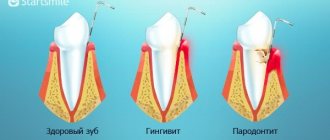
Destructive processes in the periodontium cause tooth loss. Periodontal disease is considered the most dangerous disease, as it develops unnoticed by the patient, up to irreversible changes. During the disease, the alveolar part of the jaw gradually collapses, gum recession occurs, the teeth begin to loosen, shift, forming interdental gaps, and the bite is disturbed. If the pathology is not treated, it will lead to the loss of teeth or a whole row.
The disease can cause the development of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to a violation of normal nutrition. Due to loose teeth, patients try to eat soft foods; the amount of valuable organic compounds and minerals is reduced. This, in turn, has a negative impact on the health of the entire body.
Reasons for the development of the disease
It is difficult to identify what causes periodontal disease, since the pathology develops due to internal disorders in the body. Tissue atrophy often occurs due to oxygen starvation and lack of nutrients. External factors influence the disease indirectly.
Periodontal destruction occurs against the background of:
- hormonal disorders, disruptions during pregnancy, menopause, puberty in adolescents;
- low level of immunity for a long time;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- malocclusion;
- trauma to dental tissues (fracture, bruise), poor-quality prosthetics;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- unbalanced, poor nutrition, deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- metabolic disorders, diabetes;
- long-term use of medications;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- heredity, genetic predisposition;
- serious diseases: atherosclerosis, HIV infection, oncology, autoimmune pathologies and other diseases.
The answer to the question of whether periodontitis is contagious is obvious - it is not contagious. It is not associated with infection, and therefore the patient is absolutely safe for people.
Local drug therapy for periodontal diseases
Local drug treatment of periodontal diseases includes the use of agents that affect etiological factors, pathogenetic mechanisms and symptoms of diseases. The dosage forms are dosed, the methods of using the drugs are adapted to local use. Medications can be used in the form of rinses, irrigations, gum dressings, and treatment plates.
As etiotropic treatment, antibacterial drugs are used that act on the cause of the disease and prevent secondary infection. Antiseptics are most often used (2-3% hydrogen peroxide solution; chlorhexidine digluconate - 0.05%; lizoplak; chlorophyllipt; iodinol; lozenges - ambazon, sebidine). Antibiotics can be used in the form of rinses, applications or parenterally (tetracycline ointment; synthomycin emulsion; gramicidin - 2% solution; microcide; levovinisol - aerosol; 0.1% gentamicin sulfate ointment; lincomycin - parenterally). Less commonly used are sulfonamides (streptocide - in the form of a powder; ingalipt - an aerosol), drugs of the nirofuran series (0.02% aqueous solution or 0.2% furacillin ointment).
Pathogenetic treatment consists of the use of anti-inflammatory drugs - non-steroidal (sodium mefenamate in the form of a paste, ointment; romazulan; 10% methyluracil ointment; etonium), steroidal (0.5-2.5% hydrocortisone, 0.5% prednisolone ointment, lorinden, dermosolone). These same drugs have an anti-edematous effect.
Oil solutions of vitamins A, E, rosehip oil, carotoline, AEvit, methyluracil, solcoseryl, vinylin have epithelializing and reparative effects. Galascorbine and calcium salts help reduce the permeability of the vascular wall.
The most effective is the use of broad-spectrum agents. Thus, etonium, dimexide, parodium, eludril have anti-inflammatory, local anesthetic, antimicrobial, and epithelializing properties.
Symptomatic treatment includes painkillers: parenterally (in the form of infiltration or conduction anesthesia), application in the form of solutions, ointments, aerosols (5% anesthetic ointment, 1% pyramecaine ointment, etonium, pharmacoethyl).
Local hemostatic drugs are used for appropriate indications (galascorbin, hemostatic sponge, bioplastic, capramine, racestiptin, hemocollagen, hemofibrin).
Proteolytic enzymes are used when it is necessary to soften and remove plaque (trypsin, chymotrypsin, chymopsin, papain).
Parodium paste (Pierre Fabre), containing chlorhexidine and rhubarb extract, is applied in a layer of 0.2-0.5 mm along the marginal gum and compacted with a tampon.
Therapeutic paste-bandage for the treatment of periodontal vitadont (“VladMiVa”) based on lecithin contains a complex of natural antioxidants, vitamins C, E and beta-carotene. The paste is applied to the dried mucosa, into the periodontal canals and to the edge of the gums and left for several hours.
