The treatment of “fluxes” is carried out by a dental surgeon.
Do you feel afraid of the dentist?
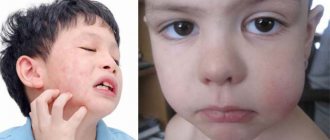
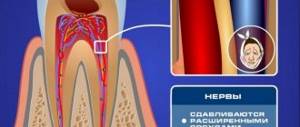
Flux is the common name for any swelling in the cheek area and partly the neck - periodontitis, periostitis, complications of pulpitis and other inflammations. If you have inflammation of any origin or form, localized on the gums and in the oral cavity in general, you should definitely see a dentist.
Treatment methods for facial neuritis
Acupuncture
The introduction of medical needles into bioactive points of the face relieves inflammation, eliminates swelling, improves blood circulation and nutrition of the facial nerve, has an analgesic effect, improves the passage of nerve impulses and eliminates numbness, restores sensitivity. The Tibetan treatise “Zhud-Shi” on acupuncture says that it “suppresses the Wind and awakens the numb.” This therapeutic effect of acupuncture is maximally manifested in the treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve.
Acupressure
Acupressure facial massage activates blood circulation, restores the tone and motor activity of the facial muscles, improves blood flow to the facial nerve and its nutrition, helps eliminate swelling and inflammation. Additionally, massage can be applied to the neck-collar area and head area.
Pharmacopuncture
The introduction of homeopathic medicines into bioactive points of the face has a mild anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-ischemic, immunomodulatory and decongestant effect. This procedure ideally complements acupuncture in the complex treatment of facial neuritis.
Moxibustion therapy
Warming up distant points on the meridians of the body increases immunity and has a healing effect on the nervous system. In the absence of an acute inflammatory process, it is possible to warm up the bioactive points of the face. This procedure has a rapid therapeutic effect for neuritis and neuroses of the facial nerves.
Treatment results for facial neuritis
Acute, most pronounced symptoms of neuritis are eliminated within the first 1-3 treatment sessions. Subsequent sessions eliminate the cause of inflammation. This ensures lasting results and minimizes the risk of re-inflammation and its symptoms.
This treatment gives positive results in 97-99% of cases of treatment of facial neuritis at the Tibet clinic in Moscow and St. Petersburg:
- symmetry is restored, paralysis and facial distortion disappear,
- ear pain, dryness, lacrimation, taste disturbance and other symptoms disappear,
- contractions of the facial muscles, free facial expressions are restored,
- the state of the nervous system improves, general and local immunity increases,
- treatment of otitis media or other concomitant diseases is carried out.
These results are achieved without antibiotics, hormonal or non-steroidal pharmaceuticals, and without side effects.
Facial nerve neurosis
Neurosis of the facial nerve is sometimes confused with neuritis, although it has nothing to do with inflammation. Tibetan medicine classifies it as a disease of the Wind system and considers its main cause to be nervous, emotional stress, psycho-emotional disorders, and mental fatigue. Often this disease accompanies depression, anxiety and fear neuroses.
Symptoms of facial neurosis are spasms of facial muscles, nervous tics in the form of blinking, twitching of the face, obsessive, involuntary swallowing. Sometimes nervous tics are accompanied by a feeling of numbness, tingling or burning.
Muscle twitching can start from the cheek, then move to the eye area, the orbicularis muscle. This causes symptoms of blepharospasm - frequent blinking, photophobia, dry eyes. When severe, blepharospasm can result in the inability to see out of one eye.
What to do if the facial nerve on the cheek twitches? Symptomatic treatment of facial neurosis consists of the use of antispasmodics, sedatives, and anticonvulsants. In Eastern medicine, these drugs are not used because they do not affect the cause of the disorder. Instead, the Tibet Clinic uses complex herbal medicine.
Herbal medicines of Tibetan medicine have an equally effective sedative, calming effect and at the same time help:
- restore the overall balance of the nervous system,
- improve and stabilize emotional state,
- restore psycho-emotional stability,
- eliminate symptoms of stress, mental overload, fatigue,
- increase the stability of the nervous system under stress.
These herbal remedies are used in the complex treatment of anxiety neuroses, fear, depressive and other disorders of the nervous system. They complement well acupuncture, acupressure, moxotherapy, relaxation massage, stone therapy and other methods of oriental medicine. With their help, doctors at our clinic effectively eliminate the symptoms and causes of facial neurosis and restore normal tone of facial muscles.
