Allergies from dentures - myth or reality?
Prosthetics are an excellent chance to restore lost teeth or correct aesthetic defects. There are contraindications for installing crowns and dentures. These include allergic reactions of the patient to the dental material used.
Denture allergies are not a myth. The problem is urgent and becoming quite global; a generation is growing with a reduced or incorrect, atopic response of the human immune system.
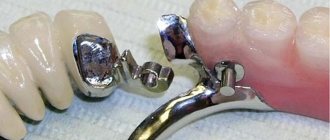
Allergic reactions very often occur to artificial crowns that are in the mouth. They mainly react to products made of metal, metal-ceramics, or more precisely, to one of the components of the alloy.
Features of operation
All described manipulations are absolutely painless for the patient. At stages when pain relief is needed, we use effective and safe drugs. After their effect wears off, the patient may feel discomfort in the area of the installed crown. But it passes quickly, and during rehabilitation the specialist will prescribe an effective pain reliever.
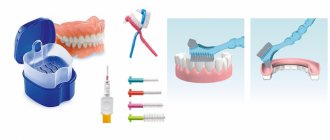
Once installed, dentures do not require special care. You should continue to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth twice a day with your regular brush and toothpaste. Additionally, it is recommended to use flosses and irrigators.
If handled carelessly, the ceramic part of the crown can be damaged. Usually the damage is limited to chips, and if such damage does not expose the metal base, then the chip can be easily repaired using composite materials. If metal is still exposed, the structure will have to be replaced.
Which components are allergens?
In the manufacture of metal and metal-ceramic prostheses, nickel-chromium or cobalt-chromium alloy and copper are used. The first option causes allergic reactions more often than others.
There is a burning sensation in the oral cavity, redness of the gums around the crowns, and swelling of the soft tissues may occur. Because of this inflammation, when chewing and chewing food, the gums begin to hurt and bleed. A metallic taste in the mouth and a tingling sensation should alert a person and force him to see a doctor at the clinic.
This type of metal dental structures is inexpensive and therefore popular.
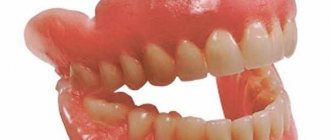
Allergic reactions to removable dentures are possible, specifically to the plastic and acrylic from which the structure is made. In addition to the material itself, the composition with which the prosthesis is painted can be an allergen. The dye used to make removable dentures pink is more likely to cause a reaction. There is a burning sensation in the mouth and swelling of the gums on which the prosthesis is located.
How does an allergy to dentures manifest?
Let's summarize. What symptoms after the prosthetic procedure should prompt a person to think about a complication - an allergy to dentures and independently contact the attending physician at the dental clinic:
- burning in the mouth
- red gums
- elevated temperature
- bleeding gums
- rash in and around the mouth
- swelling of soft tissues (cheeks, gums, tongue)
- swelling of lips, eyelids
- metallic taste
- tingling
- pain when chewing
- increased salivation
- cough as in bronchial asthma
- Quincke's edema
Allergic or infectious inflammation?
The symptoms of an allergy to a metal pin or prosthesis base and the manifestation of infectious inflammation are similar to each other, so they are quite easy to confuse. However, in the case of intolerance to metal-ceramic dentures, a pronounced metallic taste is felt in the mouth, which does not happen with infectious inflammation.
In addition, a characteristic sign of an allergy to metal-ceramic crowns is darkening of the installed structure, as well as a feeling of bitterness or acid when the cutlery touches the orthodontic product.
How to help with allergies?
What should you do if you encounter such manifestations in the oral cavity? If your allergy symptoms are severe, you should take an ambulance - an antihistamine (suprastin, zodak, etc.). And then according to plan.
First, see your dentist and find out the reason why this happened. Perhaps a specialist will suggest:
- elimination test - will remove the prosthesis, crown for 1-7 days
- exposure test - after the negative symptoms disappear, he will install the structure back and monitor the progress of the condition.
Secondly, visit an allergist and take tests, allergy tests for a reaction to dental material. Then, based on the research results, it is necessary to change the designs to those prostheses that will not cause an allergic reaction.
If the elements of the prosthesis are incompatible: what is “galvanism”
Sometimes it happens that orthopedic products installed in the oral cavity are made of materials that “conflict” with each other - in particular, this only applies to metals, and even inexpensive ones. For example, if you have had one crown for five years, and then you decide to get another one, but from a different metal. Then a weak current may form. This reaction is usually called galvanic.
