Among the many dental pathologies, there are those that are characterized as tumors. Epulis belongs to this group.
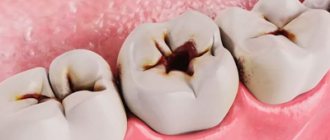
This is a tumorous, mostly benign neoplasm on the gum.
The main places of its localization are the alveolar processes in the area of the radical units (premolars) and the body of the jaw itself (usually the lower one).
Symptoms of growths on the gums
Often at the beginning of the disease, people do not complain of pain, do not experience discomfort, and sometimes do not even notice the problem. Clear symptoms appear over time and depend on the type of disease, its neglect, and the severity of the inflammatory process. Cysts are characterized by:
- swelling around the growth;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- regional lymphadenitis (submandibular, ear, cervical);
- general intoxication;
- pain (worsens at night).
Symptoms of epulis of benign etiology:
- grows slowly and not much (up to 2 cm);
- does not hurt;
- aesthetic discomfort.
Malignant epulis is characterized by:
- fast growth;
- a sharp increase in size;
- swelling of the gums at the location;
- destruction of root canals in nearby teeth;
- loosening and displacement of nearby teeth;
- bleeding gums.
Symptoms of exostosis:
- painlessness;
- no swelling;
- soft tissue injuries (over time).
Types of growths and their appearance
Neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the gums differ:
- size;
- consistency;
- color;
- structure;
- pain (not always);
- bleeding (sometimes).
Types of growths:
- epulis (fibrous, giant cell, angiomatous) - benign or malignant (rare) tumor;
- cyst - a neoplasm in the epithelium, inside of which there is pus, dead and keratinized cells;
- exostosis - a painless, dense, bone growth;
- fibropapilloma - a benign formation on the gum;
- purulent abscess - a red growth with a fistula from which pus is released.
Angiomatous epulis occurs more often in 5-10 year old children, sometimes in teenagers, and giant cell epulis occurs in people 40-60 years old, more often in women. Epulis is characterized by:
- absence of pain;
- unaesthetic appearance;
- different sizes (from 2 mm to 3 cm or more);
- pink, red, burgundy, brownish or bluish shades;
- different structure (hard, soft);
- ulcer on the surface (after damage);
- sparse bone (not always);
- localized on the jaw bone (alveolar process) in the area of small molars or on the lower jaw (rarely).
The cyst is characterized by:
- pain when pressed;
- white or light gray;
- looseness;
- localized at the site of inflammation;
- fistula entrance (wound);
- elevated body temperature (in an advanced stage).
Gum cancer
These are especially dangerous formations on the gums. Occurs due to uncontrolled division of cells susceptible to mutation. Red tumors form on the gums from the epithelium.
The exact causes of cancer are still unknown.
The patient notes:
- general weakness;
- low-grade body temperature (i.e. 37 degrees);
- sleepy state;
- loss of appetite.
The diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after a detailed examination. The treatment is long and painstaking. First, the tumor is removed (if the stage of the cancer allows), then drug treatment.
If therapy is started in a timely manner, the outcome of the disease is favorable.
Gum fibroma
Unlike cancer, this is a benign formation. It grows slowly from the connective tissue of the gum mucosa. From the outside, such a lump appears to be an extension of the gum. It is soft and flexible, with clear edges.
Most often, this tumor appears after inflammation of the oral cavity or trauma to the gums. It is with fibroids that doctors tend to think that genetic predisposition is of great importance, that is, the disease is inherited.
Treatment is only surgical. Under local anesthesia, complete removal of the fibroid occurs, followed by drug treatment.
Cyst on the gum
A cyst is one of the types of growths in the oral cavity. Appears after a long inflammatory process in the gums. It develops from the epithelium and contains pus. Such a purulent sac grows up to 3-4 centimeters.
The appearance of this growth is preceded by:
- presence of dental caries;
- poor quality filling;
- periodontitis;
- pulpitis;
- tooth extraction.
