X-ray diagnostics is the most important additional research method in dentistry. Meanwhile, many patients are afraid to take X-rays, believing that this can lead to serious harm to health (radiation!). Surprisingly, this opinion is very widespread in countries that have suffered from radiation in one way or another: in Japan they will never forget Hiroshima, Nagasaki and, more recently, Fukushima, and in our country, Russia, the memory of Chernobyl and “Mayak” is fresh. In other countries, fortunately, there are no such problems with X-ray examinations.
]CLINIC IN[/anchor] does not just treat.
He brings dental education to the masses. Today we will explain to you what radiation exposure to the body is, how much our X-ray machines “emit” and how often dental photographs can be taken. And, first, let's understand the terms.
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen (1845-1923), sidekick of Professor Ferkel Von Pfennig, discoverer of rays named after himself. And, by the way, the first Nobel Laureate in physics.
X-ray radiation is electromagnetic radiation located in the spectral range between ultraviolet and gamma radiation. It is obtained by decelerating electrons in special X-ray tubes. The wavelength of X-rays is comparable to the size of an atom, so they easily pass through “light” materials, being delayed by “heavy” ones, with a large
Sirona Xios XG digital sensors do not require a powerful emitter. They are already good.
atomic size (lead, barium, other metals). This property of X-ray radiation is used in medicine, allowing one to “see through” organs and tissues.
X-ray radiation can be divided into soft (low frequency and photon energy, closer to ultraviolet) and hard (shorter wavelength, higher energy, closer to gamma radiation). In medical diagnostics, something softer is used. Moreover, with the advent of highly sensitive electronic sensors, the need for high-energy photons has disappeared. Therefore, a modern X-ray machine is not at all the same X-ray that was 10-15 years ago. The use of digital technology has made it possible to significantly reduce the radiation dose and increase safety.
X-rays have one problem. It is impossible to make a lens capable of refracting it. You can't make a mirror. which would reflect X-rays. Therefore, all X-ray diagnostics are based exclusively on the absorption of photons by the objects being studied, in this case the human body.
Brief historical background. The glory of the discovery of new radiation belongs to Wilhelm Horse Thief Roentgen. On July 8, 1895, while playing in his laboratory with his assistant with a cathode tube made by W. Crookes, he suddenly noticed that the invisible rays emitted by the tube stripped the assistant naked, passed through obstacles and illuminated photographic plates in a closed package. This is how pornography radiography appeared, and in 1901 Roentgen received the first Nobel Prize in physics. A worthy discovery!
Radiation exposure is the radiation dose received by a person per unit time. And here everything is not so simple.
The fact is that there is a difference between the emitted dose and the absorbed dose. If only because not every photon of X-ray radiation reaches the body - some are slowed down by air molecules, clothing, water vapor, etc. Further, it makes sense to consider the absorbed dose, and not the emitted one.
The maximum permissible radiation exposure is such a dose of X-ray (or, in a broad sense, other electromagnetic radiation, at which fuck-up occurs in approximately 50% of cases. By fuck-up we mean, first of all, radiation sickness with all the consequences .
The W. Crookes tube is an excellent device if you need to look inside a person. And, preferably without opening it.
Fortunately, to get even mild radiation sickness, we have to take CBCT scans as often as some girls take toilet selfies. That is, constantly. And in normal life and with normal treatment, as you understand, this is impossible.
X-ray protection – despite all its hardcore nature, X-ray radiation is not as dangerous as is commonly believed. Especially what is used in medicine. But we live according to Soviet norms and standards and, since a real Soviet person does not recognize scientific and technological progress and does not make a difference between a Crookes tube and a modern X-ray machine, we are forced to use protection “from radiation,” a device a little simpler than the sarcophagus at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant.
In particular, the walls of our X-ray room are covered with four layers of special radio-absorbing coating. Moreover, in a reinforced concrete box. Moreover, all this coating costs as much as rare Italian tiles made of natural stone.
