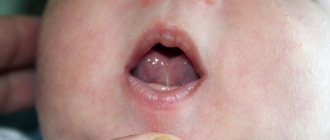
The diagnosis of dysarthria is made after a thorough examination by a neurologist and speech therapist. In differential diagnosis, an integrated approach is used, which covers not only speech activity, but also the state of the child’s higher mental functions, behavior, level of mastery of skills, state of vision, hearing, articulation apparatus and motor sphere. No less important is information about the child’s somatic condition and the possible hereditary nature of the disorder. A thorough study will allow not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also to choose the optimal method for correcting the form of dysarthria.
Possible causes of a swollen cheek in a child
Unilateral or bilateral swelling of the cheek can occur as a result of various diseases.
The main conditions causing swelling include:
- dental diseases;
- jaw injuries;
- pathologies of other body systems;
- consequences of treatment.
Causes may include illnesses and other conditions.
Possible diseases
Diseases that result in a swollen cheek in a child include the following.
| Caries | In case of toothache, swelling of the gums and cheeks, the cause may be untreated caries. Such a tumor is most often one-sided and disappears when the diseased tooth is healed. |
| Acute pulpitis | Pulpitis is a consequence of untreated caries that affects the nervous tissue of the tooth. With this disease, one cheek becomes significantly larger than the other; accompanying symptoms are a putrid odor and acute toothache. |
| Periodontitis | If the cheek is enlarged and hurts on one side, the cause may be inflammation of the apex of the tooth root. It occurs due to caries or due to an incorrectly installed filling, and is accompanied by swelling, pain and discomfort while eating. |
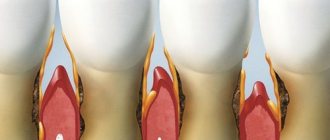
| Periostitis | Purulent inflammation in the periosteum, better known as “flux”. This disease causes redness and swelling of the gums, toothache, swelling of the cheek and a slight increase in temperature. |
| Fistula | A small growth on the gum with a purulent white tip is a symptom of a growing purulent infection and a complication of gumboil. In addition to swelling of the cheek on one side, it is accompanied by discomfort during eating and pain when touched. |
| Gum inflammation | If the cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt, the cause may be gingivitis, periodontal disease and periodontitis. In the first case, the edge of the gum is affected: on the outer or inner side. The second and third diseases cause dental swelling, swelling of the gums and cheeks on the damaged side. |
| Stomatitis | The oral mucosa in children is more sensitive to infections. Stomatitis in a child can be caused by the herpes simplex virus, oral candidiasis or other infections. If inflammation of the mucous membrane is not treated in time, it leads to ulcerative defects. |
| Mumps | An infectious disease of the salivary gland, also known as mumps. In addition to swelling of both cheeks near the ear, it is accompanied by high fever and digestive disorders: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. |
| Infectious diseases of the respiratory tract | With bacterial or viral infections, fluid is retained in the body longer than expected, which is why swelling of both cheeks and other parts of the body occurs during illness. |
| Sinusitis | When the cheek swells under the eye, the cause may be inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. Such tumors are accompanied by nasal congestion and difficulty breathing, but there is no pain. |
| Lymphadenitis | If the cheek is blown or the child has a cold, the lymph nodes may enlarge and swell the face on one side. Inflammation of the lymph nodes is a symptom of inflammatory diseases that disappears when the disease that caused it is cured. |
| Oral cyst | A lump in the mouth, similar to a lump, is formed as a result of the appearance of a cyst. Depending on the cause and type of cyst, it can be located inside the mouth in the corner, on the inside of the mouth, between the gum and cheek, or closer to the cheek. |
| Kidney dysfunction | Kidney problems cause severe swelling throughout the body. With this disease, not only the cheeks swell: the entire face, fingers and legs become enlarged. |
| Facial neuritis | Facial neuritis occurs due to compression of the nerve, causing swelling in the damaged area. The condition is treated with massage and acupuncture. |
Other factors
In addition to diseases, the cheek may swell due to the following conditions:
- From a blow: if a child hits his lower jaw or cheek and injures it, swelling will appear after 2-3 hours and last for several days.
