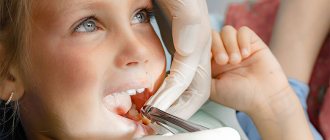
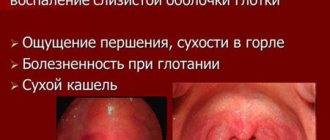
When a child complains of acute pain in the ear, cries and is capricious, this state of the baby will unbalance even the most persistent and experienced parent. Acute shooting pain in the ear is not easy for an adult to endure, let alone for children.
Pain signals the appearance of an inflammatory process in the ear. That is, otitis media develops. According to statistics, by the age of five, almost every child has suffered from this disease at least once.
To alleviate the baby’s condition and get rid of the disease, every parent should be able to distinguish the first signs of the disease, know what treatment is suitable for the child, as well as what measures need to be taken to prevent otitis media in the future. Let's figure it out!
Causes
A child’s cheek hurts for various reasons. This is often due to:
- allergies to foods or body care products;
- teething;
- a piece of food that penetrated into the gum pocket and caused suppuration;
- stomatitis;
- deep caries;
- pulpitis;
- periodontal disease;
- periodontitis;
- gingivitis;
- an incompletely removed nerve in a dental unit;
- inflammation of the facial nerve or lymph node;
- injury that occurred after a blow or bite from the inside of the cheek;
- sinusitis;
- mumps;
- temporal tendinitis;
- temporomandibular joint disease;
- tumor;
- insect bite.
Any of these reasons cause inconvenience and discomfort. Therefore, it is important to contact a doctor in a timely manner, who will prescribe treatment. This way you can safely and quickly eliminate unpleasant sensations.
Why does a child's cheek hurt? It is difficult to install this on your own. But if such a symptom is present, adults need to take urgent measures to alleviate the condition.
How to cure inflammation in the mouth on the cheek?
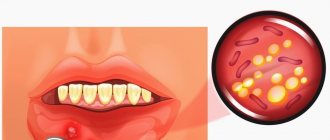
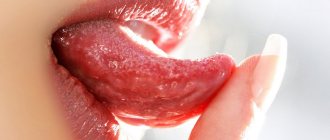
Inflammation in the mouth on the cheek in most cases is a symptom of stomatitis. This disease is one of the five most common dental ailments in terms of prevalence. Moreover, everyone is susceptible to it, from young to old. You will learn from the article what factors provoke inflammation of the cheek on the inside and how the pathology is treated.
2 style=”text-align: center;”> Why does inflammation develop on the cheek?
There can be many reasons for the development of inflammation inside the cheek. Being a kind of record holder in terms of incidence, stomatitis also breaks records in the number of factors provoking the development of the disease. Based on the causes, the following groups of stomatitis are distinguished:
- traumatic;
- infectious;
- allergic;
- symptomatic.
3 style=”text-align: center;”> Traumatic stomatitis
Inflammation on the cheek, which occurs as a result of a traumatic type of disease, occurs as a result of damage to the mucous membrane by mechanical means, as well as after chemical and thermal exposure. Injury to the mucous membrane can be either acute or chronic, observed over a long period of time.
Mechanical damage can occur when eating too rough food and products with sharp edges, for example, crackers, chips, caramel. The “culprit” could be a fish bone caught in food or a piece of nut shell. Careless handling of cutlery can also cause injury.
In addition, an incorrectly installed denture, implant, braces, or a growing crooked tooth can scratch the cheek. In the latter case, it usually becomes a dystopic wisdom tooth. Its improper growth leads to chronic injury and inflammation of the cheek near the “eight” - the wisdom tooth.
3 style=”text-align: center;”> Infectious stomatitis
The inflammatory process on the oral mucosa is commonly called stomatitis.
Inflammation of the cheek with infectious stomatitis develops against the background of an attack of the body by a viral, bacterial or fungal infection. As a rule, people with weak immunity are susceptible to this type of stomatitis. Infectious stomatitis, depending on the type of pathogen, is divided into several types:
- fungal – development is provoked by fungal pathogens, most often Candida fungi;
- viral – the disease is provoked by viruses, often the herpes virus, FLU, adenovirus, parainfluenza;
- bacterial – the cause of the disease is bacteria, most often streptococci and staphylococci.
3 style=”text-align: center;”> Allergic stomatitis
This type of disease is one of the symptoms of an allergic reaction of the body that develops when exposed to an irritant. With allergic stomatitis, in addition to inflammation of the soft tissues of the cheek and mucous membranes in other parts of the oral cavity, there is itching, burning, and the appearance of white or red rashes.
