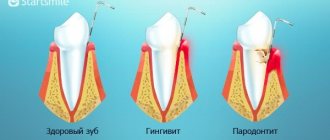
Periodontal disease, like periodontitis, is a disease of the periodontal tissues. Due to the similarity of names, these diseases are often confused. What is the difference between periodontitis and periodontal disease? The main difference between periodontal disease is the absence of tissue inflammation. In addition, if approximately 95% of the total population of the Earth over the age of 18 have periodontitis, then periodontal disease occurs only in 2-3% of people.
Always treat gum problems
When a patient comes to the doctor, he complains about something. What symptoms does he see a doctor with before receiving a diagnosis of periodontal disease? What worries him?
Literally, patients tell the doctor this: my gums have sagged, my gums have become exposed, my lower gums have receded. And for some reason the symptom of gum subsidence automatically means that the patient has the so-called. periodontal disease.
More experienced patients, who have already heard a lot of professional terms, who delve into the professional colloquial language of doctors, say this: “The necks of the teeth have become exposed a little, the teeth have become a little higher.” But, according to statistics, most patients complain about sagging gums.
And so, when patients come to the doctor with complaints about the problem of exposed tooth necks, the doctor diagnoses them with periodontal disease. Of course, he begins to treat them. And to treat it specifically for periodontal disease.
But time passes, money also goes away, and the question of why the gums recede and the necks of the teeth become exposed, why the gums recede, has not been resolved. And the patient still has periodontal disease.
Dentistry “Zuub” – quality treatment and guaranteed results
Dental provides an excellent opportunity to receive qualified medical care if you have periodontitis or periodontal disease. Experienced specialists at our clinic carry out thorough diagnosis and effective treatment of these diseases, using only high-quality modern medicines and advanced equipment. For consultation, please call the numbers listed on the website.
If you have the symptoms described in this article, be sure to make an appointment at our clinic.
Don't self-medicate! Even the smallest problem, if not treated correctly, can significantly complicate your life.
By contacting us, you can be sure that:
- Get high-quality and free consultation .
- You will receive the best prices for treatment and the opportunity to receive a special promotional price.
- Only modern equipment and materials will be used.
- You will be treated by professional doctors with many years of experience.
- We offer treatment on credit or in installments. There is also the possibility of obtaining a tax deduction.
- We work seven days a week and without a lunch break, from 9 a.m. to 10 p.m.
+7 (495) 132-02-96
Make an appointment
What tactics are used to treat periodontal disease?
I want to start with the fact that patients who come with a diagnosis of periodontal disease, they need, every single one, treatment... not from the periodontist to whom they initially turned.
If we talk about the tactics of managing patients with the so-called. periodontal disease, which then come to me again, it’s a shame to voice this, but the treatment of periodontal disease was carried out right up to injections of Lincomycin into the exposed gum.
According to statistics, almost always the treatment of periodontal disease in adults with medications is burdened with a course of some antibiotics and physical therapy.
And most importantly, the task of all these manipulations is completely unclear: what do doctors want to achieve in this way, to destroy some kind of flora or to stop some destructive processes in the gums? It is very difficult for me to say what happens to the competence of a doctor who injects antibiotics for the so-called. periodontal disease, but this is absolute blasphemy. Is it possible to cure periodontal disease by destroying the flora? As a result, the gums will never recover.
Treatment of gum periodontal disease reaches the point of absurdity
I would like to note the widest range of drugs and folk remedies that patients use to attempt self-treatment of periodontal disease at home. Among the folk remedies, one can note the treatment of periodontal disease with hydrogen peroxide, and even treatment with soda:
What about the use of various toothpastes for periodontal disease? What goals do patients have? The purpose of toothpaste is preventative, not curative. And no toothpaste will eliminate inflammation, because there is no such inflammation in periodontal disease.
It is not difficult to guess that in these combinations of procedures the question of how to cure periodontal disease remains open.
Treatment
Therapeutic treatment of periodontal disease consists of stabilizing the destructive process in the gum tissue. Periodontal disease is treated exclusively in a complex that includes:
- proper nutrition;
- gum massage;
- -treatment of chronic diseases;
- strengthening the immune system;
- therapeutic treatment.