Wokopak paste (VOKO) is used in the treatment of periodontitis, after gingivectomy and other surgical interventions.
Diplen-denta (“Nord-Ost”) - plates for the treatment and prevention of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. Several types are available: diplendenta X - with chlorhexidine; diplendenta HD - with chlorhexidine and dexamethasone; diplendenta LH - with chlorhexidine and lidocaine; diplen-denta G - with gentamicin; diplen-denta L - with lincomycin; diplen-denta M - with metronidazole; diplendenta F - with sodium fluorine and chlorhexidine; diplen-denta C - with solcoseryl.
KP-plast (“VladMiVa”) - self-absorbable plates measuring 50×80 mm for the treatment and prevention of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. They produce several types: KP-plast-phyto contains natural polysaccharides, extracts of chamomile, yarrow, calendula, vitamin C, plasticizers and antioxidants; KP-plast-vita - a plate based on natural polysaccharides, also contains vitamins C, E and beta-carotene; KP-plast antimicrobial - a plate based on natural polysaccharides and polypeptides, contains chlorhexidine and metronidazole; KP-plast-anesto - a plate with anesthetic and vitamins; KP-plast-hemostatic. To use, cut off the required fragment of the plate and place it on the affected area of the gum. Hold it for 1 hour. The course consists of 10 daily applications; if necessary, the course is repeated after 10 days.
Septo-Pak (“Septodont”) is a protective bandage for gums that contains amyl acetate, butyl phthalate, zinc oxide and zinc sulfate. Can be used with medications for local periodontitis and after periodontal surgery.
Solcoseryl dental adhesive paste (“Solko”) contains an extract from cattle blood (2.125 mg per 1 g of paste) in combination with polidocanol (a local anesthetic). A strip of paste 0.5 cm long is applied, without rubbing, to a previously dried area of the mucous membrane and lightly moistened with water. The procedure is repeated 3-5 times a day after meals and before bedtime. When treating bedsores from removable dentures, the paste is applied to a dry denture and moistened with water. Per course - 5 g (1 tube).
Differentiated choice of means and methods of treatment
Treatment of herpetic gingivitis is aimed at etiopathogenetic factors and takes into account the severity of the disease. Complex therapy includes general and local effects. From the first days of the development of the disease, it is necessary to use antiviral ointments (0.25% oxolinic; 0.25-0.5% florenal; 0.25-0.5% tebrofen; 50% interferon; 0. 25% bonaftone; 0.75% glycerin; 0.25% riodoxol; 1% alpizarin; 1% helipelin). Modern antiherpetic drugs are especially effective: acyclovir ointment, herpevir, 2% solution of Zovirax. They are recommended to be used repeatedly (3-4 times a day) after antiseptic treatment of the oral mucosa.
It is advisable to use painkillers when treating oral mucosa: 5% anesthetic emulsion, 1% pyromicaine ointment. Herbal medicinal preparations are used as antiseptics: warty birch (buds, leaves, sap), Scots pine (pine buds, resin, needles), eucalyptus leaves, colanchoe juice, calendula; collection "Elekasol" (chain grass, chamomile flowers, licorice roots, sage and eucalyptus leaves, calendula flowers). These agents have epithelializing, anti-inflammatory, antimycotic and antiviral effects against the herpes virus.
It is advisable to use painkillers when treating oral mucosa: 5% anesthetic emulsion, 1% pyromicain ointment.
During the period of extinction of the disease, keratoplasty preparations acquire leading importance: rosehip and sea buckthorn oil, carotolin, solcoseryl ointment and jelly, vinylin, oil solution of vitamin A, E, “Gipozol”, “Vinizol”.
General treatment of herpetic stomatitis should be carried out for moderate and severe forms of acute stomatitis. In the first stages of the disease, antiviral drugs are prescribed according to the age-specific dosage: bonafton 0.1, alpizarin 0.1, helipin 0.1, 2 or 4 tablets per day for 5-10 days. Acyclovir (Gerpevir, Verolex, Ciclovir) has high selectivity for the herpes virus and low toxicity. Adults need to take 200 mg of acyclovir 5 times a day every 4 hours. For children under 2 years of age, the drug is prescribed 100 mg 5 times a day, and after 2 years of age, adult doses are prescribed. Timely administration of medications leads to a reduction in future relapses of herpetic diseases.