The cause of inflammation in allergic stomatitis can be the use of certain medications, the ingestion of allergenic products, or the use of low-quality oral care products.
3 style=”text-align: center;”> Symptomatic stomatitis
This group includes stomatitis that occurs against the background of systemic diseases, for example, diseases of the digestive tract, endocrine and circulatory systems. These include diseases such as anemia, hormonal imbalances, and helminthiasis.
4 style=”text-align: center;”>Stages of the inflammatory process
Depending on the severity of symptoms, there are:
- catarrhal;
- ulcerative;
- aphthous stomatitis.
With catarrhal stomatitis, the symptoms of the inflammatory process are mild, this is the mildest form of the disease. The patient experiences swelling of the mucous membrane, redness, and moderate pain. Salivation may increase and bad breath may appear.
We recommend reading about the features of MIS dental implants and the cost of their installation.
Find out how dentures are fixed with a suction cup in the oral cavity and how reliable they are.
In the ulcerative form, inflammation develops in the affected area of the oral cavity, in our case, on the inside of the buccal mucosa, and ulcers form. They can be either single or multiple.
The aphthous form is characterized by the appearance of painful aphthae on the mucous membrane - round-shaped “spots” with clear contours, of a white-gray hue.
2 style=”text-align: center;”> How to treat inflammation on the inside of the cheek?
If your cheek is inflamed from the inside, the best solution is to visit the dentist. The doctor will examine the oral cavity and determine what type of disease it is and what triggered its development. Only after eliminating the cause of the disease can you completely get rid of its unpleasant symptoms.
The correct treatment for the inflammatory process can be prescribed by a dentist.
Often, a dental examination is sufficient to diagnose the disease. In some cases, it is necessary to additionally conduct a number of studies: take a blood test, do a microscopic examination of scrapings from the affected area, and conduct allergy tests.
Inflammation on the inside of the cheek caused by stomatitis is treated comprehensively. The main treatment is selected depending on the cause of the disease, for example:
- if the disease is caused by a virus, it is necessary to take antiviral drugs orally (Viferon, Interferon), treat the affected area with antiseptic solutions, prescribe vitamin complexes and immunostimulants;
- bacterial stomatitis is treated with antiseptics, antibiotics, and drugs with an anesthetic effect are used to eliminate painful sensations;
- a traumatic type of disease requires mandatory elimination of the cause of damage to the mucosa (removal of an abnormally growing tooth, prosthetics with high-quality dentures), the use of antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- in case of allergic stomatitis, it is important to exclude the effect of the allergen; to relieve unpleasant symptoms, antihistamines are prescribed, and antiseptic and wound healing agents are used.
We advise you to find out the difference between complete, impacted and incomplete tooth dislocation.
To speed up recovery, regardless of the cause of inflammation, the patient is advised to follow a diet that excludes the consumption of foods that irritate the mucous membranes. From the diet you need to remove spicy, salty, sour, as well as solid foods that can injure the mucous membrane. All food and drinks must be warm.
Compliance with the rules of oral hygiene plays an important role in recovery. Teeth should be brushed twice a day using high-quality hygiene products. In addition to brushing, you should use dental floss or a irrigator. It is recommended to use mouth rinses after meals. Comprehensive oral care will prevent the proliferation of bacteria and avoid many diseases, including the development of inflammation.
Inflammation of the cheek with infectious stomatitis develops against the background of an attack of the body by a viral, bacterial or fungal infection. As a rule, people with weak immunity are susceptible to this type of stomatitis. Infectious stomatitis, depending on the type of pathogen, is divided into several types:
Types of tumors on the inside of the cheek with photos
Typically, compaction formation begins with mechanical damage. The appearance of a tumor on the inside of the cheek is caused by a number of reasons:
- injury to the mucous membrane by the sharp edge of a tooth or prosthesis,
- exposure to alcohol combined with smoking,
- viral infection.
The most common viral infection leading to the formation of compacted tissue is human papillomavirus. In children, tumors may be a consequence of impaired tissue differentiation during the prenatal period.
- Seals consisting of epithelial cells are called epithelial. The most common are papillomas, nevi and Serra glands.
- The proliferation of connective tissues leads to the formation of fibromas, myomas, myxomas, pyogenic granulomas, epulises and neuromas. Compacted tissue is formed from cells of the mucous membrane, muscle tissue, and the sheath of nerve fibers.
- Tumors of vascular origin are represented by hemangiomas and lymphogiomas. This type of tumor is soft and shrinks in size when pressed.
