Review of bridge models: what cases are they suitable for, how much do they cost and how long will they last?
Article navigation
- What are bridges and what are they for?
- How are prostheses constructed and attached?
- Indications for use of bridges
- Contraindications
- Types of structures by method of fixation
- Types of structures by materials
- Types of structures by degree of fit
- Installation steps
- What are the advantages
- What are the “cons”
- Service life and care
- approximate cost
- Is it possible to remove the prosthesis?
- Could the bridge fall out?
- When is it time to remove the prosthesis?
- Is it possible to repair the product?
- Alternative options
- Patient reviews
Question for a specialist
Dental bridges are one of the most common options for restoring teeth that have been lost entirely, that is, along with the root. At all times of the existence of prosthetics, they have been popular due to the fact that they are non-removable, but at the same time they solve the problem of aesthetics and functionality of the dentition quite well.
Dental bridge: what material is best to choose from?
If we are talking about prosthetics of the front teeth, then according to statistics, most patients are dissatisfied with the bridges made for them.
As we said above, it is very difficult to make artificial crowns similar in color and transparency to neighboring teeth and, of course, good aesthetics today can be achieved mainly only by using metal-free ceramics - 1) Emax glass ceramics, 2) zirconium dioxide. But we also don’t forget about metal-ceramics, although there is one problem with it when prosthetizing the front teeth. Modern metal-ceramics in some cases can look almost as aesthetically pleasing as metal-free ceramics, but for this it is necessary - 1) to use expensive ceramic masses, 2) metal-ceramics must be made with the so-called “shoulder mass”. But this raises the cost of a metal-ceramic bridge to 20,000 rubles (for 1 Unit/crown). And this is practically the cost of 1 unit of pressed ceramics “Emax”.
Below we will talk in detail about which bridge is optimal for the front teeth (in terms of materials and budget). But with prosthetics with bridges in the area of chewing teeth, the situation is much easier, because here functionality is more important than aesthetics. And in this case, we have a number of optimal solutions, including more affordable ones, although the gold standard for chewing teeth is now expensive bridges made of monolithic zirconium dioxide.
Below we compare the following types of bridges -
- bridges made of metal-free ceramics (zirconium dioxide, E.max),
- metal-ceramic dental bridges,
- solid bridge made of cobalt-chrome alloy,
- adhesive bridge prosthesis.
What are bridges and what are they for?
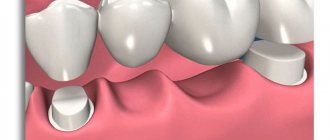
Dental bridges or dentures are the second most popular permanent orthopedic structures after single artificial crowns. They are used to replenish the dentition on the upper or lower jaw. They consist of several single crowns that are securely fixed to each other.
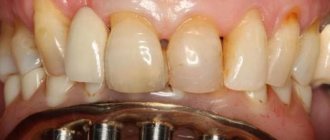
This type of product always contains the following elements - supporting crowns and intermediate crowns, which are designed to restore exactly the tooth that is missing. Look at the photo - it will be clear what such orthopedic systems look like.
Bridges allow you to restore one or more missing teeth in a row. But there is one important condition, i.e. requirement - for reliable fastening of the prosthesis in the oral cavity, several supports are required on each side of the “gap”. As a rule, these are living and strong teeth. The second option is implants (artificial roots made of titanium and its alloys, which are fixed in the bone structure of the jaws).
Many experienced specialists believe that if a patient has live, intact and healthy teeth without fillings as support, then using bridges on them is a bad idea, because. Before fixing them, it will be necessary to depulpate the supports, which will cause them to become fragile and less viable and quickly collapse. Do not forget that wearing a bridge will greatly affect them, as a result of which the patient runs the risk of quickly deteriorating them and even losing them (along with the bridge itself, of course). Therefore, if the supporting units are not damaged and healthy, then it would be more advisable to restore the “gap” in the row with an implant that does not involve the neighboring teeth in any way.
First of all, designs of this type allow you to solve the problem of missing teeth, which makes your smile attractive, and also helps restore chewing function and make the process of eating food comfortable. Bridges are also a solution that protects neighboring preserved units from displacement and from malocclusion in general. Unlike implants, systems benefit in cost, which is why they are in high demand.
BEST REMOVABLE DENTURE - 20,000 rub.
All manipulations for the manufacture, installation and fitting of the prosthesis, including impressions, are included.
Save RUB 10,000! >> Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Zirconium dioxide dental bridges –
Zirconium dioxide ceramic bridges are manufactured using CAD/CAM technology, which involves milling bridges from pressed zirconium dioxide blocks on a computer-controlled machine. Sintered zirconium dioxide has a strength comparable to metal (more than 900 MPa). Thanks to this, zirconium dental bridges can be made of any length - even horseshoe-shaped bridges with a length of 12-14 teeth (which cannot be made from any other types of metal-free ceramics).
We have already said above that a zirconium bridge is the gold standard for prosthetics of the chewing group of teeth. But there are questions about the aesthetics of zirconium dioxide bridges, and when prosthetizing the front teeth, you may encounter a big problem (the bridge will stand out against the background of the patient’s own teeth). The fact is that there are 2 types of bridges and crowns made of zirconium dioxide, and they differ from each other not only in aesthetics, but also in the risk of ceramic chips.
1) “Traditional” zirconia bridges –
For such bridges, only the internal frame will be made of zirconium dioxide, which is lined with ceramic mass, or rather porcelain, on the outside (Fig. 14). And this is due to the fact that most dental laboratories use cheap versions of zirconium dioxide blocks. This zirconium dioxide has a bright white color, plus it is completely opaque, and as a result, such a material does not allow achieving a certain degree of translucency, which is characteristic of natural tooth enamel.
