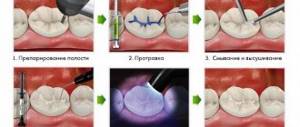
Dental treatment is a complex of medical measures aimed at combating diseases of the teeth, oral cavity, jaws and border areas of the face and neck.
The relevance of the development of this branch of medicine is determined by the wide prevalence of pathologies of the dentofacial apparatus. According to official data, at least 90% of the world's population suffers from dental diseases. That is why health authorities are constantly tasked with developing measures to prevent dental diseases, studying their causes and improving treatment methods.
Therapeutic dentistry
Therapeutic dental treatment is reduced to eliminating the manifestations of dental diseases using conservative methods.
The following areas of development of this industry are identified:
- treatment of non-carious dental diseases (hypoplasia, fluorosis and enamel erosion, wedge-shaped defects, hyperesthesia and pathological abrasion of teeth, necrosis of hard dental tissues, injuries);
- fight against caries and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis, periostitis);
- treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa (traumatic, infectious, symptomatic and specific stomatitis, glossitis, cheilitis, etc.);
- aesthetic restoration of teeth;
- dental hygiene.
It is worth noting that therapeutic sanitation of the oral cavity is the starting point for any dental procedures, both orthodontic or orthopedic, and surgical.
Periodontitis
Caries
Pulpitis
Wedge-shaped defect
Standard equipment for an orthopedic dentistry office
Appendix No. 3 to the Procedure for providing medical care to the adult population for dental diseases, approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated July 31, 2021 N 786n
STANDARD OF EQUIPMENT FOR A DENTAL CLINIC
Standard equipment for an orthopedic dentistry office
| N p/p | Code of type of nomenclature classification of medical devices <1> | Name of the type of medical device in accordance with the nomenclature classification of medical devices | Name of equipment (equipment) | Required quantity, pcs. |
| 1. | 119630 | Dental unit | Work place (set of equipment) for a dentist: Dental unit (US), including a dentist's unit (drill), a dental chair, a dental hydraulic unit, a dental operating lamp (these parts can be attached to a single supporting frame or attached mutually or separately to load-bearing structures (wall, furniture)) or Place working universal dentist (MRU), including a US equipped with a turbine, micromotor, diathermocoagulator, ultrasonic scaler, vacuum cleaner, X-ray viewer | at least 1 |
| 2.<2> | 122760 | Gas formaldehyde sterilizer | Sterilizer for instruments, in the absence of a centralized sterilization department | 1 |
| 125800 | Microwave sterilizer for unpackaged products | |||
| 330780 | Steam sterilizer | |||
| 125810 | Steam sterilizer for unpackaged products | |||
| 150480 | Ozone/hydrogen peroxide sterilizer | |||
| 173090 | Dry heat sterilizer | |||
| 183670 | Chemical liquid sterilizer | |||
| 188040 | Sterilizer-boiler | |||
| 211070 | Ethylene oxide sterilizer | |||
| 211110 | Ethylene oxide/steam sterilizer | |||
| 215790 | Plasma sterilizer | |||
| 237470 | Gas sterilizer based on hydrogen peroxide | |||
| 253700 | Steam sterilizer | |||
| 291960 | Electrolytic sterilizer | |||
| 330770 | Bactericidal sterilization chamber | |||
| 3.<4> | 119850 | External defibrillator with manual control | Automatic external defibrillator | 1 per department |
| 126500 | External automatic defibrillator for professional use, powered by rechargeable battery | |||
| 262440 | External semi-automatic defibrillator for professional use, powered by a non-rechargeable battery | |||
| 4. | 185950 | Distillation water purification system | Water distiller (medical) in the absence of a central sterilization unit | 1 |
| 5.<2><5> | 209330 | Dental X-ray intraoral system, mobile, digital | Dental X-ray machine with a digital image receiver (radiovisiograph) (in the absence of an X-ray room or an agreement with a medical organization that has a license for radiology work (services)) | at least 1 set (per department/office) |
| 191300 | Dental x-ray intraoral stationary system, digital | |||
| 191230 | Dental x-ray extraoral stationary system, digital | |||
| 173230 | Dental X-ray portable intraoral system, digital | |||
| 6.<2> | 269850 | Container for chemical disinfection system for medical instruments | Containers for disinfecting instruments | at least 1 |
| 185890 | Container for sterilization | |||
| 127550 | Ultrasonic bath for cleaning and disinfecting instruments | |||
| 7.<2> | 257280 | Container for collecting sharps and cutting medical waste | Container for collecting household and medical waste | at least 2 |
| 336200 | Package for collection, storage and transportation of medical waste | |||
| 123680 | Container for biological waste | |||
| 8. | 257280 | Container for collecting sharps and cutting medical waste | Container for disposal of syringes, needles and other disposable instruments | at least 1 |
