Leptothrix: methods of diagnosis
If this infection is suspected, tests for leptothrix are mandatory.
This is due to the fact that the pathogenic microorganism provokes symptoms similar to many other STDs.
It is impossible to make a diagnosis based solely on symptoms.
Diagnosis begins with the doctor interviewing the patient.
It is specified how long ago the complaints appeared, how severe they are, and whether they cause severe inconvenience.
The doctor also clarifies what the person associates with the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Inspection of the genital area is considered mandatory.
Women are examined on a special chair; men are examined without one.
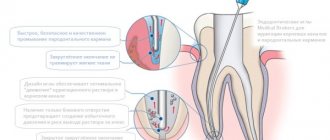
A series of tests are prescribed.
Among them:
- taking a smear, which is then examined in various ways depending on what infection is suspected of causing adverse symptoms
- inoculating urine on nutrient media, which often serves as an alternative to smear in representatives of the stronger sex, for whom the procedure can be quite traumatic
- You can also evaluate venous blood using a PCR test, but if leptothrix is suspected, the technique is practically not used
If microorganisms are detected, the patient must be tested for other STDs.
Leptothrix in gynecology
Leptothrix is often found in the urogenital system in women.
This bacterium lives in the vagina.
It may be part of an opportunistic flora.
But it is contained in small quantities.
In an ideal state of the vaginal biocenosis, the number of all anaerobic bacteria does not exceed 1% of their total number.
Among these anaerobes there is also a place for Leptothrix.
With such a small amount, these bacteria are not detected in a smear by microscopy and do not cause pathological processes.
Most often, leptotrichosis of the vagina is detected against the background of bacterial vaginosis.
The disease is manifested by discharge and the appearance of gray or white spots on the walls of the vagina.
The doctor discovers them during examination.
It is from these areas of the mucosa that smears are taken, in which leptothrix is detected.
An increase in the number of anaerobes can be caused by:
- taking antibiotics
- decreased immunity
- suffered serious illnesses
- lack of sufficient vaginal hygiene, or, on the contrary, excessive hygiene with frequent use of detergents containing antibacterial components
When lactobacilli die, anaerobic microorganisms take their place.
The vaginal pH shifts.
Lactic acid and hydrogen peroxide are not produced.
Therefore, the female genitourinary system becomes vulnerable to infections.
A woman easily becomes infected with sexually transmitted diseases through sexual intercourse.
Nonspecific inflammation is often associated.
Bacterial vaginosis associated with Leptothrix occurs without treatment for years.
Self-healing is unlikely.
Anaerobes occupy most of the biocenosis and do not allow lactobacilli to recover.
Therefore, only antibacterial treatment helps to normalize the composition of the vaginal microflora.
After it is carried out, probiotics are prescribed to populate the vaginal environment with “useful” microbes.
Treatment of leptothrix
Treatment still remains a challenging gynecological task.
There are still no special drugs or techniques aimed at getting rid of this pathology.
Therapy for the development of symptoms of vaginosis in women is based on the use of antibacterial drugs.
In each case, antibiotics are selected individually with the expectation of having the maximum effect on a specific strain of infection.
In addition to antibacterial therapy, immunostimulants are prescribed that can help the body fight microorganisms that harm it.
Post-treatment tests are required.
Only with their help can you be sure that the microorganism will no longer bother the woman.
In addition to antibiotics and immunostimulants, the doctor may prescribe the following medications to the patient:
- antihistamines that will help overcome itching in the genital area and reduce burning sensation
- local disinfectants whose task is to prevent infection by other pathogens
- anti-inflammatory medications that will help if the patient has severe inflammatory symptoms
- when taking antibiotics, pre- and probiotics are recommended to prevent disruption of the intestinal microflora
- Terzhinan, like other local suppositories, can also be used to cope with the infectious process
Treatment of dermatitis
Based on the results of microscopic examinations and studies of the immune status, the clinical picture of patients with seborrheic, oral dermatitis and leptotrichosis, it is necessary to use complex therapy .
To treat mucous membranes, bacteriophages (staphylococcal, complex) and antiseptic solutions (Betadine and Miramistin) are used by application to the tongue or for rinsing the mouth, as well as antimycotic (Orungal, Lamisil) and antiparasitic (Trichopol, Dekaris) therapy orally.
To treat skin inflammation, antibacterial (Metrogyl) and antifungal (Nizoral, Triderm, Akriderm GK, etc.) drugs are used in combination.
Source
Leptothrix during pregnancy
This is a serious reason to worry about both the health of the fair sex and the health of the unborn child developing in her womb.
After all, the activation of this opportunistic pathogen often indicates that the body has some other sexually transmitted disease.