With the appearance of a cyst in the oral cavity, the patient’s general condition worsens. There is pain when chewing, weakness, and body temperature rises. If treatment is not started at this stage, spontaneous leakage of pus or infiltration and infection of healthy gum tissue will occur.
Kinds
Based on the morphological and clinical severity, 4 types of tissue proliferation are distinguished. Each is assigned a separate code (number) according to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10).
Fibrous
It is formed from fibrous gingival tissue with transverse bone inclusions embedded in it. Formed only on the vestibular side of the first molars or premolars.
The color of the growth is completely indistinguishable from the gums, while its shape is oval or round with a dense consistency. Initially its surface is smooth, but as it grows it becomes lumpy. As it grows, it can move through the interdental spaces to the back side of the teeth.
Of all types of growths, fibromatous has a favorable treatment prognosis, grows slowly, does not turn into a malignant state, is painless and does not bleed.
giant cell
It is formed from osteogenic cells and is always located on the alveolar ridge, gradually covering the crowns. The tumor is dense, quite elastic, round, brownish-brown in color, grows slowly, but its growth can reach volumes that disrupt the symmetry of the face.
In isolated cases it is painful, and upon palpation it produces short-term bleeding. In the area of its presence, the teeth become loose.
There are 2 types of it:
- Central - develops from the jaw bone.
- Peripheral – arises from soft gingival tissues.
The pathology mainly develops in older people (after 40 years), and is more often diagnosed in women.
Angiomatous
It is an accumulation of mast cells and inflamed blood vessels with very thin walls in fibrous tissue. The main reason for its appearance is frequent trauma to the mucous membrane. It is localized near the dental neck and can form on any jaw.
It has a completely smooth or slightly bumpy surface, red color, soft consistency, develops quickly and causes severe bleeding even from minor trauma. After removal, there is a high probability of its re-formation.
Tissue proliferation is more often observed in children, adolescents and women during pregnancy.
Acanthomatous
The rarest type, also called “peripheral soft tissue ameloblastoma.” This is a painless benign formation that appears from the dental buds of the lower jaw. It appears on the surface of the gums in the form of horny pearls. After removal, the growth is characterized by recurrent growth (repeated).
Complications
Why can’t you treat a gum cyst yourself? Yes, because the infection in this case has already entered deep into the jaw tissue, where it is simply impossible to destroy the microbes yourself. As the disease progresses, putrefactive bacteria penetrate the dental pulp, from where they enter the bone tissue through the root canals.
Further, the process can provoke the development of a very serious and difficult to treat disease - osteomyelitis. In this case, the patient complains of severe weakness, high temperature, and enlarged lymph nodes. Osteomyelitis is especially common as a complication of gingival growth in children.
In addition, infection from the cystic cavity can spread throughout the body. After all, during inflammation, the body sends an increased flow of blood to the affected area. Dead blood lymphocytes settle in the gum cavity in the form of purulent secretion, the excess of which comes out through the fistula canal.
It is important to treat any oral diseases immediately after they occur. It is in the oral cavity that the blood flow is so strong that any inflammation can instantly develop and spread through the bloodstream throughout the patient’s body.
Given the close location of the brain, a purulent process from the oral cavity can spread to this organ and lead to irreparable consequences.
Possible complications
Most often, tumor removal does not bring additional problems to the patient. However, the following complications cannot be ruled out:
Re-formation of epulis. Some forms of tumor are prone to recurrence. They also appear with unstable hormonal levels and continued chronic injury to the mucous membrane. Postoperative swelling. As a rule, this is a temporary phenomenon that goes away either on its own or after using folk remedies. Bleeding. Blood and ichor may be released from the wound for some time, which brings the patient some discomfort in the postoperative period. But, again, these are temporary inconveniences. Suppuration on the soft tissues in the wound. It is caused by the contact of pathogenic organisms with damaged vulnerable matter. To prevent this from happening, you need to pay close attention to oral hygiene during the recovery period.
To avoid such troubles, you should scrupulously follow the dentist’s recommendations and take the medications prescribed by him. If a complication is diagnosed, contact a specialist as soon as possible!