Signs of galvanic syndrome:
- discomfort while eating, including a metallic or bitter taste,
- general malaise accompanied by loss of appetite, headaches or sleep disturbances,
- increased salivation or, conversely, the development of dry mouth,
- change in color of metal prostheses (darkening, loss of shine, etc.).
Important to remember! If an orthopedic structure is installed, but there is already a foreign element in the oral cavity, then it is important to consult with a specialist about the chemical interaction of these materials.
Requirements for prostheses to replace those that cause allergies
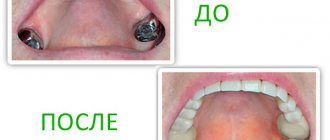
Metal-ceramic prostheses can be replaced with structures made of zirconium oxide. Zirconium does not cause allergies and does not oxidize in the oral cavity under the influence of saliva and other liquids.
Products made of gold, platinum, titanium, and precious metals are safe in this regard. But they are expensive, not everyone can afford them.
If you are allergic to an acrylic prosthesis, you should use acryfree, that is, a material that does not contain acrylic plastic. Or new generation products, with a minimum amount of substances that can cause a reaction, nylon prostheses.
Let us repeat, you can select dental material for a new prosthesis only after a complete examination by an allergist.
The main requirement for a prosthesis is not only strength and aesthetics, but also resistance to chemical attack. Do not oxidize when interacting with saliva and food, be hypoallergenic and safe for the body as a whole.
Source
Ceramics and zirconium dioxide are the lowest allergenic materials
Allergies to ceramic crowns occur very rarely – almost never. The same can be said about allergies to zirconium crowns (made of zirconium dioxide) and aluminum dioxide (metal-free ceramics). Ceramics is considered one of the most low-allergenic and inert materials in dentistry. But an individual allergic reaction still sometimes occurs, for example, if dyes were used to make the prosthesis. Or, if a ceramic crown is placed on a core inlay or implant that contains allergens (aluminum, nickel, vanadium). That is, the problem here is not in the ceramics, but in what is underneath it.
Read on the topic: ceramic metal-free dental crowns - what they are and how relevant they are today.
Complications after prosthetics
Prosthetics is a procedure for restoring teeth using individual crowns, bridges, removable jaws and other replacement structures. It requires careful preparation and compliance with the rules to restore the functionality of the dentition and aesthetics. Sometimes complications may arise after the final stage of prosthetics - unfortunately, no one is immune from this. But it is worth distinguishing between complications that can be painlessly corrected and corrected, as well as those consequences in which the result of the procedure will have to be globally corrected - up to the removal of artificial implants and work “all over again”. In this article we will talk about the main consequences, and experts will also share how patients can prevent these same complications after treatment.
| Stump tab | from 14,000 rub. |
| Tooth restoration with an onlay (ceramic E.Max) | from 40,000 rub. |
| Tooth restoration with veneer (ceramic E.Max, ceramic on zirconium dioxide, feldspathic on a refractor) | from 72,000 rub. |
| Tooth restoration with a crown (metal-ceramic, E.Max ceramic, all-zirconium, zirconium dioxide ceramic) | from 48,000 rub. |
Why can complications occur after prosthetics?
Prosthetics involves the introduction of a foreign object into the oral cavity. The body can positively perceive these elements, or it can reject the structures. When these undesirable consequences occur, it is important to determine the root cause and then correct the situation.
Clinical case: a person had a system installed poorly: they were pressed for time, the patient wanted to quickly solve the problem of missing crowns in the dentition, went to the first clinic he came across, and also saved on the prosthetic system. As a result, after a few weeks problems arose and the work had to be done again, but in a proven dental center with experienced prosthetists.
The main types of causes of complications during prosthetics. What do they lead to?
- Errors at the stage of planning the installation of the structure are a very common reason, as a result of which the shape and dimensions of the prosthetic structure were incorrectly selected. To prevent this from happening, at the preparatory stage the prosthetist dentist must take photographs (if necessary, several photographs) and comprehensively diagnose the condition of the oral cavity. It is possible that prosthetics will take a little longer than planned, but such thorough planning will guarantee effective treatment.
- Insufficient sanitation of the oral cavity. For example, when the patient was not found to have latent caries or pulpitis, but after the treatment procedure these problems made themselves felt. At the preparation stage, it is important to cleanse teeth from stone and plaque, treat all areas of inflammation, remove decayed teeth, and build up bone tissue. To avoid complications, products for this reason are placed only with absolute sanitation of the oral cavity!