Naturally, it is recommended to get tested as soon as possible.
Leptothrix provokes inflammatory processes in the genitals.
Naturally, their presence adversely affects the course of pregnancy.
As a result, a successfully proceeding process can end in the fading of pregnancy or miscarriage.
Or the development of an intrauterine infection in the fetus, which will adversely affect all organs and systems of the future person.
Treatment of pathology is not fundamentally different from the case if therapy is necessary for an ordinary woman.
True, doctors select medications that will cause the least harm to the body of the fair sex.
The negative impact of a number of medications on the fetus is also taken into account, which also affects the choice of medication.
Leptothrix in the mouth
Very often, leptothrix filaments are detected when taking a swab from the mouth.
This bacterium is normally present in the oral cavity during childhood.
It is detected in 40% of children under 1 year of age.
But adults should not have leptothrix in their mouths.
Because its presence provokes inflammatory processes and negatively affects the condition of the teeth.
Leptotrichosis usually develops against the background of immunodeficiency.
It is considered a disease close to opportunistic mycoses.
Often develops in HIV-infected people at the AIDS stage.
Also, leptothrix of the tongue can occur against the background of chronic diseases of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract.
In most cases, the patient himself does not feel anything when this disease occurs.
He has no complaints or complains of a slight burning sensation.
It is noted on the tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks.
Upon examination, the doctor finds areas of white or gray plaque.
They cover all structures of the oral cavity.
There are no obvious signs of inflammation.
Leptothrix clusters can be seen with the naked eye.
They look like small (pinhead-sized) white dots.
Plaque cannot be removed easily.
When scraped, the plaque is removed, but underneath it reveals inflamed, loose, sometimes bleeding mucosa.
Leptothrix in men
It is diagnosed very rarely in representatives of the stronger sex.
The cases can be called exceptional.
They are mainly associated with a strong decrease in the body's immune system.
In most cases, a man’s urogenital tract simply does not allow the microorganism to fully adapt and begin to cause damage to epithelial cells.
However, if this does happen, first of all the patient complains of the same symptoms as the fair sex.
Noteworthy are foul-smelling gray discharge, pain when urinating and other unpleasant symptoms.
Treatment for men is no less important than for women.
You cannot hope that the pathology will somehow resolve itself.
You need to seek help from a doctor.
The doctor will prescribe antibacterial therapy, which, depending on the severity of the pathology, can be either local or systemic.
The main thing is that the patient, having received recommendations, does not neglect them.
The role of leptotrichia in the clinical course of seborrheic dermatitis and principles of treatment
Seborrheic dermatitis is one of the pressing problems of dermatocosmetology, as there is a constant increase in this disease, causing a significant cosmetic defect in the form of thickening of the stratum corneum, oily sheen and peeling of the skin, accompanied by itching. In recent years, the role of Leptotrichia bucalis has been shown in the occurrence of seborrheic dermatitis. Seborrheic dermatitis is based on a chronic inflammatory skin disease associated with an increase in the quantity and change in the quality of sebum with localization in those areas of the scalp and body where the sebaceous glands are developed - the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, naso-buccal folds, ears, behind-the-ear spaces, anterior chest area and interscapular area. When the skin of the scalp is affected, thinning and thinning of the hair is observed, very often accompanied by small flour-like or large-plate white scales. You can often see yellowish scales - crusts and hemorrhagic crusts formed as a result of scratching, when the skin of the forehead, behind-the-ear areas, and the area of the ear canals is involved in the process. Macular-erythematous elements, plaques, and papules appear on the smooth skin of the face, back, and chest. A genetic predisposition to certain metabolic characteristics and environmental influences on the development of the disease cannot be ruled out.
The leading role in the pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp and dandruff is assigned to the pathogen Pityrosporum - yeast-like lipophilic fungi. These fungi are a permanent component of the microflora of healthy skin in more than 90% of the population with tropism around the sebaceous glands, because use the secretion of the sebaceous glands for their growth and development. Pityrosporum ovale or according to another classification Malassezia futur is more often found on the scalp. Pityrosporum orbiculare - on the skin of the trunk and face. Stressful situations worsen the course of seborrheic dermatitis due to changes in hormonal levels and metabolic disorders. The level of secretion and qualitative composition of sebum is determined by genetic and hormonal factors. Seborrheic dermatitis occurs more often in men than in women.
The most “problematic” category of patients are men aged 45–50 years. Obviously, this is due to hormonal imbalances in the form of decreased testosterone levels. In the overwhelming majority of such patients, we also observed liver dysfunction - from the phenomena of fatty hepatosis to minimal changes in the form of slight hyperbilirubinemia, fluctuations in the level of liver enzymes. Thus, the above reasons lead to the spread and increase in the number of previously saprophytic microorganisms and the development of foci of inflammation with disruption of the immune skin response, sebum secretion and keratinization of the epidermis.