During the height of the disease, physiotherapy is usually prescribed: ultraviolet irradiation, GNL, the use of percutaneous laser biostimulation of blood. In the complex of general treatment, hyposensitizing therapy (suprastin, diazolin, tavegil, pipolfen and others) is carried out in age-appropriate doses. Complex therapy includes agents that stimulate the immune system: lysozyme - 75-100 mg daily for 5-10 days; human leukocyte immunoglobulin and antiherpetic immunoglobulin 1.5-3.0 ml 1 time every 3-4 days (2 or 3 injections); leukocyte interferon, cycloferon 2.0 - 1 time per day (1, 2, 4, 6, 8 days); Thymalin; methyluracil, sodium nucleinate, decaris (levamisole), echinacea preparations (immunal, estifan).
During the height of the disease, physiotherapy is prescribed: ultraviolet irradiation, GNL, the use of percutaneous laser biostimulation of blood.
Rational nutrition involves the introduction of a sufficient amount of fluid: liquid, non-irritating, high-calorie foods.
Acute gingivitis with severe bleeding
Treatment begins after identifying the common cause with training in individual oral hygiene and recommendations on the choice of hygiene products: a soft toothbrush, non-abrasive toothpaste. Mouth rinsing involves the use of solutions that have an antibacterial effect. Hemostatic agents are used for appropriate indications in the form of applications (hydrogen peroxide, capramine, alascorbine, aminocaproic acid), treatment plates (KP-plast-hemostatic), hemostatic sponge, capramine, hemocollagen, hemofibrin.
Professional hygiene is carried out sparingly, in individual segments of the jaw, followed by the application of drugs that reduce bleeding. In the process of removing dental plaque, abundant irrigation of antiseptic solutions is performed (chlorhexidine 0.05%; furatsilin 1:5,000). In case of severe pain, pain relief is performed: application or injection. For use at home, lozenges (Sebidine, Faringosept, Drill) can be prescribed.
In the presence of local traumatic factors, overhanging edges are ground down, prostheses are corrected, etc.
General treatment is prescribed by an internist in accordance with the general condition of the patient.
Local treatment of ulcerative gingivitis
Includes the prescription of pain-relieving applications (2% oil solution of anasthesin, 1% pyromicaine ointment), lysozyme baths (1 glass of boiled water, the white of 1 egg and 1/4 part of a teaspoon of salt), rinsing with herbal decoctions (chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula), 0.5-1% aqueous solution of galascorbine, romazulan, chlorophyllipt. To cleanse the surface of ulcers and erosions from necrotic plaque, it is possible to use enzymes (trypsin, chemotrypsin, pancreatin).
When epithelialization begins, it is necessary to use agents that promote reparative processes in tissues (carotolin, sea buckthorn and rosehip oil, vinylin, vinylsol, solcoseryl ointment and jelly, etc.), immunostimulants (1% sodium nucleinate solution, 5% methyluracil ointment) .
Prevention of exacerbations consists of eliminating microtraumas of the oral mucosa, allergens that cause hypersensitivity of the body, prescribing desensitizing agents, restorative therapy, hardening the body. Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment include ultraviolet irradiation on the lesions (5-6 biodoses), low-intensity radiation from a helium-neon laser (HNL) at a power of 100 mW/cm2 for 2 minutes, number of fields no more than 5, course up to 10-15 sessions. In severe cases, supravenous irradiation of GNL blood is indicated for 20 minutes, for a course of 10 sessions (repeat twice a year in the inter-relapse period) of magnetic autohemotherapy (blood taken from a vein into a syringe, placed for 10-15 minutes in a magnetic field, after training injected intramuscularly 8-10 injections).
Prevention of exacerbations consists of eliminating microtraumas of the oral mucosa, allergens that cause hypersensitivity of the body, prescribing desensitizing agents, restorative therapy, and hardening the body.
Treatment of desquamative gingivitis
Includes the elimination of locally irritating factors, professional hygiene, and training in individual oral care. The patient is recommended to choose a soft toothbrush, interdental teeth cleaning products, and a non-abrasive paste, preferably in the form of a gel, based on herbal preparations. Local drug treatment involves the use of drugs that have an epithelializing effect: oil solutions of vitamins A, E, rosehip oil, carotoline, AEvit, methyluracil, solcoseryl, vinylin. These same drugs stimulate the regeneration of connective tissue. Oil solutions of vitamins A, E, carotoline are used in the form of applications 3-5 times a day. In the form of rinses, you can prescribe medicinal elixirs and herbal infusions (sage, chamomile).
