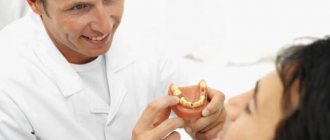
The field of dentistry combines several narrow areas: therapeutic, surgical, orthopedic, orthodontic. Each specialist performs work specific to their profile.
First, the patient is examined by a therapist, assesses the degree of damage, and whether the inclusion of a specialized doctor is necessary. If artificial structures are needed to preserve the dentition, the patient is referred to a prosthetist.
Orthopedic dentist, also known as prosthetist, who treats adults and children
A doctor, or more specifically, an orthopedic dentist, is in demand in modern medical institutions. Recovery services are in demand, everyone eats sweets. If someone decides to restore a tooth, then the orthopedist is the one who will make this possible. Beautiful teeth and an open smile are what heal self-esteem. The result depends on what kind of doctor he is and how he does his job, no matter for adults or children. Specialists recreate the integrity of the dentition in adults in the absence of its units using implants. In his work, the dental prosthetist takes into account the functional load on the jaws, as well as aesthetics. Regardless of the name of the profession, these specialists are engaged in restoring the functions of teeth. Often the name of the profession is replaced by the concept of dentist prosthetist. This happens because the doctor’s main job is to install prostheses or other special structures.
The scope of practical work of the specialist includes:
- restoration of damaged teeth with intact roots;
- preventing possible tooth decay;
- complete unit prosthetics;
- prevention of possible complications;
- elimination of associated defects to provide aesthetics;
- Specialists perform their actions consistently, following the rules.
Dentist-therapist
The second name of this specialist is odontologist. The main function of this doctor is to treat caries and its complications. The first thing you meet with a dental therapist is when you come to the dental clinic. He makes an initial examination and decides on treatment methods. His qualifications are sufficient to install fillings in carious cavities. During the filling process, the doctor examines each tooth individually in order not only to cure caries, but also to recognize other defects. He also treats gums and other inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. A dental therapist can diagnose the disease and select individual treatment or refer you to another specialist.
What qualities does an applicant need to have?
The profession of any dentist involves a set of necessary personality qualities that are needed in work and career growth. In their absence, successful performance of job duties is impossible:
- responsibility for the course of treatment;
- being careful to minimize the risk of injury or aggravation of the problem;
- tendency to work with hands, endurance;
- well-developed fine motor skills for carrying out small operations;
- friendliness and sociability.
Specialists continuously improve and expand their qualifications. What makes the specialty of an orthopedic dentist not the easiest. Therefore, applicants must be prepared for a serious approach.
Where to study
In Russia there are many educational institutions where you can get an education in dentistry. There are all comfortable conditions for improving your qualifications, various courses for moving into a related area of practice.
The profession of a medical assistant or nurse can be obtained at a medical college, where testing is carried out upon admission.
Categories of dentists
Dentists are required to confirm their qualifications every 5 years
Each dentist has a certain qualification category, which is an indicator of the level of his theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
The procedure for assigning a qualification category is determined by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
Dentists are required to confirm their qualifications every 5 years.
Those who wish to improve their qualifications themselves must wait 3 years from the date of the last certification.
Regulatory documents provide for three types of categories in ascending order:
- second (is basic);
- first;
- highest.
Requirements for various categories:
| Category | Requirements |
| Second | Work experience in the specialty for at least 3 years. Successful completion of certification. |
| First | Work experience in the specialty for at least 7 years. For a specialist with secondary education – at least 5 years. Successful completion of certification. |
| Higher | Work experience in the specialty for at least 10 years. For a specialist with secondary education – at least 7 years. Successful completion of certification. |
The profession of a dental prosthetist involves pros and cons in the work. Among the advantages:
- relevance - people have problems, dental diseases;
- prospect - possible career growth, transition to a related profession;
- flexible work schedule - you can work at a time that suits you;
- high wages are due to the growth of private dental clinics that need doctors.
Among the disadvantages:
- requirements for the profession - necessary personality qualities, skills that not everyone has;
- duration and complexity of training;
- mastering technologies, continuous training.