Treatment of periodontitis also requires an integrated approach. First, professional cleaning of the oral cavity is carried out, as a result of which all dental plaque, which is a source of infection, is removed. A course of antibiotics may then be prescribed. In the most advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, which involves deep cleaning of periodontal pockets from microbial plaque and deposits. Also, when treating both one and another disease, quite often they resort to splinting teeth, which helps to fix mobile teeth and keep them in place.
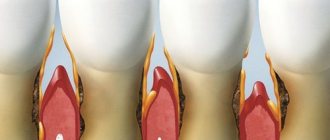
There is no inflammation with periodontal disease
When does the so-called periodontal disease, there is no inflammatory process in the gums. The clinical picture of “periodontal disease” differs sharply from periodontitis; it is with periodontitis of the tooth that inflammation occurs.
And injections into the gums, endless restorations of the necks of the gums - this is running in circles. Over time, again all the restoration fillings are chipped, and again these patients come to have these fillings restored again. And this happens endlessly
:
And the diagnosis of “periodontal disease” does not go away. As Desna ran away, she continues to leave. The fillings increase, that is, the teeth increase in size, because the gums sag more and more, and nothing useful happens.
When such a patient gets an appointment with me, unwinding his entire tangle of ordeals during the consultation, it becomes clear that all previously performed gum treatment consists of 3
factors:
- Lost time,
- lost money
- shattered hopes.
The diagnosis was incorrect and the treatment was appropriate for the incorrect diagnosis. What went wrong?
Patients should always go for a consultation with such a diagnosis... to an orthodontist
.
Because periodontal disease is an occlusal injury
.
What I see in these patients with signs of periodontal disease is a completely different diagnosis. This is an occlusal injury that can only be corrected by an orthodontist.
How will we treat ourselves?
Both diseases are similar in one more circumstance: with periodontal disease and with periodontitis, the main thing is to try to save your teeth.
In both cases, it all starts with professional cleaning - removing dental plaque and stones. In case of periodontal disease, the emphasis is on stimulating blood microcirculation and metabolic processes: gum massage, hormonal and vitamin therapy. Correction of the underlying chronic disease is also carried out, so treatment of periodontal disease is carried out together with a specialized doctor - endocrinologist, cardiologist, therapist.
With periodontitis, dental plaque must be removed every 4-6 months. It is important to eliminate the source of infection. To do this, curettage is performed - cleaning out gum pockets in the affected area around the tooth.
The last resort method for treating periodontitis is open surgical treatment, a flap operation with an incision in the gum. Its task is to clean out all subgingival deposits.
Without confusion and vacillation. How to protect yourself from periodontitis Read more
One of the most common ways to preserve teeth during periodontitis is splinting, which prevents their loosening and loss. The teeth are united using special structures. Prosthetics then help distribute the load evenly across the entire jaw. Both diseases require long-term treatment. Even when it seems that everything is fine.
What is occlusal injury
Occlusal trauma is when a tooth experiences excessive stress due to:
- the tooth is not in the dentition,
- the tooth is not in the correct position,
- the tooth has not grown physiologically,
- the tooth is tilted, at the wrong angle.
The occlusion of the teeth is impaired. That is, when chewing in a patient with impaired occlusion, a destructive force of chewing pressure is created, and the bone tissue in the area of these above teeth begins to decrease.
What is chewing from a physiological point of view?
It's teeth hitting teeth. The strongest blow, since the masticatory muscles are the strongest in the body.
In simple words, in a patient, from such a hyper-impact, hyper-contraction of the masticatory muscles, which develops during chewing, from this beating of teeth against each other, the bone begins to contract. Bone tissue shrinks. And after the bone, the gum also contracts, because the bone and gum are tightly connected. The gum descends, following the bone. And here we answered the main question - why gums recede.
Let's now begin to form an understanding of the answer to the next question: what to do if your gums have receded.
What is the difference between periodontitis and periodontal disease?
Periodontitis and periodontal disease are two completely different diseases. If the first is usually determined by bleeding gums and loose teeth, then the signs of the second include thinning of bone tissue, displacement of elements of the dentition and increased sensitivity of the enamel to external irritants.
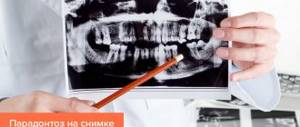
To make an accurate diagnosis, you should consult a specialist. In order to determine the disease, the dentist conducts a careful examination of the oral cavity, as well as an x-ray examination.
