From this article you will learn:
- how much does it cost to do a dental x-ray,
- what you need to know about radiation doses,
- Is it possible to take a dental photograph during pregnancy?
Dental X-ray is a traditional way to determine the quality of root canal filling, as well as to diagnose inflammation at the apex of the tooth root (with apical periodontitis). X-rays of human teeth in dentistry are most often carried out using targeted X-rays. A targeted photograph of a tooth received this name because it is small in size and shows the condition of only a few teeth and the bone tissue around them (Fig. 1-2).
Modern targeted X-rays produce a very low dose of X-ray radiation (compared to what it was 15-20 years ago). This is due both to the advent of ultra-sensitive photographic films, which require a significantly lower dose of radiation, and secondly, to the advent of special intraoral sensors that capture the image digitally and display it on a computer screen. Such digital images require several times less X-ray radiation - even compared to modern films.
Sighting and panoramic radiography in dentistry –
However, targeted images are not suitable for planning bite correction, assessing the condition of bone tissue before implantation, or planning the installation of future implants. They are not very convenient for planning treatment and prosthetics for a large number of teeth, and often do not allow detection of perforations and cracks in the tooth root. Focused photographs of the teeth may not be enough in cases where it is necessary to find problems with root canal filling in order to be able to properly treat the teeth.
Therefore, dentists very often refer patients to more complex options for x-ray examination of teeth and jaw bone tissue -
- dental computed tomography (CT),
- orthopantomogram (Fig. 3),
- teleroentgenogram (for bite correction).
In this article, we will go into detail about the pros and cons of targeted dental x-rays, and what you need to pay attention to if you need to have a dental x-ray (for your own safety). For detailed reviews on the remaining specified methods of radiography in dentistry, read the links above.
Sight image of a tooth –
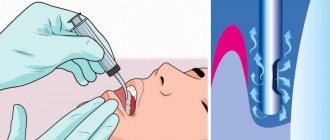
A targeted photograph of a tooth can be recorded either on photographic film or using a special intraoral sensor that detects X-ray radiation and transmits the image to a computer screen (such a device is called a radiovisiograph or simply a visiograph - Fig. 5). In both cases, an X-ray machine is used as a radiation source (Fig. 4), i.e. the only difference is in the way the image is captured - either on X-ray film or using a digital sensor.
Taking an image using a visiograph -
Digital vs Film Photography: Pros and Cons
Targeted dental x-rays using film were once the only examination option in clinics. It must be said that film photographs have a number of disadvantages that have significantly reduced their use. They require expensive consumables (film, reagents), time to develop photographs, there are difficulties with storing photographs, and over time they fade and are lost. There are also differences in patient safety.
Even modern X-ray films require 4-8 times the radiation dose compared to digital X-ray sensors. For example, the radiation dose to a patient for 1 film image is 10-15 μSv (microsieverts), and for a picture on a visiograph it is on average 1-3 μSv (this dose corresponds to the background natural radiation received by each person in 1 day).
The patient's exposure time when using film X-ray is 0.5-1.2 seconds, and using a digital visiograph sensor - 0.05-0.3 seconds. It is precisely by reducing the required exposure time when using a radiovisiograph that the radiation dose is significantly reduced. Thus, in one day of treatment at the dentist you can take no more than 3 film photographs and 5-6 digital photographs. And as you will see below, the use of a visiograph in some cases even allows you to take an X-ray of a tooth during pregnancy, but in compliance with all safety rules and for urgent indications.
How to take a picture of a tooth using a visiograph: video
Important: always try to take digital photos and inform them in advance that you want them saved to a flash drive. Firstly, then you will always have the pictures at hand, and you can always show them to another doctor. Secondly, the photographs taken for control after treatment will be your guarantee that if you received poor-quality treatment, you will always be able to prove it (the clinic will no longer be able to lose your photographs and rewrite the medical record).
Thirdly, if a digital image is printed on a printer, then the quality of the image will depend not only on the quality of the digital image, but on the resolution of the printer (rare clinics have printers that print in high resolution). Therefore, a photo in digital format will have better quality than a photo printed on paper.
