From this article you will learn:
- how much does it cost to do a dental x-ray,
- what you need to know about radiation doses,
- Is it possible to take a dental photograph during pregnancy?
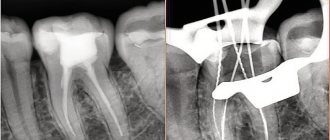
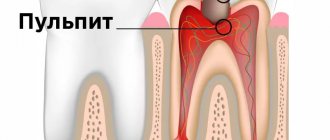
Dental X-ray is a traditional way to determine the quality of root canal filling, as well as to diagnose inflammation at the apex of the tooth root (with apical periodontitis). X-rays of human teeth in dentistry are most often carried out using targeted X-rays. A targeted photograph of a tooth received this name because it is small in size and shows the condition of only a few teeth and the bone tissue around them (Fig. 1-2).
Modern targeted X-rays produce a very low dose of X-ray radiation (compared to what it was 15-20 years ago). This is due both to the advent of ultra-sensitive photographic films, which require a significantly lower dose of radiation, and secondly, to the advent of special intraoral sensors that capture the image digitally and display it on a computer screen. Such digital images require several times less X-ray radiation - even compared to modern films.
Sighting and panoramic radiography in dentistry –
However, targeted images are not suitable for planning bite correction, assessing the condition of bone tissue before implantation, or planning the installation of future implants. They are not very convenient for planning treatment and prosthetics for a large number of teeth, and often do not allow detection of perforations and cracks in the tooth root. Focused photographs of the teeth may not be enough in cases where it is necessary to find problems with root canal filling in order to be able to properly treat the teeth.
Therefore, dentists very often refer patients to more complex options for x-ray examination of teeth and jaw bone tissue -
- dental computed tomography (CT),
- orthopantomogram (Fig. 3),
- teleroentgenogram (for bite correction).
In this article, we will go into detail about the pros and cons of targeted dental x-rays, and what you need to pay attention to if you need to have a dental x-ray (for your own safety). For detailed reviews on the remaining specified methods of radiography in dentistry, read the links above.
Sight image of a tooth –
A targeted photograph of a tooth can be recorded either on photographic film or using a special intraoral sensor that detects X-ray radiation and transmits the image to a computer screen (such a device is called a radiovisiograph or simply a visiograph - Fig. 5). In both cases, an X-ray machine is used as a radiation source (Fig. 4), i.e. the only difference is in the way the image is captured - either on X-ray film or using a digital sensor.
Taking an image using a visiograph -
Digital vs Film Photography: Pros and Cons
Targeted dental x-rays using film were once the only examination option in clinics. It must be said that film photographs have a number of disadvantages that have significantly reduced their use. They require expensive consumables (film, reagents), time to develop photographs, there are difficulties with storing photographs, and over time they fade and are lost. There are also differences in patient safety.
Even modern X-ray films require 4-8 times the radiation dose compared to digital X-ray sensors. For example, the radiation dose to a patient for 1 film image is 10-15 μSv (microsieverts), and for a picture on a visiograph it is on average 1-3 μSv (this dose corresponds to the background natural radiation received by each person in 1 day).
The patient's exposure time when using film X-ray is 0.5-1.2 seconds, and using a digital visiograph sensor - 0.05-0.3 seconds. It is precisely by reducing the required exposure time when using a radiovisiograph that the radiation dose is significantly reduced. Thus, in one day of treatment at the dentist you can take no more than 3 film photographs and 5-6 digital photographs. And as you will see below, the use of a visiograph in some cases even allows you to take an X-ray of a tooth during pregnancy, but in compliance with all safety rules and for urgent indications.
How to take a picture of a tooth using a visiograph: video
Important: always try to take digital photos and inform them in advance that you want them saved to a flash drive. Firstly, then you will always have the pictures at hand, and you can always show them to another doctor. Secondly, the photographs taken for control after treatment will be your guarantee that if you received poor-quality treatment, you will always be able to prove it (the clinic will no longer be able to lose your photographs and rewrite the medical record).
Thirdly, if a digital image is printed on a printer, then the quality of the image will depend not only on the quality of the digital image, but on the resolution of the printer (rare clinics have printers that print in high resolution). Therefore, a photo in digital format will have better quality than a photo printed on paper.
Changes for dental clinics LLC
Even if dentistry is registered as an LLC and has a separate room for x-ray examinations, the new rules create additional difficulties for it. This is due to the fact that the updated requirements for x-rays in dentistry require the mandatory placement of a visiograph and a panoramic x-ray machine in the office. If there is only one device installed in the room, it is necessary to purchase a second one.
Installing any additional equipment that generates radiation in buildings is a whole problem. In the clinic, there is a need to organize additional protection for staff and patients, as radiation doses increase. Protective materials must be used to prevent increases in radiation levels in adjacent rooms to the X-ray room. It is also necessary to ensure compliance with air exchange standards.