Crowns and bridges made from such material will have an unnatural milky white color, plus there will be no translucency characteristic of natural teeth. Therefore, in order to improve aesthetics, only the internal frame is milled from such zirconium dioxide, which gives strength to the structure, and then the dental technician, by applying layers of porcelain, gives the crowns of the bridge the final shape and color. But even despite this, the aesthetics of such crowns and bridges will be far from perfect.
Plus, this manufacturing method has another disadvantage. We have already said above that zirconium dioxide has the strength of a metal (from 900 MPa), however, the layer of porcelain mass on the surface of the zirconium frame has a strength of only 80-120 MPa. This leads to chips of the ceramic mass (according to statistics, within 6 years they occur in approximately 10% of patients). The chips are repairable, but the reliability of such repairs leaves much to be desired.
Conclusions : we do not recommend using zirconium dioxide bridges (made with a surface layer of porcelain) for prosthetics of chewing teeth, because in this case there will be a high risk of chipping. When replacing front teeth with prosthetics, this option is not very successful, because the crowns of the bridge will still have an unnatural milky tint, standing out against the background of your own teeth (Fig. 15-16). Plus, there is still a risk of chipping the porcelain lining.
The aesthetics of such structures are
Such milky-white crowns and bridges made of zirconium dioxide will look acceptable only in one case - if you are going to simultaneously prosthetize all the teeth that fall into the smile line on both the upper and lower jaws (i.e. at least the fifth teeth inclusive ). Otherwise, such a bridge will be very noticeable against the background of your own teeth.
2) Zirconium bridges using “Multi-layer” technology –
But the problem of poor aesthetics and chipping was solved by the advent of the next generation of zirconium dioxide blocks/discs. Currently, a number of manufacturers produce zirconium dioxide with “Multi-layer” technology. Discs made from such zirconium dioxide are “pre-colored”, i.e. they have a color gradient that is characteristic of the enamel of real teeth. The second difference: due to the stabilization of zirconium dioxide by yttrium, such blocks will have varying degrees of “transparency”, i.e. translucency.
As a result, crowns and bridges made from such material will have a gradient of color and transparency, which will vary from the neck of the tooth to the incisal edge (the cusps of the chewing teeth). Those. The closer to the incisal edge, the lighter and more transparent the zirconium dioxide becomes. But multi-layer technology can provide more than just good aesthetics! In this case, there is no need to use surface layers of porcelain, and therefore crowns and bridges will be made of monolithic zirconia.
Clinical case No. 1 – below you can see the aesthetics of newly made single crowns and bridges made of zirconium dioxide, made using the “Multi-layer” technology (they are not yet fixed in the oral cavity, but are on a plaster model of the patient’s teeth). The bridge prosthesis in the projection of 14-15-16 teeth is made with artificial pink gum, and the remaining units are made in the form of single zirconium crowns. With these photos we want to show a smooth transition of color and transparency.
Therefore, if you want to get decent aesthetics, then when you go to a dental clinic, you need to find out whether they use “Multi-layer” zirconium dioxide. High-quality discs using this technology: these are 2 variants of Katana® discs - UTML or STML (Japan), as well as Prettau® Anterior (Germany). The cost of one such disk starts from 16,500 rubles. For example, a disc made of ordinary white opaque zirconium dioxide costs only 4,500 rubles, and therefore many clinics, in an attempt to save on costs, work with cheap, outdated materials.
Conclusions: if you need a bridge prosthesis on implants, or a bridge prosthesis in the area of chewing teeth, then a bridge made of monolithic zirconium dioxide using the Multi-layer technology is not the cheapest, but the best option. When it comes to front teeth prosthetics, if you want to get the best aesthetics possible, there are limitations. For example, if you are planning to make a bridge or crowns on all front teeth (falling into the smile line), then Multi-layer zirconium dioxide will allow you to get the ideal aesthetic result.
However, if you need a bridge for only 3-4 teeth, then even with the help of the Multi-Layer technology, a dental technician is unlikely to be able to make such a structure absolutely indistinguishable from neighboring natural teeth. In this case, to achieve ideal aesthetics, it is worth choosing a bridge not from zirconium dioxide, but from pressed Emax ceramics. This is due to the fact that when working with Emax, the dental technician will have significantly more color options in his arsenal (than when working with any option of zirconium dioxide), which will make the bridge as similar as possible to the neighboring teeth.
Cost – for zirconium bridges, the price for 2021 in Moscow will be on average from 30,000 to 40,000 rubles (for 1 Unit/crown). Thus, the cost of a 3-unit bridge will be at least 90,000 rubles. However, in a number of clinics you may well be offered a price of less than 30,000 per unit, but in this case the bridge will clearly not be “multi-layer” or monolithic.
How are bridges constructed and how are they attached?
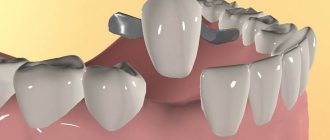
A classic bridge is a one-piece device that consists of interconnected crowns. However, in his system it is possible to distinguish an intermediate part - this is an area that imitates lost teeth, as well as lateral supporting crowns - there are two of them (one on each side of the product). They are hollow inside and are literally put on top of the “supports” and firmly fixed to them using dental cement.
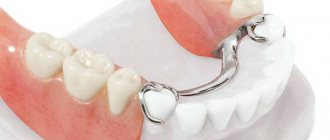
There is another fastening system: dental bridges with locks. There is also a central crown that replaces the tooth. There are two small locks inside it. And inside the supporting “neighbors” is another part of the fastening. This system ensures the safety of teeth from grinding. But, of course, the cost of this type of prosthesis is higher.
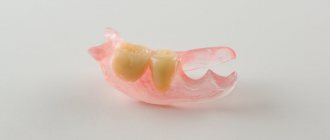
It is also worth noting that today there are not only classical bridges, but also adhesive ones (they will be discussed further in the material). They have a slightly different device. In the center there is a crown that restores a lost tooth, on the sides there are peculiar “wings” made of fiberglass or metal. Such plates are glued to the inside of the two lateral teeth.