In recent years, the interest of dermatovenerologists in anaerobic microorganisms, namely bacteria of the genus Leptothrichia and Leptothrix, has increased. According to the ninth edition of Bergey (1993), leptotrichia are assigned to the kingdom Procaryotae, division 1 Gracilicutes, family Bacteroidacea, genus Ltptotrichia, type species Leptotrichia bucalis, inhabitant of the human oral cavity. Leptotrichia look like straight or slightly curved rods with a diameter of 1.0 - 1.5 microns with pointed or rounded ends. Grammar, motionless. Two or more cells unite into septate filaments up to 200 microns thick and intertwine with each other, forming “felt”. In the micropreparation, filamentous rods consist of alternating light and dark areas, reminiscent in their structure of transverse striations (“slagbaum”).
With prolonged parasitism of leptotrichia on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and genital organs, leptotrichosis infection leads to a general decrease in the resistance of the macroorganism, which is a trigger factor in the development of seborrheic dermatitis.
Diagnostics. Scrapings from the lesions are studied. The main criterion for diagnosing leptotrichosis lesions is the detection of the pathogen (10-15 bacteria in all fields of view) with the presence of inflammatory elements (leukocytes, histiocytes). Without the absence of inflammatory elements, it should probably be considered a bacterial carriage, which, under certain conditions of the macroorganism, can transform into a leptotrichosis infection. The tonsils, the lateral and posterior parts of the pharynx, the tongue, and the vaginal part of the cervix are mainly affected. Leptotrichosis is a pseudomycotic lesion of the oral mucosa. Objectively: a grayish-whitish coating initially appears on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, tongue, arches of the soft palate and on the mucous membranes of the genitals, transitioning to a light brown, brown color, which cannot be easily removed with a spatula.
The diagnosis of the disease is made on the basis of characteristic clinical data and the microscopic picture of the specimen stained according to Romanovsky-Giemsa. We studied the role of leptotrichosis infection in the pathogenesis and clinical picture of seborrheic dermatitis: microscopy of leptotrichia, immunological parameters, the influence of complex treatment with immunocorrective and specific therapy on the clinical picture of seborrheic dermatitis in combination with leptotrichosis. Under our supervision in 2021 there were 49 patients with seborrheic dermatitis, in 2021 - 32.
Microscopy revealed spores and pseudomycelium of the genus Candida in scrapings from the mucous membrane of the hard palate - 29 patients, and leptotrichia with elements of inflammation from the tongue in 38 patients. Therefore, the correct interpretation of bacterioscopic preparations should be carried out, taking into account that the treatment of candidiasis and leptotrichosis is not the same. Under microscopy, the filaments of Leptothrix are often straight, do not branch, do not bud, and do not have fruiting organs. The abundance of leptothrix in all fields of vision, in combination with active exudation on the surface of leukocytes, is regarded as leptotrichosis. In patients with seborrheic dermatitis, microscopy of the tongue revealed leptotrichia. As a result of mycological studies of pathological material of the smooth skin of the face, neck, chest, back (scales in patients with seborrheic dermatitis, contents of elements), piterosporal fungi were found in 17 patients out of 39 patients with leptotrichosis. It has been established that the bulk of the studied immunological parameters in patients do not undergo significant deviations from the parameters of healthy individuals and lie within the limits of individual fluctuations, and only the phagocytic activity of neutrophils is significantly suppressed. The phagocytosis process averaged 45 + 8.7 with a norm of 58 + 7.1, the phagocytic number was 1.33 + 0.11 with a norm of 3.8 + 1.1, and the completion rate was 1.5 + 0.14 with a norm of 1.9 +0.7.
Treatment Based on the results of microscopic examinations and studies of the immune status, the clinical picture of patients with seborrheic dermatitis and leptotrichosis, complex therapy was used. For treatment, staphylococcal and combined bacteriophage were used by applying to the tongue or rinsing the mouth with 20 - 40 ml 1-2 times a day. The course of treatment is 8-10 days. Alternating applications of Betadine liquid to the tongue were carried out: bacteriophage in the morning, Betadine liquid in the evening. Immunoglobulin was administered parenterally 1-2 times a week. The course of treatment included 5 injections. All patients received specific therapy. It included the following drugs: Trichopolum 0.25, 2 tablets 2 times a day for 10 days, or Tiberal 1 tablet 2 times a day for 14 days. Patients with combined flora received antimycotic treatment. Of the 39 patients, 32 achieved clinical cure, which consisted of complete cleansing of the affected areas from plaque and elimination of subjective complaints. Erythema and inflammatory rashes on the smooth skin of the face and trunk resolved, hyperkeratosis decreased, and the feeling of itching disappeared. In 7 patients, the plaque became softer and was easily removed.