Treatment at home
To eliminate pain in the oral cavity and inflammation that accompanies the appearance and development of a growth at home, you can use the following recipes:
- It is necessary to mix table salt and baking soda in equal quantities (it is recommended to take 5-6 teaspoons of each product), dilute the resulting mixture in 300 ml of boiling water. When the solution has cooled to a comfortable temperature, the child should rinse his mouth with the product. The procedure must be repeated 4-6 times a day. Salt and soda help disinfect the oral cavity, reduce suppuration, and relieve pain.
- Herbs (yarrow, thyme, chamomile flowers) are poured with boiling water and left for 1-2 hours in a dark and cool place. After this, the infusion is filtered. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with the resulting product 2 times a day. Herbs can relieve inflammation and soothe affected areas of the gums.
- Mix rose hips (2 parts) with fireweed and mint (1 part each), add boiling water, heat in a water bath for 20 minutes. After this, the product must be filtered and cooled. Use as a general strengthening drink once a day. The decoction helps increase the body's defenses and its ability to resist infections and microbes.
Attention! These recipes are only suitable for eliminating the symptoms of pathology, while the causes that led to its appearance are determined and eliminated only in the dental office. Unauthorized prescription of potent antibacterial drugs will not only not give the expected effect, but can also harm the child’s health
Often, parents simply do not pay attention to the appearance of small growths in the child’s mouth, especially if they do not cause the baby much concern. Nevertheless, this situation is very dangerous, since its occurrence can be provoked by reasons of a rather serious nature. Therefore, if changes are detected in the oral mucosa, it is necessary to show the baby to the dentist. The doctor will determine the causes of the pathology and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Our expert dentist will answer your question within 1 day! Ask a Question
denta.guru/detskaya-stomatologiya/bolezni-desen/narost.html" denta.guru
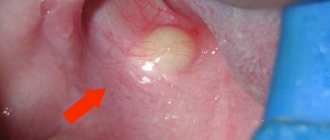
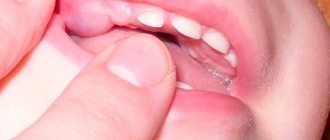
Lump on the gum.
Often, both adults and children develop a lump on the gum. The cause of its appearance can be both infectious and other factors. The main provoking factors in patients are still poor oral hygiene and dental pathology, which requires treatment.
Visually, the lump on the gum looks like a compaction. However, it can mask various diseases and neoplasms, for example:
- A fistula is a purulent lump that has holes for pus to escape.
- Exostosis is a lump caused by excessive bony protrusion of the jaw in a certain area. Such a bump will not differ in color from the gums.
- Epulis is a benign pedunculated neoplasm that occurs predominantly over small molars.
- Periodontitis - with this disease, a non-painful hard lump appears above the root of the tooth.
- Hematoma.
- Flux is a painful purulent lump that occurs as a result of periostitis.
- Gingivitis is characterized by red bumps.
How does a purulent lump appear over a sore tooth, can a lump appear after tooth extraction, what different lumps look like in a child’s photo, methods of treating them - all this is in this article.
Signs
Usually this growth does not cause pain to a person, but it causes significant discomfort and disrupts aesthetics, because noticeable when talking and smiling. In the case when the formation is neglected or has turned into a malignant state, the specificity of the symptoms increases (all signs worsen the general condition, they are unpleasant and quite painful).
Its external appearance is determined by the following parameters:
- Shape - it is compared with a mushroom, since the formation has a distinctly different stalk (the area where it is attached to the gum) and a body (similar to a mushroom cap).
- Size - always depends on the morphological and clinical form, and can vary from 2-3 mm (almost invisible) to several centimeters.
- Color - depends on the type of growth. So, fibrous is identical in color to the gum, giant cell is brown-brown or bluish, angiomatous is from bright red to dark red. If it is frequently injured by fillings, teeth, or prosthetic clasps, its surface becomes severely bruised and changes color.
- Consistency - depending on the type of cells that served as the source of its growth, the density can be different: soft or hard.
The x-ray image clearly shows that at its base there is a slightly different consistency than the general one. The same image shows the change in the condition of the bone: in the area of the growth it is discharged.