There is another variety - cantilever structures. They are designed to replace the outermost teeth in a row. Those. To fix them, just one support is enough. They consist of a strong base and the crown itself. Such products are used quite rarely in medical practice. Most often, experienced dentists do not recommend them; in extreme cases, you can only rely on temporary fixation of the crowns of such bridges, because they quickly lead to wear and tear of the supporting units and can even contribute to their dislocation and complete destruction.
Contraindications
It will not be possible to use bridge prosthetics if:
- The defect is terminal (the outermost teeth in the row are missing, and one of the lateral supports for the “bridge” is missing).
- The quality of the supporting teeth is low. They are loosened by periodontal disease, have large fillings, have chronic periodontitis, etc.
- The length of the defect is more than 2-3 teeth.
- The supporting teeth have a pathologically low crown part.
- Abutment teeth have different functional orientations.
Indications for use of bridges
- with prosthetics on natural “supports”: the absence of one to several teeth (no more than four), provided that there are supporting teeth on both sides to secure the bridge, i.e. the defect must be “on”,
- for prosthetics supported by implants: absence of two units in a row to the entire row,
- absence of extreme units: only console devices are suitable for their restoration,
- the need to remove a tooth: in this case, it is recommended to install a bridge no earlier than a month after the procedure, because the hole and damaged tissues need time to recover, and the structure can put pressure on the mucous membrane and contribute to inflammation.
Bridge installation: contraindications and indications
Direct indications for the installation of bridges are the absence of one chewing tooth or from one to four front teeth with supporting teeth on either side of them that can withstand the increased load. Dental prosthetics using a bridge has a number of relative and absolute contraindications. These include:
- absence of no more than 4 incisors, 2 premolars, 1 molar in a row;
- bruxism (involuntary grinding of teeth, the harm from which can be mitigated by wearing special mouthguards);
- pathology of the bite (in this case, you will have to undergo orthodontic treatment before prosthetics);
- periodontitis and severe periodontal disease;
- pathological abrasion of hard dental tissues;
- diseases of the bone tissue of the jaw (for example, osteoporosis, osteomyelitis);
- acute inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity;
- poor oral hygiene.
This also includes general contraindications to surgical intervention as such: such as, for example, problems with blood clotting, allergies to painkillers, chronic diseases in the acute stage, taking anticoagulant medications, mental illness, and more.
Contraindications for prosthetics
It is impossible to solve the problem of edentia with this type of fixed structures if the patient has an inflammatory process in the oral cavity, periodontitis or periodontal disease - these dangerous diseases lead to loosening and displacement of teeth, so there is no need to talk about the durability of the restoration here, because it will wobble and may even fall out along with the "supports". Also, wearing devices is contraindicated in case of osteoporosis. They cannot be fixed during bruxism, when the patient suffers from involuntary clenching of the jaws, or with serious malocclusions.
It is impossible to solve the problem of edentia with classical bridge prosthetics if the patient is missing more than 5 teeth in a row. In this case, the extended structure will not have stability and stability, and the supporting teeth will very quickly fail. Extended bridges can only be created from such a durable material as zirconium dioxide, but only if the prosthetics are carried out on implants.
What to do if the supporting units are severely damaged? For example, deep caries, pulpitis or trauma. In this case, doctors do not recommend prosthetic bridges, because They will not last very long, because the supporting elements are already weakened from the very beginning. But in some cases, the supports can still be pre-strengthened with a pin or, more preferably, a stump insert. Read a related article about stump inlays and find out why this is a very effective solution.
Patients prone to allergic reactions should also be careful when choosing the type of prosthesis. After all, some materials from which structures are made can cause allergies. Most often these are alloys of base metals.
General overview
A classic fixed bridge consists of two crowns that are placed on supporting elements, and an artificial tooth (or several) in the middle.
Prosthetics with such a design begin with scrupulous treatment of supporting units, removal of roots, and often require surgical correction of the gums.
Immediately before creating a bridge system, the supporting units are prepared , that is, they are ground to the shape of future crowns.
Only after this, impressions are taken and a prosthesis is created in a technical laboratory, which is subsequently relocated to the patient’s oral cavity. The success of the final stage directly depends on the quality of the preparation - the better the teeth are processed, the tighter the structure will fit.
However, it happens that the supporting elements cannot be processed properly. For example, they are strongly inclined towards the midline of the face (medial position) or deviated towards the temporomandibular joints (distal position). “Eights” are often positioned abnormally this way – they don’t have enough space in a row, and they grow crookedly.
A healthy figure eight can be a good option for supporting a bridge device. But to give it the desired shape, you will have to cut off a thick layer of hard tissue, to the point that the remaining part will be unsuitable for fixing the abutment crown.
It is for such clinical situations that composite bridges were created. Instead of the usual crown, the middle part of the structure is attached to the supporting unit using:
- hooks (clasps);
- tabs;
- rings;
- locking fastenings of various types;
- telescopic crowns.
Due to the method of attachment, the composite model is not removable. Otherwise, the design is similar to a conventional “bridge” - artificial teeth made of metal, metal-ceramics or acrylic.
Objective reviews about ceramic crowns for teeth and the cost of products. Come here to become more familiar with the CBW prosthetics technique.
At this address https://dentist-pro.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnye/mosty/mnogoobrazie-zubnyx-kak-vybrat-luchshij-variant.html we will consider in detail the types of dental bridges.