One of the key conditions for installing a new device is the need to increase the area of the office by at least 4 square meters. This is necessary to comply with safety standards. An increase in area entails the need to issue a new technical passport for x-rays. If you do not complete this procedure by January 1, 2020, you may lose your license.
Dental X-ray – price for 2021
The cost of one digital X-ray in Moscow will average from 250 to 350 rubles in different clinics. In addition, this price may only apply to a diagnostic initial image, while all other images taken during the treatment phase may cost less (about 150 rubles per image). Therefore, you should carefully read the clinic’s price list.
It should also be noted that there are a large number of clinics in which the cost of dental treatment is indicated on an all-inclusive basis. Accordingly, the cost of treating your tooth will already include the required number of x-rays (usually 2-4 pictures), for which you will no longer pay anything extra.
What else you need to pay attention to is that the price list of some clinics may state that the cost of a targeted x-ray indicated on the clinic’s website applies only if you are a patient of this clinic. Therefore, if an image is taken to be submitted to another clinic, its cost may be 100 rubles higher).
In addition, if you need a printout of a digital image, some clinics may also charge you about 50 rubles for this. The same applies to the description of the x-ray image: if you want to receive a written description of the image taken by a radiologist, then in some clinics they may additionally ask you for about 100-150 rubles.
Radiation doses and safety –
A patient's radiation exposure is measured in either microsieverts (µSv) or millisieverts (mSv). The recommended radiation dose for the population received as a result of X-ray studies (according to the recommendations of SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03) should not be more than 1000 μSv per year (= 1 mSv per year).
Below we will give examples of different types of images in dentistry and the corresponding radiation exposure to the patient (data from the Ministry of Health of Russia dated July 22, 2011 and December 21, 2012)…
- Targeted images on a digital radiovisiograph – → lower jaw in adults – 2 μSv, → lower jaw in children under 15 years old – 1 μSv, → upper jaw in adults – 5 μSv, → upper jaw in children under 15 years old – 3 μSv.
- Sight shots using film – 10-15 µSv.
- Digital panoramic image – 55 µSv, but if the patient is less than 15 years old – 24 µSv.
- Digital teleroentgenogram – 7 µSv.
Conclusions: thus, targeted images using a radiovisiograph provide the lowest radiation dose compared to other types of x-ray examination in dentistry. During one visit to the dentist, you can take 5-6 pictures on a digital radiovisiograph without risk to health, but no more than 100 such pictures during the year. A digital orthopantomogram (panoramic x-ray of the jaw) can be done 1-2 times a month, but no more than 10 times during the year. Panoramic films on film provide a greater radiation dose to the patient, and they can be taken less frequently than digital ones.
OPTG or CT
Let us, however, draw attention to one annoying discrepancy between Rules No. 560n and the draft Procedure for the provision of medical care to the adult population for dental diseases. Rules No. 560n provide for the presence of an orthopantomograph in the Republic of Kazakhstan. At the same time, according to the draft Order, the standard equipment for this structural unit includes an orthopantomograph or computed tomograph (hereinafter referred to as CT). That is, the office may provide not an OPTG, but a CT scan. How both acts will be applied (if the new Order is adopted) remains a mystery. Thus, Rules No. 560n are a special act in relation to the Procedure for providing medical care for dental diseases and regulate relations related to x-ray examinations. In contrast to the draft, Rules No. 560n contain Rules for organizing the activities of a dental x-ray office and recommended staffing standards. In turn, the draft Order specifies only the equipment standard for the X-ray room. At the same time, the new Procedure will be later than Rule No. 560n; accordingly, following the conflict rules, the rules of the new Procedure must be applied. Thus, in the theory of law there are arguments in favor of the supremacy of both one and the second (future) act.
But the main thing here is different - legal grounds are needed to place both OPTG and CT in dental X-ray rooms. We hope that the legislator will take into account the requirements of modern dentistry and include in Rule No. 560n the optional placement of CT scans (in the standard equipment of the X-ray room).
Is it possible to take a dental x-ray during pregnancy?
Is it possible to take a photograph of a tooth during pregnancy? This issue is regulated by the recommendations of SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03. These recommendations do not prohibit taking dental x-rays during pregnancy, but it is strongly recommended to use x-rays only in truly necessary cases, for example, in case of acute pain and the provision of appropriate emergency care.
It should be noted that over the past 20 years, the radiation doses received by patients with 1 x-ray of the teeth have become tens of times less, thanks to the advent of radiovisiographs and ultra-sensitive photographic films, which require significantly lower x-ray radiation (24stoma.ru). Therefore, the risks of fetal pathologies have decreased significantly in recent years.
Of course, if possible, X-ray examination of teeth should be avoided, but there is nothing terrible about this today, because The radiation dose of 1 image on a radiovisiograph is approximately equal to the radiation dose of any person to natural background radiation in 1 day. In addition, the irradiation time on the visiograph will be only 0.05-0.3 seconds, which, if protective measures are observed (lead apron), can significantly increase the safety of the procedure.