What to do if your tooth hurts and your cheek is swollen?
Everything was fine in the evening, but in the morning the gums near the tooth were swollen, what to do in such a situation and why did the swelling appear? The reasons can be very different, from pericoronitis (inflammation at the apex of the tooth root), which did not manifest itself until a certain time, to difficult eruption of wisdom teeth.
What to do if your cheek is swollen from a tooth?
If painful swelling of the gums and cheeks appears, you should urgently make an appointment with a dentist. Only a doctor can accurately determine the cause of this condition and effectively eliminate it. The causes of swelling may be:
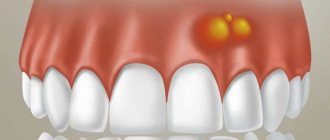
- Pericoronitis (tooth cyst) and its complication – gumboil, or periostitis.
- Difficulty in teeth eruption, most often observed with wisdom teeth (they are also third molars or “eights”).
- Injury to the tooth itself or the gums around it - for example, from too hard food or from an impact.
Whatever the reason, only an experienced dentist with accurate diagnostic equipment can identify it. Under no circumstances should you try to treat your teeth on your own, so as not to provoke serious complications and deterioration of your condition.
What to do if your wisdom tooth is cutting out and your gums are swollen?
The eruption of wisdom teeth in most people occurs with complications, this is due to the late appearance of “eights”, when the entire dentition is already essentially formed, and to the lack of space on the jaw. The jaw of a modern person has shrunk by about 10-12 mm over the past hundreds of years, so the third molar now does not always have enough space for normal eruption. That is why it cuts with difficulty, moves the remaining teeth and puts pressure on them, and often “goes” to the side, injuring the gums and mucous membrane of the cheek.
Therefore, there are often cases when a wisdom tooth comes out and the gums become swollen . Let's figure out what to do in such a situation? First of all, do a thorough cleaning with a brush and paste, if possible removing food debris not only from the interdental spaces, but also from the so-called “gum hood” (a flap of gum that covers the cutting molar). You can also rinse your mouth several times with antiseptic solutions (chlorhexidine, sodium-salt solution) or decoctions of herbs that have antiseptic properties (sage, chamomile flowers).
And, of course, you need to immediately contact your dentist. Most likely, the “gum hood” will need to be excised to make it easier for the tooth to erupt. If the situation is complex, the “eight” is cut crookedly or threatens the health of the entire dentition or neighboring units, it may require its removal.
Before visiting a doctor, it is advisable not to take painkillers so as not to complicate the diagnosis.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
What not to do if your tooth hurts and your gums or cheek are swollen.
When the gum above a tooth is swollen, the first thing to do is brush your teeth and go to see a doctor. Here is a list of what not to do if your cheek is swollen from a tooth:
- Warm the sore spot. Warm compresses and poultices can only accelerate and aggravate the inflammatory process.
- Trying to “treat” the disease with folk remedies. Many of them simply do not have any effect, but there is also downright dangerous advice. Therefore, it is better not to self-medicate and consult a doctor.
- Rinse your mouth with alcohol or alcohol-containing products. A chemical burn to the mucous membrane is exactly what you are missing in addition to a sore gum.
The only thing that a person whose gums and cheeks are swollen, teeth hurt, or whose third molar is difficult to cut needs is qualified dental care.
Peroneal nerve neuritis
The peroneal nerve is responsible for extension of the foot. When it becomes inflamed, it becomes difficult to unclench the toes, the foot hangs down and turns inward. The gait changes - the person cannot immediately step on the heel. When walking, he strongly bends his leg at the knee and throws his foot forward, and when lowering it, he rests first on his toes, then on the outer side of the foot, and only then on his heel. This gait is called a “cock walk.”
Sensation in the lower leg and foot is impaired and numbness is felt. Over time, the disease can lead to muscle atrophy and shrinkage of the leg.
The causes of the disease are multiple microtraumas or physical overstrain of the leg in the lower leg area, infections, endocrine disorders, intoxication, and hypothermia. Possible vascular causes - impaired blood supply and nerve nutrition against the background of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities.