Before enrolling in training in this area, you should carefully, slowly, consider the positive and negative aspects. To build a successful career, desire alone will not be enough.
Orthopedist, orthodontist, periodontist, dentist, paramedic, dentist... What do these definitions mean, what diseases are treated by doctors of these specializations, and which of them should you contact in a particular case?
Who is a dentist? To become a dentist, you must graduate from medical school or college. A specialist with secondary medical education is trained to perform relatively simple dental procedures. This does not mean that it is not able to cope with more complex cases, but its theoretical and practical basis is limited, and does not involve performing operations on teeth of the highest level of complexity.
Who is a dentist ? Dentist is a unifying definition applied to a dental specialist with higher education. (Stoma, stomatos means mouth in Greek, logos – teaching). To become a dentist, you need to graduate from a medical academy, institute or university. The duration of their studies is at least 5 years. Along with dental diseases, future dentists study many medical sciences - biochemistry, physiology, therapy, histology, etc. They are prepared not only theoretically, but also practically, having completed a one-year internship or a 2-year residency.
What is the difference between these concepts? The difference between a dentist and a dentist is the level of training and the type of treatment they can perform. The list of works provided for by the job description of a dentist includes: A dentist is a general specialist, diagnostics; treatment of relatively simple diseases of teeth and gums - gingivitis, stomatitis, caries and some others; removal of teeth not complicated by periodontitis; treatment of simple maxillofacial injuries. Carrying out physical procedures; consultation regarding the choice of oral hygiene products (OR); cleaning teeth from plaque and tartar, and some others. In case of more serious dental pathologies - malocclusion, pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, lesions that have caused tooth destruction by more than 50%, and in other cases requiring the participation of a more trained specialist, the dentist gives the patient a referral to a dentist of the appropriate specialization.
A dentist is a general specialist. He has theoretical knowledge and practical skills sufficient to perform therapeutic, orthodontic, orthopedic and surgical operations. Although, like a dentist, when faced with a particularly difficult case, he can refer the patient to a doctor of narrow specialization.
Narrower specializations: a large number and complexity of pathologies of the dentofacial apparatus, constant improvement of existing treatment technologies and the development of new ones require in-depth, specific knowledge and skills from dentists. This feature has found its implementation in the concept of narrow specialization of dentists. Depending on the type of work performed, the following specializations of dentists-therapists differ; orthodontist; surgeon; orthopedist; hygienist; pediatric dentist. Dentists often combine several specializations at once.
Dentist-surgeon. The prerogative of the profession of a dental surgeon is the following operations: Dental surgeons often treat diseases that are within the competence of dentists of other specialties; tooth extraction; treatment of tumors in the oral cavity; elimination of TMJ dysfunctions, diseases of the salivary glands and trigeminal nerve; primary treatment of wounds and injuries of the mouth, neck, face; plastic surgery and reconstruction of jaw bones; operations on periodontal tissues (gingivectomy, gum pocket removal, soft tissue transplantations, gingivoplasty, plastic surgery of the oral vestibule and frenulum); correction of dental anomalies, implantation. Dental surgeons often treat diseases that are within the competence of dentists of other specialties: phlegmon, periodontitis, sinusitis, periostitis, abscesses, osteomyelitis. They also diagnose specific diseases, the symptoms of which may appear in the PR - syphilis, tuberculosis, actinomycosis.
Dentist-therapist. Typically, patients seeking help from a dentist first see a therapist. A dental therapist is the broadest specialization in dentistry. Typically, patients seeking help from a dentist first see a therapist, who in most cases is able to cope with their problem alone. Job description The instructions of the dentist-therapist provide for the following work: examination of the oral cavity; diagnostics; treatment of teeth (caries, pulpitis, etc.) and periodontal disease (gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis); preparation of PR for prosthetics, its sanitation; whitening and PG of teeth; preventive examination and advice on caring for RP.
Orthopedist.