- Due to chronic trauma: the condition occurs as a result of an incorrect bite or overly sharp teeth that constantly wound the cheek from the inside.
- After insect bites: if the cheek is slightly swollen, does not hurt and is constantly itching, this is a normal reaction to the bite. If swelling and discomfort are severe, an allergy to insect bites is likely, requiring a visit to the doctor.
- Due to allergies: swelling may occur after anesthesia or after root canal filling. In the first case, the allergy soon goes away on its own; in the second, the filling needs to be replaced with a hypoallergenic one.
- After treatment of pulpitis: swelling and pain after removal of the nerve during treatment indicate incomplete completion of the operation.
- After an incision in the gum: When inflammation causes pus to form in the gum, it is removed through an incision. The gums are very sensitive, so after this procedure pain and swelling persist for several days.
- When extracting a tooth: if the extraction was difficult, or postoperative recommendations were not followed, swelling and discomfort may appear. It goes away on its own after 2-3 days.
- When the 3rd large molar erupts: the wisdom tooth breaks through painfully, especially in childhood. In addition to pain and discomfort during eating, swelling often appears.
- With prosthetics: if a child wears braces or other prostheses in the mouth, if they are installed incorrectly, swelling, malocclusion and other pathological conditions may occur.
To make sure that these reasons are safe for the child’s health, you should visit a pediatric dentist for a consultation and examination.
An insect bite can cause a swollen cheek
Formation of correct speech in children with dysarthria
Svetlana Ermakova
Formation of correct speech in children with dysarthria
Motina A. A., Ermakova S. G.
speech disorders dysarthria occupies a special place , which manifests itself in limited mobility of the speech apparatus: the soft palate, tongue, lips. The consequence of this is defects in pronunciation, changes in voice timbre, and underdevelopment of speech .
Success in overcoming these disorders largely depends on the right combination of special treatment, education and family education.
The most common form of childhood dysarthria is pseudobulbar , which is a consequence of organic brain damage suffered in early childhood, during childbirth or in the prenatal period (encephalitis, role trauma, tumor, intoxication, etc.)
.
The child’s general and speech motor skills are impaired, and the nature of these disorders can be different. Conventionally, there are three degrees of pseudobulbar dysarthria : mild, moderate, severe,
1. A mild degree of pseudobulbar dysarthria is characterized by the absence of gross disturbances in the motor skills of the articulatory apparatus. Articulation difficulties lie in slow, insufficiently precise movements of the tongue and lips. Chewing and swallowing disorders manifest themselves in subtle ways, with occasional choking.
speech is somewhat slow , and there is blurring when pronouncing sounds. The pronunciation of Zh, Sh, R, Ts, Ch, which are complex in articulation, suffers more often. Voiced consonants are pronounced with insufficient participation of the voice. Soft consonants are difficult to pronounce, since their articulation requires raising the middle part of the back of the tongue to the hard palate.
In most cases, children with mild dysarthria experience some difficulties in the sound analysis of a word; in their speech there are specific errors in replacing sounds (for example, T-D, Ch-Ts, etc.)
.
Thus, the leading defect in children suffering from mild pseudobulbar dysarthria is a violation of the phonetic aspect of speech .
2. Children with moderate dysarthria make up the largest group. They are characterized by amicability: the child cannot puff out his cheeks, stretch out his lips, or close them tightly. Tongue movements are limited. The child cannot lift the tip of his tongue up, turn it to the right , left, or hold it in the desired position. A significant difficulty is the transition from one movement to another. The soft palate is often inactive. Characterized by profuse salivation. The acts of chewing and swallowing are difficult.
