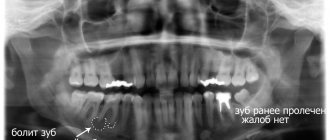
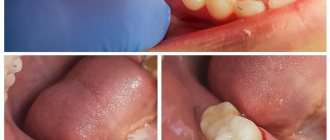
Diagnostics is an important stage of competent dental treatment. One of the most popular methods is a targeted photograph of the teeth. X-ray, regardless of the type of disease, makes it possible to carry out both diagnostics and preparation of the tooth, and certain manipulations in the tissues.
Thanks to the resulting image, a flat projection of the desired area is obtained. As a rule, this is enough to determine the condition of the tissues around the tooth. And after endoscopic treatment, it is important to examine the internal tissues of the tooth, how tightly the filling fits and whether the bacteria are completely removed. It is in this case that this examination option is useful.
The Implantmaster company offers to take targeted photographs of the teeth, the price of which is affordable. We guarantee high-quality results that will help in the diagnosis or treatment of diseases of the teeth and gums.
Sight shot: concept and purpose
Targeted dental radiography of teeth is one of the simple, quick and accessible diagnostic techniques in the dentistry industry.
We are talking about a traditional 2D image that shows the doctor the condition of 1-3 adjacent teeth. To perform this type of X-ray, clinics use X-ray equipment called an analog X-ray machine or digital radiovisiograph. A targeted X-ray of a tooth solves a couple of main problems:
- Helps make a diagnosis. For example, to identify the inflammatory process occurring in the area of the apexes of the roots of the teeth.
- Helps control the quality of sealed canals and the restored bone structure. Taking such a measure is important in the treatment of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, as well as as part of the preparatory stage before prosthetics.
The dentist prescribes a referral for the described x-ray to the patient in the following cases:
- for pathological conditions of the gums (periodontal disease, periodontitis);
- acute pain syndrome;
- for dental diseases (pulpitis, caries);
- to diagnose injury;
- for the purpose of quality control of sewer cleaning;
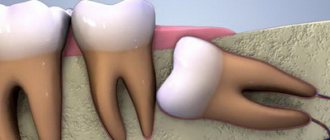
- if necessary, draw up a picture of the growth and condition of wisdom teeth.
It is not advisable to take a targeted photograph on the eve of bite correction or implantation - a panoramic photograph will tell you more about the current condition of the teeth. Such an x-ray is not justified when planning therapy and prosthetics for 4 or more teeth. It also will not help identify perforation and cracked tooth roots.
Indications
The procedure can be scheduled at your first visit to the dentist.
It is recommended to check any suspected pathology. This is done by analyzing the captured image.
Indications for such a procedure may be:
- mechanical damage to the tooth;
- quality control of dental canal filling;
- periodontal diseases;
- caries;
- pulpitis;
- painful eruption of wisdom teeth;
- pain after dental treatment.
A dental examination may be necessary for many other problems that arise in the oral cavity.
Restrictions and contraindications
Standard contraindications for dental x-rays using the targeted image method are the first and third trimesters of pregnancy. This type of examination is also not prescribed when acute viral diseases are detected.
A relative contraindication is the period of lactation. It is usually recommended not to breastfeed your baby immediately after having an x-ray. Milk should be expressed, and feeding should begin no earlier than three hours after the end of the procedure.
Age and condition restrictions are waived in life-threatening situations.
Types of X-ray
Depending on the equipment used, there are two types of X-ray images:
- An image on film (created on an analog X-ray machine). Gradually the picture fades.
- Electronic image (obtained using a digital radiovisiograph). It is possible to enlarge a certain area for detailed diagnostics.
In practice, there are two types of effective images: interproximal (helps in assessing the diagnosis of the dental crown), periapical (created to study the tissue near the tooth).
The whole truth about a visiograph in dentistry
Radiovisiographs came into the practice of Russian dentists more than 10 years ago, but still raise questions. The most popular is “Is this the same as an x-ray?” We answer right away: not really. We invite you to understand together the main features of the device and debunk the myths that worry doctors and patients.
How much safer is a visiograph than a regular x-ray?
The device itself is not an emitter, but only receives rays. Consists of a sensor, an analog-to-digital converter and a wire. Nowadays, most models are lightweight and are produced without a separate digitizing unit, that is, they are connected directly to the computer. There are also wireless visiographs that are placed in a special scanner to read the image.
The visiographic complex includes:
- X-ray machine;
- visiograph with software;
- computer.
Yes, the visiograph will not work without an X-ray machine. So why is it even needed then? Isn't it easier to do a regular x-ray?