The sensitivity of the gums to irritants is an indication for the prescription of painkillers. In the form of applications, you can use a 5% anesthetic emulsion, 1% pyromecaine ointment. It is recommended to eat bland food. Vitamin therapy is indicated.
General medications are prescribed by an internist in accordance with the identified diseases. Along with drug treatment, laser therapy is recommended. Irradiation technique: remote, stable, light guide with a conical attachment is located 3 mm from the gum surface, the diameter of the light spot is 3 mm. Physical parameters: LILI in the red range of the spectrum, power 5 mW, PPM ~ 70 mW/cm2, exposure 40 seconds, radiation dose per field 2.8 J/cm2, 10 irradiation fields per session. The course of treatment is 10 sessions.
Treatment of periodontitis
In mild cases, it is limited to local influences (in the absence of a common etiological factor). General strengthening drugs (vitamins) and an adaptogen (Eleutherococcus in microdoses) may be prescribed.
Motivation and training in individual hygiene is carried out on the first visit. Depending on the clinical situation, a toothbrush, interdental agents and toothpaste are selected. If dense plaque is detected and there is no bleeding gums, a high-hardness brush is recommended, and an abrasive paste is recommended.
In other cases, choose a brush with medium-hard bristles and a therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste, including ingredients with an anti-inflammatory effect (Elgidium).
Professional hygiene is carried out by a dentist in several stages. The number of visits depends on the method of removing dental plaque. The use of the Vector system ensures the treatment of dentition in one session. Sound scalers allow you to limit yourself to two stages. Manual removal will require an additional visit to polish the root surfaces.
During the first or second visit, other locally irritating factors are eliminated: overhanging edges of fillings, spaces between teeth, etc. Selective grinding of the teeth is performed. According to indications, surgical interventions are performed: excision of the frenulum, removal of a tooth located outside the arch, etc.
Drug treatment depends on the pattern of symptomatic gingivitis and can be used minimally. Rinsing, irrigation of solutions in the process of professional hygiene. Applications at home of oil solutions of vitamins A, E in the presence of epithelial desquamation. Physiotherapy methods include hydromassage and electrophoresis with galascorbine. The laser beam has a good effect.
Treatment of a patient with moderate severity of periodontitis
Includes general and local effects. Therapy for a concomitant disease is prescribed by a specialist in a specific branch of medicine. In parallel, agents that increase the overall resistance of the body may be recommended: vitamins, Eleutherococcus extract in adaptive doses, potassium orotate.
Local exposure involves motivation, training in individual oral hygiene with a careful selection of products and methods used 2-3 times a day at home. In cases of violation of the integrity of the epithelial cover of the gums (desquamative or ulcerative gingivitis), severe bleeding and hyperesthesia of the teeth, preference is given to a brush with soft bristles and gel toothpaste based on herbal preparations. Dental floss, brushes, and toothpicks are used extremely carefully.
The sensitivity of the gums to irritants is an indication for the prescription of painkillers. In the form of applications, you can use a 5% anesthetic emulsion, 1% pyromecaine ointment. It is recommended to eat bland food. Vitamin therapy is indicated. Professional hygiene can combine the removal of heavy dental plaque with hand instruments followed by treatment of the root surface with ultrasonic tips. The number of visits depends on the clinical picture and methods used. Studies have shown that the use of an ultrasonic scaler allows you to limit yourself to two sessions; manual instruments require additional stages of work. The most gentle way is to use the Vector system. A prerequisite is to reduce or eliminate irritating influences. The dentist-therapist performs correction of low-quality restorations. According to indications, tooth depulpation can be performed.
The orthopedist corrects low-quality dentures, carries out selective grinding, and, if necessary, splinting of mobile teeth.
The choice of medications depends on the clinical manifestations, namely the symptoms of gingivitis. An obligatory element of the medicinal effect is the use of antiseptics (2% hydrogen peroxide solution, potassium permanganate, chlorhexidine bigluconate).
According to indications, hemostatic agents (capramine, hemofibrin), analgesics (ethonium, anesthesin), and epithelializing agents (vitamins, sodium mefenamate, methyluracil) are used. The patient can independently use rinse solutions, aerosols (proposol), lozenges (strepsil), and spray.
Gum dressings (parodium, vokopak) and treatment plates (diplen-denta) are professionally applied. Treatment of a patient with severe (chronic complex) periodontitis includes general and local treatments.