We looked at the causes and treatments for bad breath in a separate article. In this review you will find information about methods of treating dental granuloma at home.
Causes of gum tumors
The appearance of a lump on the gum can be completely painless. The patient does not immediately notice the formation and, in the absence of painful manifestations, does not attach importance to it. This is a big mistake.
If you find any formations in the oral cavity, even if they do not cause concern, you should immediately consult a doctor: even a small lump can signal the onset of a serious illness.
There are several reasons why a lump may appear. But none of them are harmless. In some cases, surgery may also be necessary.
Therefore, even if the patient believes that nothing terrible has happened, it is still necessary to consult a doctor.
A lump on the gum under the tooth can occur due to the following diseases:
- inflammatory process inside the gums;
- formation of odontogenic fistula;
- periodontitis;
- inflammation of the periosteum;
- jaw cyst;
- benign tumor;
- hematoma.
In addition to the above diseases, a lump on the gum of a child or an adult can occur and hurt when teething.
In this case, the occurrence of edema is natural and does not require any treatment, which cannot be said about other causes.
The inflammatory process in the pulp or soft tissues surrounding the tooth is often accompanied by swelling of the gums. This swelling hurts when you press on it with a finger, a toothbrush, or when chewing food.
The pain can be either dull, aching at the onset of inflammation, or quite sharp and severe with a progressive abscess.
When you feel the gums, the swelling has a dense and hard structure. Its surface is smooth, reminiscent of a pomegranate seed.
The swelling may or may not be redder than the adjacent gums. To carry out treatment, it is necessary to determine the localization of the inflammatory process.
Therefore, if, as a result of inflammation, a lump with pus appears on the gum, then before prescribing treatment, the doctor will send the patient for an x-ray.
The reason for their formation is the same inflammatory process. The diseased tissue suppurates, the purulent contents increase, and the body cannot cope with the infection on its own.
In this case, a fistula forms in the gum, through which part of the contents comes out.
The appearance of a fistula is accompanied by cutting, throbbing pain. Despite the fact that such a lump may be small in size and not seem dangerous, if it is detected, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Before treatment, you will also need to take an x-ray to determine the location of the infectious focus.
Fistulas can make their way from the roots of the tooth not only through the soft tissue of the gums, but also through the jawbone, so treating them independently with improvised means is out of the question.
Elimination of the infectious source and treatment of the fistula should be carried out by a doctor, based on the X-ray images.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis is made on the basis of a complete examination by a specialist and his study of histological and instrumental examination data. It is important to correctly differentiate epulis from similar conditions:
- hypertrophic gingivitis;
- false epulis;
- gum or pulp polyp;
- osteoblastoclastomas.
A mandatory type of examination is also radiography. It allows you to accurately determine the degree of bone involvement in the pathological process.
The patient is prescribed blood tests: PCR, general and biochemical. If their results reveal an increased level of leukocytes against the background of low hemoglobin, another examination is prescribed for the presence of cancer cells.
What is epulis?
Epulis is a soft tissue formation that appears on the mucous membrane of the alveolar process. It has synonymous names - epulid, supragingival, or giant cell granuloma. In most cases, the growth zone is adjacent to the teeth, especially premolars, but sometimes you can notice a formation on the body of the lower jaw.
Epulide occurs in adults, females are especially susceptible, but can also occur in children. You should be especially careful about the appearance of the supragingival in children and pregnant women:
- Infants are susceptible to growth during the teething period. The most common is the angiomatous form, but other varieties can also be found. Do not delay your visit to the dentist in order to promptly eliminate epulis, the uncontrolled growth of which leads to its proliferation;
- women expecting a baby are at risk for giant cell epulidus due to altered levels of hormones in the body, so it is necessary to periodically carefully examine the oral cavity in order to detect a tumor in a timely manner.
Do not confuse epulis with a lump of pus on the gum, because these are completely different diseases.
Prevention
Since hormonal changes in the body as the cause of pathology are almost impossible to exclude, preventive measures come down to timely and systematic sanitation of the mouth.
