Features of dental x-rays for children
Previously (about 10-15 years ago), x-rays of baby teeth were not a common procedure. Some parents even believed in the myth that baby teeth have neither a root nor a nerve, so the causes of toothache must lie somewhere on the surface, that is, on the crown. This is absolutely not true, and childhood toothache can be caused by the same reasons as in an adult (more on this below).
When asked whether children undergo dental x-rays, we can confidently answer that yes, they do. Moreover, to accurately diagnose the problem and build the correct treatment plan, this is necessary. Another thing is that preference should be given to relatively safe types of x-ray examination, for example, digital.
There are several recommendations for parents to listen to when going for an x-ray with their child:
- You need to come to the clinic in advance so that you have time to psychologically prepare your child for the procedure. You need to tell him that the x-ray will not cause any pain, so you shouldn’t be afraid of it.
- The child's clothing should be loose, easily removable and without complex metal decorations.
- As for girls, you need to give them a simple hairstyle, without using metal pins, bobby pins, etc.
Types of X-rays for children
Like adults, children may be prescribed different types of x-rays.
Sight radiograph
A targeted radiograph is performed using a special digital visiograph. A specific problematic tooth or several adjacent ones (maximum 4) are removed.
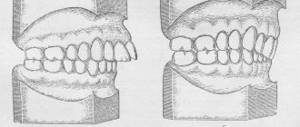
Panoramic radiograph
The panoramic image shows the entire oral cavity: the upper and lower dentition, teeth that have not yet erupted, and the jaws. It also affects the sinuses. An orthopantomogram (this is what a panoramic image is called) is often prescribed to young patients when it becomes noticeable that their teeth are erupting incorrectly: with an inclination, rotation, and so on. In this case, X-rays help to understand whether there is an anomaly in the development of the jaw bone. There are cases when, after the loss of baby teeth, permanent teeth do not appear for a long time. An x-ray will help identify the cause of this deviation.
What does an x-ray of baby teeth show in children?
X-rays of baby teeth show the condition of soft tissues and inflammatory lesions of the oral cavity.
The complete list of pathologies that can be identified using orthopantomography (OPG) is as follows:
- caries;
- carious spots in interdental spaces;
- determination of tooth loss due to gum disease;
- study of root changes;
- assessment of the location of the primordia of primary teeth;
- identification of an abscess;
- study of anomalies in the structure of the dentition.
Pediatric dentistry cannot be complete without radiography. With the help of an X-ray examination, doctors can identify caries, determine the timing of the loss of baby teeth, study the condition of the jaw and identify the presence of ratified (curved) rudiments.
X-rays are very useful in pediatric dentistry. Nevertheless, parents often ask specialists whether x-rays are harmful. Radiation exposure when taking photographs of baby teeth, even in minimal quantities, does exist. To reduce radiation exposure, special schedules for radiography of children's teeth have been created.
Display of permanent rudiments on an orthopantomogram
Approximate timing of x-ray examination of the oral cavity in children:
- small children (before the presence of permanent teeth) – bitewing and periapical photographs are taken once every 2 years;
- adolescents – periapical and bitewing radiography – once every 1.5-3 years;
- after 18 years - once every 1-1.5 years;
- adults - orthopantomography, panoramic and full-mouth photographs are performed according to indications.
There are high-risk categories that require frequent dental x-rays. These are children and adults after restoration, consuming large amounts of sugar, and people who smoke.
Indications for testing
- To determine the extent of caries damage
Children's teeth are susceptible to caries. We cannot assume that caries of baby teeth is not dangerous, since they will fall out anyway. Pathology can spread to permanent teeth even before they erupt. Therefore, it is very important to identify caries and carry out effective treatment.
- To identify periodontitis and pulpitis
Periodontitis (tooth root pathology, pulpitis) is an inflammation of the pulp where the nerve is located. It is clear that such diseases cannot be detected during the initial examination, because they are hidden in the tooth itself or inside the gums. The child’s main complaint is pain in his baby teeth, and the ability to identify its cause is through an X-ray photo.
- When planning endodontic treatment
Endodontic treatment is a set of procedures aimed at preserving a tooth. When emerging caries causes complications, such as pulpitis or periodontitis, the doctor needs to perform therapeutic manipulations inside the tooth. To understand how much pathology has affected the tooth, what percentage of it is destroyed, you need to take an x-ray.
- To assess the condition of the permanent tooth buds
An assessment of the condition of the permanent tooth buds is also required before endodontic treatment. It is necessary in order to understand whether the permanent teeth have been affected by pathology and how close they have already descended to the milk teeth.
- To diagnose and determine treatment regimens for pathologies of occlusion or teething
At an early age, it is still relatively easy to correct an incorrectly formed bite or correct the position of erupted teeth. This can be done using braces or other special systems. However, to begin orthodontic intervention, you need to understand how serious the pathology is. X-rays help with this.