General therapy is carried out by a specialist in accordance with the underlying disease. In parallel, drugs are prescribed that increase the general resistance of the body: vitamins, Eleutherococcus extract in adaptive doses, potassium orotate.
Treatment by a dentist involves motivation, training in individual oral hygiene with the selection of optimal products and methods used at home.
For desquamative or ulcerative gingivitis with bleeding gums and dental hyperesthesia, select a brush with soft bristles and gel toothpaste based on herbal preparations. Dental floss, brushes, and toothpicks are used only after eliminating defects in the gum mucosa.
Professional hygiene is carried out gently, step by step, using painkillers. Removal of heavy dental plaque is carried out with hand instruments, followed by treatment of the root surface with ultrasonic tips and polishing pastes.
Movable teeth must be splinted before professional hygiene. The number of visits depends on the clinical picture, in particular the condition of the gums. The use of an ultrasonic scaler allows you to limit the number of sessions compared to manual instruments.
A prerequisite for specific treatment of periodontitis is the reduction or elimination of irritating influences.
The dentist-therapist makes corrections to existing restorations. According to indications, tooth depulpation is carried out. The peculiarity of endodontic treatment is the need to treat retrograde pulpitis or tooth depulpation with reduced electrical excitability of the pulp.
An orthopedist corrects low-quality dentures, carries out selective grinding when splinting mobile teeth, and immobilization of teeth precedes professional hygiene.
The choice of medications depends on the clinical manifestations, including symptoms of gingivitis. Local therapy affects etiological factors, pathogenetic mechanisms and symptoms of the disease.
Treatment by a dentist involves motivation, training in individual oral hygiene with the selection of optimal means and methods used at home. In addition to solutions, ointments, and powders, medications can be used in the form of gum dressings and treatment plates. A layer of 0.2-0.5 mm of parodium is applied along the marginal gum and compacted with a tampon. Vokopak is used in the treatment of periodontitis, after gingivectomy and other surgical interventions. Diplen-denta (Nord-Ost) - plates for the treatment and prevention of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. Septo-Pak (“Septodont”) is a protective bandage for gums that contains amyl acetate, butyl phthalate, zinc oxide and zinc sulfate. Can be used with medications and after surgical interventions on periodontal tissues.
Suppuration from pockets requires the most intensive drug therapy, so local use of antibiotics is justified. The choice of antibiotic is best done by determining the sensitivity of microorganisms to it.
Surgical interventions can consist of eliminating the root cause (excision of frenulum, strands of the mucous membrane) or eliminating the inflammatory process (gingivotomy, gingivectomy, open curettage, flap surgery). Anesthesia and surgical intervention are performed in accordance with local and general indications.
Physiotherapeutic treatment can be carried out before and after surgery. Good results are shown by the use of a helium-neon laser, which has an analgesic, bactericidal, and epithelializing effect.
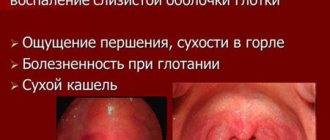
Symptoms of periodontal disease
The symptoms of the disease are subtle, especially at the initial stage of development. The patient cannot independently detect destructive processes in deep tissues. The disease in the first stages can only be seen by a periodontist after instrumental diagnosis. After a certain degree of destruction, the first symptoms appear, which begin to intensify as the pathology progresses.
How does periodontal disease manifest?
- increased sensitivity of teeth to cold, sour foods;
- paleness, thinning of the gums, exposure of the neck, root part;
- the appearance of a wedge-shaped defect, the visibility of the enamel border;
- itching, aching gums;
- bad breath;
- loosening of teeth.
When a bacterial infection occurs, the gums may become inflamed, bleed, and pus may be released from the gum pockets. However, inflammation is not directly related to the disease, but can be a complication.
How is it classified?
To draw up a treatment regimen, it is important to conduct a detailed diagnosis and determine the characteristics of the disease.
Periodontal disease occurs:
- localized - destruction of the tissues of one or several teeth;
- generalized - destructive processes affect the entire jaw.
This is a chronic, sluggish, progressive disease. The acute form is rare, since the pathology is not infectious. In the acute period, bleeding from the gums, pain, and discomfort during chewing are observed.
The progress of periodontal disease is divided into stages according to the degree of pathological changes in bone and soft tissue.
Stages of pathology progression
The disease develops over the years without causing significant discomfort to the patient. Severe loosening and loss of teeth occurs on average 10 years after the onset of destructive processes.