Sanitation is a set of dental measures carried out to eliminate existing problems: removal of plaque and stone, poor-quality fillings, treatment of identified diseases.
Sanitation also includes orthodontic correction of the bite, since incorrect position of the teeth also injures the mucous membrane.
Regular visits to the dentist will allow you to timely detect and eliminate the causative factors of injury, and therefore one of the main causes of epulis. Strengthening the immune system plays an important role. With strong immunity, the likelihood of developing acute inflammation is minimal.
Epulis is not a dangerous disease, but it causes a lot of discomfort to a person. Its early detection and relief prevents the manifestation of negative sensations, pain and complications.
Preventive actions
Any disease is much easier to prevent than to treat. A lump formed on the gum is no exception. What to do to prevent the disease?
Everything is simple here - prevention consists of ordinary hygiene procedures
However, it is important to do them carefully and regularly. Keeping your mouth in order can not only prevent gum tumors, but also keep your teeth healthy.
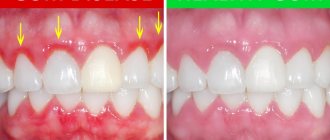
There are several diseases that cause gum swelling, but all of them can occur due to improper brushing of teeth.
To prevent any dental diseases, regular thorough oral care is recommended.
Dental plaque is carbohydrate-based food debris teeming with millions of bacteria. But this is not the worst thing.
It is not the bacteria themselves that pose a much greater danger to oral health, but their metabolic products.
One such product is lactic acid, which is released during the breakdown of sugars.
It corrodes the most durable tissue of the human body - tooth enamel, thereby depriving the teeth of protection and opening the way for microorganisms inside the dentin, to the pulp.
Video:
Without regular oral hygiene, plaque deposits accumulate, mineralize, and harden.
Such deposits are called tartar. The appearance of tartar is not only a cosmetic defect, but also leads to various gum diseases and loose teeth. It is impossible to remove it yourself at home.
Thus, just careful regular oral care can prevent many dental diseases.
Such a phenomenon as “bad teeth” most often becomes a consequence of the patient’s laziness or illiteracy.
To maintain oral health and protect yourself from many problems, dentists recommend:
brush your teeth twice a day every 12 hours; The cleaning procedure should last 2-3 minutes; When brushing, you should pay attention not only to the front sides of the teeth, but also to the internal and chewing surfaces; the paste should be selected in accordance with the age and condition of the dentition; Do not overuse whitening pastes; Tooth powder for brushing teeth can be used no more than twice a week; For healthy teeth, it is recommended to use a medium-hard brush; The toothbrush should be replaced every 2-3 months; For high-quality cleaning of interdental spaces, you can use dental floss or an irrigator; rinsing the mouth with special means after each meal allows you to reduce the amount of deposits before the next mechanical teeth cleaning; foods high in simple carbohydrates (sugars and starches) should be consumed only after the main meal; Even if you are confident in your overall oral health, you should visit your dentist twice a year for a preventive examination.
Not only a beautiful smile depends on the condition of a person’s mouth.
Dental health also affects the functioning of the digestive and immune systems and is directly related to human life expectancy.
Compliance with the rules of oral care not only eliminates the troubles associated with dental diseases, but also helps maintain human health for many years.
Healthy teeth and a beautiful smile!
Therapy
To combat pathology, surgical, laser (as the newest surgical method), medicinal methods and traditional medicine are used as a means of complementing the main therapy.
Surgical
It is carried out when the tumor has grown significantly by completely removing it. The operation involves its dissection and takes place in several stages:
- Administration of anesthesia (depending on the epulis clinic, local or general anesthesia is performed).
- As soon as the anesthetic takes effect, the doctor, stepping back 1-2 mm from the stem of the growth, makes an incision around the soft tissue of the gums to their entire depth, capturing the periosteum.
- The flap is peeled off along its entire circumference.
- If the disease has affected bone tissue, the affected area is dissected down to healthy tissue.
- The wound surface is cleaned, washed with an antiseptic solution and covered with a swab soaked in iodoform composition.