- Violation of one of the stages of the prosthetic procedure. These could be errors at the clinical stage or at the technical stage. In the first case, the teeth are often not sharpened well enough, impressions are taken incorrectly, the frame is not fitted correctly, the technology for installing the structure was violated, or the specialist initially incorrectly determined the type of bite. Main technical errors: incorrectly selected shape of the teeth, poor-quality frame for the structure, errors when casting plaster models of the structure, etc.
- General diseases. Common causes that lead to system rejection are osteoporosis, diabetes, latent or chronic inflammatory processes in the body. One way or another, prosthetics is a burden on the body, and with a weakened immune system, the patient is not immune from possible complications. First, it is necessary to treat the diseases or bring them to the stage of stable remission, and only then proceed to the installation of structures.
- Poor hygiene. Failure to comply with hygiene rules leads to the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms and irreversible complications. Bacteria provoke caries and inflammation of the gums, against which prosthetic structures can be rejected.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
TOP 9 complications after prosthetics
We present to your attention the 9 most common complications after the installation of prosthetic structures:
- The development of inflammation of the gingival tissue - as a result, leads to gingivitis, stomatitis in acute and chronic forms. As a rule, such a complication in the oral cavity occurs due to poor fit of the tooth replacement structure. The process goes like this: the structure puts pressure on the tissue, blood vessels die, there is no blood supply to the tissue, and inflammation develops.
How to solve a problem?
The dentist recommends treating the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, as well as special gels to activate tissue regeneration processes. With regular treatment and oral care, the gums are soothed.
Carious formations - as a result, the supporting teeth are affected by pulpitis or periodontitis. This usually occurs due to the accumulation of food debris between the prosthetic structure and living tissues. The problem leads to the fact that the teeth are gradually destroyed, cease to perform their supporting functions, and the fixation of the prosthesis is disrupted.
How to solve a problem?
At least twice a year (or even more often) undergo a full examination by a dentist. Not a single prosthesis, even a well-made one, will stand in such a way that bacteria will not accumulate under it. Care for the cavity with such products should be twice as thorough as usual!
Infectious lesions of soft and bone tissues – periodontitis. Often obvious destructive changes are noticeable around the product: the gums acquire a bluish tint, swelling and bleeding of the tissue develops. As a result, this leads to tooth loss and disruption of the fixation of the replacement structure.
How to solve a problem?
First, the dentist must prepare the teeth without creating so-called ledges. Secondly, the design must be selected strictly; several fittings and adjustments of the product may be required. Thirdly, before installing a prosthetic product, it is necessary to treat the gums. Regular therapy may be needed to maintain the health of the oral soft tissues.
Rejection of the structure due to an allergic reaction. It can manifest itself as swelling of the gums, itching, rash and redness in the mouth. In some cases, difficulty breathing and a constant feeling of dry mouth and fever may occur. Allergies may appear in the first few hours after installation of the structure or after several weeks.
Allergy to crowns: types, symptoms and what to do?
A common dental service is the restoration of elements in the dentition using prosthetics. Some of the materials offered to customers may cause allergic reactions. In this regard, many people want to know about crown allergies: types, symptoms and what to do.
- Pathological signs of allergies
- Reaction to metal-ceramic crowns
- Causes of allergies to dentures
- Provoking factors
- Diagnostic methods
- First aid and therapeutic methods
- Allergy prevention
Treatment and prevention
First of all, you should remove all the crowns or agree to shielding - chemically silvering the prosthesis. You can also do electroplating - applying gold to the crowns.
If eczema or stomatitis is diagnosed, you need to start taking symptomatic medications and antihistamines, the latter are more effective in injection form. Tavegil or Suprastin are mainly prescribed. If the patient has swelling, bronchospasms, his serious condition is difficult to relieve, an erosive process is diagnosed, glucocorticoids are prescribed: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Diprospan and Celeston.
Allergic processes lead to painful and unpleasant sensations in the mouth, which makes it difficult to eat. In such cases, antihistamines block H1 receptors, which will produce the expected pharmacological effect within half an hour. If pain is not observed, you can use H1-antihists, for example: Telfast, Claritin, Zartec or Erius. The entire group of drugs is sold exclusively in tablet form.
If you have difficulty swallowing or chewing, you should use toothpaste that contains an anesthetic. An alternative is soda rinses. Complete care of the oral mucosa is complemented by washing it with a weak solution of furatsilin. To relieve itching and treat epidermal complications, ointments and creams from the group of glucocorticoids are used: Elokom, Triderm, Celestoderm, Garamiciton and Advantan. Ceralip is used for lips.