There are 5 stages:
- The initial stage of periodontal disease is asymptomatic. At this stage, even during an examination in a clinic, it is difficult to identify the disease, but it is possible. The gums become lighter and lose their shine. Teeth sensitivity to sour and sweet foods increases slightly. An X-ray image shows a slight loss of alveolar bone. The interdental papillae become more rounded, normally triangular. Destructive processes can be reversed if the cause is identified and eliminated.
- At the first stage, changes in bone tissue are already obvious, but pronounced symptoms are still not observed. There may be itching, burning in the gums, slight exposure of the neck - up to 1.5 millimeters, a slight discrepancy of the teeth in the front row. The x-ray shows bone resorption (no more than one third). There are no abnormalities in the cortical plate. The teeth are motionless, well fixed in the socket. Therapeutic treatment and observation by a doctor every six months are required.
- At the second stage, the patient can already independently recognize the problem. The sensitivity of the teeth increases, a dull pain appears, itching in the gums, the neck is exposed by 5 millimeters, the discrepancy of the anterior dental units becomes more noticeable, and a pathological bite is formed. Visually you can see the border between the enamel and hard root tissue. X-rays show two-thirds bone resorption and severe changes in the alveolar process. Bone tissue becomes denser and chewing efficiency decreases. Complex treatment is required: therapy, physiotherapy, splinting. After therapeutic treatment, bone grafting is recommended.
- The third stage is characterized by high tooth sensitivity to hot, sour and cold foods, looseness, and severe discrepancy. Gum recession increases, the roots are exposed by more than half. An x-ray shows a decrease in the alveolar part of the jaw by a centimeter. At this stage, it is impossible not to notice the problem visually. When diagnosing, the doctor evaluates the appropriateness of therapy.
- At the fourth stage, the root part is exposed by two-thirds. The roots are held in the hole only by the tip. Teeth lose functionality and it is almost impossible to save them.
How to treat periodontal disease
Treatment of pathology must be carried out strictly under the supervision of a periodontist. The use of folk remedies is possible, but only as an addition to the main therapy. Is periodontal disease completely curable? It is possible to cure the disease if the cause is identified and eliminated, and comprehensive therapeutic measures are carried out aimed at restoring lost tissue and functions of the teeth. To determine the provoking factor, the patient must undergo a complete examination of all organs and systems.
The doctor draws up a treatment regimen depending on the stage of the disease. The patient is prescribed medications, physical therapy, caries is treated, rotten teeth are removed, splinting, and tissue plastic surgery are performed. If the teeth are very loose or damaged, they are removed. Subsequently, implantation or prosthetics are performed.
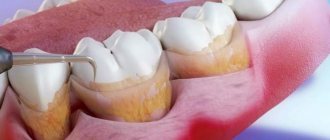
Plaque removal, caries treatment
If there are dense formations on the teeth, then professional cleaning is carried out. Stones lead to inflammation of the gums and rapid development of the disease. If caries is present, it is necessary to urgently clean and fill the carious cavities. The infection accelerates the atrophic processes, causing pain, swelling, bleeding and suppuration from the gums.
Drug therapy
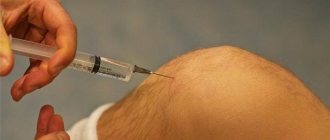
Since the main causes of tissue destruction are a lack of vitamins, minerals, and decreased immunity, the patient is prescribed vitamin-mineral complexes and immunostimulants. The doctor gives nutritional recommendations. When an infection occurs, antihistamines and antibacterial agents are prescribed.
To restore the volume of the gum tissue, injections are made with stem cells, collagen, and growth factors. The drugs accelerate regeneration processes, cell renewal and growth, restore volume, increase protective properties and local immunity.
Splinting
Teeth mobility disrupts the bite, impairs the process of chewing food, and most importantly accelerates the destruction of bone tissue. To prevent the disease from worsening, the dental units are fixed with splinting threads. In case of partial absence, teeth are strengthened with clasp dentures.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures improve nutrition, tissue trophism, increase blood flow, and reduce tooth sensitivity.
What procedures may be prescribed:
- darsonvalization with a weak high-frequency current improves metabolism, blood supply to tissues, and stops destructive processes;
- vacuum, hydro or manual massage - works similarly;
- electrophoresis with calcium gluconate to reduce cervical hypersthesia.
Surgery
Used if the alveolar processes and gums are severely atrophied. When the gum tissue becomes thin, gingivoplasty is performed. The procedure allows you to restore a beautiful smile, closes the roots and strengthens the teeth.
