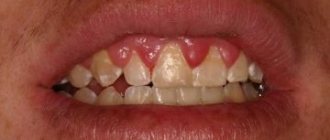
What is epulide
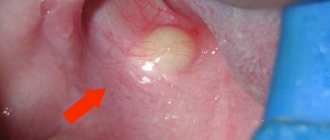
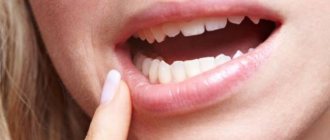
Epulis is a tumor of a predominantly benign nature. It has a stalk (the base from which it grows) and a cap (the tip that rises above the gum). Depending on the type, the pathology can be of different shades and have different sizes. In some patients it does not exceed a few millimeters, in others it reaches 1-2 centimeters in diameter. In the absence of adequate treatment, the tumor gradually increases in size and grows to the point that it becomes capable of filling the entire space in the oral cavity. In addition, epulis can degenerate into a malignant tumor, which becomes life-threatening.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on examination by a specialist and histological examination. A differential diagnostic method is used to exclude the presence of hypertrophic gingivitis in the patient. It has similar symptoms to epulis. An x-ray is also used for diagnosis, where, with epulide, rarefaction and destruction of bone tissue due to inflammation are observed.
Epulis can often be confused with gingivitis
Signs of epulis
The following signs are characteristic of a neoplasm:
- consistency is soft or compacted,
- may be located on one side of the gum or on both,
- in advanced cases, teeth located nearby may become mobile,
- a person gets the feeling that there is not enough room for the tongue,
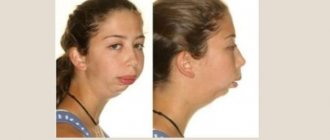
- with large tumor sizes, the face becomes asymmetrical,
- When eating, accidentally biting or touching with a toothbrush, bleeding occurs.
Important! Since epulid is easy to touch with a toothbrush, touch with the tongue, or have any mechanical impact on it, there is a risk of damaging the tumor and causing a bacterial infection. In this case, without timely treatment, an inflammatory process may develop inside the tumor and its degeneration into a malignant formation. Negative changes can also be caused by the presence of any dental diseases, for example, pulpitis or cysts.
Preventive actions
Prevention consists of regular oral hygiene. At the same time, you need to understand that due to hormonal imbalances, the disease can still occur.
It is necessary to resort to sanitation of the oral cavity within the walls of the clinic. In addition to treatment, dentists will remove tartar and perform professional cleaning. If necessary, doctors will correct the bite, which also leads to the formation of epulis. As a result, the risk of tumors and other dental diseases is reduced significantly.
In addition to the above, it is very important to avoid gum injuries and promptly detect dental diseases.
Benign and malignant tumors: what are the differences?
The malignant course of the disease and the formation of a benign nature differ in symptoms. In the first case, the tumor on the gum grows quickly, is large, causes pain, and destroys neighboring teeth. A malignant tumor causes severe swelling of the soft tissues and bleeding gums.
Benign epulis is usually no more than 2-3 centimeters in circumference. The growth rate is low, so the tumor remains invisible for a long period of time. There is also no pain or swelling, and complaints are focused mainly on the aesthetic component.
Reviews
Epulis in medicine is classified as a tumor neoplasm, but there is no need to be afraid of this disease. Unattractive appearance and aesthetic changes are perhaps the biggest problem during the course of the disease.
However, for many, the tumor causes a lot of inconvenience and is difficult to treat with medication. In addition to the information in this article, readers will be interested to know how the operation is performed and how long the recovery period lasts.
What medications helped reduce the tumor or get rid of it completely? Share your experience and impressions in the comments.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Why does epulid develop?
Of one hundred percent of all cases of epulis development, eighty are provoked by trauma to the mucous membrane. The alveolar ridge can be damaged by a splinter from a cracked or chipped tooth, an improperly installed filling, a removable denture, or braces. An incorrect bite can also cause damage.
Among other causes of epulide on the gums, the following are often found:
- injuries of the maxillofacial apparatus as a result of falls, fights, accidents,
- changes in hormonal levels: for example, with diabetes, pregnancy, menopause, adolescence,
- the presence of plaque, hard deposits and stone on the teeth,
- thermal and chemical burns,
- decreased local immunity,
- in childhood – teething.
Constant irritation of the mucous membrane leads to the active proliferation of its cells and the appearance of a tumor.
Where to get treatment in Moscow, clinics, prices?
To remove epulis, you must contact dental clinics that have surgeons on staff. Average cost of the procedure (in rubles) in some Moscow clinics:
- Center for Aesthetic Dentistry – 6000.
- Denta-El – 5000.
- Dantistoff – 7500.
- Inpromed – 5500.
- Capital – 7600.
After surgery, it is very important to follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding wound care, treatment and oral hygiene, and diet. This will prevent the development of complications and relapses.
It is also important not to forget that the primary prevention of the appearance of tumors is timely dental examinations, hygiene, removal of tartar, adjustment of dentures, braces and fillings.
What types of pathology occur
There are three types of epulis on the gum. They differ in structure, symptoms of manifestations, color
Angiomatous type
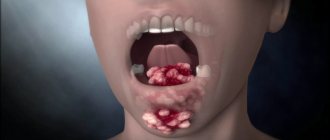
Angiomatous epulis has a reddish-bluish tint, as it is penetrated by a large number of blood capillaries. It mainly develops in childhood and is localized in the area of the neck of the tooth. The pathology is characterized by a wide base, high density, pronounced hypertrophy of the mucosa, and deformation of the alveolar process. The slightest damage leads to bleeding, which is often caused by the lumpy surface of the tumor.
