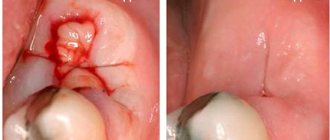
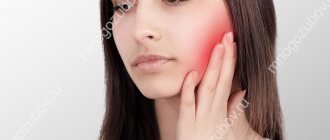
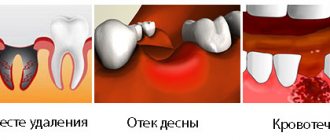
Exacerbation of the inflammatory process in the tooth sometimes leads to swelling of the cheek. The symptom of swelling occurs due to inflammation of the periosteum, which in dental terms is called periostitis.
It must be said that swelling indicates that the stage of inflammation is seriously advanced. If the cheek is swollen from a tooth, then most likely the patient ignored the long period when the tooth was destroyed by caries. Then the infection penetrated into the pulp chamber, where the nerve of the tooth is located, and pulpitis began. But even at this stage the patient did not visit the dentist, but endured acute tooth pain with the help of painkillers. Then the pathogenic bacteria penetrated deeper into the periodontal tissues, which connect the root of the diseased tooth with the alveolar processes of the jaw, and from there they reached the periosteum, causing periostitis.
Why do my cheeks swell?
Reasons why a child's cheek swells include:
- bad teeth;
- temporomandibular joint disease;
- inflammation of the salivary glands;
- flux;
- allergy;
- sinusitis;
- lymphadenitis;
- neuritis;
- phlegmon.
This is not a complete list of possible causes. To establish an accurate diagnosis of edema in a child, you should contact the clinic. You may need to undergo testing. But only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment.
Causes of inflammation
Inflammation of the gums near the eighth tooth is accompanied by pain and discomfort. To diagnose the disease, it is necessary to take an X-ray of the tooth and take a blood test. Based on the results of the studies, the doctor makes a decision:
- Remove the tooth.
- Prescribe therapeutic treatment.
- Or cut the gum.
The gums can become inflamed and painful, most often due to the incorrect position of the tooth, which has difficulty erupting and grows in the wrong direction relative to the dental arch. The number eight can take a very long time to erupt, up to several years.
Dental treatment
To avoid unpleasant health events, you need to constantly monitor the health of your child’s teeth. The child's body is not able to fully resist infection. Growing and changing teeth is an additional burden on the oral organs. It is necessary to sanitize the child’s oral cavity once a year. This will help avoid health problems.
Allergic reactions
If the cheek is swollen, but the child is not in pain, then this is a direct indication of an allergy. Allergic reactions are caused by food, animal hair, flowering plants, and medications. In addition to swelling, there may be watery eyes, a runny nose, or a cough.
Skin itching and rash are signs of allergies.
Allergies often manifest as swelling of the cheeks, lips, or entire face. If children have no pain in the oral cavity, then if a child has a swollen cheek, it is necessary to visit a pediatrician and consult with an allergist.
Removal of a tooth
Healthy teeth are the key to the well-being of the whole body. Food enters the stomach through the oral cavity. Oral hygiene determines what goes into the body. Teeth are the first to respond to digestive problems. If a child’s teeth begin to actively deteriorate, this is an excuse to visit a gastroenterologist. Frail enamel of children's teeth, errors in nutrition, lack of vitamins and microelements lead to irreversible tooth loss. As sad as it may sound, even children sometimes have to have their teeth removed.
If a child has a tooth removed and then his cheek becomes swollen, what should he do? A slight swelling immediately after removal is a natural phenomenon. But if it does not go away for two or three days, you should visit the dentist again. The cause of swelling in a child in this case will be the spread of infection from diseased teeth and the development of inflammatory diseases in the oral cavity.
Nerve removal
Dental treatment is a complex process. Sometimes it is accompanied by removal of the nerve, cleaning and filling of the canals. The procedure is complex and traumatic. If the child had a tooth treated, the nerve was removed and the canals were filled, then the swelling will last for about a day. Then it will slowly begin to subside.
If after three days the discomfort in the treated tooth and swelling in the child does not go away, this is also a sign of pathology. Swelling may indicate inflammation. You should contact your dentist again.
Gum section
Such an operation is resorted to if a cavity forms in the gum and pus accumulates. Suppuration invariably leads to swelling of the gums. This pathology is possible with periodontitis - inflammation of the connective tissue between the teeth and jaw.
The disease does not begin immediately. The appearance of swelling in this situation is preceded by an unpleasant odor from the child’s mouth and bleeding gums. When the infection spreads sufficiently, it manifests itself as severe throbbing pain, swelling of the gums and adjacent tissues. An incision in the gums is resorted to in extreme cases. An operation to remove suppuration and disinfect the cavity helps save the child’s tooth.
When is swelling after tooth extraction not a health threat?
If the following symptoms occur, swelling does not require immediate medical attention:
- The swelling is small and does not increase over time (for example, the cheek is slightly swollen immediately after surgery, such swelling most often goes away on its own after a couple of days).
- The body temperature is not elevated, which means that inflammation does not occur in the body (an exception is that if the temperature was high before removal, then after it it should slowly drop to a normal value).
- The pain in the socket is not critical (the main thing is that it decreases over time, not grows; with simple removal it goes away in a couple of days, with complicated removal it can last for several weeks).
- There is no bad smell (if there is one, it is possible that the tissue covering the hole is rotting).
Local infections
In addition to dental lesions, other infections also spread in the oral cavity:
- Sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses. Maxillary sinusitis stimulates swelling of the cheek.
- Oncology of the salivary glands.
- Keloids. These scars are formed due to excess scar tissue.