The Dental Center of the University of Zurich takes a much simpler approach to radioprotection. They simply did not have Soviet SanPINs and party education.
In addition, it is equipped with a separate and very special ventilation system with a special filter system. A special door with a lead equivalent (what the hell is that?!) of 1.3 mm protects the reproductive organs of everyone who is in the clinic lobby. Before the study, we put on a special protective apron weighing 100,500 kg for each patient - this is, of course, inconvenient, but it’s the way it’s supposed to be. In general, if we wanted to install a nuclear reactor in our X-ray room to produce, say, weapons-grade plutonium, and an IAEA commission armed with Geiger counters would sit in the clinic’s lobby, then damn they would have detected us. This is how safe we are.
For comparison, pay attention to the arrangement of dental offices at the Dental Center of the University of Zurich (Switzerland). And the local level of protection from radiation. This is because in Switzerland there were no Soviet Sanitary Regulations and a bunch of shoddy dissertations defended on the Chernobyl tragedy. Such a situation with radio protection is everywhere where the hand of the Soviet bureaucrat did not reach: in Europe, the USA, Canada, Brazil, etc. And in our country... however, you know.
An X-ray machine is, in the broad sense of the word, a device that uses X-ray radiation for something. In our narrow dental understanding - for visualization, i.e. diagnosis of what is not visible to the naked eye. In dentistry, we use three such devices: a high-resolution cone-beam computed tomograph, a radiovisiograph and a special cephalostat for teleradiography. What these devices are and what data they produce can be read here>>.
Radiation exposure to the body is measured in special units named after Rolf Sievert, a Swedish scientist who studied the effects of radiation on biological objects, and designated as Sv (in English).
In outline,
1 Sievert is radiation with an energy of 1 Joule absorbed by 1 kg of the body, equivalent to a dose of gamma radiation of 1 Gy (Gy).
In principle, Gray and Sievert are almost the same thing (in some instructions and books it is Gr), but Sievert takes into account all radiation, and Gray only takes into account gamma. Therefore, further we will talk specifically about Sieverts.
1 sievert is a very large value. Thus, the maximum permissible annual dose for workers in the nuclear industry in the Russian Federation is 0.02 Sieverts, radiation sickness can be obtained at 1 Sv, and death at 7 Sieverts. In medical radiology we work with much less radiation, so we measure it in microSieverts:
That is, 1 microSievert is a millionth of a Sievert, and is related to each other as a meter and a micrometer (a thousandth of a millimeter). It is in μSv that we will measure radiation exposure during radiography.
To begin with, let’s turn to authoritative sources and ask what our Roszdravnadzor writes about this.
According to SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03 (last amended in 2006), the maximum dose during X-ray examinations should not exceed 1000 μSv per year. That is, 1 milliSievert per year or 0.001 Sievert, if you like. Let us note that this is not the “old Soviet norm”, but a completely modern one; we can find almost the same figures in any other country in the world.
Another thing is that X-ray machines have changed significantly even since the last changes in the mentioned SanPiNs. If earlier, about thirty years ago, we were all examined for something like this:
and such a device irradiated a little less than a nuclear reactor, then almost all modern X-ray devices use digital, highly sensitive sensors, and therefore the need for radiation, from which a person would then glow, like a deep-sea squid at night, disappeared. For comparison, the difference between a film and a digital dental “sight” image looks like this:
That is, it is very, very difficult to obtain at least half of the permissible annual dose in a modern clinic with a modern X-ray room. And that's why:
it turns out that for exposure to 500 μSv (half the annual maximum permissible dose), it is necessary to take 166 targeted or 83 panoramic photographs or 50 computed tomograms of the maxillofacial area. In what cases such a large number of x-ray examinations may be required is difficult to even imagine. For example, if we count all the pictures we take during dental treatment, we will get the following numbers:
Of course, the type and number of images depends on the clinical situation and medical expediency, but, in general terms, the table above provides comprehensive information about the dose of absorbed radiation in microSieverts and an idea of how insignificant these numbers are. Again, for comparison, one hour of flight in a modern aircraft at a normal flight level gives you approximately 3 μSv. Consequently, flying from Moscow to Yekaterinburg and returning back means approximately four targeted images or one computed tomography.