The speech of such children is usually very slurred, blurred, with a noticeable nasal tint. Characterized by unclear articulation of vowels due to inactivity of the lips and tongue. The sounds A and U are not clear enough, the sounds I and Y are usually mixed. Of the consonants, the most commonly pronounced correctly are P , T, K, M, N, X, Whistling, hissing, Ch and C, R and L are pronounced as a nasal exhalation with an unpleasant “squelching”
overtone.
The exhaled mouth stream is felt very weakly. Voiced consonants are almost always replaced by voiceless ones. Often, sounds at the end of a word and when consonants are combined are omitted, while in the latter case one (squirrel - beka)
or both sounds
(snake - iya)
.
Due to the difficulty when switching from one syllable to another, there are cases of their assimilation (dishes - posyusya, scissors - yosisy)
.
Impaired motor skills of the articulatory apparatus ultimately leads to noticeable difficulties in mastering sound analysis. Children cannot correctly select pictures whose names begin with a given sound, come up with a word containing a given sound, or analyze its sound composition. For example, the task is given to find pictures whose names contain the sound B; children select the following: can, drum, pillow, scarf, saw, squirrel. Or the task is given to find pictures whose names contain the sound 3; Children put aside pictures depicting a snake, a hare, a beetle, a pike, a brush, an acorn, and tongs.
3. The more severe degree of pseudobulbar dysarthria - anarthria - is characterized by deep damage to the facial muscles and complete inactivity of the speech apparatus. The child's face is mask-like, the lower jaw droops, and the mouth is constantly open. The tongue lies motionless on the floor of the oral cavity, lip movements are sharply limited. The acts of chewing and swallowing are difficult. There is no speech, sometimes the child makes inarticulate sounds. But even with such a severe disorder, systematic sessions with a speech therapist have a positive effect.
In children with dysarthria , late development of speech and limited speech experience lead to insufficient accumulation of vocabulary. Most children with articulation disorders often use words with inaccurate meanings, replacing them with adjacent ones based on sound or situational similarity: loop - hole, vase - jug, acorn - nut, hammock - mesh, rails - sleepers, thimble - finger,
Characteristic for children suffering from dysarthria is a fairly good orientation in the environment. But the absence of speech or limited use of it leads to a discrepancy between active and passive vocabulary.
Children with severe articulatory disorders often have a large passive vocabulary . They know and can show in a picture such objects as a swing, a well, a buffet, a monument, a carriage; determine profession (pilot, teacher, driver, etc.)
; understand the actions of the persons depicted in the picture, show objects painted in different colors.
Dysarthric children are characterized by insufficient mastery of the grammatical forms of the language . In their speech , they often omit prepositions, leave out endings or use them incorrectly , do not master the category of number, and find it difficult to coordinate and control . For example: The cat climbed into the cage; He sat down at the bench; I go to school with a briefcase; The sky is clear.
In order to master the pronunciation of sounds, children with dysarthria need special training exercises. The system of exercises, their sequence and duration, specific techniques necessary for a given child are planned by a speech therapist. Some of them, requiring repeated repetition, can and should be done at home.
Children suffering from dysarthria , in most cases, do not know how to breathe smoothly and deeply. Their breathing is intermittent, the exhalation is short, uneconomical, carried out simultaneously through the mouth and mine. Children have difficulty pronouncing long words and phrases.
To practice proper breathing skills, the following exercises are used;
1. Inhale - exhale through the nose.
2. Inhale through your nose - exhale through your mouth (if you exhale through your mouth and nose at the same time, you need to pinch your nose with your fingers,
3. Inhale through the mouth - exhale through the nose,
4. Inhale and exhale through your mouth.
First you need to ensure that the child learns to make a free, smooth, extended exhalation through the mouth. After this, train a smooth long exhalation with silent articulation of the vowels A, O, or consonants S, Sh. The adult should ensure that the child correctly imitates the desired sound, and encourage the length of the exhalation (mark the time by counting)
.