| 9. | 113870 | Air compressor for medical products | Dental compressor (oil-free), in the absence of MRU and US or a centralized compressed air supply system | by design power |
| 10.<2> | 131980 | Ultraviolet bactericidal lamp | Germicidal irradiator/air purifier/device for disinfection and (or) air filtration and (or) disinfection of surfaces | 1 |
| 209360 | Mobile laminar flow installation | |||
| 152690 | High-efficiency filtering air purifier, mobile | |||
| 152700 | High-efficiency filtering air purifier, stationary | |||
| 292620 | Electrostatic deposition air purifier, mobile | |||
| 11. | 121250 | Dental/surgical polymerization lamp | Dental lamp for photopolymerization (light curing) in the absence of MRU and US | 1 |
| 12. | 282070 | Dental drill motor with remote control | Dental micromotor with or without optics if MRU and US are not included in the kit | at least 2 |
| 13.<2> | 119690 | Dental drill handpiece | Straight dental mechanical handpiece for micromotor if MRU and US are not included in the kit | at least 2 per workplace |
| 256310 | Handpiece of a combined dental drill with mains power | |||
| 282060 | Dental drill handpiece, with remote control | |||
| 14.<2> | 119690 | Dental drill handpiece | Dental mechanical angular handpiece for micromotor if MRU and US are not included in the kit | at least 2 per workplace |
| 256310 | Handpiece of a combined dental drill with mains power | |||
| 282060 | Dental drill handpiece, with remote control | |||
| 15. | 216740 | Dental drill handpiece, pneumatic | Dental turbine handpiece without fiber optics if MRU and US are not included in the kit and installed without fiber optics | at least 2 per workplace |
| 16.<2> | 238570 | Medical X-ray viewer, with power supply | X-ray viewer if MRU and US are not included in the kit | 1 per department |
| 238840 | Medical X-ray viewer, without electrical control | |||
| 17.<2> | 146180 | LED dental lamp, mains powered | Dental lamp without MRU and US included in the kit | 1 per doctor’s workplace |
| 151730 | Dental reflected light lamp | |||
| 18. | 270010 | Surgical instrument table | Dental table | 1 |
| 19. | 121630 | Dentist stool | Chair for a dentist if MRU and US are not included in the kit | 1 |
| 20.<2> | 119180 | Cabinet for dental instruments | Medical cabinet for storing consumables | 1 |
| 260470 | General purpose rack | |||
| 139690 | Medicine storage cabinet | |||
| 270000 | Medical cabinet for instruments | |||
| 21. | 215850 | Pharmaceutical refrigerator | Refrigerator for storing medicines | 1 per medical organization |
| 22.<4> | 279970 | First aid kit containing medicines | Layout of emergency prevention of parenteral infections for primary health care, emergency medical care, specialized medical care and palliative care <3> | 1 per office |
<1> Part 2 of Article 38 of the Federal Law of November 21, 2011 N 323-FZ “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation” (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2011, N 48, Art. 6724).
<2> One of the following items must be present.
<3> Clause 5.2.12 of the Regulations on the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 19, 2012 N 608 (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2012, N 26, Art. 3526; 2021, N 9, Art. 1268 ).
<4> Recognized as invalid according to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated February 18, 2021 No. 109n “On introducing changes to the Procedure for providing medical care to the adult population for dental diseases, approved by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated July 31, 2020 No. 786n.”
<5> Updated in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated February 18, 2021 No. 109n “On amendments to the Procedure for providing medical care to the adult population for dental diseases, approved by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated July 31, 2021 No. 786n.”
Surgical dentistry
So, surgical dentistry is one of the most significant and complex sections of modern medical science. Many people mistakenly believe that the competence of specialists in this field includes only performing simple tooth extraction operations. In fact, doctors of this profile perform a huge variety of different manipulations, ranging from tooth-preserving procedures to plastic surgery.
The competence of specialists in the field of dental surgery includes:
- treatment of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity (periostitis, periodontitis, osteomyelitis, abscesses, phlegmon, etc.);
- carrying out implantation;
- treatment of tumor diseases of the oral cavity;
- carrying out tooth-preserving procedures;
- treatment of pathologies of the temporomandibular joint;
- tooth extraction;
- combating diseases of the trigeminal nerve;
- performing operations on periodontal tissues;
- elimination of malfunctions of the salivary glands;
- primary treatment of wounds in the neck, face and oral cavity;
- carrying out reconstructive and plastic surgeries.
Dental surgery is directly related to such branches of medical science as implantology, orthodontics, orthopedics and aesthetic dentistry. This is why dental surgeons work closely with specialists in these fields.