Types of structures according to the method of fixation in the oral cavity
- conventional dental bridges are based on living teeth preserved in the oral cavity, which are previously ground down: this method of restoration is considered the most common to this day, despite the emergence of more modern options,
- dental bridges with locks: in such systems, as we noted earlier, there is one crown (no more), inside it and in the crowns of neighboring teeth there are small fasteners that snap securely,
- adhesive bridges: their fixation system is somewhat different - supports are also necessary, but the prosthesis does not completely cover them like a crown, but is glued to the back wall without grinding the teeth. This system allows you to protect the “supports” from preparation, but at the same time the service life of the product itself is significantly reduced (excessive load is contraindicated). Doctors advise using this restoration option only for certain indications1 (young people with a correct bite and high clinical crowns), and exclusively as a temporary measure, whose service life should be limited to a maximum of a couple of years. After this period of time, it is better to install a more reliable design that meets the functional requirements,
- Implant-supported bridges: pre-installed artificial metal roots allow you to preserve adjacent teeth in their natural state without involving them in prosthetics. There are two options for fixing the prosthesis to implants. The first is using a screw connection (used more often, because it allows, if necessary, to remove the product for correction). The second is using cement fixation.
Installation process
The entire installation process of a solid cast structure includes the following activities:
- Sanitation of the oral cavity.
- Turning of abutment crowns using anesthesia. About 1.5 mm of tissue is removed. The crown is given a special shape for a secure fit of the prosthesis.
- Taking an impression.
- Trying on a temporary prosthesis with its subsequent fixation.
- Trying on a permanent structure and checking the quality of fit.
- Fixation of the permanent structure with cement.
Types of structures by materials
Solid cast (metal)
Dentures are created from one piece of material - solid polished metal. Like single solid crowns, such a bridge can be made from various alloys of both base metals and precious metals based on gold/silver. Its advantages (in particular, we are talking about products made from inexpensive metal alloys) are low cost and extraordinary strength. But there are also disadvantages - poor aesthetics, the impossibility of frontal prosthetics, a high probability of developing an allergic reaction to metals, oxidation, rapid wear and tear of antagonists on the adjacent jaw that are in chewing contact.
All-ceramic
These types of bridges are created only from pressed ceramics of the E.Max or Empress brands because they are characterized by increased strength (ordinary ceramics are not used in the manufacture of bridges due to their fragility). Such products will look good for restorations on the front teeth in the smile area, but only if it is necessary to restore no more than one lost unit. Those. the design itself can consist of three crowns, no more. Their installation requires minimal turning and preparation of the supports, which means they can better withstand the load and last longer. It is also worth noting that this type of ceramic does not chip, does not crack, and perfectly retains its positive external and functional properties throughout its entire service life.
All-ceramic aluminum oxide and zirconium dioxide
They are created using special CAD/CAM technology on special computerized equipment, which determines their positive characteristics and advantages: wear resistance, tight fit to the supports, taking into account all the individual anatomical features of the patient, accuracy of restoration. The basis of such a bridge consists of a single piece of aluminum oxide or zirconium dioxide. On top of the prosthesis is covered with a layer of dental ceramics of the selected shade, or simply painted.
Thanks to the outer ceramic, the product is given the final natural shape and transparency of natural enamel. This is a plus, but the minus is that the ceramic layer of such products sometimes chips (according to some studies, chips occur in approximately 10% of patients after six years of use). But it should be noted that it is precisely thanks to the strength of zirconium dioxide that it is possible to create the longest bridges in length supported by natural teeth and even bridges for a full jaw when solving the problem of edentulism on implants - up to 10-12 units in a row.
Made of metal ceramics
This type also refers to a one-piece construction. First, a metal frame is created, and then it is covered with a layer of aesthetic porcelain (ceramics), thanks to which the final shape is created and the desired color of the prosthesis is achieved. Due to the strength of the metal frame, bridges of any length can be created. The metal at the base of the bridge can be made of various alloys - both precious and ordinary, which significantly affects the cost of the product. Metal-ceramic bridges are used both on natural teeth and on implants as a permanent type of prosthetics (i.e. after the implants and bone have fused).
When mentioning metal-ceramic structures, it is worth noting their main advantages and disadvantages. The advantage is that the systems can withstand heavy chewing loads, which means they are well suited for chewing teeth. They are also optimal in terms of price-quality-aesthetics ratio. Therefore, a large number of patients choose them.
But we should not forget about the possible disadvantages of such products: when using bridges without “shoulder mass” (their cost is higher than the usual classic ones), part of the mucosa comes into contact with metal, which is not insulated at the base with ceramics. As a result, metal oxidation occurs, and the gums around may turn blue. It is also impossible to exclude the occurrence of an allergy to metals or galvanic syndrome if there are other prostheses in the mouth made of metals that react with new structural materials.
Made of metal composite
Just as in metal-ceramic products, the frame of such a bridge is created from metal and cast as a single structure. The top of the frame is lined with a special light-curing composite, matched to the color of natural enamel or the patient’s choice. The composite coating is significantly less wear-resistant compared to ceramics, so metal-composite prostheses are used quite rarely. Also, a combination of metal and composite is used to make adhesive bridges.
Made of metal-plastic
The basis of the prosthesis is a solid metal frame, and the covering is made of plastic, which is selected in color depending on the shade of the adjacent teeth. Due to the fragility and relative fragility of such a coating, metal-plastic bridges, as a rule, perform the function of temporary fixed prosthetics on implants. Indications for wearing are implantation with immediate loading, that is, the prosthesis is placed immediately after implantation. But the wearing period is no more than 3 years, after which it needs to be replaced with a more durable design.
Metal-plastic bridges are rarely used on natural teeth; in most cases, patients choose them for reasons of economy. But given the short service life, doctors recommend choosing stronger and more durable products that will not have to be replaced in a few years.
Soldered structures
A soldered bridge consists of several artificial crowns that are soldered to each other. This is a much less common option, since dissimilar metals are used for its manufacture (for the crowns themselves and for their connection), which is extremely harmful to the body and mucous membranes. In addition, the strength of the structure is far from that of solid cast ones, since damage is possible at the soldering points. This option for manufacturing bridges is practically not used today.