Why do you need a panoramic dental photograph?
An X-ray panoramic image of the teeth is called an orthopantomogram and is an image of the jaws with soft tissues, made on film or paper. A high-quality panorama of the oral cavity provides the doctor with detailed information about the condition of the dental apparatus and provides a good view of the mouth in those places that are hidden from the eyes of a specialist.
If you take a panoramic photo of your teeth, your dentist can see:
- carious lesions of roots;
- hidden caries on the contact surfaces of the tooth;
- teeth that have not erupted or are not fully erupted;
- neoplasms, granulomas, cysts;
- general condition of periodontal tissues and partitions between teeth.
What difficulties does radiophobia create during bite correction?
Every sane person who decides to invest substantial funds in correcting a bite with braces wants to get an answer from the dentist to three main questions during preliminary consultations.
- What's wrong with my teeth?
- How can I improve the situation?
- How to save money on braces treatment?
At the same time, the most demanding clients often refuse an X-ray examination: “I will not be exposed to radiation again. It’s enough that they recently forced me to undergo fluorography.”
What should a potential patient of the orthodontist center understand? Locks glued to tooth enamel alone will not correct the bite. The treatment program is developed, activated and controlled by a person. This is a professionally trained specialist who, even before installing metal or aesthetic ceramic braces, must see the goal and imagine the path leading to it.
Teeth can be moved in different ways. The main task that the doctor solves is to choose:
- the correct direction of their movement;
- a device that can do this in the optimal way - effective and most comfortable for the patient.
For this, in-depth diagnostics are performed, and the provider of the most important diagnostic information is precisely the X-ray examination.
When is an orthopantogram performed?
An OPTG (orthopantomogram) is recommended for any type of dental care. Using the resulting image, it will be easier for the dentist to understand the problem and promptly prescribe the correct treatment. Telo's Beauty clinic specialists can refer you for a panoramic dental image in several cases:
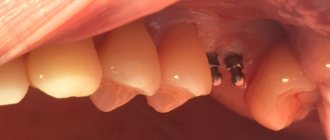
- before implantation to assess the condition of dental bone tissues and select suitable implants;
- with the growth of wisdom teeth;
- during the alignment of the dentition for an objective assessment of its condition and working out the stages of treatment;
- before tooth extraction;
- with periodontal disease;
- for early diagnosis of caries and dental tumors.
Types of OPTG
The types of orthopantomogram vary depending on the equipment used to obtain the image. You can take a panoramic photograph of your teeth using two types of devices:
- Film orthopantomograph. An outdated type of x-ray that can still be found in city clinics. When using it, the jaws are scanned, after which the result appears on x-ray film. The device does not produce a high-quality panoramic image, which can blur or fade over time.
- Digital orthopantomograph. Modern equipment that scans the image and transfers it in digital format to a computer monitor. Subsequently, the orthopantomogram is printed onto portable media (paper, film). The device gives less radiation exposure compared to film and provides high image clarity.
To perform a panoramic image of the upper and lower teeth, our clinic uses an innovative digital 3D orthopantomograph, which gives a high effect in diagnostics and helps to easily track the patient’s medical history.
What is an x-ray?
This is one of the types of radiation. If you think that X-ray radiation is present only in the X-ray room, then we can say right away that you are very mistaken. Let's remember physics lessons. We receive small doses of radiation every day:
- outdoors, from a natural source of radiation - the sun;
- at home from household sources located in the apartment: from a TV, various gadgets, a refrigerator, etc.
Radiation is measured in sieverts. What is the rate of radiation that a person can consume? Acceptable is 1000 sieverts per year.
Now let's remember mathematics and calculate how many X-rays can be taken for a person. A targeted image of one tooth is equal to 2-3 microsieverts. You can take 300-500 x-rays per year. A panoramic photograph (all teeth) is equal to 16-18 microsieverts. You can take 60-70 x-rays per year.