- Seals consisting of epithelial cells are called epithelial. The most common are papillomas, nevi and Serra glands.
- The proliferation of connective tissues leads to the formation of fibromas, myomas, myxomas, pyogenic granulomas, epulises and neuromas. Compacted tissue is formed from cells of the mucous membrane, muscle tissue, and the sheath of nerve fibers.
- Tumors of vascular origin are represented by hemangiomas and lymphogiomas. This type of tumor is soft and shrinks in size when pressed.
Diseases of teeth and gums
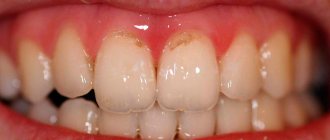
When examining a child's mouth, pay attention to the teeth and gums. Often their pathologies lead to pain in a given place. Black holes in the tooth enamel may be visible. Even if they are small. Caries develops deep inside, but on the surface it will be little noticeable. This process develops from dietary fibers stuck between the teeth and causing inflammation of the gingival papilla. Hard food often remains between the teeth and gums, leading to putrefactive processes.
Various dental ailments lead to both a violation of the integrity of the teeth and a change in the color of the enamel. If a child’s cheek is swollen and painful, this may be due to this particular problem. There may also be itching, bad breath, severe redness of the soft tissues. With flux, a bubble of pus is observed.
If a child has a tooth filled or removed, but pain persists for more than 2-3 days, most likely the procedure was performed incorrectly. This leads to pathologies in the gums. If a child has a sore cheek and a fever, as well as a headache, then there is a risk of periostitis. The presence of pain when swallowing food with swelling indicates inflammation of the tonsils. To prevent diseases of teeth and gums from causing pain, they must be treated in a timely manner. This way you can avoid complications.
What do stomatitis on the cheek look like, what to do with it and how to treat it?
The oral mucosa is exposed to various irritating factors , which leads to the widespread occurrence of diseases such as stomatitis.
Stomatitis is an inflammatory lesion of the oral mucosa.
Stomatitis is an inflammatory lesion of the oral mucosa.
Injuries
When a child’s cheek hurts, it may be due to injury to the oral mucosa or teeth. If no damage is found on the external part, it is possible that the cheek was damaged from the inside by the dentition. Bruises, abrasions, and swelling are noticeable on the inside. Or the mucous membrane and gums may be scratched. Then the wounds will be noticeable. Trauma is considered a common cause of pain, especially if the child is very active.
It also happens that due to an impact, a piece of enamel breaks off and the stem of the tooth breaks. In the latter situation, the tooth may be intact, but slightly loose. These damages are detected upon inspection. You won’t be able to get rid of the problem on your own; you need the help of a dentist. If the child’s cheek not only hurts inside, but also dizziness and nausea are observed, you should urgently call an ambulance. An ambulance is also needed if there is severe bleeding in the mouth.
Why does my gum hurt?
It is difficult to determine the cause of gum pain without the help of a dentist, because there are a large number of reasons for this:
- using an unsuitable toothbrush (the degree of hardness does not correspond to the level of sensitivity of the gums);
- injury to the gums by hot, spicy or hard foods;
- diseases of the oral cavity (caries, gingivitis, periodontitis and others);
- recent tooth extraction;
- damage to the gums during recent dental treatment;
- eruption of wisdom teeth.
If your gums hurt in the area of one or two teeth, then the cause most likely lies in tooth disease. Pain throughout the mouth indicates gum disease. Reddened and swollen gums near one tooth, especially in combination with rising body temperature, indicate the likelihood of gumboil development.
Infection
If a child’s cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt, then the cause may be fungi, bacteria and viruses. Because of them, stomatitis appears, in which painful ulcers appear in the mouth. Soft tissues also become inflamed. The infection enters the mouth with unwashed hands, toys, and dirty dishes. Its activation occurs with seasonal weakening of the immune system or colds. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the baby’s health so that no unpleasant symptoms appear.
If there is swelling not only on the cheek, but also on the neck, and there is also dry mouth, high temperature (38-39 degrees), then there is a risk of mumps or mumps. Due to pathological infections, sinusitis may occur, which involves inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. The pain from this disease can radiate to the tissues of the cheeks, nasal congestion is observed, and by night the general malaise may intensify.
Teething
If a child's cheek hurts on the inside, this may be a confirmation of teething. During this process, swelling of the gums appears, and maybe fever. Through the translucent gingival tissue, whitish dental units and bluish hematomas can be seen breaking through to the top, which appears during teething. Children become capricious, sleep poorly and refuse to eat.