Tabbed systems
In some cases, if one tooth is missing and the neighboring ones are partially destroyed, it is possible to install bridges on inlays. If the damaged crowns are subject to restoration, it is possible to make a single ceramic or zirconium dioxide structure, which will consist of two restoration inlays along the edges and a crown in place of the missing tooth; in this case, there is practically no injury, since turning for crowns and depulping is not required - the tooth is already fully prepared and will last longer than a living, but not fortified one.
Combined type
If you want to reduce the cost, then technicians can create a prosthesis specifically tailored to your wishes, which will consist of crowns made using different materials. For example, metal-ceramic crowns will be made in the smile area, and solid-cast ones will be used to restore chewing units.
Solid bridges
Solid-cast bridges are that intermediate link when aesthetics are at a low level, but the functional properties are already high. This determines the area of their application: chewing teeth, more often in older people, when restoration of aesthetics is not in the first place. The principles of preparation and manufacturing methods make it possible to achieve excellent marginal fit of the prosthesis to the supporting teeth and complete restoration of occlusal relationships. Because of this, the advantages of solid-cast bridges are:
- high percentage of restoration of chewing efficiency, if it is advisable to use this type of prosthetics
— good marginal adaptation allows for adequate individual hygiene and does not complicate self-cleaning in the oral cavity
— the one-piece design prevents breakage of the prosthesis along the line of connection of the supporting and intermediate parts.
Along with this, solid bridges have disadvantages characteristic of this particular type of prosthesis:
- low aesthetic characteristics reduce the scope of application of this type of prosthetics to the chewing group of teeth
- metal in the oral cavity is less compatible with the body than ceramic materials, which can cause galvanism and allergic reactions to metals in rare cases.
Types of structures according to the degree of adherence to the mucosa
Bridges are usually divided not only by the method of fixation and by the materials from which they are made. The degree of contact between the intermediate part of the prosthesis and the mucous membrane is also important when choosing. Let's look at the possible options:
- flushing: the most common type. The bridge with its intermediate part (i.e. the crown that directly restores the missing tooth) does not fit tightly to the gum. Therefore, several millimeters of free space remain between it and the mucous membrane. Firstly, the gap is washed with saliva, thanks to which it is possible to achieve cleansing of the oral cavity in a natural way. Secondly, the microslot allows the patient himself to successfully carry out hygiene procedures,
- tangents: the bridge is in contact with the mucosa on only one side. As a rule, this option is relevant when restoring the anterior units, where the aesthetics of the smile is extremely important,
- saddle-shaped: structures that are completely under the gum and are in contact with it on both sides. They are quite rare, since from a hygienic point of view they are completely unsafe, but in some cases you cannot do without them.
Complex on 4 OSSTEM implants with delayed loading - 150,000 rubles.
Complex implantation Osstem (South Korea) with delayed loading after 4-6 months.
Doctor's work guarantee - up to 5 years (under an agreement on the provision of medical services) Call now or order a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Stages of installation of a bridge structure
Installation usually takes several days - from the preparation of the supporting units to the actual fixation of the bridge. Most of this takes up the time spent on manufacturing the structure in the laboratory (this can take up to several weeks, depending on the workload of the technicians). So, let's look at the clinical stages of prosthetics.
Stage No. 1: sanitation of the oral cavity
It is necessary to first remove all carious lesions, inflammation, deposits and plaque to ensure a long service life of the dentures. This stage is relevant both for prosthetics on your teeth and on implants.
Stage No. 2: preparation and preparation of “supports”
The doctor must perform depulpation, i.e. removes the nerve. The procedure is unpleasant, but can be easily tolerated under local anesthesia. Next, the supports are given a cone-shaped shape, which in the future will be equal in size to the internal cavity of the outermost crowns in the prosthesis - while the prosthesis is being manufactured, the doctor installs temporary pads on them to protect the crowns from the effects of external aggressive factors. If the top of the “support” is severely damaged, it may be necessary to strengthen the root using a stump tab or a pin.
Are you worried about how the process of preparing supporting teeth for prosthetics will go, and whether it will hurt? Be sure to read the article - grinding teeth before dentures. Learn how to prepare and grind down enamel.
Stage No. 3: taking impressions of both jaws
The future prosthesis should be as convenient and comfortable as possible during use, it should correspond to the characteristics of your bite, therefore impressions are taken from both jaws to create the correct bite when making the prosthesis. During the period of time while the impressions are transferred to the laboratory and go through the stages of manufacturing the structure, the doctor fixes plastic caps on the prepared units, which will protect the sensitive enamel from the harmful effects of the environment, bacteria, food, and chewing pressure.
Stage No. 4: fitting and fixation of the prosthesis
This is done using special dental cement-glue: first, the doctor performs temporary fixation of the crowns, and your main task at this stage is to assess the quality and level of comfort, and report problems to the orthopedist. The so-called “trial period” lasts about a month.
Only after all defects have been eliminated and adjusted, the product will be fixed with permanent cement, after which it will be too late to think about how to remove the bridge - only a doctor can do this. Moreover, the process will be irreversible, the structure will not be able to be removed without damage, intact and intact, because it is designed for constant wear, and special cement eliminates the possibility of its decementing. You'll just have to cut it up.
How to put a bridge on teeth -
Installing a bridge on teeth is carried out as follows... The teeth located on the sides of the missing one will act as support for the bridge. If only 1 tooth is missing, crowns are usually taken on one tooth on each side of the missing one. If 2 teeth are missing in a row, then a total of at least 3 teeth are taken under the bridge supports (one on one side of the dentition defect, and two on the other).
How to put a bridge on teeth: diagram and photo
Installing a bridge requires grinding down the supporting teeth for crowns, and here it must be taken into account that for different types of artificial crowns the thickness of the preparation will differ. For metal-ceramics, teeth are ground from the chewing surface by 2.0-2.5 mm, from the lateral surfaces by 1.5 mm (Fig. 4). For crowns made of metal-free ceramics - only 1.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively (Fig. 5). Moreover, the more tooth tissue is preserved under the artificial crown, the longer its service life will be.