Now let's look at computed tomography. 1 photo taken on this device is equal to 60-80 microsieverts. You can take 16-20 x-rays per year.
We are now considering the maximum dose limits for X-ray equipment. Our clinic has a radiovisiograph and a computer tomograph of the latest generation made in Germany. The load on the devices is reduced to a minimum.
Previously, when taking an x-ray, the exposure time (you hear it as a beep) was approximately 2-3 seconds. Now this time has been reduced to 0.05 seconds.
Now let's talk about household radiation. If you watch TV for 3 hours at a distance of less than 2.5 meters from the screen, you get approximately 0.5 millisievert, i.e. Watched TV for 5 days, get 1 x-ray. If you sit in front of a computer monitor for more than 3 hours, you get 1 microsievert, 1 x-ray. We flew by plane to Turkey, where the flight is 3-3.5 hours, you get 10 millisieverts or 5 targeted shots. And add radiation from TVs, refrigerators, microwave ovens and you will understand that you will not receive terrible radiation in the X-ray room.
Indications for panoramic dental imaging
Orthopantomograms are performed on patients of any age. It can be prescribed both to correctly select a treatment plan and to evaluate the patient’s current therapy. The main indications for performing a panoramic photograph are:
- caries;
- periodontal disease;
- periodontitis;
- pathologies during teething;
- inflammation of bone tissue;
- suspicion of neoplasms in the jaw area;
- jaw fractures;
- implantation;
- prosthetics;
- sinusitis, polyps;
- installation of braces.
Techniques
If the patient needs to take a panoramic photograph of the teeth, then after the x-ray the dentist uses various techniques for reading the orthopantomogram. Initially, the quality of the image is assessed with an emphasis on its sharpness, completeness of coverage, and possible projection distortions. Particular emphasis is placed on identifying the object directly under study and assessing the tissue surrounding the teeth.
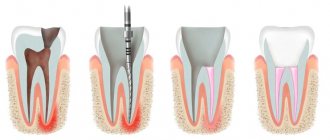
Of great importance is the analysis of the tooth shadow, in which the doctor monitors the characteristics of its cavity, the condition of the root, root canals and periodontal gap. In addition, the study gives an idea of the presence of fillings, their possible defects, as well as the ratio of the tooth cavity to the bottom of the carious cavity.
How safe is a dental x-ray?
Most dental patients are concerned about whether dental x-rays are harmful. This procedure is not harmful to health. Its safety is due to the use of a small amount of radiation and the use of a special apron. X-rays are also used to diagnose diseases of primary teeth. However, in the case of children, the procedure is resorted to if there is an extreme need for it.
Please note: If the patient is in serious condition or is bleeding, x-rays are contraindicated.
X-ray during pregnancy and breastfeeding
During pregnancy, x-rays are used with restrictions. It is used only in cases of diagnostic difficulties. The procedure should be abandoned in the first half of pregnancy. The doctor makes the decision on the need to conduct an x-ray examination after clarifying the duration of pregnancy.
Breastfeeding is not a contraindication to dental x-rays. It is safe for both mother and child. During the examination, the doctor takes the necessary precautions. All parts of the body that do not require x-rays are protected with a lead apron. Only modern equipment is used for research. E-class film is selected. Due to this, the radiation exposure is reduced. A woman can breastfeed her baby immediately after the procedure without worrying about any harm to the baby. There is no need to express milk or wean your baby off the breast for a while.
Advantages and disadvantages of panoramic dental photography
By taking a panoramic photograph of the teeth, the dentist significantly simplifies the diagnosis and treatment of dental diseases. An orthopantomogram has many advantages, but at the same time it also has some disadvantages.
pros
- Quickly obtain images of the jaw system.
- The ability to simultaneously examine all defects of the oral cavity.
- Optimal conditions for monitoring treatment dynamics.
- Detailing of individual areas of the mouth by enlarging the X-ray image.