Removable prosthetics
Do you think that only pensioners use removable dentures? False teeth (as these orthopedic products are sometimes called) are worn by people of different ages, including children. Young patients are fitted with removable dentures after the procedure to remove temporary teeth. Why is this being done? To prevent abnormal growth of molars. The fact is that curvature of the remaining teeth in the row may occur. And even though they are milky, their improper growth will lead to improper growth of the indigenous ones. And to avoid this, you need to install a removable denture.
Orthopedic products are easy to use. So, they can be taken off and put on at any time. Removable dentures can be made of nylon or plastic and consist of a base and teeth that imitate real ones. Orthopedic products are either full or partial. The latter are essentially permanent bridges. To secure the prosthesis, different types of locks and materials are used.
As you can see, prosthetic dentistry is required for people of all ages. With its help you can get rid of almost any problem. But it is important to contact an experienced specialist who knows how to solve them quickly and correctly. Our dental clinic employs professionals who know first-hand how to perform orthopedic work.
Orthopedic treatment in dentistry
Orthopedic dental treatment is a set of measures aimed at eliminating anomalies, deformations, damage and acquired defects of the dentofacial apparatus.
Methods used by orthopedic dentists to combat the above disorders include:
- removable and fixed prosthetics;
- microprosthetics;
- installation of combined prostheses.
Modern technologies allow dentists to produce any orthopedic devices in the shortest possible time. At the same time, dentures installed in the patient’s oral cavity do not cause him any physical discomfort or aesthetic inconvenience.
Orthodontic treatment
Orthodontic treatment is a complex set of medical measures aimed at eliminating dental anomalies. The competence of orthodontists includes the correction of aesthetic disorders and functional failures that arise during the formation of the masticatory apparatus (for example, genetically determined defects). The fight against pathologies that develop as a result of diseases or injuries is the responsibility of orthopedic dentists, surgeons and therapists.
Methods used in orthodontic treatment include:
- hardware (use of braces, retainers, etc.);
- surgical;
- functional (therapeutic gymnastics, etc.);
- combined.
Timely and competent course of therapy allows patients to get rid of dental deformations, malocclusions, abnormalities in the position of teeth and other pathologies.
Methods and means used in dental treatment are constantly being improved. Today, dental clinics use the latest equipment, advanced technologies and the highest quality materials, which allows you to speed up the treatment process as much as possible and minimize discomfort. Thanks to this, fear of visiting the dentist for most patients no longer becomes an obstacle to a beautiful, healthy smile.
Pediatric dentistry: Orthopedics
It is important to maintain the integrity of the dentition even in childhood. This will help prevent not only various dental pathologies in the future, but also some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and musculoskeletal system.
Prosthetics even for severely damaged baby teeth help them perform their functions until they are replaced with permanent ones. With healthy teeth, it will be easier for a child to practice diction, and with a beautiful smile, he will feel more confident.
This treatment result is guaranteed by expert doctors at GUTA CLINICS, relying on their practical experience (more than 17 years of experience), advanced medical technologies and knowledge in the field of pediatric orthopedic dentistry. Our orthopedic dentists are able to find a way to approach any child and establish a trusting relationship with him, which also has a positive effect on the outcome of treatment.
Methods of pediatric orthopedics at GUTA CLINIC
A reception at the office of the pediatric orthodontist GUTA CLINIC is special. For a small patient, this is primarily a game where the tooth is a fairy-tale character who needs help. During this game, the child learns how important it is to take care of teeth, and the doctor can calmly “save them from destruction”:
- carry out diagnostics;
- give anesthesia;
- prepare the tooth cavity for treatment;
- cure a tooth;
- restore missing hard tooth tissues;
- select and install an orthopedic design.
Installation of children's orthopedic systems, unlike adults, does not require grinding of teeth. This significantly simplifies the prosthetic procedure and makes it as comfortable as possible for a small patient.
Depending on the clinical situation, the doctor will determine which type of prosthesis is optimal for your child: therapeutic, fixative or prophylactic; removable or non-removable - and will offer options for its installation. The choice will be yours.
We will calculate the cost of all services for installation of an orthopedic structure individually and record it in the treatment plan agreed with you.
The most common method of prosthetics for baby teeth in GUTA CLINIC is the installation of crowns. They are caps that accurately replicate the anatomy of the tooth. Each group of primary teeth has its own set of crowns, so you don’t have to wait for the crown to be made in the laboratory - it will be installed on the day of your visit.
We use only materials approved for pediatric dentistry from leading manufacturers of dental products. Therefore, the finished orthopedic structure for your child will be hypoallergenic, durable, lightweight and aesthetically attractive.
After treatment with our orthopedic dentists, children feel as comfortable as with their natural teeth.
Take care of your child’s dental health - contact GUTA CLINIC!