Schemes for preparing teeth for crowns –
Moreover, please note that in the gingival zone, the tooth crown is ground in such a way that a so-called “ledge” (i.e., a step, Fig. 6) is formed along the entire perimeter of the tooth stump. The service life of the crown will largely depend on the quality of the ledge formation, because poor/inaccurate fit of the crown to the neck of the tooth in the area of the ledge - leads to the gradual entry of bacteria under the crown and the beginning of decay of the tooth tissue. And this happens very often.
Preparation of supporting teeth for prosthetics –
In many cases, teeth under artificial crowns are subject to depulpation, i.e. the nerve will need to be removed. This is due to the fact that deep in the tooth there is a neurovascular bundle (pulp), and the more tissue is ground off when preparing a tooth for a crown, the higher the risk of nerve injury. Accordingly, because Under metal-ceramics, more tooth tissue is ground off - here it is possible to leave mainly only large molars alive (they have a greater thickness of hard tissue around the nerve).
But for ceramic crowns, almost 2 times less tooth tissue is ground off, and in this case, almost all the teeth can be left alive. Keeping your teeth alive is very important because... after removal of the neurovascular bundle, the tooth stops receiving moisture and nutrition from the inside, which leads to an increase in the fragility of the hard tissues of the tooth and reduces its service life. The cost of removing nerves and filling root canals will depend on the number of root canals in the supporting teeth, and on average will be (for 1 tooth) –
- tooth with 1 root canal – from 2500 rubles,
- tooth with 2 channels – from 3800 rubles,
- tooth with 3 channels – from 5,000 rubles.
Dental bridge: before and after photos
Important: if the adjacent teeth from the missing one do not have fillings and are alive, then prosthetics with a bridge and grinding down the adjacent teeth for crowns is actually a very bad idea. The price of a dental bridge of 3 units made of ceramics or good metal-ceramics (taking into account the cost of preparing teeth for prosthetics) is almost always higher - when compared with the cost of installing 1 economy-class implant.
A dental bridge should be done only if the adjacent teeth from the missing one have large fillings (taking up more than 1/2 of the tooth crown in volume), and also if the nerves have been removed from them. Remember that the service life of the best crowns will be, at best, no more than 10-15 years, and what will happen to the supporting teeth after this time, and whether they can be re-used with prosthetics is still a big question. Your own living teeth (as opposed to artificial crowns) can last you much longer.
What are the advantages of installing dental bridges?
- the possibility of permanent prosthetics, which means comfort for the patient and the absence of fear that the dentures will fall out of the mouth at the most inopportune moment,
- the ability to use various materials, a wide selection of designs for the patient to choose from: you can choose a temporary or permanent option that will last 8-10 years,
- excellent aesthetics: in particular when using highly aesthetic materials (zirconium dioxide, aluminum oxide, solid ceramics), as well as metal ceramics,
- durability, strength and wear resistance of bridges with metal or zirconium dioxide frames,
- the possibility of root restoration during prosthetics on implants: the chewing load is transferred to the bone through the implant, which allows you to restore the natural metabolic processes in the jaw bone and prevent its atrophy,
- the possibility of prosthetics without turning and depulping abutment teeth when choosing the method of adhesive prosthetics, prosthetics with micro-locks or a bridge on inlays, however, such products are not suitable for every patient.
What are the “cons” of installing dentures?
The use of modern materials allows the patient to choose the most optimal restoration option - in terms of cost and quality. But prosthetics also have a number of disadvantages:
- the need to sharpen natural teeth that are used as supports - but they can be absolutely healthy,
- the possibility of damage to the “supports” under load, since they bear a greater load than before installing the bridge on them,
- reduction of bone tissue under the prosthesis - the pressure from chewing food falls only on the supporting units, and under the prosthesis the bone does not receive the necessary load, as a result its atrophy begins. Over time, a gap will form between the gum and the prosthesis, caused by the process of decreasing bone volume, and the structures themselves will begin to move away from the gum and may even become loose and shift. This is why it is recommended to install implant-supported bridges.
Materials used
For the manufacture of solid-cast prostheses, gold (both in pure form and sputtering) and stainless metals, or rather their alloys, are used.
The materials used can be combined, and such a prosthesis will be classified as combined or with veneer. The following materials are used as the base material for the manufacture of a solid-cast bridge:
- gold;
- silver and palladium;
- cobalt and chromium.
Structures made of chromium and cobalt can be improved by manufacturing in their natural form, gold plating, or ceramic coating to resemble natural hard tissues of teeth.
Service life and care
The service life of bridges depends on the materials from which they are made, as well as on the prosthetic method itself. For example, modern bridges made of dioxide will last more than 15-20 years. While an adhesive bridge lasts from 6 months to 2 years maximum (with careful handling), since it is held very precariously.
The service life of the prosthesis may change regardless of the material from which it was made: for example, if the supporting units are damaged or adjacent units are lost - in the second case, some of the teeth may shift towards the vacated space.
The length of service life is influenced by several important factors: the health of the supporting teeth and the condition of the mucous membrane in the mouth, the length of the bridge, the material from which it was made, the distribution of the chewing load (for example, if you chew only on the side of the jaw where the prosthesis is installed, it will will fail faster than expected).
To extend the life of dentures, do not forget about regular hygiene care (brush, paste, rinse, irrigator, floss and brushes can be used with extreme caution) and visiting your doctor for preventive purposes. It is also necessary to take special care of the supporting teeth, because in fact, the period of successful operation of dentures is limited by their health and strength.
Zirconium dioxide crown on an implant for the whole 70,000 rubles.
OSSTEM implant (South Korea), individual zirconium abutment, gum former, impression taking.