Painful sensations appear when sharp fangs or molars with a wide chewing surface grow. Pain in the cheeks sometimes occurs in older children, especially during the period of replacement of milk teeth with molars. This phenomenon occurs in almost all children. Parents need to monitor the child’s condition, and if unpleasant symptoms appear, seek help from a doctor.
How to cure inflammation in the mouth on the cheek?
Inflammation in the mouth on the cheek in most cases is a symptom of stomatitis. This disease is one of the five most common dental ailments in terms of prevalence. Moreover, everyone is susceptible to it, from young to old. You will learn from the article what factors provoke inflammation of the cheek on the inside and how the pathology is treated.
2 style=”text-align: center;”> Why does inflammation develop on the cheek?
There can be many reasons for the development of inflammation inside the cheek. Being a kind of record holder in terms of incidence, stomatitis also breaks records in the number of factors provoking the development of the disease. Based on the causes, the following groups of stomatitis are distinguished:
- traumatic;
- infectious;
- allergic;
- symptomatic.
3 style=”text-align: center;”> Traumatic stomatitis
Inflammation on the cheek, which occurs as a result of a traumatic type of disease, occurs as a result of damage to the mucous membrane by mechanical means, as well as after chemical and thermal exposure. Injury to the mucous membrane can be either acute or chronic, observed over a long period of time.
Mechanical damage can occur when eating too rough food and products with sharp edges, for example, crackers, chips, caramel. The “culprit” could be a fish bone caught in food or a piece of nut shell. Careless handling of cutlery can also cause injury.
In addition, an incorrectly installed denture, implant, braces, or a growing crooked tooth can scratch the cheek. In the latter case, it usually becomes a dystopic wisdom tooth. Its improper growth leads to chronic injury and inflammation of the cheek near the “eight” - the wisdom tooth.
Severe pain
Pain can be both moderate and severe. In any case, it causes inconvenience, so it is better to get rid of it as soon as possible. If the pain is severe, it may be due to:
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- temporal tendinitis;
- Ernst syndrome.
When the buccal nerve is inflamed, there is loss of movement of the painful cheek. Much depends on the children and parents themselves. It is important to spend time on hygiene and follow preventive measures.
When visiting a doctor, he first examines the oral cavity. The specialist also asks about complaints and symptoms. Depending on the problem, a referral to a specific specialist may be provided.
Help
When a child’s cheek hurts, what should you do? If you have not yet been examined by a doctor, without a diagnosis and prescription of therapy, assistance must be carried out carefully. We must not allow the pathology to worsen. And for this it is prohibited:
- unauthorized use of antibiotics and other drugs that are sold in pharmacies only with medical prescriptions;
- perform warming up using lamps and warm compresses;
- give your child sweets and solid foods;
- feed cold or hot foods, give sweet, sour, fizzy drinks.
First aid can be performed using pharmaceutical drugs and traditional methods. They will improve the child’s condition, but then you still need to visit a doctor.
Diagnostics
In order to take action, you need to determine your general health condition and be examined by doctors. Most often it turns out that the cause is dental pathology. However, to make a correct diagnosis and determine the necessary measures, it is necessary to conduct the following studies:
- Anamnesis collection which is compiled based on the patient’s complaints, examination and test results.
- X-ray of the jaw.
- X-ray of the skull, a thorough examination of the condition of the jaw bones.
- An orthopantomogram is a panoramic X-ray image of the entire area of the dental system.
- analysis .
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Computed tomography (CT).
If necessary, the patient is referred for examination to other specialists: therapist, neurologist, surgeon.
Medicines
If a child’s cheek hurts on the inside, then painkillers with ibuprofen (Ibuprofen, Nurofen), paracetamol (Calpol, Panadol), which can also relieve fever during teething, help.
Older children (from 12 years old) are given medications with nimesulide (“Nimesil”, “Nimegesic”). The use of “adult” painkillers (“Analgin”, “Ketanov”) is permitted from the age of 14. But you still need to read the instructions for the medications. And it should be borne in mind that giving a child painkillers without consulting a doctor for more than 3 days is considered dangerous.