Allergic reactions to crowns, if prescribed therapy is followed, have a good prognosis. All medications should be used only after consultation with an allergist or immunologist and only according to the prescribed dosage.
Prosthetics are a quick and easy way to restore the functionality of your teeth and the aesthetics of your smile. This method has fewer side effects and contraindications than implantation, but one complication exists in each type - an allergic reaction. Allergy is the body’s reaction to the introduction of a foreign structure, followed by its rejection and the appearance of severe symptoms, irritation, and pain.
Pathological signs of allergies
The process is a reaction of the human body to contact with a certain substance called an allergen. There are cases where after prosthetics an allergic reaction to the prosthesis occurs. In this case, the following pronounced symptoms appear:
- pain is felt while eating; a burning sensation, itching of the mucous membranes and tongue appears in the oral cavity; the gum membrane, nose, and larynx swell; redness of the mucous membranes; salivation increases; a rash appears on the skin; unpleasant taste; decreased sensitivity; soreness and cough occur; bleeding gums are observed; temperature increase; exacerbation of existing chronic ailments.
Such manifestations do not occur immediately after the installation of crowns. They can appear after a few days, weeks, months, and for some, years. It is important to respond to the reaction that appears in a timely manner.
Allergy concept
Allergy is understood as a certain reaction of the body to a foreign object, which manifests itself in the form of irritation of the mucous membrane and painful sensations.
For 10 years now, allergies have been a real problem among the population and doctors. The number of cases is increasing every year. Ten percent of the world's inhabitants suffer from various forms of allergies. Moreover, the disease occurs everywhere, regardless of climate, country and region. Monetary wealth also does not play a role here. Allergies can bring severe discomfort to a person's life. It can even make him unable to work and significantly reduce his quality of life.
An allergic disease is a certain form of disease in which the body's immune system reacts to an allergen.
In almost 99% of cases, before prosthetics, a person is unaware of the possibility of such a reaction. Symptoms appear after the procedure. In this case, there seems to be only one way out: removing the source of irritation from the oral cavity.
Reaction to metal-ceramic crowns
Metal-ceramic products are in great demand in orthopedics. They are durable, have a considerable service life, and are aesthetically pleasing. In rare cases, an allergic reaction occurs with this type of prosthetics.
Among the structural components are ceramics and a metal alloy. It’s the second ingredient that can cause allergies.
Among the metals that most often provoke side effects are:
- Nickel is a component of stainless steel. When it comes into contact with saliva, irritation may occur. The element is considered the strongest irritant.
- Manganese, cobalt, chromium are also found in stainless steel. When they come into contact with saliva, they cause irritation and the development of stomatitis.
- Copper is often included in gold alloys to reduce cost. Its oxidation can lead to intoxication.
- Platinum and palladium are not entirely resistant to corrosion; they cause increased sensitivity in the owner of the prosthesis.
- Zinc is used to protect products from moisture. Constant interaction with saliva gradually destroys it, releasing toxic substances.
- Lead – rarely used in orthopedics. But there are cases of its use to reduce the cost of materials. It has a bad effect on the nervous system; in large quantities there is a risk of seizures. It is toxic and gradually poisons the body.
There are metals that are anti-allergenic:
- gold; silver; zirconium (zirconium dioxide is used); titanium.
These metals have good compatibility with the human body, but they are more expensive. They are considered to be the safest prosthetic options.
Reasons for appearance
To solve this problem, it is first important to determine the cause of its occurrence.
In the general list of factors leading to an allergic reaction, the crown material comes first. A similar effect can also be produced by individual components included in its composition.
Typically, this phenomenon greatly complicates the patient’s life and is accompanied by:
- discomfort in the oral cavity;
- general malaise;
- unusual taste in the mouth (metallic, sour or other);
- the appearance of headaches or insomnia;
- change in color of metal prostheses.
Most often, allergies are provoked by the presence of the following elements in the crown material or prosthesis design:
- Nickel . Most often used in dentistry. When this metal interacts with saliva, some people may develop immunity to it, expressed in the form of a severe allergy.
- Copper is often included in expensive alloys. Sometimes it can also be the cause of a negative response of the whole body.
- Cobalt, chromium, manganese - constant contact of such components with the oral cavity (especially with insufficient hygiene) can provoke allergic diseases. The most common among them is stomatitis.
- Zinc . When exposed to high humidity for a long time, the metal begins to oxidize. This process leads to its gradual destruction. It is accompanied by a toxic effect on the mucous membranes of the mouth and other organs.