Creation of a Prettau zirconium crown using 3D modeling technology. Consultation with 2 doctors: an orthopedist and an implantologist for free! Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Periodically evaluate the following parameters: whether the supporting units are wobbly, whether there is swelling and bleeding of the mucous membrane under the prosthesis, whether there is discomfort during chewing food and pain when pressing on artificial crowns. If you suspect any of these problems, be sure to consult your doctor.
Manufacturing process
The cast bridge is made and installed in several stages. To do this, it is important to contact a highly qualified specialist who follows all the rules and installation sequence.
Let's take a closer look at the manufacturing stages:
- Carrying out an initial inspection, identifying hidden defects and damage if any. If any oral diseases are detected, they must be cured. Particular attention should be paid to the teeth to which the prosthesis is planned to be attached. If necessary, a seal is placed on them. It is also important that the gums where the prosthesis will be installed are in perfect order. In case of periodontal diseases, they are cured. Next, the specialist draws up a plan for the upcoming treatment.
- Grinding of support teeth on both sides. In this case, anesthesia is used, since the procedure is painful. The supporting teeth should be ground down to a thickness equal to the thickness of the crown (approximately 1.5 - 1.7 mm). In addition, they need to be given a certain shape, which will facilitate reliable fixation of the bridge. Sometimes the nerve in supporting teeth has to be removed.
- An impression is taken from the patient’s jaw, from which a plaster model of the prosthesis is made in the laboratory. Next, it is based on this model that the solid-cast structure itself will be manufactured.
- Selecting the color of the bridge that matches the shade of living dental organs.
- A temporary bridge is made from plastic. It is installed while the main structure is being made. The temporary prosthesis is fixed with a special solution. At this time, the dental technician in the laboratory is engaged in the manufacture of the product itself through casting.
- After making a permanent product, it is tried on. If it suits the patient in all respects, it can be covered with lining or spraying. If there are any inconsistencies, the product is sent back to the laboratory for revision.
- Next, the installation of a permanent prosthesis begins. Before doing this, it is important to once again evaluate how tightly the structure fits and how comfortable it is for the patient. After this, the product is fixed with special cement.
Approximate cost of prosthetics
Only a doctor who will conduct a thorough examination of the oral cavity can tell you the real price. After all, there are many components that make up the final cost of restoration - this is the number of missing teeth, and the condition of the supporting units (it is quite possible that they will have to be treated or strengthened with a pin or stump insert). And these are additional expenses. Naturally, prices for installing a classic design and an adhesive one will vary. You will have to pay completely different money for treatment with bridges on implants.
Let's look at the classic situation when a bridge is installed if one tooth is missing, and the surviving neighboring ones act as a support for it.
| Product type | Price |
| Made of metal | About 10-12 thousand rubles |
| Made of metal ceramics | About 20 thousand rubles |
| From zirconium dioxide | About 40 thousand rubles |
For the manufacture and installation of adhesive devices you will have to pay about 10 thousand rubles (when using the simplest materials: composite and fiberglass) and about 30 thousand rubles if we are talking about a metal-ceramic structure on inlays.
Price
The cost of dental bridges, like other dental services, largely depends on the marketing and pricing policies of a particular clinic. Also important is the material chosen by the patient. Metal ceramics will be the most affordable and will delight you with practicality. Zirconium dioxide, a representative of elite dental orthopedics, will cost more, but such a bridge will last 2-3 decades with proper care.
Average cost of installing bridges in Moscow:
- Metal ceramics from RUB 2,950. up to 16,000 rub.
- Ceramics from RUB 11,500. up to 25,000 rub.
- All-metal from RUB 2,100. up to 4,500 rub.
Is it possible to remove the prosthesis?
Many patients are interested in the question of how a bridge is removed. Do not forget that the structure after final fitting and fixation is considered permanent, i.e. You won’t be able to remove it from your mouth on your own. Even a doctor will not be able to remove it without compromising the integrity of the materials. If it becomes necessary to remove the classic device, the doctor will use a diamond bur and other specialized tools with which he will cut the material. Then, accordingly, you will have to make a new product, but it will no longer be possible to install the old one. The only way this can still be done is by depressurizing the bridge structure. Here, the specialist will first check its integrity, the condition of the supporting units and mucosa, and if there are no problems, the doctor will re-fix it with permanent cement.
If the bridge was fixed to the implants using a screw connection, then the doctor can safely remove it without damaging the material and without removing the artificial roots themselves.
Can a bridge fall out and what to do in such a situation?
This situation is possible. There are several reasons. The first is the destruction of the supports: in this case, the device simply will have nothing to support it. The second is inflammation of the gums at the junction of the central crown. The third is de-cementation (the expiration date of the cement has passed or low-quality glue was initially used) or poor fit of the product even at the installation stage.
In all of the above cases, you should immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will determine how to proceed further based on a visual examination of the oral cavity and an assessment of the condition of the product.
When is it time to remove the prosthesis?
On average, the service life of a bridge is 5-7 years, less often 15 or more (made of zirconium dioxide). These deadlines are determined by the quality of the materials from which the products are made. Despite the declared long period of operation, many patients turn to doctors to remove bridges much earlier. Often the cause is inflammation of the mucous membrane under the prosthesis, destruction of the supporting teeth (they have to be removed after the structures are removed), or the presence of caries under the supporting crowns. Another reason is atrophy of the jaw bone, due to which the prosthesis begins to move away from the mucous membrane, and, accordingly, the aesthetics of the smile are disrupted.
Is it possible to repair the product?
If the surface layer of the crown has chipped, the restoration can be carried out using composite materials. If the product breaks, a crack forms on it, or the middle crown falls out, then such defects cannot be repaired - the design will have to be completely changed. However, situations with serious bridge failures are quite rare, and may indicate either that the product was initially manufactured and installed incorrectly, or that the patient is placing an inadequate load on it.