During a control microscopic examination after treatment, no leptotrichia were found in 29 patients, and single leptotrichia in 10 patients. These patients received a repeat course of specific therapy. Combinations of drugs were prescribed: miramistin, clotrimazole solution, sporobacterin, as well as thymogen, myelopid, decaris, nizoral, orungal. Metrogyl gel, 2% nizoral cream, clotrimazole, lamisil, lotion and cream “Elocom” and “Elocom-S” were used as local forms.
No relapses of the disease were detected during the observation period. Observations were carried out over time after 1, 3, 6 months. When studying the immune status over time, there is a tendency towards normalization of immunogram parameters within 3 months. Consequently, the results of the complex method of treating patients with seborrheic dermatitis and leptotrichosis that we use are quite effective and pathogenetically substantiated, which must be taken into account when choosing a method of treating these diseases.
Leptothrix: what complications to expect
Leptothrix is a disease that may not show any signs of itself for a long time.
In this case, the pathogenic microorganism will cause harm to the body, which will be extremely difficult to resolve in the future.
Any inflammatory process in the genitourinary system, first of all, negatively affects reproductive functions.
Both women and men face infertility.
Infertility is difficult to treat, especially if its cause is opportunistic microorganisms.
In addition to infertility, the patient may face:
- impotence, which can be caused by both prostate and testicular damage
- decreased libido in the fair sex, which is explained by discomfort during sexual intercourse, lack of pleasure
- damage to the child’s body if the disease is diagnosed in a woman during pregnancy
- if the oral cavity is affected, tooth decay, inflammatory diseases of the gums and oropharynx are possible
Leptothrix in women and the stronger sex is not a harmless infection that can be ignored.
Adequate therapy for exacerbation of the disease is mandatory!
Leptothrix in a smear - what is it?
Leptothrix can be detected in urogenital or oropharyngeal smears.
This bacterium can be seen under a microscope.
It consists of thin threads with segmented ends.
During microscopy, the laboratory technician notices long chains in the form of dots and dashes.
Leptothrix does not always cause inflammation.
But in some cases they are possible.
The bacterium exhibits pathogenicity most often in the presence of other microorganisms.
It intensifies inflammatory processes against the background of sexually transmitted infections.
It is also one of the causative agents of bacterial vaginosis.
When it enters the oral cavity, leptothrix provokes inflammation of the gums, tonsils, and tongue.
May lead to darkening and destruction of tooth enamel.
Tests for leptothrix
Leptothrix is not at all difficult to detect.
This bacterium is visible under microscopy.
In most cases, targeted testing for leptotrichosis is not carried out.
The pathogen is identified during a bacterioscopic examination.
A swab is taken from the mouth or vagina of women.
Gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria are found in the clinical material.
They form chains in the form of alternating dots and dashes.
In turn, the detection of leptothrix is the reason for a more in-depth examination of the patient.
Because the presence of this microorganism is an indicator of other diseases.
Against the background of leptotrichosis, the following are very often detected:
1. Sexual infections.
In approximately 60% of cases, along with leptothrix, a thorough examination of the patient reveals candida, ureaplasma, trichomonas, chlamydia or other pathogens.
Therefore, all women diagnosed with leptotrichosis are prescribed a smear from the urethra, vagina and cervix for sexually transmitted diseases.
PCR is mainly used for diagnosis.
2. Bacterial vaginosis.
It can be diagnosed by microscopy alone, which is supplemented by an amino test.
Bacterial vaginosis is said to occur when leptothrix and other anaerobic flora significantly outnumber lactobacilli.
Vaginal dysbiosis is considered a condition when the number of lactobacilli is less than 90%.
To clarify the state of the biocenosis, seeding or PCR may be prescribed.
3. Immunodeficiency states.
Leptothrix is considered an indicator of reduced immunity.
This is because in most patients, Leptothrix does not cause symptoms and does not multiply to the point of being detected by microscopy.
If this happens, it is likely that the immune system has failed.
It cannot inhibit the proliferation of the microorganism.
Therefore, patients diagnosed with leptothrix are often tested for HIV.
All patients are recommended to consult an immunologist.
The doctor may order an immunogram.
Based on this, the presence or absence of immunodeficiency is determined.
If necessary, immunocorrection is carried out in the future.
Occasionally, PCR or tank culture is used to detect leptothrix.