- Affordable research – a panoramic image is cheaper than an x-ray of each individual tooth.
Minuses
If we talk about the disadvantages of the examination, the most significant disadvantage is obtaining a flat image, which does not provide sufficient diagnostic information about the size and shape of anatomical formations. In addition, it is not always possible to take a panoramic photograph of your teeth. It is extremely rarely prescribed to pregnant women, as well as people suffering from thyroid diseases, kidney failure, diabetes, and mental disorders.
“
Telo's Beauty is in the top three best dental clinics in Russia according to the Start Smile portal
and
the Kommersant publishing house
Safety in use
The average radiation dose from a single use of an orthopantomograph ranges from 0.006 to 0.02 mSv. People usually receive a similar X-ray load during one two-hour plane flight. Since the maximum permissible dose for a person per year reaches 150 mSv, we can say with confidence that the study is practically harmless to health. In addition, when performing a panoramic photograph of the teeth, the patient is put on a lead apron, which allows him to partially protect his body from the effects of x-rays.
How often can an x-ray be taken and is there a maximum permissible x-ray dose?
The permissible lifetime dose of radiation is considered to be 500 millisieverts. In this case, when examining the lungs using a digital device, the patient receives a load of up to 0.04 millisievert.
Therefore, it is almost impossible to receive a high dose of radiation while undergoing diagnostic tests. X-rays should be taken as often as required to make a diagnosis or monitor the dynamics of the patient’s condition. No doctor wants to harm the patient, therefore, if X-ray diagnostics are prescribed, there is a need for it.
Work order
Before taking the photo, the patient is asked to remove any metal products located in the head or neck area. Otherwise, the image may not be accurate. Next, an apron is put on him, he is brought to the orthopantomograph and the scanning procedure is performed in several successive stages:
- The patient's head is fixed so that it remains motionless during the X-ray.
- To take a high-quality panoramic photograph of teeth, a plastic tube is inserted into a person’s mouth, and cotton wool rolls are placed in places where teeth are missing.
- The orthopantomograph plate is moved tightly towards the chest, while the patient should grasp the fixing handrails of the device with his hands.
- After turning on, the equipment begins to scroll around the head, and the picture automatically appears on the monitor screen.
Is it possible to give X-rays to pregnant women?
Here's what they write to us about this in official documents (SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03): 7.18. X-ray examinations of pregnant women are carried out using all possible means and methods of protection so that the dose received by the fetus does not exceed 1 millisievert* for two months of undetected pregnancy. If the fetus receives a dose exceeding 100 mSv, the doctor is obliged to warn the patient about the possible consequences and recommend terminating the pregnancy. *1 millisievert (1 mSv) = 1,000 microsievert (1 μSv) That is, in the first half of pregnancy it is definitely not worth taking pictures, but in the second half - 1 mSv for a visiograph - this is practically without restrictions.
I would also like to add here that I have often encountered the militant obstinacy of this opinion: an x-ray at the dentist during pregnancy is an absolute evil. And after all, while “fighting” radiation at the dentist, the same people often calmly fly south to bask in the sun and eat fresh fruit. Moreover, during a 2-3 hour flight to a country with a warm climate, a person receives 20-30 μSv, i.e. the equivalent of approximately 10-15 images on a visiograph. In addition, 1.5-2 hours in front of a cathode ray monitor or TV gives the same dose as 1 picture... How many pregnant women, sitting at home, watching TV series, hanging out on the Internet, think about how many pictures they “took” while watched another program, and then discussed it with friends on the forum and social networks? Almost no one, because the average person does not associate all this with ionizing radiation, unlike an image in a doctor’s office.
Cost of panoramic dental x-ray
If you are looking for affordable treatment options, welcome to Telo's Beauty Clinic! We offer affordable prices for the services provided and guarantee a clear panoramic photograph of the teeth, regardless of the patient’s financial capabilities. Today, the cost of orthopantomography is 2,500 rubles, which allows the patient to benefit from a comprehensive examination of the jaw and allows the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis of the disease.