If the cheek is swollen, but the child’s tooth does not hurt, then this is a possible sign of infection of the oral cavity by a virus. The most common problem is stomatitis, an inflammatory disease of the tissues in the oral cavity.
The causes of this disease are not completely clear. Patients pay attention to the fact that stomatitis occurs when dirt gets into the child’s mouth. Dentists recommend using only personal hygiene products: a toothbrush, a glass for rinsing and other dental supplies.
Swelling of the mucous membranes of the cheek in a child is possible after using novocaine. This is the result of an allergic reaction to the anesthetic. A burn to the oral cavity from hot food is also accompanied by swelling.
Tip #5: Avoid activities that cause blood flow to the head
Blood rushing to the soft tissues in the facial area increases pressure on the sore area, increases discomfort, increases swelling, and increases the spread of bacteria. To make the swelling of the cheek less significant and painful, we will tell you how to act. Of course, it will not be possible to remove it completely, but it will be possible to reduce the intensity of the unpleasant sensations.
First, temporarily exclude from your diet foods that increase blood circulation: hard and hot, spicy and salty foods. Avoid drinking caffeinated and alcoholic drinks. Try not to drink too much, because... this provokes internal swelling of the tissues. You should also chew food on the side of the jaw that is opposite to the swollen side, so as not to further injure the tissue.
Avoiding coffee helps reduce swelling
Secondly, try to keep your head upright. To do this, use a high pillow when sleeping or resting.
Thirdly, reduce physical activity and avoid sports while swelling of the cheek is present. Also avoid visiting saunas and steam rooms, beaches (on hot sunny days), and do not take a hot bath. And, of course, give up such a bad habit as smoking.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 4 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
toothache
- Minaeva N.V. Modern strategy for antibacterial therapy of upper respiratory tract infections in children in outpatient practice / Medical Council. – 2021.
Expert “Before treating or removing a tooth, or any other surgical procedure, an experienced dentist must find out whether the patient has diseases or allergic reactions to medications that can lead to swelling. If a person suffers from hypertension (high blood pressure) or has problems with blood clotting, then the likelihood of developing edema increases sharply. The doctor’s task is not only to warn the patient about possible consequences, but also to minimize the risk of their occurrence with the help of supportive drug therapy.” Implant surgeon, ch.l.h. Vedeneeva Alla Sergeevna
Consulting specialist
Kashaeva Victoria Nikolaevna
Specialization: Dental hygienist Experience: 7 years
Salivary glands
The salivary glands produce saliva, which is a digestive enzyme. It is an independent organ with a complex structure. Like any other organ, a child's salivary glands can become inflamed.
The causes of their inflammation are different:
- viruses and bacteria;
- blockage and stone formation;
- lack of proper oral hygiene;
- complications after illness;
- intoxication with salts of heavy metals;
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- dehydration of the body.
If a child has a swollen cheek, then the reason may be one of the pathologies of the salivary glands.
Associated symptoms
The symptoms that accompany cheek swelling are directly related to the main cause of the swelling. Some of the most well-known symptoms associated with swollen cheeks include:
- hives;
- a sore throat;
- toothache;
- addition of infection;
- rash;
- redness;
- seals;
- oily, itchy or dry skin;
- painful sensations;
- temperature increase;
- itching in the eyes;
- sneezing;
- labored breathing;
- paresthesia of the jaw and cheek;
- swelling of the face, tongue or lips.
To make a full diagnosis, proper treatment, and reduce swelling of the cheeks, it is necessary to find out the causes of the symptoms. The most likely causes of swelling:
Dental problems
A swollen cheek due to problems with teeth and gums is a fairly common situation. Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity often lead to swelling. Among them:
- toothache;
- tooth abscess;
- affected 3rd molar (wisdom tooth);
- tooth decay or;
- tooth infection;
- removal of a tooth.
Poor oral hygiene and consumption of sugary foods can lead to the destruction of tooth enamel.
Bacteria that settle on tooth enamel feed on sugar and produce acid, which destroys this enamel, leading to tooth damage.
Wisdom tooth
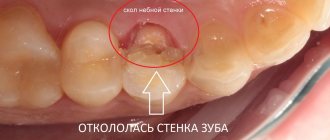
Wisdom teeth are also often the cause of cheek swelling due to their location. Infection, abscess, trauma (filling or broken tooth) can often lead to a swollen cheek due to wisdom tooth disease.
A swollen cheek due to an abscess is a fairly common occurrence. According to [webmd.com], “an abscess is a painful infection at the root of a tooth,” which usually results in complete destruction of the tooth. Causes of an abscess include trauma (such as a chipped or broken tooth), gum disease, and gingivitis. If a tooth abscess is ignored, the enamel can break down, allowing bacteria to move into the dental pulp and spread to the tooth root and jaw.
Some of the common symptoms of a tooth abscess include fever, bitter taste in the mouth, swollen tonsils, swelling, redness and swelling in the lower and upper jaw area, gum pain, sensitivity to cold or hot foods, pain when eating and chewing.
In case you have a tooth abscess, seek medical help from your dentist and try various home remedies, which we will discuss later, to reduce the pain.
After tooth extraction
Temporary swelling after tooth extraction, especially if the procedure was quite traumatic, is normal. Most often, this situation occurs when a wisdom tooth or other molars are pulled out, since after this a temporary deep wound usually forms. Fortunately, it will drag on in any case, although sometimes it can take a month. The swelling usually goes away after a few hours, or less often, days. For severe pain and swelling, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be used during the first days.
But you should be careful and distinguish between normal swelling of the cheek after tooth extraction and after infection in the wound. Although the second, if you follow the basic recommendations, happens extremely rarely.