Orthodontics comes to the fore
Today, a huge mistake is happening both in the search for the causes of periodontal disease and in making a diagnosis, as well as in the method of effective treatment. Instead of putting the tooth into occlusion, removing it from a traumatic bite, patients are offered all these manipulations that I have previously voiced, which are not at all aimed at getting rid of these complaints, but only at the fact that patients are wasting time, the processes are getting worse.
In the treatment of the so-called periodontal disease is a big problem in the loss of time for inadequate treatment, and the loss of time for the patient is a complication of the pathology of dental occlusion, and the transition of the stage of the disease to a more advanced form.
If a patient, for example, three years ago had a loss of bone tissue of two millimeters, then due to the “treatment of periodontal disease” he has already lost five millimeters, that is, we have lost time.
And if he came to the orthodontist with a loss of bone tissue of two millimeters, then it would be easier to stop the loss of gums, it would be easier to eliminate the development of gum pathology after orthodontic treatment, when the teeth become aligned with the dentition.
We can already talk about the fact that we close all exposed necks of gum recession, thereby treating the neck of the tooth. But when patients waste time on treatments that are inadequate for the disease, sometimes closing the recession is no longer possible. Because there are also strict indications and contraindications for the treatment of gum recession.
Reasons for appearance
The exact causes of the development of periodontal disease have not yet been established. It is believed that its occurrence is influenced by factors such as:
- genetic predisposition;
- diabetes;
- improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- atherosclerosis;
- impaired functioning of blood vessels;
- hypovitaminosis.
Periodontitis, as a rule, appears against the background of a growing infection in the oral cavity. Most often, the main cause of the disease is dental plaque, which consists of food particles and bacteria. If plaque is not removed, it will spread under the gum and gradually destroy tooth enamel. The main reasons for the development are:
- poor oral hygiene;
- malocclusions of various types;
- reduced immunity;
- poor nutrition;
- the presence of certain chronic diseases;
- bad habits.
If the disease is left untreated, the infection will spread not only under the gums, but also into the interdental spaces, thereby provoking the formation of periodontal pockets. These pockets will trap food particles, germs, and dead cells, causing pus to accumulate and eventually leak out. Also, quite often, periodontitis is a consequence of untreated gingivitis.
Treatment of periodontitis: the new Vector procedure will strengthen the gums and eliminate bleeding
Seeing blood on your toothbrush and in the sink while brushing your teeth every day is not pleasant. You can solve the problem of bleeding gums in just one visit with the help of deep mouth cleaning using the Vector device.
This procedure does not provide visible aesthetic results: the teeth do not become noticeably whiter or straighter, so patients tend to classify it as a minor procedure. This is a fatal mistake, because it is with tartar, bleeding and periodontitis that serious problems with teeth begin: loosening, exposure of roots and loss of dentition units.
The Vector device fights gum problems, strengthens tissue, cleans out inflamed pockets, destroys germs, saving gums from infection. The complex effect of Vector restores the adherence of the gums to the teeth, closing periodontal pockets that are attractive to infections.
The revolutionary principle of longitudinal movement of the Vector Paro Pro!
- Non-traumatic
- Antibacterial
- Strengthening method
It is the tartar deposited in the pockets that is the main cause of bleeding gums, since when you press on this place with a toothbrush or while eating, the gums are injured, wounds appear, into which pathogenic bacteria enter - the cause of inflammation of the oral cavity.
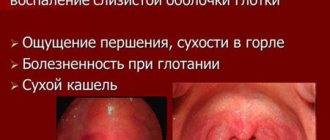
How gum and dental diseases manifest themselves
Regardless of the nature and complexity, dental diseases must be treated. People who visit the dentist at least twice a year protect themselves from the development of dental pathologies and dental diseases with regular visits to the doctor. Timely consultation with a doctor allows not only to carry out gentle treatment and prevent the development of the disease, but also to completely eliminate the consequences of the disease. Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner can lead to the development of complications, the appearance of concomitant diseases, damage to healthy teeth, tooth loss and disruption of chewing functions.