To build up the damaged areas of the bone, osteoreplacement drugs and other materials are added. In this way, a new alveolar process is created, which holds the dental unit in the socket.
Prosthetics
In case of a generalized form of the disease, especially in the last stages, radical measures are resorted to - complete removal of the dentition. In this case, basal implantation can be done. Modern technology allows you to install artificial teeth in just a few days. A fixed prosthesis is installed not in the alveolar part of the jaw, but in the basal layer, so bone augmentation is not required. Plus, it has a gum margin, so you won't have to pay for gingivoplasty.
Treatment at home
It is impossible to get rid of the disease on your own. However, folk remedies can increase the effectiveness of traditional therapy. Medicinal herbs strengthen the walls of blood vessels, help relieve inflammation, saturate tissues with valuable elements, and speed up metabolism.
Gargling with decoctions or infusions of lingonberry leaves, calendula, Kalanchoe juice, green tea, and garlic is useful. Some healers recommend rinsing your mouth with a tincture of kombucha, rich in vitamin C and other beneficial substances.
Stages of treatment
Treatment of periodontal disease is carried out in close cooperation with a periodontist, therapist and endocrinologist.
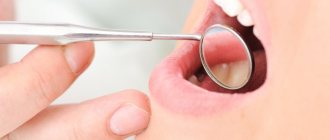
1. Diagnostics.
At the initial stage, the causes of the development of the disease are identified. The dentist performs a visual examination of the oral cavity. An anamnesis is collected—detailed data about the patient’s health status.
If necessary, additional examination is carried out. For example, an orthopantomogram helps to see the degree of bone resorption. X-rays help assess the degree of periodontal deformation and changes in bone tissue.
In most cases, consultation with an endocrinologist or immunologist is required.
2. Comprehensive oral hygiene.
Soft and hard plaque is removed using the Air Flow system. Caries is treated (if present). Fillings are changed. Rotten and damaged teeth are removed.
3. Drug therapy.
It includes taking medications (vitamins, antibiotics, hormonal drugs, etc.) to stop gum tissue atrophy.
4. Physiotherapy.
A set of physiotherapeutic procedures is carried out. The main goal is to improve blood circulation in periodontal tissues.
- Laser treatment
. Quickly stops the inflammatory process, restores soft tissue, relieves swelling and kills bacteria. - Electrophoresis
. The procedure effectively eliminates dental hyperesthesia, i.e. heightened sensitivity to irritants. Calcium gluconate is used as the main active ingredient. - Darsonvalization
. Reduces tooth sensitivity and pain. Accelerates blood supply to the gums. It is carried out only after removal of dental plaque.
5. Surgery.
To reduce tooth mobility, which provokes accelerated bone resorption, splinting is used. The teeth are united by a special design that evenly distributes the load.
At an advanced stage, it may be necessary to remove the inflamed bone tissue followed by osteoplasty.
6. Implantation.
At an advanced stage of periodontal disease, it is impossible to save teeth. The best solution to restore the integrity of the dentition is all-on-6 implantation (all on 6 implants).
Artificial roots are implanted bypassing the inflamed and atrophied areas of the bone (into the deeper layers) and can be loaded with a temporary prosthesis on the same day.
Is it possible to cure periodontal disease at home?
Periodontal disease in adults is not associated with an inflammatory process in the oral cavity. This means that periodontal disease cannot be cured once and for all by rinsing with folk remedies (decoctions, hydrogen peroxide, etc.) or applying applications to the gums.
Attempts to treat periodontal disease at home only aggravate the problem and “steal” precious time.
Even in a dental clinic, moderate and severe periodontal disease is difficult to treat. You can only stabilize the process or slow down its progression.
You should not self-medicate. It is better to seek help from a dentist as soon as possible.
Still, folk recipes can have a positive impact on the dynamics of treatment.
Prevention of periodontal disease
Preventive measures are aimed at maintaining the health of the dentofacial system and the body as a whole.
Periodontists recommend:
- eat well, eat more fruits, raw vegetables, seafood;
- take vitamin and mineral complexes in winter;
- Take daily care of your oral cavity, use dental floss to remove food debris from the interdental spaces;
- temper the body, treat diseases in time;
- undergo regular medical examinations with a dentist and have your teeth professionally cleaned;
- stop smoking, eliminate alcohol.
If any unpleasant symptoms appear in the oral cavity, you should immediately contact a dental clinic.