- If the affected area is large, its edges are tightened with sutures.
Teeth located nearby are pulled out only when they are mobile (grade III) or when their roots are exposed to 2/3 of their length.
Have you discovered an abscess on your child’s gum? We'll tell you what to do. On this page: https://dentist-pro.ru/lechenie/desny/gingivit/osobennosti-razvitiya-i-taktika-gipertroficheskogo.html - you can find out the etiology of hypertrophic gingivitis.
In the next review we will talk about the approximate prices of plasma lifting in dentistry.
Laser Application
In many large dental centers, lasers are used as a surgical instrument for interventions of this type. During the operation, the patient is given infiltration anesthesia.
The advantage of using this method is that the laser simultaneously eliminates (cauterizes) the tumor and disinfects the area affected by it. As a result, the rehabilitation period is significantly reduced, and postoperative complications are reduced to a minimum.
This is how epulis on the gum is removed using a laser:
Medication
Therapy includes taking drugs that stop the growth of epulis and lead to the regeneration of its tissues. The list of prescribed medications includes:
- "Traumel S " is a homeopathic remedy that has pronounced regenerative and hemostatic effects.
It perfectly restores weakened oxidative processes in all tissues and slows down the formation of granulations. Can be taken as tablets or drops in the dosage: 1 tablet/10 drops. three times a day in a course of 10-14 days. - "Dimexide" is an anti-inflammatory, antihistamine, analgesic, antiseptic drug. Its active components, penetrating into cells, have a fibrinolytic effect, which helps curb tumor growth. Prescribed by applications: applied for 20 minutes. on the pathogenic area 4-6 times/day.
- "Miramistin" is a spray that exhibits its antiseptic activity against bacteria and viruses that cause the disease. To achieve the effect, irrigate your mouth up to 4 times during the day.
- "Vagotil" - has a pronounced sclerosing effect due to the elimination (cauterization) of the affected tissues. During treatment, a bandage is formed, moistened with the drug and applied to the problem area for 3-5 minutes. Important: the procedure can be carried out no more than 3 times a week.
- "Resorcinol" is an antiseptic, has strong antimicrobial, wound-healing, regenerating, anti-inflammatory, and antiseborrheic effects.
Its use can lead to complete removal of the growth. For treatment, an ointment of 5-10% is used, which is applied to the affected tissue twice a day.
Important: all of the listed medications can be used in treatment only after they have been prescribed by a dentist. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable.
Folk recipes
Complete treatment using only traditional recipes is impossible. They can, together with medical treatments, speed up recovery during the rehabilitation period.
All recipes are based on the use of rinses with decoctions prepared from various medicinal herbs and remedies:
- Calendula: 2 tbsp.
l. dried plant pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave until cool, strain and rinse your mouth up to 4 times a day. The plant has a good anti-inflammatory, wound healing and antiseptic effect. Calendula can be replaced with other equally effective plants: sage, eucalyptus, chamomile . A decoction of them is prepared in the same way. - Baking soda : 1 tsp. dissolves in 1 tbsp. warm clean water. Rinsing with it prevents further spread of suppuration, infection and inflammation. This result is achieved due to the fact that soda has a strong disinfectant, antiseptic and mild analgesic effect.
- Salts: dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of hot water. salt, but can be used only after the solution has cooled (6-8 times a day). It relieves swelling well and prevents the spread of bacteria.
All infusions used should be at room temperature, since hot ones can lead to tissue burns, and cold ones can lead to hypothermia.
Before you start using this or that drug in treatment, you need to check with your doctor to what extent its use is indicated in this case.
Other diseases accompanied by gum swelling
A lump on the gum above a tooth can also occur as a result of granulating periodontitis. Chronic inflammation of the connective tissue can not only cause flux to pop out, but also cause tooth loss.
The danger of periodontitis lies in the fact that the infection can spread to the jaw bones, and in such a situation even the formation of a fistula will seem less of a problem.
However, the absence of pain does not make the disease less dangerous: while a person believes that everything will go away on its own, the disease progresses.