Dental X-ray – price for 2021
The cost of one digital X-ray in Moscow will average from 250 to 350 rubles in different clinics. In addition, this price may only apply to a diagnostic initial image, while all other images taken during the treatment phase may cost less (about 150 rubles per image). Therefore, you should carefully read the clinic’s price list.
It should also be noted that there are a large number of clinics in which the cost of dental treatment is indicated on an all-inclusive basis. Accordingly, the cost of treating your tooth will already include the required number of x-rays (usually 2-4 pictures), for which you will no longer pay anything extra.
What else you need to pay attention to is that the price list of some clinics may state that the cost of a targeted x-ray indicated on the clinic’s website applies only if you are a patient of this clinic. Therefore, if an image is taken to be submitted to another clinic, its cost may be 100 rubles higher).
In addition, if you need a printout of a digital image, some clinics may also charge you about 50 rubles for this. The same applies to the description of the x-ray image: if you want to receive a written description of the image taken by a radiologist, then in some clinics they may additionally ask you for about 100-150 rubles.
Dentistry for pregnant women
The pregnancy period is a serious test for a woman, since at this time part of the body’s reserves are transferred to the fetus, so calcium deficiency often occurs, which cannot but affect the condition of the expectant mother’s teeth. In addition, already at 6-10 weeks, the rudiments of all your baby’s milk teeth are formed, and the health of his teeth largely depends on the health of his mother. In this regard, during pregnancy it is very important to carefully monitor oral hygiene and regularly visit the dentist.
Radiation doses and safety –
A patient's radiation exposure is measured in either microsieverts (µSv) or millisieverts (mSv). The recommended radiation dose for the population received as a result of X-ray studies (according to the recommendations of SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03) should not be more than 1000 μSv per year (= 1 mSv per year).
Below we will give examples of different types of images in dentistry and the corresponding radiation exposure to the patient (data from the Ministry of Health of Russia dated July 22, 2011 and December 21, 2012)…
- Targeted images on a digital radiovisiograph – → lower jaw in adults – 2 μSv, → lower jaw in children under 15 years old – 1 μSv, → upper jaw in adults – 5 μSv, → upper jaw in children under 15 years old – 3 μSv.
- Sight shots using film – 10-15 µSv.
- Digital panoramic image – 55 µSv, but if the patient is less than 15 years old – 24 µSv.
- Digital teleroentgenogram – 7 µSv.
Conclusions: thus, targeted images using a radiovisiograph provide the lowest radiation dose compared to other types of x-ray examination in dentistry. During one visit to the dentist, you can take 5-6 pictures on a digital radiovisiograph without risk to health, but no more than 100 such pictures during the year. A digital orthopantomogram (panoramic x-ray of the jaw) can be done 1-2 times a month, but no more than 10 times during the year. Panoramic films on film provide a greater radiation dose to the patient, and they can be taken less frequently than digital ones.
How does the procedure work?
We use modern digital pantomographs. Their advantages include:
low radiation exposure, which allows repeated examinations to monitor the effectiveness of prosthetics and therapy;- the ability to obtain a digital image, which can be optionally recorded on any medium (disk, USB flash drive), sent to the attending physician by e-mail;
- ability to enlarge the image of the area of interest.
Before starting the study, you are asked to remove all jewelry (they can distort a panoramic photo of your teeth) and put on special devices to protect the body from excess radiation doses. The position of the pantograph plate is then adjusted based on the patient’s height. X-rays can also be performed in a sitting position (for example, if a person cannot stand on his or her feet for health reasons). At the request of the radiologist, you should bite down on a special plate - this is necessary to center the jaw. If it is necessary to visualize the temporomandibular joint, an x-ray is taken in two projections: with the mouth open and with the mouth closed.
During operation of the pantomograph, remain motionless. Sometimes, to improve visualization, you are asked to tilt or turn your head. The procedure itself takes no more than 5 minutes (including the time required for preparation). After another 10–15 minutes, a transcript is given to you along with a printed image, and, upon request, an external medium with a recording of the radiograph.