Popular recipes for the treatment of periodontal disease
Traditional medicine offers a lot of recipes that help (not cure) stop the disease. Here are a few of them.
1. Garlic infusion
. Crush the peeled garlic, pour boiling water over it and let it brew. Rinse your mouth with the resulting infusion 2-3 times during the day for 5-7 minutes.
2. Calendula infusion
. Pour 4 tablespoons of calendula into a liter of boiling water and leave to brew for half an hour. Rinse your mouth with the infusion 6-7 times a day.
3. Hydrogen peroxide
. Moisten the swab and rub well into the gums. Or dissolve 2 hydroperite tablets in 100 ml of water and rinse your mouth.
4. Sea salt
. A tablespoon of fine sea salt must be mixed with the same amount of olive or sunflower oil. Rub the resulting mixture onto your teeth and gums in the morning and evening for several minutes.
5. Native American toothpaste
. To prepare it, you need 3 tablespoons of ground sea salt, 1 teaspoon of spruce resin, 3 pinches of burnt banana peel ash, olive oil. All ingredients are thoroughly mixed until a medium thick paste is formed. It needs to be used to treat the gums. Be sure not to spit out the resulting saliva for 10-15 minutes. The procedure is recommended to be carried out in the morning and evening.
Be sure to consult with your doctor about what folk remedies are best to supplement the treatment of periodontal disease at home!
PREVENTION
The essence of preventive measures is aimed at creating conditions for good blood supply to periodontal tissues.
- Diet
. Eat foods containing flavonoids, copper, zinc and iron. Be sure to include raw vegetables and fruits in your diet. They help cleanse teeth from plaque and have a massaging effect on the gums. Reduce your consumption of sweets and carbohydrates, which provoke the activity of pathogenic bacteria. - Medicinal toothpastes
. To prevent periodontal disease, your dentist may recommend special pastes that effectively remove plaque and reduce bleeding gums. - Timely treatment of systemic diseases
. Most patients with periodontal disease are diagnosed with autoimmune diseases. Visit your endocrinologist and therapist regularly to monitor your systemic diseases. - Regular exercise
. They strengthen the entire body, increase immunity and, as a result, have a beneficial effect on the condition of the gums. - To give up smoking
. Nicotine provokes periodontal disease and has a negative effect on the condition of the body.
Periodontitis and periodontal disease - what is the difference?
The name has a common root, which means both are associated with a disorder in the periodontium - the tissue that serves as a support for the tooth. The etiology, course, symptoms, and speed of destructive processes in pathological tissues differ.
With periodontitis, there is inflammation, swelling, bleeding gums, severe pain, and bone destruction occurs faster. A disease of an infectious nature, bacteria multiply in periodontal pockets, leading to the development of abscesses. When the infection is destroyed and the interdental pockets are thoroughly cleaned, the dental tissues are restored.
With periodontal disease, pockets do not form, the mucous membranes are light, there is no swelling, no inflammation. The pathology is characterized by a slow, progressive course and is often detected in the last stages. It is difficult to identify and eliminate the cause. More common is the generalized form, in which the entire dentition suffers. The treatment is long-term and complex. Complete remission is not always achieved.
Closed curettage of periodontal pockets
Closed curettage or curettage is one of the few methods of treating periodontitis that allows you to eliminate granulations and various types of dental plaque from periodontal pockets. However, due to the lack of visual control, the doctor is not always able to completely eliminate these problems, which reduces the effectiveness of this method. That is why it is used for shallow periodontal pockets, which is typical for the earliest stages of the disease. With a more extensive lesion, the technique can only temporarily improve the patient’s health, but sooner or later periodontitis will begin to recur, which will require re-treatment.
Among the advantages of this type of surgical treatment are:
- Good aesthetic result.
- Rapid gum recovery.
- Minor blood loss.
Due to the features described above, closed curettage is not always used.
Cost of treatment
With early diagnosis, treating periodontal disease will be faster and cheaper than in the later stages. The price is influenced by diagnostic methods, treatment, area of tissue damage, number of visits to the doctor and other factors.
Our clinic provides accurate diagnostics, professional cleaning of teeth from stone, antiseptic treatment in case of infection, splinting, and installation of dentures. Our doctors work with modern equipment and use only effective, safe drugs and materials. We always strive to preserve the integrity of the dentition. If this fails, we install high-quality implants.
You can make an appointment with a periodontist by phone. The treatment plan and prices are discussed with the patient before the start of the procedures.