Read also: How to treat gum inflammation
Toothache
Toothache caused by any of the problems mentioned, including dental abscesses, infection or tooth decay, can also cause the cheek to become enlarged, especially on the side of the diseased tooth. Typically, swelling of the cheeks is accompanied by some pain.
Root canal filling, extraction and cleaning procedures
Dental procedures such as tooth extractions, root canal cleanings, and cosmetic dental surgery cause short-term swelling from the procedures performed. Swelling, pain and discomfort should disappear after a few days.
Trauma, piercing or surgery to the cheek
Facial surgery may be accompanied by short-term swelling. Also, swelling on the face may appear after piercing or injury. When soft tissue is damaged due to a bruise, nose job, puncture, or other injuries, it is normal to experience slight swelling of the cheek. In such cases, the swelling is accompanied by pain, slight bleeding, as well as redness and bruising. The severity of these symptoms is directly related to the size of the affected area. The swelling will subside over time. To help reduce swelling and pain, try a variety of home remedies, such as cold compresses or pain relief medications.
Mumps and swollen parotid glands
Mumps or mumps is another possible cause of swelling on the cheek. Its main symptoms are increased body temperature, fatigue, muscle and headache, lack of appetite, swelling of the cheeks, neck, and then swelling of the salivary glands. Symptoms of mumps begin 16-18 days after infection and can last up to 7-10 days.
Allergic reaction
Individual intolerance to certain foods, pet hair, medications, some components of cosmetics and other substances can provoke an allergic reaction, which can sometimes cause swelling of the cheeks and eyes, nose, face, tongue or lips. Allergic reactions are often accompanied by hives, itching, rash, watery eyes, nasal congestion and other symptoms.
Lymphadenopathy or swollen lymph nodes
Sometimes swelling can appear due to inflammation of the lymph nodes that are located behind the ear. Swollen lymph nodes can be due to dental infection, cancer, and others.
Inflammation of the salivary glands
When the salivary glands, which are located in the cheek, are inflamed, the swelling is located closer to the ear or eye. Swelling of the submandibular and sublingual glands is manifested by swelling of the lower part of the cheek and near the chin.
The cause of swollen salivary glands is most often bacterial or viral infections, which lead to swelling and inflammation. Common causes of swollen salivary glands include HIV, mumps, salivary stones, tumors, Sjögren's syndrome, malnutrition, influenza A, poor hygiene and dehydration.
With sialolithiasis (clogging of the salivary duct with stones), swelling of the cheek may occur.
Before starting treatment for inflamed glands, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis. Only after this the doctor will be able to select the necessary medications.
Swollen cheekbone
Sometimes swelling of the cheeks may occur as a result of swelling of the cheekbone. This can happen due to factors such as:
- trauma (for example, from a blow);
- sinusitis;
- salivary gland infections;
- infection or tooth extraction.
In this case, swelling can be in the area of the upper or lower jaw on either side or simultaneously on both. It may be painful when you lie on the affected side.
Bulimia is a psychological disorder associated with sudden changes in food intake, in which a person suffers from bouts of food bingeing (eating large amounts of food in a short period of time), followed by an attempt to get rid of the food consumed (purging), [Wikipedia.org] , by inducing vomiting, exhausting physical activity and taking laxatives.
Uncontrolled fast eating, gastric reflux after eating, usually destroys teeth, causes swelling of the salivary glands and cheeks, [helpguide.org]. Treatment for this condition includes working with a psychologist to develop behavioral changes, taking antidepressants, physiological therapy and stress management courses.
Other reasons:
- Cystic acne – Cystic acne on the cheek can lead to swelling, especially on the acne-affected side.
- A skin boil or abscess is “a localized infection in the skin that begins with redness.” [Medicinenet.com], lead to the formation of pus under the skin, and resulting swelling.
- Neoplasms and Keloids – Keloids are caused by excess scar tissue formation and are usually painless.
- Cellulite is a purulent inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue, due to which the skin swells and turns red, and a local increase in temperature is also possible.
- Sinus swelling in the cheek. Sometimes severe sinusitis, especially maxillary sinusitis, can lead to swelling in the cheeks. This will be accompanied by symptoms such as cheekbone pain, swollen and red cheekbone, nasal discharge and fever.
- Side effects of certain medications. Some people have experienced swelling of the cheeks and gums after taking novocaine (Novacaine).
- Ingrown hairs
- Rosacea (rosacea)
- Sebaceous cysts
- Seborrhea
- Cancer of the salivary glands, skin or mouth
- Malnutrition
- Hereditary angioedema
- Burns
- Ulcers on the inside of the cheek
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. They are located in the maxillary region. When they become inflamed, pus accumulates in them. This stimulates the cheek to enlarge and the eye may become swollen. If a child's cheek is swollen in the upper part, but the tooth does not hurt, it is worth thinking about sinusitis.
Additional signs of inflammation include:
- nasal congestion,
- night cough,
- headache over the bridge of the nose,
- pain in the cheeks under the eyes.
Possible causes and symptoms of cheek swelling
Dental diseases
When identifying the causes of swelling of the buccal area, the first thing that comes to mind is the assumption of pathology in the oral cavity, namely the teeth. Possible causes of swelling may be dental disorders:
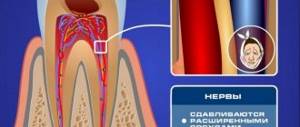
- Inflammatory diseases. With pulpitis, the pathological process affects the complex of soft tissues located in the dental canal. Often the disease is complicated by advanced caries. Apical periodontitis is characterized by the development of inflammation at the apex of the roots with further destruction of the tooth ligaments and bone tissue. The consequence of untreated pulpitis, periodontitis or an independent primary process is inflammation of the periosteum of the jaw - flux. A probable or obligatory clinical sign of the listed pathologies is local swelling of the gums and cheeks. The appearance of the symptom is associated with infiltration of soft tissues adjacent to the affected area by exudate. However, usually the affected tooth or gum also hurts. If therapy is delayed, the condition may be complicated by an abscess and phlegmon.