When performing these exercises, it is very important to constantly monitor the child, since at first it is difficult for him to feel the leakage of air through the nasal passages. Various control techniques are used: a mirror, cotton wool, or strips of thin paper are applied to the nasal passages.
The following exercises also contribute to the development of active exhalation;
1. Blow on a “curtain”
.
2. Blow on a flag made first from thin colored paper and then from thicker paper.
3. Blow on paper butterflies, pinwheels, flowers, brooms, acrobatics figures, etc. You can make a small stand to which you attach various light objects or cotton balls on a string.
4. Blow no plastic toys floating in the water.
5. Blow through a straw into a bottle of water. You need to ensure that the exhalation is even and long, then the water will bubble for a long time and evenly.
6. Roll the balls or pencils on a smooth surface with a strong blow.
7. Blow through a short tube onto finely cut pieces of colored paper or cotton balls. The task gradually becomes more difficult by increasing the distance to objects, which requires a stronger exhalation,
8. Inflate rubber toys and balls.
9. Play lip instruments.
It is useful to evaluate each exercise done by the child; “Now you exhaled correctly through your mouth ”
.
“You took a long exhale through your mouth,”
etc.
Blowing exercises should be alternated with exercises that develop lip and tongue movements. Let's list some of them that can be easily done at home:
Exercises for lips and cheeks
-Pouting of lips and cheeks,
-Inflating the cheeks alternately.
-Retraction of the cheeks into the oral cavity between the teeth,
-Sucking movements - closed lips are pulled forward with the proboscis, then return to their normal position; jaws are closed.
-Grin; the lips are strongly stretched to the sides, so that both rows of teeth are exposed.
-Stretching the lips with a narrow funnel (as when whistling)
.
-Movement of lips folded with a proboscis, left-right ,
-Vibration of lips ( “coachman”
sound).
-Hold a rubber tube or long caramel with your lips.
Exercises for the lower jaw
-Opening and closing the mouth (with teeth clicking)
.
-Biting a gauze pad or rubber band with your teeth. In these cases, an adult, holding a napkin or tourniquet, tries to pull it out. The force he applies gradually increases.
Exercises aimed at developing tongue mobility require great attention. If the child’s tongue moves poorly (does not rise to the upper teeth, does not deviate to the sides, etc.), then reflex (involuntary)
movements.
Tongue exercises
-To move the tongue forward, a piece of candy is pulled towards the lips; the lower lip is coated with jam, and the child licks it; a piece of paper is attached to the lower lip, the child tries to push it off with his tongue,
-To shorten the tongue, place pieces of sugar on the tip of the tongue,
-To develop sideways tongue movements, place a piece of sugar between your cheek and teeth and spread the jam on the corner of your mouth.
In cases where active movements of the tongue are difficult, passive gymnastics is used. For example, an adult grabs the child’s tongue with a gauze napkin and makes the necessary movements: back and forth, up and down, left and right .
A child’s speech activity also depends on his communication with others.
Children with dysarthria are often very critical of their defect, are silent a lot, use gestures instead of words, and are embarrassed to speak in front of strangers. Parents gradually get used to this and do not properly activate the child’s speech. This can have detrimental consequences.
It is very important to support the first attempts at independent speech , to encourage the most indistinct words, to repeat them clearly, so that the child can correlate his pronunciation with the correct one .
Games that develop auditory attention and the ability to distinguish sounds by pitch and duration are useful. For example, an adult selects various sounding toys (bell, rattle, drum, flute, etc.)
and hides behind a screen or screen. The child must guess which toy makes which sound.
You can use the following game tasks. In front of the child is a picture depicting various fruits. The task is given - to raise your hand when “lemon”
An adult pronounces slowly: apple, peach, pear, lemon.
Pictures are laid out in front of the child, depicting objects that sound similar. An adult names one of them. The child must show the desired picture. For example: a rooster is a shepherd, a butterfly is a grandmother, a pipe is a booth, etc.