- Lead . It is used extremely rarely in modern dentistry due to its toxicity. It is able to penetrate all systems of the body, leading to its gradual poisoning.
- Polymers . The porous surface of such crowns creates the most favorable conditions for the accumulation and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. The result of this can be various fungal diseases, for example, candidiasis.
Information. Statistics and studies show that the safest are crowns made of gold, platinum, titanium, ceramics, and zirconium dioxide.
Sometimes the cause of an allergy lies in the toxicity of some small element in the crown material or in the design of the prosthesis. This could be glue, a coloring component, or any fastener (hook, screw).
Provoking factors
There are several provoking moments in dental practice. The most common of them:
- The structure’s not quite tight fit to the gum causes friction when chewing food. The temperature is rising. Heat exchange is disrupted. In this case, vasodilation is observed, soft tissues change structure - they become loose. Accordingly, there is an increase in the absorption of harmful substances - products of destruction and oxidation. The prosthesis needs to be replaced.
- Each method of prosthetics has its own specific period of operation. After the expiration date, the material loses its properties and undergoes destruction. The highest quality care of the device does not eliminate the need to replace it. Otherwise, there may be risks of allergic processes.
- For a number of reasons, for example, the presence of pathologies, dietary intake, or changes in climatic conditions, the client’s saliva acid composition may change. In this case, oxidation and galvanism are not excluded.
- The drug used for anesthesia can cause allergies.
- The incompatibility of the components used in prosthetics and their chemical interaction can cause an unpleasant reaction in the human body.
It is simply impossible to foresee and eliminate all possible probabilities of an allergic reaction. But familiarizing yourself with them will help eliminate or even alleviate unpleasant sensations.
Diagnostic methods
If any symptoms appear, you should urgently contact a dental clinic for consultation. Additional examination by specialists of a narrow profile may also be required: an immunologist, dermatologist, allergist and others. If an allergy to crowns is suspected, the doctor should evaluate:
- Visible defects and deviations.
- The condition of the structure, its wear, change in color.
- Viscosity and composition of saliva.
For correct diagnosis, a dental and allergy history is collected. The latest medical history will include data on hereditary predisposition to allergic reactions. The doctor must find out whether the patient suffers from allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, eczema and other pathologies.
To determine the irritant, allergy tests are performed:
- intracutaneous – injection of the allergen with a needle under the skin; provocative - the allergen is applied to the irritated area; scarification - a drop of irritant is left on the scratch; application - the fabric is moistened in a dissolved allergen and placed on the skin.
Laboratory tests are ordered. Blood testing is mandatory. An elimination or exposure test is often practiced - when the prosthesis is removed for a while, observing the impact.
Relying on the examination results and symptoms, the specialist prescribes effective and appropriate treatment.
Doctor's help
The situation is under control, and now it’s worth seeking advice from specialists. Who should I visit besides the dentist? An allergist, immunologist, endocrinologist and dermatologist will help to identify the culprit and cope with the problem.
For diagnosis, doctors may offer an exposure and elimination test (return the prosthesis and observe the reaction), patch tests (the allergen is applied to the skin), or a blood test.
The dentist may suggest remaking the device without “suspicious” materials or shielding the device, this is when a special metallized anti-allergenic coating is applied.
Fitting a denture in a dental laboratory
First aid and therapeutic methods
If signs of an allergy from a prosthesis are detected, urgent measures must be taken immediately. The main task is to eliminate the source of the body’s allergic reaction. If the device is removable, then this is easy to do - you need to remove and remove the structure from the oral cavity. If the prosthetic element is a permanent crown or bridge, then a visit to a medical organization is immediately required. Before visiting the dentist, it is recommended to rinse with disinfectant solutions.
It is recommended to take antihistamines for symptoms of unwanted allergic manifestations. Enterosorbents will help quickly cleanse the body of toxic products. When soft tissue is affected, healing gels should be applied.
If severe pain is present, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are needed. If the pills do not help, the situation is advanced, then you need to call an ambulance.
The most correct solution in case of an allergy to prosthetics would be to change the design to a new one. It must be made from a well-compatible, hypoallergenic composition. This is the only true way out.
Allergies are very dangerous. Prompt treatment will help stop the development of the reaction, and you can avoid the risk of complications. If urgent measures are not taken, the patient’s condition will only worsen. This can ultimately lead to Quincke's edema, respiratory arrest, and malfunction of internal organs and the heart.