- Lesions of a dystrophic (non-inflammatory) nature. Such pathologies that can cause swelling of the cheek area include periodontal disease. With this disease, atrophy of the structures surrounding the tooth and enamel occurs. There is a high probability of infection penetrating the affected tissues. A fairly common symptom accompanying the pathological process is the sudden appearance of swelling of the gums and cheeks.
- Anomalies in the eruption of third molars – wisdom teeth. In this case, a pocket of mucous membrane may form above the unit, which is practically inaccessible for cleaning from food debris. Over time, irritation and inflammation of the gums in this area, and the development of edema and swelling of the cheek over this area are possible.
Complications after treatment
If after visiting the dentist the child’s cheek is swollen, then it should be assumed that a source of inflammation has arisen or persisted. This is possible due to poor-quality treatment: poor sanitation of the tooth cavity before installing a filling, incomplete removal of the inflamed pulp, violation of the rules of asepsis and antiseptics. In these cases, as a rule, the tooth no longer hurts, but external signs of the inflammatory process remain - swelling of the gums and cheeks. It is necessary to repeat the trip to the clinic to determine the cause of persistent abnormalities and their treatment.
After complex dental procedures, swelling may persist on one side, corresponding to the intervention zone, for 2-3 days. This is considered as a variant of the norm, which the doctor will definitely warn parents about. The tooth extraction procedure can lead to complications if it is carried out incorrectly or if the specialist’s recommendations are not followed in the postoperative period. In case of unfavorable development of events, swelling of the buccal area is accompanied by developing inflammation in the socket, a large hematoma or abscess, which requires repeated consultation with a specialist.
Other diseases
The list of conditions in which swelling of the cheek appears in a child that has no connection with dental pathology is very long. But, as a rule, these disorders have a corresponding history and other specific signs, according to which a specialist will make a diagnosis and prescribe the required treatment.
Possible non-dental causes of swelling:
- Allergic reactions. They are typically associated with taking new foods, medications, or using atypical hygiene products. Often, local hyperreactivity of the body develops in response to insect bites. A rapid increase in the volume of not only the cheek area, but also the child’s neck indicates Quincke’s edema, which requires emergency medical attention.
- Lymphadenitis. An increase in size of the lymph nodes is a reaction to inflammation in nearby organs or a systemic disease of a bacterial or viral nature. Diseases such as tuberculosis, infectious mononucleosis and diphtheria can cause lymphadenopathy.
- Inflammation of the salivary glands due to mumps or other causes.
- Sinusitis. The pathology has a similar clinical sign, which is most often characterized by bilateral spread.
- Neuritis of the facial nerve. The picture of the disease is so specific that any pediatrician should immediately suspect it and send the child to a neurologist. In this condition, the affected half of the face hurts.
- Cellulitis of the cervical tissue. Occurs rarely - in extremely advanced cases. It is characterized by a severe course and requires urgent treatment in a hospital setting.
- Traumatic injuries to the cheek. On the inside, the cause may be a tooth or its fragment, on the outside – a blow with a blunt object without violating the integrity of the skin.
- Neoplasms of nearby tissues and anatomical structures.
The lymph nodes
In children, lymphadenitis caused by viruses is possible. This is especially true during the cold season. If a child’s cheek hurts during a cold, this raises suspicion of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the ear area. A cold leads to otitis media. Accordingly, the lymph nodes in the ear area become inflamed.
This can be easily checked by pressing on the area in front of the ear canal. When there is inflammation, pain of varying degrees will be felt there. Other lymph nodes are located under the jaws. On palpation, pain will be felt there.
Oral infections can cause these lymph nodes to become swollen in a child. Whatever lymph nodes in the facial area undergo an inflammatory process, this will lead to a tumor on the cheek.
Consequences of a jaw bruise
Negative consequences of a jaw strike:
- tooth damage;
- inflammation of bone tissue;
- limitation of joint mobility;
- traumatic brain injury, concussion;
- deformation of the nose, which causes breathing problems, development of chronic sinusitis, rhinitis;
- inflammation of the hematoma;
- cyst formation.
A severe blow can cause asphyxia, shock, scarring, even disability if the eye or optic nerve is affected. Pain and hematoma can hide damage to the facial skeleton, especially during the formation of the periosteum.
No one is immune from such a nuisance - you may not be a professional participant in “fights without rules” and get hit in the face after a fall, as a result of unsuccessful braking and many other reasons. If you take care in a timely manner about how to remove swelling from the face after an impact, you can significantly reduce the consequences of the injury.
What to do immediately after being hit in the face?
The reason for the appearance of a tumor on the face after an impact is a violation of the integrity of the subcutaneous capillaries and tissues. The skin itself may remain undamaged, but blood and lymph from damaged vessels accumulate under the epidermis layer. In order to stop or minimize this process in time, you need to urgently apply cold to the site of the impact. Ideally, this is ice from the freezer, wrapped in a plastic bag and a linen napkin.
If there is no ice, apply the following to cool the impact site:
A napkin soaked in cold water, green tea (such a compress needs to be refreshed more often);
Copper or any other coin.
All these measures are applicable if the integrity of the epidermis is not compromised and there is no risk of wound infection. Applying cold is advisable in the first 15-20 minutes after injury; after a quarter of an hour, it will no longer be possible to prevent subcutaneous hemorrhage.