An advanced form of periodontitis is fraught with serious complications, which may take years to treat.
As a result of inflammation of the periosteum, a hard lump on the gum can also appear.
Moreover, the disease develops rapidly - no sooner has the flux sprung up than in a few hours its head can break through and the pus will begin to come out or inside.
Video:
The latter variant of the development of the disease is more dangerous, since the infection spreads inside the jaw bone.
After the pus is released, the pain syndrome decreases, and the person is not aware of the complexity of the situation.
With this course of the disease, in order to sanitize the infectious focus, it is often necessary to remove a relatively healthy tooth.
Therefore, if suppuration is suspected, the patient should consult a doctor as early as possible, even before the flux breaks through.
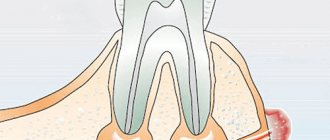
A cyst is a cavity between the root of the tooth and the gum with a volume of up to 1 cm, filled with liquid.
The only possible manifestation of such formation may be an unpleasant odor that cannot be eliminated after brushing the teeth.
In uncomplicated cases, the cyst can be easily removed, but sometimes it is necessary to remove the tooth closest to it. Other benign gum tumors are treated in the same way.
If a child has swelling and redness on his gums, this may be caused by rapid teething.
This is a natural process and no treatment is required, although swelling may be accompanied by pain and fever. Before teething, babies may put fingers and other objects in their mouth.
In addition, as the first tooth appears, salivation increases. You can alleviate the child’s condition with the help of pain-relieving gels or special teething toys.
The eruption of a wisdom tooth in an adult can cause many more problems than the appearance of the first tooth in a baby.
The last tooth in a row often has an incorrect location, and therefore, instead of coming out, it puts pressure on the neighboring tooth.
In this case, the tooth will not be able to erupt without medical help. Sometimes, due to the anatomical structure of the roots, an incorrectly located tooth has to be removed even before it appears.
If necessary, the source of infection will be sanitized. A purulent lump on the gum often requires surgical intervention.
If the swelling is not of an inflammatory nature, but arose, for example, after a bruise, then the attending physician can use conservative treatment methods.
A lump on the gum after tooth extraction may be a hematoma that appears due to tissue damage during the operation.
The hematoma does not require special treatment. If you follow the doctor's instructions, the tumor will go away on its own.
Video:
You should not put off going to the doctor, as there are many reasons why swelling near a tooth can form.
Most of them are not harmless and threaten the development of various pathologies, even sepsis. It is also not possible to understand why the tumor formed on its own.
Gum diseases in children deserve special attention. Since under the milk teeth there are the rudiments of permanent teeth, any disease can provoke their damage or even destruction.
Causes and associated symptoms
All neoplasms on the gums can be divided into three large categories - those that develop for physiological reasons, those that are formed under the influence of pathological factors and those caused by conditionally pathological circumstances.
Physiological reasons
These include a tooth eruption cyst and a submucosal hematoma. In the first case, the neoplasm is formed at the stage of active growth of a baby or permanent tooth, which for some time cannot cut through the gum, and causes protrusion of tissue outward, which looks like a soft growth on the gum. This condition can be uncomfortable, but is rarely painful.
A submucosal hematoma develops after a gum bruise - an injury in which the integrity of the tissue is not violated, but the applied force leads to damage to small vessels. This is often observed when a baby chews hard foods and before teething, when he tries to relieve itching and tension in the gums by “chewing” hard objects.
This condition may cause mild pain at the time of injury, but goes away without consequences within a few days. A submucosal hematoma looks like a rounded formation of a dark color (from bluish to black-violet), the growth on the gum does not hurt and is rarely large.
Pathological causes
This category includes diseases of an infectious and traumatic nature that cause uncontrolled tissue growth or the formation of abscesses and cysts.
When an infection gets into any part of the gum, tooth, periodontium or jaw bone, a pathological focus is formed - an abscess or cyst. They are a cavity filled with infected contents. The only difference is that with an abscess, pus accumulates in the tissues, and with a cyst, a connective tissue capsule is formed, limiting the spread of pathogenic microorganisms.