Children with dysarthria often experience significant impairment of hand and finger movements. The child cannot dress himself, comb his hair, or handle small objects. Therefore, it is necessary to systematically apply exercises to form a variety of movements with the fingers and hand. First, coordinated movements are practiced with larger objects, then with small ones. It is necessary to teach the child correctly grasp objects, hold them and put them down. For this purpose, toys and household items are specially selected, varying in size, shape , color and weight. It is useful to teach your child to move objects from one place to another. To do this, outlines of various objects are prepared on thick paper, and the child, according to instructions, places the corresponding object in its “place”
.
You can invite him to distribute toys or objects by size, color, determine their weight and choose those that are the same in weight. To develop more subtle finger movements, it is very useful to place small objects (buttons, sticks, grains, etc.)
in small boxes or bags. Exercises of this kind should be varied, and the child’s success should be encouraged in every possible way. Children have fun stringing beads, rings, buttons onto a thread, moving the bones on the abacus, cutting out pictures from paper along the outline and coloring them. Squeezing a rubber sponge strengthens the arm muscles well.
We suggest the following exercises:
-On thick cardboard, draw the outline of the child’s hand with fingers evenly apart. The child fixes his hand according to the contour.
-The child places his hand on the table and, at the request of the adult, lifts the necessary fingers one by one. If this exercise does not work out right away, an adult can hold with his hand those fingers that should remain motionless.
-The child folds his palms, squeezes them and taps the fingers of each pair.
To increase muscle load, you can put a thin elastic band of small diameter on each pair of fingers.
-According to the instructions of the adult, the child shows fingers one by one, one at a time, two at a time, three at a time; pushes the second and fifth fingers forward (the rest are clenched into a fist)
.
-Beating a beat with each finger, imitation of playing the piano,
- Shooting a cotton ball, checker, etc. with one, two and four fingers.
Home activities with a child suffering from dysarthria should include the gradual development of the accuracy and smoothness of movements needed for writing. The following exercises contribute to this:
-Coloring pictures,
-Accurate tracing of object contours.
-Drawing simple objects using marked dots.
-Connecting these points with lines of different directions .
-Shading (colored pencils are used)
.
It is very important to be able to convince the child of the importance of such tasks and carefully monitor his progress, noting even the most insignificant ones.
Literature
1. Filicheva, T. B. Elimination of general speech underdevelopment in preschool children: a practical guide / T. B. Filicheva, G. V. Chirkina. – M.: Iris-press, 2004. – 224 p.
2. Filicheva, T. B. Children with general speech . Education and training: educational manual / T. B. Filicheva, T. V. Tumanova. – M.: “Gnome – Press”
, 1999. – 80 p.
3. Zhukova, N. S. Speech therapy. Overcoming general speech underdevelopment in preschool children / N. S. Zhukova, E. M. Mastyukova, T. B. Filicheva. – Ekaterinburg: IRD LTD, 1998. – 320 p.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have a swelling of the cheek, you should first consult a dentist.
If the cause of the swelling is not dental, your doctor will refer you to other specialists:
- see a therapist for bacterial and viral infections;
- see a neurologist for neurological diseases;
- to an ENT specialist for inflammation of the ear and salivary gland;
- see a nephrologist for kidney pathologies;
- see a traumatologist or maxillofacial surgeon for trauma to the lower jaw.
What to do if your child has a swollen cheek?
You can quickly remove cheek swelling using medications and traditional medicine recipes.
Medicines
| Group of drugs | When to use | Examples |
| Antiseptics | They are used to disinfect the oral cavity for any reason for cheek swelling. | Stomatin, Mevalex, Givalex |
| Antibiotics | Used to treat bacterial infections that cause swelling of the cheek. | Lincomycin, Doxycycline, Amoxiclav |
| Analgesics | Relieves pain in the cheek. | Analgin, Tempalgin |
| NSAIDs | They relieve pain and have an anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effect. | Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Ketorol |
| Antihistamines | They are used to relieve swelling, but do not treat the cause of the swelling of the cheek. | Suprastin, Loratadine, Claritin |
Important! Any medication must be prescribed by a doctor, otherwise it can harm the child’s health.