Angiomatous epulide is characterized by rapid growth in a very short period of time and the likelihood of relapse. If education develops in young children, it can become an obstacle to subsequent teething and cause their displacement, as well as one of the factors in the formation of malocclusion.
Fibrous type
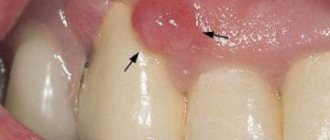
It occurs more often than other types of pathology. Fibrous epulis looks like a small lump that can be located on the gum or on the hard palate. It does not cause pain and is round or oval in shape. Its surface is smooth and its base is wide (it looks like a mushroom on a thin stalk). The color of the tumor is bluish-purple.
The neoplasm is characterized by the absence of bleeding, grows and increases in size very slowly. In some cases, ulcerations may be observed on the mucous membrane. With a large size of fibromatous epulide, difficulties arise with chewing food and closing the dentition.
Giant cell type
Giant cell epulis is characterized by rapid growth, absence of painful sensations when pressed, soft consistency and a wide stalk. The surface of the tumor is smooth, brown in color, and antagonist teeth are often imprinted on it.
Giant cell epulide leads to tooth decay and displacement. Often occurs in childhood in the presence of pathologies of the jaw bone. It is characterized by a tendency to malignancy, which is taken into account when making a diagnosis.
Clinical forms
The disease has a malignant and benign clinical form. Depending on whether a particular case belongs to them, epulis will have characteristic symptoms characteristic of a neoplasm.
Benign
Signs of a benign form of the supragingival (epulis) include:
- slow growth;
- diameter up to 20 mm;
- proceeds painlessly.
Malignant
The malignant form of the disease is characterized by:
- swelling of the gums in the damaged area;
- intensive growth;
- painful sensations;
- destruction of the root canals of dental units located in the affected area;
- loosening of adjacent teeth with subsequent displacement;
- bleeding gums during hygiene procedures using a brush and when chewing food.
Composition and action of the Mexidol line of toothpastes, their advantages and disadvantages. Come here to see photos of the stages of dental implantation.
Follow the link https://dr-zubov.ru/lechenie/zuby/plomby/posle-bolit-kto-vinovat-i-chto-delat.html to find out what you can and cannot do if your tooth hurts badly after filling.
How does the disease progress?
The course of the pathology in all cases is practically no different from each other. At the beginning of the disease, a mushroom-shaped seal appears on the gum. It does not bring any pronounced sensations or discomfort. Only aesthetic discomfort is possible if the tumor forms in the smile area.
As the epulid grows, it interferes with chewing, the normal position of the tongue in the oral cavity, and, if large, does not allow the jaws to completely close. Pain and bleeding occur when the tumor is constantly injured or becomes malignant.
How is the disease treated?
The disease is treated in several ways. Basically, surgical removal of epulis on the gum is used. Before the operation, the doctor gives the patient local anesthesia or anesthesia (depending on the type of tumor and the complexity of the operation, the individual characteristics of the patient). Next, the surgeon excises the tumor, often along with a portion of the periosteum. In difficult cases, resection of the jaw bone is performed.
Another option is laser removal of epulis on the gums. The method makes it possible not only to carry out bloodless manipulations, but also to simultaneously disinfect the surface of the fabric being treated. Laser treatment reduces the likelihood of complications in the postoperative period and significantly shortens it.
Removal of epulis on the gum can also be done through cryotherapy. Although cryodestruction of bone tissue has not been studied well at the moment, the use of the method gives a positive result in 97% of cases of the disease.
Is it possible to use traditional medicine?
Treatment with folk remedies is allowed during the rehabilitation period after removal of the epulis. Basically, rinsing the gums with solutions that have an antiseptic, healing, and anti-inflammatory effect is used. For this purpose, decoctions and water infusions of medicinal plants are used: chamomile, calendula, sage. Procedures are carried out up to 5-7 times a day, especially after meals. In addition to decoctions of beneficial herbs, solutions of baking soda and salt are used (one teaspoon per 200 ml of warm water).
If the tumor appeared during pregnancy
The development of epulis in women during pregnancy has a high probability of relapse. This is due to changes in hormonal levels. Any damage to the gum mucosa can not only lead to pathology, but also accelerate its growth due to endocrine disruptions and metabolic disorders in the body. After childbirth, due to the stabilization of hormones, the neoplasm may slow down its development, but will not disappear.
“When I was pregnant with my second child, I was diagnosed with epulis. It’s good that there was only a little time left before giving birth, I was so worried... I was afraid that it would develop into cancer. As soon as I gave birth, two weeks later I went to remove it with a laser. Everything worked out well, so far there are no relapses, and I hope there won’t be…”
Elena P., 32 years old
Features of the course of the disease in children
Epulis on a child’s gums often occurs during teething, as injury to soft tissue triggers the process of abnormal cell growth. Childhood is characterized by a transition of the disease from one type to another. The most common type is angimatous, which eventually gives way to fibromatous. Also, relapses of the disease are diagnosed in children more often than in adults.
The development of pathology can also occur in adolescents due to hormonal changes. The risk of the appearance of epulid increases in the presence of an incorrect bite or in the case of incorrect installation of braces. In girls, the disease can be triggered by the use of incorrectly selected hormonal contraceptives.
Attention! The growth of epulis in childhood can lead to speech impairment. Painful sensations provoke problems with chewing food. This, in turn, leads to disruption of the digestive tract.