REPROSTHETICS WITH ACRYLIC PROSTHETICS - RUB 200,000.
Re-prosthetics with an acrylic bridge on a metal frame (all included) up to 12 units.
Save RUR 30,000. Call now or request a call
Read on the topic - in as much detail as possible about the repair of dentures. You will find answers to questions about why “artificial teeth” can be damaged and what defects can be corrected.
Recommendations for caring for dental bridges
In addition to the general rules of daily hygiene (cleaning with paste and brush at least twice a day - morning and evening, as well as every time after eating), additional requirements must be observed. So how do you clean dental bridges? In addition to the usual brushing with a soft toothbrush (each tooth separately, sweeping movements from the gum to the cutting edge), you must also use an irrigator, and if you don’t have one at hand, thoroughly rinse your mouth with water. The presence of a flushing hole between the central part of the dental bridge and the gum greatly facilitates the daily care of the denture. In addition, during professional oral hygiene, which, by the way, must be carried out at least twice a year, the hygienist should pay special attention to the bridge prosthesis - check for food debris and plaque accumulation at the junction of the prosthesis and gums, and also carefully polish artificial teeth and crowns on supporting teeth.
Alternative solutions to the problem of edentia
The main alternative in the absence of a small number of individual teeth (not in a row) are single crowns on implants. Such prosthetics allows you to restore not only the crown, but also the root, and at the same time achieve high aesthetics. The cost of prosthetics is also comparable to classic bridge prosthetics and varies depending on the selected materials and implant system. However, implantation has a number of limitations, which are discussed with the doctor at the initial consultation.
An economical option for solving the problem of edentia is removable prosthetics (partial or complete), however, “removable jaws” have a number of significant disadvantages that the patient must take into account before choosing this type of treatment.
According to studies, removable devices are only 60-65% capable of restoring chewing function - this is their most significant drawback, because problems with chewing lead to atrophy of the jaw bone, diseases of the digestive tract, and even disruption of the aesthetics of the face and smile. Bridges cope with the task better, but in 70% of all cases, in order to fix them, it is necessary to depulpate the supporting teeth, which undermines their wear resistance. But implantation is the best method of dental restoration, which provides great potential benefits2 for patients.
E.max ceramic dental bridge –
If you are planning prosthetics on your front teeth, then a dental bridge made from IPS E.max ceramics is the best option in terms of aesthetics (even compared to bridges made from Multi-layer zirconium dioxide).
The “Emax” material refers to glass ceramics, because this material consists of 70% lithium disilicate crystals. Due to the fact that the E.max glass matrix is as similar in structure and transparency as possible to natural tooth enamel, crowns, veneers and bridges made from this material can be made completely invisible against the background of neighboring teeth. Clinical case No. 1 – before and after photos
Clinical case No. 2 – before and after photos
Advertising
E.max glass ceramics is practically the only material that allows achieving good aesthetics in patients with a high level of transparency of tooth enamel (if the transparency coefficient is low, then good aesthetics can be achieved with zirconium dioxide). E.max crowns require less grinding of the supporting teeth, which increases their service life. And besides, the use of this material practically eliminates the occurrence of ceramic chips.
Important points - E.max ceramics are available in several versions, but for the manufacture of bridges it is best to use “IPS E.max PRESS”. Bridges are made from this material by pressing under conditions of very high temperature and pressure, making the finished structure very strong (about 400 MPa). However, there are several limitations for E.max bridges...
Firstly, you can make bridges from E.max with a length of no more than 3 units, i.e. They can only restore a single missing tooth. Secondly, their safety margin is sufficient to restore mainly only the anterior group of teeth (the distant abutment tooth should be no further than the 5th tooth inclusive). Therefore, if you need to restore the chewing group of teeth, then a priori the choice falls on bridges made of zirconium dioxide or metal ceramics.
Conclusion: The E.max glass-ceramic bridge is the best option if you require a 3-unit bridge in the anterior area and if you have the highest esthetic requirements. Considering that 1 crown made of E.max PRESS material will cost in Moscow in 2021 - from 26,000 rubles, then the cost of a bridge of 3 units will already be about 72,000 rubles. In the regions, the price for 1 unit may be slightly less (from 20,000 rubles). And don’t be confused by the fact that E.max is cheaper than bridges made of zirconium dioxide - it’s just that very expensive equipment is used in the manufacture of the latter, which affects the cost.
Patient reviews
“I had two bridges. They were installed at different times by different doctors. The one that was installed first stands like a glove, although 7 years have already passed. The second one was installed about 2 years ago, and I’ve already suffered enough with it. At first it was installed poorly, it seemed to be in the way, then everything started to ache and ache. In the end, everything had to be removed, plus one tooth was removed. I come to the conclusion that everything depends on the quality of preparation for prosthetics and on the doctor who did it all.”
Detkova, review from correspondence on the baby.ru forum
“I installed an adhesive device a year before implantation. I just needed time to save up, I was a little short on money. I liked that the native tooth was not damaged by it, not during installation, not while wearing it. I was satisfied with everything, but, as the doctor told me, it was no longer possible to wear it, otherwise the supporting tooth underneath would have already begun to deteriorate severely and be damaged. And so, everything is OK!”
Marinel, otzovik.com
“Metal ceramics solved my little problem with my molars very successfully. I've been wearing it for 9 years without any complaints. One drawback is that it has already become quite noticeable that the gums have sagged under the central crown and food gets in there; it can only be cleaned out with an irrigator. I'll probably wear it until it won't bother me, because... I don’t have it in front, but on the side – when I smile and talk, it seems to be unnoticeable to others.”
Kisa, woman.ru
- Bazhenova N.P. Experience in the use of bridges made of light-curing composite. Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin, 2006.
- A.A. Kushnareva, A.R. Sargsyan. Dental implantation as an alternative to bridges and removable dentures. Health and education in the 21st century, 2014.
Author: Sambuev B. S. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)