Is it possible to take a dental x-ray during pregnancy?
Is it possible to take a photograph of a tooth during pregnancy? This issue is regulated by the recommendations of SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03. These recommendations do not prohibit taking dental x-rays during pregnancy, but it is strongly recommended to use x-rays only in truly necessary cases, for example, in case of acute pain and the provision of appropriate emergency care.
It should be noted that over the past 20 years, the radiation doses received by patients with 1 x-ray of the teeth have become tens of times less, thanks to the advent of radiovisiographs and ultra-sensitive photographic films, which require significantly lower x-ray radiation (24stoma.ru). Therefore, the risks of fetal pathologies have decreased significantly in recent years.
Of course, if possible, X-ray examination of teeth should be avoided, but there is nothing terrible about this today, because The radiation dose of 1 image on a radiovisiograph is approximately equal to the radiation dose of any person to natural background radiation in 1 day. In addition, the irradiation time on the visiograph will be only 0.05-0.3 seconds, which, if protective measures are observed (lead apron), can significantly increase the safety of the procedure.
Additionally, it is worth considering the following recommendations –
It is better not to do a dental x-ray during pregnancy in the early stages, because at this most important time for the laying of organs and tissues of the fetus. And if x-rays are taken, then it is in the second half of pregnancy, because the risks to the fetus during this period are significantly reduced. Please note that you can only take pictures using a modern digital radiovisiograph of the latest generation, because Their radiation dosages are significantly lower than those of outdated digital radiovisiographs and, even more so, film devices.
Features of the event
The main role in diagnostics using gamma irradiation is played by its correct implementation. Despite the fact that the procedure is considered conditionally safe, it can only be prescribed if there are certain indications .
In this case, it is necessary to take into account the duration of pregnancy and ensure compliance with all safety measures for this procedure.
In what cases is the procedure necessary?
© Halfpoint / Fotolia
If you have a toothache, don’t worry in advance; dentists often treat and remove teeth without examining an x-ray. This approach is possible in case of obvious caries, in the absence of hidden, inexplicable problems.
It is important to illuminate the tooth and see what is happening inside when the carious process is advanced.
Indications for the study include:
- extensive focal infection. For example, deep caries of a group of teeth;
- hidden pathologies of the crown or root part of the tooth;
- inflammation of periodontal tissue;
- purulent pathologies: cyst, abscess;
- diseases that occur during the development and eruption of wisdom teeth;
- injury to the crown or root part;
- deciding whether to preserve or remove a tooth.
Any dental intervention must be based on a detailed picture of the condition of the units being examined, since even the most professional dentist cannot accurately determine the position of the roots, dental canals and the condition of the pulp chamber .
Only thanks to this, treatment can be carried out efficiently. In the absence of all the necessary data, therapy will not give the desired effect and will lead to an exacerbation of the disease, which will require re-treatment.
But if you take pregnancy planning seriously and monitor the condition of your oral cavity, then caries of such proportions will not have time to develop. And new, superficial caries, with a 99% probability, will be treated without x-rays.
What is dental physiotherapy and how is it performed.
This publication describes fissure caries.
Will garlic help with toothache? Details at the link.
Optimal timing
Dental treatment and x-ray examinations should be carried out in accordance with the timing of pregnancy. The most dangerous option would be a study conducted in the first trimester .
It is the most important for the normal development of the fetus and the most risky in terms of negative effects on its developing body. According to statistics, the largest number of miscarriages and the development of fetal pathologies occur during this period.
The first weeks of gestation are considered especially dangerous. At this time, diagnostics can be carried out in exceptional cases when the indications for the procedure do not allow for a delay.
But, as a rule, such situations arise in isolated cases and examination, as well as treatment, can be postponed until later in pregnancy.
© Halfpoint / Fotolia
If the x-ray was taken before the woman found out about her pregnancy, then in the future it is necessary to conduct genetic screening to identify abnormal fetal development in the early stages.
The most optimal period for carrying out such procedures is the second trimester . At this time, all the systems and organs of the child are already fully formed, and the influence of external negative factors has minimal impact on them.