Additionally, it is worth considering the following recommendations –
It is better not to do a dental x-ray during pregnancy in the early stages, because at this most important time for the laying of organs and tissues of the fetus. And if x-rays are taken, then it is in the second half of pregnancy, because the risks to the fetus during this period are significantly reduced. Please note that you can only take pictures using a modern digital radiovisiograph of the latest generation, because Their radiation dosages are significantly lower than those of outdated digital radiovisiographs and, even more so, film devices.
Results
In general, we did not find any fundamental changes in connection with the adoption of the new Rules for conducting X-ray examinations. There is no requirement for mandatory availability of OPTG in dental clinics. Medical organizations both had and have the right not to allocate an X-ray room as a separate structural unit, and to provide for the placement of a radiovisiograph at the dental chair directly in the doctor’s office. If you want to place an OPTG, you must provide a separate X-ray room (as was the case).
However, from 01/01/2021, when a separate X-ray room is allocated, it will be necessary to equip it with both an orthopantomograph and a radiovisiograph. That is, from this date it will not be possible to take only the radiovisiograph into a separate room (previously this was permissible). In our opinion, such restrictions are not entirely justified and do not take into account the organizational and economic wishes and capabilities of the clinic itself. We also consider it an omission that CT is not included in the standard of equipment for a dental clinic in the Republic of Kazakhstan in the new Rules No. 560n.
Analysis of targeted dental images –
Analyzing X-rays is not difficult if they are of good quality.
Almost any patient will be able to see signs of periodontitis or cysts in the image, and will also be able to determine how well his root canals are filled. All you need here is skill. But it is worth remembering that absolutely everything cannot be diagnosed using X-rays, for example, inflammation of the nerve of a tooth. You can diagnose from the image -
- caries (but not in full),
- periodontitis (granulomas, cysts),
- quality of root canal filling after treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis,
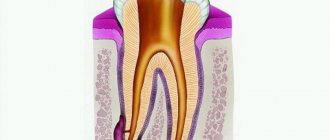
- perforations and root cracks,
- fragments of instruments in root canals,
- presence of periodontal pockets...
1) A group of images indicating the development of inflammation (periodontitis) at the apexes of the roots of previously untreated teeth. In this case, you will always see a clear or vague darkening at the apex of the tooth root, which can be of different sizes and shapes.
2) A group of photographs taken after root canal filling. The first 2 pictures (Fig. 14-15) show what well-filled root canals look like. The following images show poor quality treatment and complications that arose (read the descriptions in each image).
Summary: important points
As a practicing dentist who knows the system from the inside, I want to draw your attention to the following points that are important for your safety. If the clinic has an X-ray machine, then a license must be obtained for it, the issuance of which presupposes the mandatory presence of a certified radiologist on the staff of the dental clinic. However, in reality, even in large clinics and public clinics, it is not always the case that x-rays will be taken by a trained specialist.
Even if he is, he may go on vacation or get sick, and a regular nurse (dental assistant) will take the pictures instead. This is a gross violation that leads to both the production of low-quality images and an increase in the radiation dose. In small clinics, the risks of receiving a poor-quality x-ray examination are much higher, and the first thing that makes you suspect a forgery is if the picture is taken not by a special employee, but by a nurse from the dentist you came to see.
The second very important point: if you see that the x-ray is not done in a special room, but the x-ray machine is located right next to the dentist’s chair, then you should change the clinic and the doctor. The fact is that all objects in this office (including the dental chair and doctor’s instruments) will have an increased background radiation, and this is no longer safe for health. We hope that our article on the topic: X-ray of the jaw and teeth was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author’s education in therapeutic and surgical dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience in therapeutic and surgical dentistry, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Digital and film radiography in outpatient dentistry” (Chibisova), 5. “X-ray diagnostics in dentistry" (Lutskaya I.K.).
Requirements for placing an x-ray room in dentistry
In our country, dentistry is often located on the territory of a multi-story residential building. This is not prohibited by SanPiN standards. But there are limitations associated with the hardware of such a clinic.
A digital dental radiographic system (radiovisiograph) can be installed in an office located in a residential building. The principle of its operation is based on the use of solid-state X-ray sensitive detectors, which are inserted into the patient’s oral cavity. The radiation level during the procedure does not exceed the permissible SanPiN standards.
But not all dental X-ray machines fall under these standards. Orthopantomographs can be placed in residential buildings, but only in stand-alone X-ray rooms.
Before installing any type of dental X-ray machine, you must notify Rospotrebnadzor. The model of the selected X-ray machine must be registered in the database of the Russian Ministry of Health. If there is no modification of the device in the database of the Ministry of Health, radiation-hygienic tests of the device should be carried out.