- To determine the reasons for the delay in the appearance of permanent teeth
If a child does not have baby teeth before one year of age, the doctor may order an X-ray to predict their appearance. Of course, such a developmental pathology as adentia (when there are simply no rudiments of baby teeth) is extremely rare, but it is still worth excluding it completely and understanding how soon the first tooth can appear.
Safety
Computed tomography of the jaws. allows you to see the location of the perihilar cyst and the permanent tooth germ located in its cavity.
Modern X-ray equipment makes it possible to significantly reduce the dosage of X-ray radiation through the use of digital sensors instead of X-ray film. A digital X-ray sensor has greater sensitivity than X-ray film, which makes it possible to significantly reduce the strength of X-ray radiation. This is why digital dental x-rays can be used in young children in pediatric dentistry. The undeniable advantage of digital dental photographs is that they are all saved on a computer, which allows you to view them at any time and monitor the quality of the treatment performed over time.
The BabySmile Clinic is equipped with the most modern radiovisiographic equipment for both targeted and panoramic images of teeth, and 3D tomography of teeth and jaws. Targeted photographs of teeth can be taken in each of the treatment rooms without leaving the chair, which significantly increases the comfort of the treatment.
How is research conducted?
Panoramic dental x-rays are done for children, just like for adults:
- The child stands inside the orthopantomograph.
- He clamps the plastic tube between his teeth and keeps his lips closed.
- The device blade is moved as close to the patient as possible.
- A picture is taken (while the device rotates around the child’s head). This takes no more than 20-30 seconds, during which you cannot move or breathe.
A targeted photograph is taken as follows: the child sits on a chair and approaches the device. Next, he wraps his mouth around the digital sensor and clenches his teeth. A picture is taken (takes a few seconds); during this process you cannot move or breathe.
To protect the body from exposure to x-rays, a special apron is worn.
How often can dental x-rays be taken?
Dental X-rays have always given patients such a small amount of radiation that their effects are considered harmless.
Dentists and hygienists are specially trained in details and subtleties, they are told about radiation doses and its interaction with the human body, but unfortunately the population is not educated.
To be clear, in practice, dental staff often compare the amount of dental radiation dose to the amount of natural radiation a person receives during a few minutes of flying on an airplane or at the beach.
Questions from citizens about radiation emitted by dental X-ray machines arise regularly and some people even refuse exposure to the detriment of their own oral health.
Even we on our website could not go through this side of the topic because technically x-ray is a non-destructive testing method.
Technology has changed a lot over the past few years and these advances have made a big difference to dentists now being able to see using radiographic images.
Use of digital technologies
The transition from analog equipment to digital had a great impact on dose reduction. This is mainly due to the fact that there is no need to repeat x-rays, because digital devices are much gentler, but also because the exposure time required to create the image has been reduced.
However, the advent of Cone Beam CT volumetric imaging technology or 3D technology in dentistry - whatever it is called, these technologies have led to a reduction in radiation dose to the patient, even more than the transition from analogue to digital imaging.
What does this mean for a population that is afraid of radiation?
First, let's look at why X-rays are always taken so small. There is nothing magical about dental x-rays. These are the same types of X-rays that are used in hospital departments.
A tooth is a calcified structure like all the other bones in your body, so the amount and energy required to penetrate that bone and create an image is the same. A dental x-ray is actually very similar to an x-ray of a finger or hand.
The bone is about the same diameter, and the amount of soft tissue is also very similar. In fact, the technical aspects of finger and tooth imaging are approximately the same. And similarly, the amount of radiation dose required to penetrate the jaw and form an image for panoramic radiography is similar to the radiation required for the arm.
Know! That the dose from two dental films is 0.002 mSv. And to take a picture of the lumbar spine, 2.2 mSv is needed. This is more than 1000 times more than for a tooth.
It is also necessary to take into account the difference between the distance that radiation needs to travel, between the width of a finger and the stomach - a big difference! For most people it's about 20 times!
The big difference between lumbar spine scans and oral scans is that the same amount of radiation in one area of the body can be more damaging than in another area of the body. This is because some tissues or organs are more sensitive to radiation than others.
Contraindications
- If there is bleeding
Bleeding in the mouth, caused, for example, by problem gums, can affect the quality of the X-ray image. First, the doctor must prescribe hygiene procedures that can stop the bleeding, and only then send for x-rays.
- If you feel unwell
If your child is sick, has a fever, or simply feels unwell, you should not take him for an x-ray. It is better to postpone this procedure until complete recovery.
- In the presence of serious pathologies of the thyroid gland
The thyroid gland is very sensitive to external factors, so dental x-rays are contraindicated for children with pathology of this organ.
Category Children Published by Mister stomatolog