Inflammation of the facial nerve
Inflammation of the facial nerve manifests itself very quickly. Its signs:
- paralysis of facial muscles;
- stiffness in mouth movements;
- severe burning pain on one side of the face;
- numbness;
- tearfulness;
- edema.
The facial nerve ganglion is located in front of the ear. Three branches depart from it:
- in the eye area;
- in the nose area;
- down the jaw.
All branches pass through the cheeks, so when inflammation occurs, the child’s cheek swells. Accordingly, pain can be felt in any area, or it can be wandering. It all depends on the area of the affected branch.
Treatment with medications and folk remedies
Swelling of the cheek area is only a symptom, a consequence of illness or injury. Therapy should be aimed at combating the main disease, when cured, the unpleasant symptom will disappear. If there are dental problems, the doctor will take the necessary actions and prescribe therapy: analgesics, a course of oral antibiotics, rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions, etc. Here you can resort to folk remedies - decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, oak bark are excellent for this purpose .
A specific treatment regimen, determined by a doctor, is required by systemic diseases accompanied by swelling in the cheek area - infectious mononucleosis, diphtheria, damage to the salivary glands, inflammation of the facial nerve or maxillary sinuses, etc. When the cheek is swollen after a blow, local treatment with cooling compresses and ointments is used - Troxevasin , Heparin or NSAID based. To stop the allergic reaction, exclude the irritating factor and prescribe a short course of antihistamines, for example, Suprastin, Fenistil or Cetirizine.
A swollen cheek in a child is a symptom indicating an oral disease, a sign of injury or other dysfunctions in the body. Let's look at the treatment of cheek swelling in children using available medicines and traditional medicine.
Has your cheek started to swell? This is an injury or inflammation in the mouth
Deep phlegmon of the cervical tissue
Phlegmon is purulent inflammation. The purulent focus is located in the subcutaneous fatty tissue. If the development of a purulent inflammatory process occurs in the deep tissue of the neck, then phlegmon can cause serious complications.
Signs of inflammation in a child are high fever, a grayish tint to the skin of the face, and impaired swallowing reflex. The swelling of the child's cheek will spread from bottom to top.
The mechanism of formation of swelling and bumps during a bruise
Immediately after the injury, the swelling is soft. It is growing quickly. After a few hours, the blood clots and a hematoma appears. Solidified blood is dark red at first, turning blue, then purple.
Hemorrhage has several mechanisms of spread. A cavity forms in the interstitial space, which fills with blood, or injured tissues become saturated with blood without forming a cavity. Swelling on the face is more pronounced than on other parts of the body. This is due to many capillaries and fat cells.
Injuries
The constant causes of cheek swelling in a child are minor and major injuries that he receives in the process of life. If the baby falls, hits himself and has a bruise, then a bruise on the cheek will invariably lead to swelling. This is normal for any injury. Facial tissues are delicate, especially in children. They get injured faster, although healing is also faster than in adults. Sometimes children fight. They can hit each other or throw a heavy object. They do this spontaneously. But, as a rule, an object sent in the direction of the offender hits the head. This happens because the opponents are approximately the same height. As a result, the child gets hurt. After a blow to the forehead, the hematoma slides down, forming swelling on the cheek.
Other injuries also occur in children. One of the most common is biting. Running, jumping, playing around, a child can bite not only his lip, but also the back of his cheek. After biting hard, the cheek swells, but it hurts from the inside. More serious injuries to the cheek are also possible: cuts, burns, punctures. All of them will lead to swelling of the sore spot.
The most affordable and fastest methods for relieving swelling on the face from a bruise
It is generally accepted that swelling on the face from a blow appears from male activities. But in everyday life, both men and women are much more likely to get swelling and bruising on the face. Here fights or conversations “like a man” have a rest. Here are just a few examples of this.
- Cleaning mezzanines when objects that are taller than your height fall on your head;
- All kinds of contact sports and regular exercises in the fitness room;
- active recreation in nature;
- And many other such trivial cases when something falls or comes into contact with the face at speed.
Each specific case will have its own reason for the appearance of swelling on the face. But this does not change the result - there is swelling and a hematoma on the face (in common parlance, a bruise).
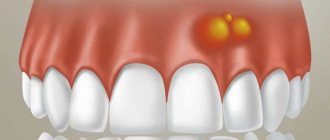
Flux
Flux is a purulent disease. The process occurs in the subgingival region of the periosteum. Flux occurs more easily in children than in adults. This is due to a weaker immune system.
Flux symptoms:
- severe pain in the affected tooth, fever,
- pain when pressing on a sore tooth,
- pronounced redness of the gums with inflammation,
- swelling of the cheek.
If you notice swelling of the cheek in a child with symptoms of gumboil, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Inspection after first aid
After applying cold, the condition of the victim should be assessed. How big is the swelling? It's just a swelling or a big lump. What color is she: pale? Immediately flushed? Or is there a noticeable bruise? Where exactly did the swelling form: eye, cheek, lip, soft tissue? It is important to clarify whether there is dizziness or nausea. All types of swelling on the face after a blow can be divided into the following categories:
Soft tissue swelling
There may be swelling or bumps (on the forehead, cheeks, cheekbones), but their color will be pale or slightly pink. It's important to keep the cold as long as possible, but you shouldn't let your face get cold.
This swelling can be removed using ointments or folk remedies. As a rule, applying cold for a long enough time will effectively help relieve swelling and bumps. You need to hold it until the swelling goes away, this significantly reduces the possibility of a subcutaneous hematoma.
Swelling of the lip(s)
The lips are supplied with a large number of blood vessels, which makes the swelling very noticeable. In addition, delicate skin is more susceptible to tears than on the cheeks. Therefore, along with swelling, small wounds oozing blood often appear on the lips. To quickly remove puffiness, you need to follow these steps.