Treatment with folk remedies
Non-traditional methods are used more often as an addition to the main treatment.
Applying cold
Ice, cold bottled water, chilled metal and frozen foods applied to the face will help reduce swelling:
- The source of cold is wrapped in a soft, not very dense fabric.
- Cold is applied to the face for 10-15 minutes.
- The procedure is repeated after half an hour 2-3 times.
Cold sessions of 2-3 applications are performed several times a day until the appearance of the cheek improves.
A cold compress reduces swelling
Soda and salt
A salt-soda solution will help get rid of a sore tooth and swollen gums.
It is used as a rinse or compress:
- 1 tsp. soda and 1 tsp. salts are mixed with 200 ml of water at room temperature.
- The mouth is rinsed with the solution every 2 hours.
- A compress with the solution is applied to the cheek for half an hour 2-3 times a day.
For the best effect, you should use both a compress and rinsing.
A cold compress reduces swelling
Soda and salt
A salt-soda solution will help get rid of a sore tooth and swollen gums.
It is used as a rinse or compress:
- 1 tsp. soda and 1 tsp. salts are mixed with 200 ml of water at room temperature.
- The mouth is rinsed with the solution every 2 hours.
- A compress with the solution is applied to the cheek for half an hour 2-3 times a day.
For the best effect, you should use both a compress and rinsing.
Soda-salt solution helps with swollen gums
Herbal rinse
Herbal teas help relieve inflammation and reduce swelling.
Rinsing with them is done like this:
- Mix 3 tbsp. l. herbs peppermint, angelica, periwinkle and birch buds.
- The herbs are poured into a liter of hot water, boiled, and infused for 1 hour.
- The mouth must be rinsed every 2-3 hours until the swelling subsides.
This herbal infusion can also be used as a compress.
Gargling with a mint-herbal infusion helps reduce swelling.
Eating sage
Sage is a natural and effective anti-inflammatory agent.
Medicinal tea with sage is prepared as follows:
- Fresh grass must be dried.
- 2 tablespoons of dry herb are poured into 500 ml of boiling water.
- The tea is infused for 30-60 minutes, then filtered and drunk.
In addition to oral use, you can rinse your mouth with sage and apply it as a compress.
Gargling with a mint-herbal infusion helps reduce swelling.
Eating sage
Sage is a natural and effective anti-inflammatory agent.
Medicinal tea with sage is prepared as follows:
- Fresh grass must be dried.
- 2 tablespoons of dry herb are poured into 500 ml of boiling water.
- The tea is infused for 30-60 minutes, then filtered and drunk.
In addition to oral use, you can rinse your mouth with sage and apply it as a compress.
Sage decoction has anti-inflammatory properties
Application of propolis
You can remove swelling and inflammation by rinsing with a pharmaceutical propolis tincture.
The solution from it is made as follows:
- 5 drops of the product are mixed with 200 ml of boiling water.
- The solution is cooled to room temperature.
- The throat is gargled every hour for 1-2 days.
If the tumor has not completely disappeared within 2 days, you can extend the period of use.
Propolis tincture will help reduce swelling
Potassium permanganate solution
Potassium permanganate is a proven antimicrobial agent that cleanses the oral cavity from bacteria and inflammation.
The potassium permanganate solution is prepared as follows:
- 2-3 manganese crystals are diluted with 200 ml of warm water.
- The mixture is thoroughly mixed so that no undissolved particles of the substance remain.
- If the solution does not have a faint pale pink tint, but a rich color, it must be diluted.
The mouth is rinsed with manganese 3-4 times a day, the rinsing should be short: 1-2 minutes.
Propolis tincture will help reduce swelling
Potassium permanganate solution
Potassium permanganate is a proven antimicrobial agent that cleanses the oral cavity from bacteria and inflammation.