Another common cause is diseases of the spine, such as osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region, protrusion, disc herniation. The peroneal nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve, the inflammation of which often begins in the lumbosacral spine.
To treat this disease, the Tibet clinic uses complex therapy, which includes acupuncture, acupressure, moxotherapy, therapeutic massage of the foot and lower leg and other procedures for individual indications.
If the cause is lumbosacral osteochondrosis or its complications, comprehensive treatment of this spinal disease is carried out. This therapy shows high efficiency and gives positive results in more than 90% of cases:
- eliminating the cause of peroneal nerve neuritis,
- improvement of gait,
- restoration of sensitivity, elimination of numbness and other symptoms,
- normalization of blood circulation in the foot,
- prevention of muscle atrophy and other complications.
The dangers of flux and the dentist's tasks
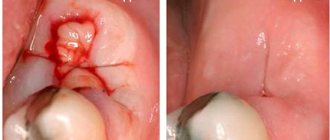
It is the identification of such foci and their elimination, especially in persons suffering from inflammatory processes of internal organs and in pregnant women, that is one of the essential tasks of a dentist. Untimely sanitation of the oral cavity or its absence in the presence of teeth affected by chronic periodontitis can lead to the development of a number of more severe inflammatory processes, the first of which is acute purulent periostitis.
Purulent periostitis
This disease is an acute purulent inflammation of the periosteum of the alveolar process of the jaw and accounts for up to 40% of complications of odontogenic infection, mainly chronic periodontitis. The cause of the development of this disease is most often large molars, which are primarily affected by the carious process.
The clinical picture of acute purulent periostitis is diverse and depends on the nature of the microflora, localization and extent of the inflammatory process. When the upper jaw is affected, the external manifestations of acute inflammation, in particular hyperemia, infiltration and swelling of soft tissues, are usually more pronounced than when the flux is localized in the lower jaw. However, the phenomena of general intoxication are more pronounced when the alveolar process of the lower jaw is affected, which is due to the difference in the anatomical and topographic relationships of soft tissues and jaw bones.
When examining the oral cavity, smoothness or swelling of the transitional fold of the mucous membrane of the vestibule of the oral cavity, its hyperemia, and sharp pain when touched by the dentist’s hands or instruments are noticeable.
It should be borne in mind that the pain in the “causal” tooth due to the release of exudate (liquid released into the tissue or cavity of the body from small blood vessels during inflammation) beyond the periodontal gap subsides to a certain extent, but slight mobility of the tooth appears. This circumstance sometimes serves as a justification for delaying visiting a doctor and as a cause of aggravated course of the inflammatory process in the future.
The diagnosis of “acute purulent periostitis” is an absolute indication for surgical intervention in the form of opening and drainage of the periosteal purulent focus and removal of the “causal” tooth.
Options for non-drug treatment (physiotherapy) depend on the patient’s general condition, age, and concomitant chronic diseases. In the latter case, the volume and nature of drug treatment is determined by the dentist of the appropriate profile. It is especially important to carry out adequate treatment in patients suffering from rheumomyocarditis, diabetes mellitus, nephritis and some other chronic diseases.
Another complication of chronic granulating periodontitis is the development of acute odontogenic osteomyelitis , accompanied by the formation of phlegmons and abscesses of the cellular spaces of the face and neck.
These complications of flux are the most severe and dangerous result of the progression of odontogenic infection, and depending on the location and nature of the microflora, they can lead to severe complications including the development of sinus thrombosis and mediastinitis.
It is their timely diagnosis in somatic patients that largely determines the outcome of the disease.
The clinical manifestations of phlegmon are different and depend on the location of the flux (deep, superficial), the nature of the pathogen (aerobic, anaerobic flora), body resistance, concomitant diseases, age, etc.
Today, persistent, sluggish chronic necrotic processes in the bone and soft tissues of the face often occur against the background of drug addiction.
Deep phlegmons of the pterygomaxillary, infratemporal, peripharyngeal spaces are manifested by sharp pain of the corresponding localization, severe manifestations of general intoxication up to acute intoxication psychosis, severe inflammatory contracture of the masticatory muscles, pain when swallowing, with an almost complete absence of external manifestations: hyperemia, infiltration, fluctuations, etc. .
Underestimation of certain symptoms of gumboil can lead to a delay in seeking dental care, ineffective therapy and progression of the inflammatory process.