- Apply cold to the area of swelling.
- Treat the wound with an antiseptic. If the lip is too cut and the bleeding does not stop, a stitch may need to be placed.
- In any case, lubricate the swelling with a gentle ointment, but so that the medicine does not get into the open wound.
- Treat the wound until it dries. And apply medicine to relieve swelling.
Bruised eye
Swelling will occur around the eye, and this can happen even when the blow falls on the bridge of the nose or cheekbone. There are a large number of blood vessels around the eyes, and there is practically no adipose tissue. The likelihood of swelling and hematoma occurring here is very high.
In this case, it is important to immediately pay attention to whether redness has appeared in the eye. With this alarming symptom, two things should be done:
- Apply cold to the bruised eye.
- Contact an ophthalmologist immediately.
These actions must also be done when double vision, dizziness or nausea appear in the eyes.
In all other cases, swelling under the eye can be removed in the same way as in other places on the face. You just need to remember that the skin around the eyes is very delicate; applying the ointment should be alternated with fatty creams.
Inflammatory infiltrate
Infiltration is the accumulation of blood clots, lymph particles, and remains of dead cells in the tissues of the body. Such a dump promotes the growth of bacteria and leads to inflammation. The causes of the phenomenon are injuries and inflammatory diseases. Inflammatory infiltrate occurs at any age.
Signs of this inflammatory process are:
- develops gradually
- the temperature does not rise,
- swelling occurs at the site of the lesion,
- the lump is dense to the touch,
- the swelling has clear outlines,
- palpation does not cause pain.
If a baby’s cheek is swollen after tooth extraction, and the child does not react when pressed, then the formation of an inflammatory infiltrate should be assumed.
My cheek is swollen and my temperature has risen: what to do and what folk recipes can help?
Therapy at home involves the use of traditional medicine. But such methods can only be used after consultation with a specialist. Treatment in this way is not so fast, but effective. Most often, for swelling of the cheeks, accompanied by an increase in temperature, rinsing is indicated. The most effective recipes:
1. Take sage, oak, calamus and nettle in equal proportions. Mix the mixture well and pour boiling water over it. Leave the product to infuse for several hours. Rinse your mouth every 2 hours.
2. To irrigate the oral cavity, you can prepare a product from a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide. The solution should be mixed with boiled water in a ratio of 1 to 1. Afterwards, rinse your mouth every two hours.
3. Garlic remedy is an excellent antiphlogistic agent. To prepare it, take a few cloves and grate them on a fine grater. Pour the resulting pulp with a glass of boiling water. When the infusion cools, rinse your mouth with it.
4. Propolis tincture has a positive effect on swelling of the cheeks. The tincture is purchased at the pharmacy. Soak a cotton pad in it and apply it to the affected cheek from the inside. Dry propolis is also suitable. It must be ground and applied to the sore spot for 40 minutes.
With proper use of recipes, you can completely overcome the disease.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums. The disease occurs due to microbial plaque. Plaque appears due to poor oral hygiene. A breeding ground for bacteria is food debris that is not removed from the child’s teeth in time. Sweets are especially dangerous. Milk and sugar are an excellent nutrient medium for the development of pathogenic flora.
If a child has a weakened immune system, the inflammatory process can drag on for a long time. The following symptoms appear with this disease:
- bleeding gums;
- swelling of the gums;
- enlargement of gum papillae.
Swelling of the gums is expressed by swelling on the child’s cheek. The cause of the tumor is an acute inflammatory process. If the gingivitis is fibrous, then the child has little or no swelling. But the papillae grow greatly, and the gums change shape. Gingivitis is a serious inflammatory disease. It has several forms and can lead to necrosis of gum tissue. If you notice signs of gingivitis, you should seek help from your dentist. Treatment of the disease is comprehensive in combination with an individual approach. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate.
The mechanism of swelling due to bruise
To effectively remove swelling on the face from a blow, first of all, you should understand how the process of its formation itself takes place. Thus, from sharp compression of tissues at the site of impact or sharp pressure, the integrity of tissues and small blood vessels is damaged. At the same time, the skin is stronger, it is usually intact, but under it, fragile vessels burst from compression, and fluid is released from the tissues.
These two factors provoke the appearance of swelling. In this case, at first the swelling is soft and in many cases quickly increases in size, and then after 8–10 hours a hematoma begins to appear. The blood under the skin hardens, the skin first turns purple, gradually turning into dark blue and then purple.
If the blow was strong, the swelling will not go away for several days. And the purple spot will increase in size for about three days and only then will begin to lose its color and go away.
What to do if swelling appears?
The appearance of swelling is an alarming signal and requires immediate action. They can significantly reduce the risk of large swelling and bruising.
So, all activities can be divided into several stages:
- urgent and immediate assistance immediately after the impact;
- consultation with a doctor is required if nausea, dizziness, or redness of the eye occur;
- treatment of edema and hematoma.
Urgent care for swelling from a bruise
It is very important to apply cold to the impact site immediately after the incident. Usually everyone advises to apply ice, but it is important to do this as quickly as possible, so it is not necessary to look for ice. You can use any cold object that is close, for example, a metal spoon. And then look for a more permanent source of cold.
The cold will stimulate the constriction of the blood vessels, which will stop the bleeding and stabilize the situation. The less blood there is under the skin, the less swelling there will be, and in the future, a hematoma (bruise).
Be sure to keep it cold for at least 1 hour. A short time will not allow the burst vessels to thrombose, and the blood will flow further, which will cause an increase in swelling and hematoma.
Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is a degenerative dystrophic disease of the oral cavity. It is not associated with inflammation. The cause of periodontal disease is a lack of minerals in the body. The process is associated with changes in periodontal tissues. The disease manifests itself in infancy during teething or during adolescence. Periodontal disease affects a child's jaws. The disease itself does not cause inflammation, but it is caused by a weakened immune system and the accumulation of bacteria.
In severe forms of periodontal disease, suppuration begins on the periodontal tissue. The gums around the tooth swell. The swelling spreads to the cheek from the tooth. What to do? See a doctor immediately. The disease leads to changes in bone tissue and tooth loss
Some tips for treatment
What should I do?
- To treat swelling on the face, use a number of ointments of pharmaceutical origin: first of all, this is Troxevasin. It will not only help relieve swelling, but also promote the resorption of hematomas. It is possible to use Heparin ointment.
- It should be remembered that most pharmaceutical ointments are designed to relieve not swelling, but a hematoma (bruise) and are of little help in treating swelling.
- Cabbage leaf with honey is good for relieving swelling. You can put the cabbage through a blender (or grate it) and mix it in a 1:1 ratio with honey. Then apply the paste as a compress for 1.5–2 hours.
- Often, grated raw potatoes are used to relieve swelling. Or even circles as a compress. The duration of the compress is from 0.5 hours to 40 minutes.
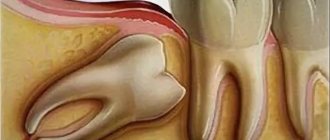
Incorrect growth of wisdom teeth
Changing teeth is a natural process and most often painless. But it happens that a tooth that has not yet appeared already hurts. This applies to eights, colloquially called wisdom teeth. They are called that because they are the last to appear. Their growth can stretch from 14 to 20 years. The appearance of the last teeth is complicated by their location. If the jaw is not sufficiently formed, growth will be difficult. Wisdom teeth cause swelling of the gums, spreading to the cheek.
If the tooth is located horizontally, then by its appearance it damages the adjacent teeth. Inflammation occurs in the area of the eighth tooth. This is due to the accumulation of food debris. Inflammation leads to swelling of the child's cheek. A damaged tooth causes pain, as well as swelling of the cheek visible to the naked eye. If the pain is severe, you should contact your dentist. The doctor will inject lidocaine and make an incision in the gum. Has your cheek become swollen after a lidocaine injection? The swelling goes away on the second day.
When to see a doctor
If you have followed all the rules, carried out all the procedures aimed at reducing swelling, and your condition continues to worsen, then this is a sure sign that you need to urgently consult a dentist. Immediate medical attention is required if:
- the next day the swelling increased, and the pain did not decrease;
- the temperature has risen, general health has worsened;
- opening the mouth is accompanied by painful sensations, and the smell of rotting from the hole is felt.
All these symptoms should prompt an immediate visit to the dentist to avoid serious consequences.
Treatment of a swollen cheek
If a child has a swollen cheek, then the first thing you need to do is find out the cause of the swelling. Only then can you decide on treatment. The most correct option would be to consult a doctor to clarify the reasons. Both medications and folk remedies are used to treat edema.
Medications
If your cheek is swollen, you need to visit the dentist. The doctor will identify the causes of swelling or refer you for examination. Only correct diagnosis is the key to correct treatment.
If a child clearly has a toothache and a swollen cheek, first aid can be provided at home. Ibuprofen relieves toothache well. It is an anti-inflammatory and antipyretic agent. It is an analgesic, perfectly relieves toothache and reduces swelling.
Amoxicillin helps fight pus. This broad-spectrum antibiotic has an antibacterial effect. It should be noted that this is only an “ambulance”. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor.
If your cheek is swollen after dental treatment, you should not rush to take any medications. The swelling was due to tissue injury. Gradually it will go away on its own. If your cheek is swollen after tooth extraction, and the swelling does not go away for a long time, you should consult a doctor. This may be due to infection in the wound. Repeated dental intervention, disinfection of the tooth socket, and antibacterial therapy will be required. Self-treatment will not help here.
Rinsing your mouth with a soda solution will help relieve pain and swelling a little. A teaspoon per glass of warm boiled water will be enough for an antiseptic solution. The frequency of rinsing depends on the degree and nature of the pain. If necessary, you can repeat every hour.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers its own means of combating swelling on the cheeks.
If a child has had a tooth removed, his cheek is swollen and needs help, traditional medicine recommends rinsing with herbal decoctions. For this, oak bark and chamomile flowers are traditionally used. Nettle, sage, and calamus have a good effect. Raw materials can be used both fresh and dried. Brew 1 tsp of the selected product with a glass of boiling water and allow to cool. It is necessary to rinse several times a day. In the absence of herbal ingredients, you can simply rinse with a solution of baking soda mixed with table salt in equal proportions.
Traditional medicine recommends compresses. For them, tea tree or sea buckthorn oil, propolis, and Kalanchoe juice are used. A cotton swab is moistened in the chosen product and placed between the cheek and gum. Keep it for half an hour. For a compress, you can simply use an aloe leaf, which should first be kneaded. Propolis cake gives good results.
Garlic and onion lotions are a very old remedy. A crushed clove of garlic mixed with a chopped piece of onion is poured into 50 ml of boiling water and allowed to cool. It is recommended to apply the lotion on both sides. A tampon is moistened in this decoction and applied to the inside of the cheek. At the same time, a moistened napkin is applied externally. Attention! Under no circumstances should you use fresh onions and garlic. The juice of these plants contains strong acids that burn the mucous membrane. For the same reason, it is unacceptable to apply tampons with iodine.