The potassium permanganate solution is prepared as follows:
- 2-3 manganese crystals are diluted with 200 ml of warm water.
- The mixture is thoroughly mixed so that no undissolved particles of the substance remain.
- If the solution does not have a faint pale pink tint, but a rich color, it must be diluted.
The mouth is rinsed with manganese 3-4 times a day, the rinsing should be short: 1-2 minutes.
Potassium permanganate solution destroys bacteria and microbes
Aloe or Kalanchoe
Aloe and Kalanchoe are similar plants with a pronounced medicinal effect. They help with inflammation of various origins, including swelling of the cheeks.
Appearance of plants in the photo:
Aloe medicinal plant
Kalanchoe leaves
Method of use:
- Tear or cut off one leaf and rinse thoroughly.
- Cut the sheet into 2 halves.
- Apply the cut to the inflamed gum and leave for half an hour.
Compresses with these plants should be made 3-4 times a day.
Correction of dysarthria
Speech therapy work will depend on the speech therapy report; programs for working with GSD (general speech underdevelopment) and FFND (phonetic-phonemic speech disorder) are used. The speech therapist conducts classes in three stages:
Stage 1. Preparatory
Includes normalization of breathing and muscle tone, articulatory gymnastics, development of fine motor skills, work with the prosodic side of speech, clarification and development of passive-active vocabulary and the formation of the need for verbal communication. For increased tone, a relaxing massage
, which parents can do at home.
Massage of facial muscles (1.5 - 2 min.) from the temples to the center of the forehead, from the ears to the nose, from the ears to the chin. Massage the lips from the corners to the center along the upper and lower lips, massage the tongue in both directions through a handkerchief. If muscle tone is reduced, a firming massage
for 3 minutes. from the center to the periphery: from the center of the forehead to the temples, from the nose to the ears, from the corners of the mouth to the ears. The child's lip muscles are trained by grasping and holding lollipops, sticks of different diameters with the lips, and drawing in liquid through a straw.
Articulation gymnastics
is aimed at training the muscles of the tongue: introducing the position, fixing the articulatory pose and withdrawing from it.
Work with prosody
is aimed at differentiating different shades of expressiveness, perceiving a rhythmic pattern (clapping, tapping), becoming familiar with narrative, exclamatory and interrogative intonation and their differentiation, and forming various voice modulations (loud, quiet). Dysarthrics have a clavicular type of breathing, so work with them should begin while lying on the speech therapist’s lap. Through tactile sensations - one hand on the stomach, the other on the child's chest - learn to breathe with the stomach and chest.
Stage 2. Formation of primary communicative pronunciation skills
Its goal is to develop control over the position of the mouth, lips, and tongue, the formation of articulatory movements, the development of correct pronunciation of sounds using specially selected speech material, and sound analysis of words. Specific tasks are production, automation and differentiation of sounds.
Work is being done to develop the sensations of articulatory movements and motor-kinesthetic feedback.
Exercises
used include straightening the cheeks, shaking the upper and lower lips, lowering and raising the lower jaw. Sounds are produced in three ways: mechanical, imitative and mixed. Automation includes training exercises with sound in syllables, words, phrases, sentences. Speech material should not include impaired sounds.
How to prevent cheek swelling in a child
Inflammation and swelling of the cheek in a child can be prevented by following preventive measures:
- Timely treatment of caries and other dental diseases.
- Prevention and treatment of respiratory tract infections.
- Correcting malocclusion in a child.
- Rinse your mouth after every meal.
- Reducing the amount of sweets in the diet.
- Systematic examinations at the dentist.
Kalanchoe leaves
Method of use:
- Tear or cut off one leaf and rinse thoroughly.
- Cut the sheet into 2 halves.
- Apply the cut to the inflamed gum and leave for half an hour.
Compresses with these plants should be made 3-4 times a day.