Firstly, modern equipment is superior to devices of previous generations in terms of safety. If earlier installations emitted wide radiation, now a thin and targeted beam is captured by a sensitive sensor.
Secondly, the sensor recognizes even the smallest particles of radiation in less than half a second or even faster.
I would also like to note the advantage of digital visiography over film devices. Even if you take high-quality film and a good new generation of dental X-rays, it will take approximately 0.6 seconds to take a high-quality image. The same with digital radiography with a sensor is performed in 0.06 seconds. The sensor adequately perceives the signal at exposure from 0.3 tA/sec to 1.8 mA/sec.
So we have the answer to the first question. Radiovisiography is based on the same principles as conventional radiography. At the same time, the level of X-ray radiation during the operation of a radiovisiograph is much lower.
What dose of radiation do patients receive?
We believe you have heard this question from your patients more than once. When X-raying the teeth of the lower jaw using a visiograph, this value is 2 microsieverts, for the upper jaw – 5 µSv.
If film radiography is carried out using highly sensitive film and a low-dose device, the same indicator will be equal to 7 and 13 μSv. When working with old domestic equipment and low-quality film - up to 80 µSv.
How many pictures can you take? It is difficult to regulate the exact number of x-ray examinations, since not all devices are equipped with a dose counter. Accordingly, you will need to calculate it for each type of device and for each tooth. It is logical to focus on the maximum permissible effectively equivalent dose for a person per year, excluding its excess.
According to SanPiN, when carrying out preventive medical x-ray procedures and scientific research, this dose should not exceed 0.001 sievert per year (1 millisievert, 1000 microsievert). The load is equivalent to three plain chest films.
Is it possible to take dental photographs of pregnant and lactating women?
Radiovisiography is allowed only for clinical indications when there is a threat to life. We recommend that private doctors treat this with special care: for example, the patient’s signature on the card has no legal force, and all responsibility lies with the dentist.
Breastfeeding mothers can take photographs, since ionizing radiation is scattered when passing through soft tissues and biological fluids of the body. Thus, it will not affect the child in any way. To make the patient feel calmer, you can skip the next feeding after the photo.
Where can a visiograph be placed?
Since the device only works in conjunction with an X-ray machine, you must have a license that gives you the right to use equipment that generates X-ray radiation. The standard kit for obtaining a document contains a planned diagram of the office for using a visiograph.
Depending on the characteristics of specific equipment, biological protection is calculated by supervisory authorities. They also study the area of the office, the lead equivalent of the wall materials, the location of the office in the building, and the average workload of the imaging unit.
We talked more about organizing an X-ray room in our guide “How to open an X-ray room in a clinic.”
Our resume
A visiograph greatly simplifies the dentist’s work and allows you to quickly obtain digital images. Thanks to the user-friendly software, all images can be edited, archived and compared.
Despite the greater safety of the visiograph compared to standard X-ray machines, do not forget about the protection of personnel. You must stand behind a state-issued protective screen or leave the premises. If your practice has lead aprons, you can stand at least 2.5 meters to the side of the X-ray tube.
Features of the procedure
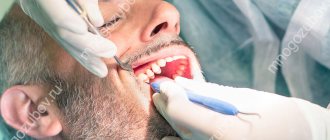
How are targeted dental photographs taken? The manipulation is carried out by a doctor in a separate room. The mechanism for performing radiography using a digital device:
- The subject sits in a chair. The doctor gets acquainted with the area where the problem is located.
- To prevent the adverse effects of rays on the body, a protective layer is provided: the patient’s body is covered with a special apron.
- The doctor fixes the patient's head in a given position to obtain a clear x-ray image.
- At the target area (inside the oral cavity just behind the teeth or on the front side), the specialist directs a beam of rays using a digital sensor.
The process takes a few minutes. After a quarter of an hour, the patient is given an image on paper, sometimes in electronic form.
During the X-ray process, the patient must remain motionless.
Description of dental radiograph
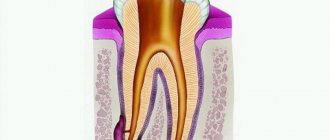
The radiograph is read by a dentist or radiologist. Describing the resulting image, the doctor makes a qualitative assessment of it.
Then the specialist examines the level of rigidity, density, homogeneity of the bone structures of the upper (lower) jaw, and the placement of elements of the dentition.