Tip No. 2: monitor the state over time
If your cheek is swollen from a tooth, this is not always a reason to panic. Often, minor swelling is considered a normal reaction of the body to surgical intervention and medical manipulations by a doctor. For example, such as removing the pulp or the tooth itself, treating advanced periodontitis, placing medications in the tooth canals, and injecting an anesthetic. Swelling of the cheek could be a consequence of dental implantation or surgery to increase jaw bone tissue. Indeed, in all of the above situations, the specialist acted on living tissues, nerve endings, blood vessels and capillaries.
Remember that swelling of the soft tissues is considered normal during the first 2-4 days after exposure to a traumatic factor (treatment, surgery), then it should subside. During these periods, it is best to monitor your condition over time and pay attention to accompanying symptoms.
Minor swelling of the soft tissues of the face may be associated with the eruption of baby and permanent teeth in children. In this case, it is better to consult a specialist in order not to miss a serious inflammatory process and to correctly distinguish the pathology from diseases with similar symptoms (mumps, bacterial infections of the upper respiratory tract1, inflammation of the lymph nodes).
The reason for an emergency visit to a doctor should be a sharp deterioration in health: an increase in body temperature several days after treatment, the appearance of bad breath, difficulty breathing, increased swelling, severe pain. In all other cases, there is no reason for an unscheduled visit to the clinic, and measures taken at home, which we will discuss below, will help cope with swelling.
The tumor should always be monitored over time
“A month and a half ago I had the following problem: my cheek was swollen and there was a sharp pain. True, I almost immediately guessed what was wrong and went to the dentist. Three years ago, my wisdom tooth began to grow; on an x-ray, the doctor determined that it was growing into my cheek, and even then he suggested removing it. I refused because... I hoped that there would be no problems, and if there were, I would quickly deal with them... Then the doctor warned that at least once every six months I need to take an x-ray and see what’s wrong with this tooth. But, naturally, I gave up on this. All this time I did not go to the dentist at all. And here you are... The tooth had to be removed urgently, due to acute inflammation. It took a very long time to heal, I had to take antibiotics. I even had to take sick leave for a week, I felt so bad. Now I think that I waited in vain, then I suffered so much.”
Markov Alexander, review from 32top.ru
Symptoms that require you to visit a doctor
The child's cheek is swollen. When should you see a doctor?
A number of symptoms can lead you to decide which specialist to visit:
- The cheek is swollen, but the reasons for the swelling are unclear. Contact your pediatrician immediately.
- The upper cheek is swollen, the eyes are red and watery, and a suffocating cough is tormented. If facial swelling is accompanied by at least one of the listed symptoms, you should visit an allergist.
- The cheek is swollen, the condition is aggravated by diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, and fever. These are direct indications of infectious mumps, called mumps. You need to quickly call a doctor at home.
- The child's cheek is swollen in the lower part and his tooth, gums, and jaw hurt. You need to visit the dentist as soon as possible.
- The cheek is swollen, the child shows increased activity, has trouble falling asleep, often cries, and is capricious. You need to visit a neurologist. The problem is related to a nervous disorder.
- The cheek is swollen; upon palpation, pain is felt behind the ear or in front of it. Need an ENT consultation.
- Swelling of the cheek is accompanied by pain in the lumbar region of the back. It is associated with kidney disease. You should visit a nephrologist.
- The swelling of the cheek was due to injury. This is the field of activity of a traumatologist or maxillofacial surgeon.
You should always remember that you can treat yourself only when the diagnosis is precisely known. In other cases, any medications can be used only after consultation with a doctor.
Medications to relieve swelling from the face after a stroke
The resulting swelling should be shown to a traumatologist so as not to miss serious complications.
Reason to see a doctor:
Extensive area of edema;
The impact damaged the eye;
Combination of injury with fever, dizziness, headache, unusual sensations;
Swelling persists for 3-5 days.
If there are no serious symptoms, you can try to remove the swelling from the face after the blow yourself. For this purpose medications are used:
Ointments with Arnica, Comfrey, Larkspur;
A proven remedy for eliminating swelling is Badyaga, the skeleton of a freshwater sponge crushed into fine powder. When using all medications, you should take into account contraindications for use and carefully follow the instructions. With proper use of these gels and ointments, you can reduce the duration of swelling by several days.
Prevention
Regardless of why the cheek swells and what are the causes of its swelling, it is necessary to follow simple rules to prevent diseases of the oral cavity. Basic preventive measures:
- Compliance with oral hygiene procedures. It is necessary to brush your teeth for at least 10 minutes 2 times a day. It is worth using dental floss to remove food debris and plaque. Remove plaque as thoroughly as possible, it creates an optimal environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microbes.
- Regular visits to the dentist. A visit to a specialist will help prevent many diseases, identify existing problems, and avoid complications. The dentist will conduct a professional examination of the oral cavity and professional teeth cleaning. If necessary, a set of therapeutic measures will be prescribed.
- Balanced and rational nutrition. A nutritious diet strengthens the body, ensures it is saturated with necessary elements, which has the most beneficial effect on the health of teeth and gums. Resistance to harmful microorganisms and the ability to restore soft and bone tissues increase.
- The use of vitamin complexes that restore the balance of nutrients and elements, replenishing their deficiency.
- Physical exercise. Physical activity improves the general condition of the body, strengthens the immune system, enhances metabolic processes, and improves the functioning of all systems.
- Healthy psycho-emotional background. Many unpleasant symptoms occur against the background of psychoemotional disorders, including neurological pain and swelling in the face.
- Regular visits to a therapist will help cure diseases that provoke inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, disorders of the regenerative ability of bone tissue, and dental problems.
The condition when swelling of the cheek area occurs can be caused by a number of reasons. It is necessary to contact a doctor immediately to find out and eliminate the factor that caused the swelling and prevent possible complications.