An orthopedist specializes in restoring teeth using prosthetics. A doctor of this specialization is engaged in the restoration of dilapidated, missing or lost aesthetic teeth using prosthetics. Orthopedist: takes impressions of the teeth, from which the dental technician subsequently makes a prosthesis; tries on, adjusts and secures the prosthesis on the patient. Prosthetic structures are crowns, bridges, inlays , veneers, removable dentures.
An orthodontist adjusts the position of teeth using removable and non-removable orthodontic devices. Orthodontics is a subsection of dentistry dedicated to dental anomalies. The scope of activity of an orthodontist includes: prevention of deformations of individual teeth, dentition and jaws; normalization of occlusion; correction of jaw development; teeth alignment. Correction of the position of teeth is carried out using removable and non-removable orthodontic devices - mouthguards, braces, braces.
General dentist
The specialty “General Dentistry” was introduced by orders of the Ministry of Health No. 553 and 112. This specialty is of particular importance for rural areas, where it is desirable to have a specialist who can provide assistance in several clinical areas. However, until now, due to a number of organizational, educational and legal problems, general practice in dentistry has not received proper development.
Children's dentist. Children and adolescents under the age of 17 are patients of the pediatric dentist. A child's teeth have many differences from adult teeth. This includes the presence of baby teeth, the constant renewal and formation of the dentofacial apparatus, and the inability to use certain anesthetics for children. And the reaction of children to the dental chair creates increased problems. A dentist treating children must not only be able to distinguish pathology from the age norm, detect deviations in bite and tooth formation in time, but also be a bit of a psychologist.
Hygienist. The goal of a hygienist is to prevent dental diseases. Dental hygienist is a relatively new specialization in dentistry. Its goal is the prevention of dental diseases, its field of activity is dental hygiene, proper dental care. A dental hygienist performs the following work: diagnosing dental diseases; professional teeth cleaning; disease prevention; training in proper dental care skills; educational activities (inspections in kindergartens, schools, institutions, organizations, enterprises). © Source: https://dentoland.com/lechenie/chem-otlichaetsya-zubnoj-vrach-ot-stomatologa.html
What knowledge does the specialist have?
The doctor must know the intricacies not only of his specialty, but of general dentistry as a whole, namely:
- anatomy, physiology, structural features of the jaws and teeth of people of different ages;
- special pharmacology (medicines used, related materials);
- methods of diagnosis, treatment;
- interpretation of radiographs;
- possession of special equipment and tools.
In addition to theoretical knowledge, you also need good developed motor skills; without them it is impossible to work in this field. Well-developed fine motor skills and accuracy will allow you to quickly complete your work with good results and delight your patients.
What is the difference between these concepts?
The difference between a dentist and a dentist is the level of training and the type of treatment they can perform.
The list of works provided for in the job description of a dentist includes:
- A dentist is a general specialist
diagnostics;
- treatment of relatively simple diseases of teeth and gums - gingivitis, stomatitis, caries and some others;
- removal of teeth not complicated by periodontitis;
- treatment of simple maxillofacial injuries.
- carrying out physical procedures;
- consultation regarding the choice of oral hygiene products;
- cleaning teeth from plaque and tartar, and some others.
In case of more serious dental pathologies - malocclusion, pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, lesions that have caused tooth destruction by more than 50%, and in other cases requiring the participation of a more trained specialist, the dentist gives the patient a referral to a dentist of the appropriate specialization.
A dentist is a general specialist. He has theoretical knowledge and practical skills sufficient to perform therapeutic, orthodontic, orthopedic and surgical operations.
Although, like a dentist, when faced with a particularly difficult case, he can refer the patient to a doctor of a narrow specialization.
Job Description - Briefly
The job description was developed and approved in accordance with the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, its main provisions:
- An orthopedic doctor must know the laws, regulations that regulate the activities of healthcare institutions, methods, rules of care, etc.;
- the specialist is responsible for the proper and timely performance of his duties;
- the employee must have a higher medical education and appropriate training;
- complies with the rules of labor protection, sanitation, safety regulations, and also monitors compliance with the prescribed rules by lower-ranking personnel;
- patient management tactics are established in accordance with established rules and standards;
- provision of medical care using modern diagnostic and treatment methods.