During the treatment of wounds in the mouth, ulcers, and inflammations, gels, ointments, and oils are used that have an antiseptic effect and stimulate recovery. These are Acyclovir, Cholisal, Karotolin. Sprays are used - “Ingalipt”, “Miramistin”, as well as balms and solutions intended for rinsing - “Rotokan”, “Vinilin”, “Chlorhexidine”. But it must be borne in mind that these are only temporary measures that cannot replace professional help. Even if it seems that the disease has subsided, you still need to consult a doctor.
ethnoscience
If a 5-year-old child has a sore cheek, traditional medicine can alleviate the condition. Cold compresses are considered effective, in which ice must be wrapped in a cloth and applied to the sore area. This allows you to relieve discomfort. Instead of ice, you can apply half a raw potato with the cut side to the skin.
Antiseptic rinses with a baking soda solution help. For this, 1 tsp. The product is dissolved in a glass of warm boiled water. Herbal infusions based on chamomile, calendula, green or black tea, oak bark and other herbal infusions have anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effects. Preparation is carried out by brewing 2-3 tbsp. l. raw materials with a liter of boiling water.
Treatment of acute illness: where to start?
Seeing the child’s reaction to acute pain, many parents are lost and do not know what to do to alleviate the baby’s condition. At the slightest suspicion of ear inflammation, you should seek medical help, especially if you notice purulent discharge from the ear. The sooner you start treating otitis, the faster the recovery will come, and the risk of complications will be reduced to zero.
Only an ENT doctor should treat otitis media! If for some reason it is not possible to immediately consult a doctor for treatment (for example, a sharp pain occurred at night), you need to numb the ear. For acute pain, children are given medications based on paracetamol or ibuprofen (for example, Panadol or Nurofen). And in the morning you need to go to the clinic.
At the appointment, the ENT specialist will examine the child using an otoscope or a special ear specula, determine the location of the inflammatory process, its nature (the baby is suffering from an acute or chronic disease) and give recommendations for treatment.
You should not treat otitis media yourself! At home, in addition to taking painkillers, you need to carefully blow the patient’s nose, and remove mucus from the baby with a special aspirator. This should be the end of your own treatment.
Some parents mistakenly, without consulting a doctor, try to alleviate the patient’s condition and cure acute otitis in their child with ear drops. But if the eardrum has burst, using, for example, alcohol drops is not only undesirable, but also dangerous!
Dentists' recommendations
Dentists may advise following simple rules to prevent cheek pain:
- Do not use hot compresses.
- Do not self-medicate.
- If your cheek is swollen, you should not disturb it. At this time, you should not eat very hot or cold foods, nuts, spicy foods, or toffees.
- You should not self-prescribe antibiotics.
You should not delay treatment, especially if a tumor appears. If it increases, then this is considered a sign of the development of a purulent process in the cheek. In the absence of professional help, the situation can only worsen.
Outer and inner ear: causes of inflammation
Inflammation of the outer ear occurs when trying to clean the ears with foreign objects, during which infection penetrates into them. Otitis media can occur when bacteria enter the bloodstream through wounds and damage to the skin of the ear. Therefore, parents need to ensure that the baby never picks the ear canal with a sharp object.
Some parents are overly zealous, giving their children ear hygiene and cleaning wax out of their children every day, which is fundamentally wrong. Sulfur is a natural barrier against pathogens, so such excessive cleanliness opens the way for bacteria to distant areas of the ear.
The appearance of otitis externa can be caused by water that contains pathogens getting into the ear, for example, while swimming in polluted waters.
Labyrinthitis or internal otitis in acute form manifests itself in the absence of timely treatment for the acute course of otitis media. The infection can enter the inner ear through the membranes of the brain (with meningitis) or through the bloodstream if pathogens are already present in the body. Children with this diagnosis need immediate help from an otolaryngologist. If proper treatment for inflammatory disease of the inner ear is not provided, the prognosis for life and health may be unfavorable.
Prevention
To prevent your child from having a sore cheek, you need to take care of prevention. It is necessary to adhere to simple hygiene rules. It is important to brush your teeth regularly (as soon as you have them). At first, this is done not with a brush, but with a finger with gauze wrapped around it. It is necessary to teach your child to rinse his mouth with boiled water after each meal. From 6 years old, you can floss.
You should examine your child’s mouth at least 2 times a week. If you find food particles stuck between your teeth, they should be removed with a toothpick. The children's menu should consist of apples, carrots, and crackers. Calcium-fortified dairy products and vitamin-rich greens are also needed. This is necessary to strengthen dental tissues. The child should drink clean water, as it is the basis for the production of saliva that washes the mouth. It’s better to exclude sweets.
Do not allow your child's face and ears to become hypothermic. In very cold weather it is better not to walk. Colds in the facial nerve, colds, sinusitis, and mumps should not be allowed to occur. You should visit the dentist twice a year (even if there are no complaints).