The following symptoms are reasons to consult a doctor:
- change in tooth color;
- The appearance of painful and uncomfortable sensations in the tooth or surrounding tissues;
- Sharp reaction of teeth to cold and hot foods;
- Mechanical damage to the tooth;
- Bad breath;
- Presence of tartar and abundant plaque.
Forms and types
Depending on the type of periodontitis, treatment will vary. It is important to carry out a differential diagnosis, as there are many overlapping symptoms. A detailed diagnostic examination will help identify the causes and determine a treatment regimen.
The disease is classified by:
- course - can be acute, chronic, aggravated;
- degree of severity - mild, moderate, severe;
- localization of inflammatory processes - focal (localized in one tooth), diffuse (dentition is affected);
- degree of mobility - from 1 to 4, depending on the instability and movement of the dental unit; at degree 4 it can be rotated around its axis.
Acute periodontitis
It has acute symptoms and a rapidly developing inflammatory process. The gums become swollen, bleed, sharp pain occurs, and purulent exudate may appear.
Chronic periodontitis
Characterized by periods of exacerbations and remissions. In the first case, the symptoms are pronounced, in the second they are absent. May have a generalized form.
Purulent periodontitis
Pus is released from the gum pockets. Often leads to an abscess (abscess form).
Generalized periodontitis
The pathology develops gradually against the background of weak immunity. The infection involves the entire alveolar ridge of the upper or lower jaw. Due to an insufficient immune response to the infection, it is practically asymptomatic. There may be mild clinical manifestations at the initial stage.
Localized periodontitis
The spread is focal - on one or several teeth. Often the cause of development is constant trauma to the mucous membrane in a certain place, for example, with a crown. Usually begins acutely, suddenly. It manifests itself as severe pain and other clinical symptoms characteristic of the acute form.
- Mild degree. Dental units are immobile. The alveolar bone is reduced by no more than a third of the height of the root. The depth of the periodontal pocket is less than 3.5 millimeters.
- Average degree. The pocket deepens up to 5 millimeters, and the alveolar bone decreases by half the height of the root part. Teeth looseness appears at the 1st and 2nd degree levels.
- Severe degree. The gum pockets are deep, more than 5 millimeters, and there is also a strong loss of alveolar bone. As a result, the degree of loosening of the dental units increases.
Aggressive periodontitis
The pathology has an atypical course. Compared to the typical development of the disease, with AFP bacteria penetrate faster and more actively into the deep layers, causing severe destructive changes.
The development of ACE is influenced by many different factors, so it has an additional classification.
- Adult periodontitis affects the periodontium after 35 years of age. Caused by gram-negative bacteria. Bone loss is often horizontal.
- Prepuberant - develops immediately after the eruption of molars. Rarely seen. Can be focal or diffuse. In females it is diagnosed 3 times more often.
- Juvenile - occurs in adolescence. Mostly molars are affected, sometimes incisors; a generalized form is possible. Vertical bone loss, no inflammation observed.
- Rapidly progressive - type A is diagnosed in adolescents and adults up to 26 years of age, type B - up to 35 years of age. There is marked loss of alveolar bone tissue of various types. Increased risk of STDs in people with diabetes mellitus and Down syndrome. The disease is difficult to treat and relapses are frequent.
- Refractory - degenerative phenomena in bone tissue appear simultaneously in several areas. Continues to progress with therapy.
- Ulcerative-necrotic - develops against the background of acute ulcerative-necrotic gingivitis. It is characterized by a cyclical course - frequent relapses. Periodontal tissues are destroyed, and interdental and gingival craters are formed in this area.
Periodontitis may not bother the patient for a long time, but destructive processes continue to develop. There are many causes of the disease, which means it can occur in almost every person. For early detection of periodontal pathology, it is recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations with a dentist.
Symptoms of periodontal disease depend on the stage and characteristics of the disease.
The first stage is characterized by a complete absence of complaints and symptoms, despite the fact that pathological changes are already slowly beginning to occur in the periodontal structure. The second stage is manifested by a decrease in the interdental septa. The patient complains of blood, itching and unpleasant pain, and possible food debris getting stuck between the teeth. The third stage is the complete and irreversible destruction of the periodontal space. The main complaints are severe bleeding even with minor mechanical impact, pain, the appearance of ulcers and erosions, pathological mobility of teeth progresses, and possible tooth loss.