Studies have shown that in women who underwent this type of diagnosis, the fetus developed without any abnormalities. Therefore, all existing pathologies that require medical attention must be examined and treated precisely at this time, since in the last trimester the risk of negative effects increases again.
Before going to the dentist, it is recommended that you also read this article, which tells you whether pregnant women can have their teeth treated.
Security measures
Even during the safest period of the second trimester, x-rays must be carried out in compliance with certain safety measures, which include:
- Use of special protective aprons and collars . They consist of lead plates that do not transmit gamma radiation. To prevent the metal from injuring the patient, it is placed in a cover made of thick fabric, which is shaped like an apron.
- Ensuring optimal distance . To obtain a detailed diagnostic picture, the maximum distance is selected. The farther the woman is from the beam tube of the equipment, the less radiation she will receive.
- Selection of the required exposure time to radiation . For one visit, no more than 5 photographs are allowed, with an interval of several minutes between them. In this case, the woman should not remove her protective apron for another 5 seconds after radiation exposure, since the decay time of gamma rays lasts up to 5 seconds.
Compliance with these rules for the safe conduct of x-rays will protect the woman and child from negative effects.
Analysis of targeted dental images –
Analyzing X-rays is not difficult if they are of good quality.
Almost any patient will be able to see signs of periodontitis or cysts in the image, and will also be able to determine how well his root canals are filled. All you need here is skill. But it is worth remembering that absolutely everything cannot be diagnosed using X-rays, for example, inflammation of the nerve of a tooth. You can diagnose from the image -
- caries (but not in full),
- periodontitis (granulomas, cysts),
- quality of root canal filling after treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis,
- perforations and root cracks,
- fragments of instruments in root canals,
- presence of periodontal pockets...
1) A group of images indicating the development of inflammation (periodontitis) at the apexes of the roots of previously untreated teeth. In this case, you will always see a clear or vague darkening at the apex of the tooth root, which can be of different sizes and shapes.
2) A group of photographs taken after root canal filling. The first 2 pictures (Fig. 14-15) show what well-filled root canals look like. The following images show poor quality treatment and complications that arose (read the descriptions in each image).
What can be seen when interpreting an x-ray
In the picture you can see:
- Borders, cavity of the maxillary sinuses.
- Position of the jaw joints.
- Condition of periodontal tissues, canals, periosteum
- Carious lesions: their exact localization, the size of the focus of dentin destruction.
- Cysts, granulomas, their size and location.
- Foci of the inflammatory process.
- Previously placed fillings (how tightly they fit to the dentin, are there any secondary carious cavities under them, etc.), dental implants.
- Unerupted permanent molars, incisors and canines.
Summary: important points
As a practicing dentist who knows the system from the inside, I want to draw your attention to the following points that are important for your safety. If the clinic has an X-ray machine, then a license must be obtained for it, the issuance of which presupposes the mandatory presence of a certified radiologist on the staff of the dental clinic. However, in reality, even in large clinics and public clinics, it is not always the case that x-rays will be taken by a trained specialist.
Even if he is, he may go on vacation or get sick, and a regular nurse (dental assistant) will take the pictures instead. This is a gross violation that leads to both the production of low-quality images and an increase in the radiation dose. In small clinics, the risks of receiving a poor-quality x-ray examination are much higher, and the first thing that makes you suspect a forgery is if the picture is taken not by a special employee, but by a nurse from the dentist you came to see.
The second very important point: if you see that the x-ray is not done in a special room, but the x-ray machine is located right next to the dentist’s chair, then you should change the clinic and the doctor. The fact is that all objects in this office (including the dental chair and doctor’s instruments) will have an increased background radiation, and this is no longer safe for health. We hope that our article on the topic: X-ray of the jaw and teeth was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author’s education in therapeutic and surgical dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience in therapeutic and surgical dentistry, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Digital and film radiography in outpatient dentistry” (Chibisova), 5. “X-ray diagnostics in dentistry" (Lutskaya I.K.).