, iron, copper and zinc. Due to the absence of toxic compounds, they can be used to restore the mineral composition of primary teeth in children aged two years and older.
- 10% solution of calcium gluconate or chloride. Applying gauze swabs soaked in the preparation to the dental surface allows you to compensate for calcium deficiency. For more complete penetration into tooth tissue, the electrophoresis method can be used.
- Sodium fluoride. The compound is most often applied to the enamel after using calcium-containing preparations. Sodium fluoride helps to activate the process of protein metabolism in tooth tissues, as well as reduce permeability.
Indications
Remineralization of teeth is recommended in the following cases:
- painful reaction to cold and hot, sweet and sour foods;
- caries in the stain stage, which does not affect the deep layers of hard tooth tissue;
- thinning of the enamel (for example, after whitening, removing deposits, correcting the bite);
- congenital insufficient mineralization of teeth;
- enamel damage due to trauma;
- increased consumption of minerals by the body (during pregnancy, menopause, adolescence).
Types of dental remineralization
Natural
The enamel is saturated with essential minerals using nutritional correction. Products useful for this include cottage cheese with a fat content of at least 5%, milk with a fat content of at least 2.5%, hard cheeses, legumes (beans, beans, peas, lentils, chickpeas, etc.), nuts, green vegetables, fluoridated water (the amount of drinking such water should be agreed with your doctor).
Artificial
It involves covering teeth with artificial enamel - varnishes, gels and other products containing active fluorine and calcium.
Indications
Most often, medicinal solutions such as 5-10% calcium chloride or gluconate (in combination with vitamin C and PP), 2.5% glycerophosphate solution (enhances anabolic processes) and copper-calcium hydroxide solution (anti-inflammatory, osteotropic, antiseptic effect). The main indications are listed below.
- Increased sensitivity of teeth.
- Caries and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis).
- Gum diseases (stomatitis, gingivitis, alveolitis, periodontitis).
- Diseases of the temporomandibular joint.
- Pain after treatment or tooth extraction.
- Neuralgia.
The action of electrophoresis has a bactericidal effect and reduces the amount of microflora in the tooth canal by 86%.
Gels
At the initial stage of demineralization, it is possible to prevent its further progression through the use of the following drugs:
- Amazing White Minerals. This gel allows you to fight caries at the stage of its occurrence, reduces the sensitivity of teeth and increases the duration of their whiteness after professional whitening.
- Vivax Dent. The remineralizing balm contains sodium fluoride, a peptide complex, kelp extract, and castor oil. The product is intended for daily use and has antibacterial and antiseptic properties.
- ROCS Medical Minerals. The drug is intended to strengthen sensitive teeth. It contains compounds of magnesium, calcium and fluorine, which help increase the strength of enamel and suppress the activity of bacteria.
- Lakalut Alpin is a toothpaste with anti-caries and anti-plaque properties. Thanks to sodium fluoride and a mineral complex, the product tones the gum tissue and slows down the formation of mineralized plaque.
- Elmex gel contains sodium fluoride and amino fluoride, which promote mineralization and strengthening of enamel. The instructions suggest cleaning your teeth with the product no more than once a week.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the main causes of cheek swelling: treatment methods
Contraindications
There are a number of contraindications for both the use of physical factors and the use of calcium supplements.
- Oncological diseases.
- Presence of a pacemaker.
- Diseases or injuries of the oral mucosa.
- Individual intolerance.
- Diseases of the heart and blood.
- Acute inflammatory or purulent diseases.
- Mental disorders.
Our body does not produce calcium on its own. We get it by eating foods with phosphate, calcium carbonate, lactate, caseinate. Often this is not enough and we have to enrich the body with the help of medicines. But the use of calcium also has a number of contraindications:
- High level of Ca ions in the blood (no more than 12 mg%).
- Hypercalciuria (Ca in the urine).
- Tendency to thrombosis.
- The use of cardiac glycosides (will lead to arrhythmia).
- Stones in the kidneys and urinary tract.
Clinical studies have shown that Ca preparations are absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract by only 1/5. To maintain its high level, you need to eat foods rich in calcium: milk, cheese, cottage cheese, sesame seeds, greens, poppy seeds, nuts, fish, beans, garlic, cabbage.
Efficiency
Electrophoresis with calcium gluconate has only positive effects on teeth.
- It acts locally, without entering the lymph and bloodstream.
- The ionized molecule binds to fluorine much more actively and forms a strong structure.
- Weak currents activate immune processes in the body and chemical and biological reactions.
- A small dose is administered, but the effect is prolonged.
- The sensitivity of hard tooth tissues decreases.
- The antiseptic effect reduces the risk of complications.
Calcium preparations, in addition to electrophoresis, can be administered orally or intravenously. But the percentage of their absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is very small, and when administered into a vein, a number of side effects are observed (fever, tachycardia, etc.).
After electrophoresis, it is necessary to carry out fluoridation of the teeth. Without fluoride, calcium is not able to strengthen in the crystalline structure of the enamel. It is hydroxyfluorapatite that gives enamel hardness and resistance to infection.