But with an increase in the number of purulent masses, they “look” for a way out, as a result of which a fistula can form. In this case, a white growth is observed on the child’s gum - a moderately dense formation with a white or slightly yellowish top.
When the pus breaks out, the neoplasm decreases in size or disappears completely, but the outlet remains - pus and ichor continue to be released through it.
Traumatic growths develop due to tissue hyperplasia.
This can occur with constant mechanical impact on the gums of such irritants as incorrectly installed braces, chronic trauma to soft tissues from a decayed tooth, etc.
Tissues exposed to constant pressure and friction begin to grow uncontrollably, forming epulis - a soft, irregular growth that can be located in any area of the gum (interdental space, lingual or vestibular surface of the gum).
Such a growth does not cause pain or discomfort as long as its size does not interfere with the chewing process, teeth closure, or articulatory mechanisms. But, reaching an ever larger size, it begins to cause unpleasant symptoms.
Conditional pathological causes
This category includes all conditions that are normally not dangerous to health and develop without the participation of pathological processes, but under unfavorable conditions can lead to complications. In children, exostoses are most often observed - a hard growth on the gum that resembles a thorn or is irregular in shape.
This is an overgrowth of the bone tissue of the jaw, which is formed due to a genetic predisposition or as a consequence of injury. It does not cause harm and usually does not grow actively.
But if its size exceeds the permissible limits or the growths are multiple, the exostosis can be subject to constant trauma, as a result of which inflammation begins in this area with the addition of a bacterial infection.
During pregnancy
When carrying a baby, a woman's body undergoes changes. Changes in hormonal levels and their surges during this period are considered normal. But the appearance of epulis is associated with this process.
The root cause of its formation is also chronic injury, but in this situation the growth of the growth itself and the processes occurring in it are accelerated. There is evidence that after childbirth, when hormone levels are normalized, tissue growth slows down significantly.
How to treat a cyst
If a child develops a cyst on the gum, treatment should begin immediately. There is a high probability that the infection will go deep into the tissues, even if a baby tooth has been affected; the rudiment of a molar tooth may also “deteriorate”
The main reason for the appearance of a cyst is advanced caries, which was not paid attention to in time.
At the first stages, the development of a cyst in the mouth goes unnoticed, but over time, a red growth appears on the child’s gum. If pus accumulates, it will be impossible to touch the affected tooth.
The cyst will not burst on its own and a fistula will not appear on the child’s gum, how to treat the cyst? Unfortunately, treatment is only carried out surgically. There are two treatment options:
- Cystomy: the anterior wall of the cyst is removed. If it appears on baby teeth, you can save the molars.
- Cystectomy: the entire cyst is removed. If it is less than 1.5 cm, the operation will be performed by cutting the apex of the root. If the cyst is too large, the gum will have to be opened. Removal of a baby tooth cannot be avoided.
A cyst on the gum of a small baby is a fairly rare occurrence; most often this disease occurs in an adult. In addition, growths are not always dangerous: pearls that appear on a baby’s gums may turn out to be Epstein’s pearls - a harmless phenomenon that goes away on its own; no treatment is required.
Course of the disease
Angiomatous epulis is common in children. But other types may also arise. The tumor is more common in girls than in boys. The disease usually affects young patients during teething. Why is this happening? Teething is accompanied by severe trauma to the gums and mucous membrane. The tumor grows greatly in the oral cavity and begins to seriously bother. The child’s parents need to seek help from a specialist as soon as possible. The faster help is provided, the easier the consequences will be.
In adolescents, epulis can also occur as a result of trauma. Another reason is hormonal changes in the body. Most often, tumors occur during puberty. It can also occur as a result of taking inappropriate medications.
It’s interesting, but in children, one form of epulis often turns into another. For example, when granulomatous epulis occurs, this type eventually turns into angiomatous and then fibrous. This transition is observed in 14% of cases of the disease.
Due to hormonal imbalance or changes in the body, epulis occurs in pregnant women. If we add trauma to this, the tumor grows quite quickly.