Symptoms that may appear on x-ray are described in the table below:
| Diagnosis | Visualized features |
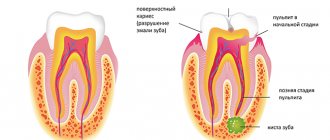
| Caries | A carious formation, expressed in the transparency of the enamel and the hard part of the tooth (the area of tissue destruction). The sign of clearing is a focus of unnatural shapes with an implicit edging. |
| Pulpitis | Symptoms of bone damage are loss of its homogeneity in the interroot area against the background of hypertrophy. |
| Periodontitis | Granuloma in the area of tartar formation, enlargement of the gap due to periodontitis, blurring of the edges. When pus forms, the x-ray demonstrates a clinical history of osteoporosis; during the granulation process, destruction of the hard part of the tooth and cement is observed under the influence of the active progression of the granulation process. |
| Periodontitis | Symptoms of osteoporosis: the density of bone structures decreases, the same happens with the height of the partitions between the elements of the dentition, and “pockets” are formed. |
The doctor determines whether there are signs of clearing or darkening. In this case, we are talking about cavities, cysts, granulomas, inflammations and neoplasms.
Detailed analysis
The patient receives a traditional x-ray image from an analogue machine on photographic film. It is placed in a plastic or paper bag. The package indicates his last name, execution date and dental unit number.
In many clinics, the procedure is performed using digital devices. In this case, it is stored electronically on a computer, flash card or any other medium.
The taking of images should only be carried out by a qualified specialist who has undergone the necessary training. Quality largely depends on the correct implementation of the regulations adopted for these procedures.
Attention! The requirement to comply with the regulations also applies to the patient. If he wants to get a high-quality result, he must also follow the rules posted in front of the X-ray room.
The research data is reviewed by the attending physician. Based on them, the dentist receives detailed information about the condition of the tooth that is bothering the patient.
The following pathologies can be identified from the image:
- Pulpitis. appears at the bottom and center of the tooth. You may also find deposits in the root canal or dental cavity. This suggests that the disease has become progressive.
- Caries. If it is present, a change in the density of tooth enamel is noticeable. At the site of a carious lesion, the enamel will have a lighter appearance. If deformation of the tooth structure is visualized, then complicated caries occurs.
- Cyst. It can be traced in the form of an oblong figure with clear contours and a uniform structure. Its size and location are also well defined.
- Periodontitis. It is characterized by a sharp darkening in the upper part of the tooth root.
- Periodontal disease. At the same time, a decrease in bone tissue and signs of sclerosis and atrophy are visible.
This is interesting: Resection of the apex of the tooth root: when is it necessary, how is it carried out
In addition to a specific disease, the dentist can also detect concomitant dental anomalies (if any).
The examination will show the location of the tooth in the jaw, its inclination, and the presence of un-erupted neighboring teeth. This information can not only help in treating a specific disease. It can help prevent some problems in the future.
Carrying out x-rays in children
Practice helps to conclude: radiography in children is carried out much more often than in adults.
This fact is explained by the fact that the baby teeth of young patients are especially susceptible to caries. In this case, the lesions are localized in those areas that cannot be seen in any other way. X-rays help identify defects in the process of eruption of distant elements of the dentition, ailments of dental and bone tissue, and effectively treat teeth and gums. The same diagnostic method is relevant if orthopedic manipulation is necessary for problems in the process of jaw formation in children.
The procedure is carried out for a child in a similar way. For children (children under 2 years old), radiography is prescribed only in extreme cases. For example, in case of injury during childbirth (to monitor the development of the dental system) or a child falling from a height (to assess the integrity of the teeth).
The dangers of dental x-rays
Digital radiovisiograph (without applying film)
In modern medical practice, when creating a targeted image, a digital radiovisiograph is used, which is characterized by a reduced level of radiation, in contrast to devices used as screening diagnostics. Radiation exposure at the time of examination for an adult is 7-15 μSV. For comparison, the natural background in Moscow is 20 µSV.
This fact allows the equipment to be used to obtain a clear image in the treatment of preschool children without dangerous consequences for the child’s body.
The permissible annual dose for the population is 5000 µSV, and for regular visits to the dentist, a person may need no more than 100 spot images - this will total 1 mSV. There is no need to worry about the degree of harmfulness of such tiny radiation on the human body.
Frequently asked questions from patients
Are x-rays harmful?
Radiography is based on radiation exposure. This sounds quite threatening to the average person. Meanwhile, every person receives a dose of radiation every day, even our bodies are radioactive. The background radiation level per day is 10 μSv (microsieverts). To obtain 4 photos with a bitewing X-ray, the patient receives 20-51 μSv. A panoramic image gives 5-25 μSv. CBCT is accompanied by a higher radiation dose; in one session a person receives from 20 μSv to 700 μSv. The level of radiation will depend on the settings and type of device, and the width of the area being studied.
Thus, there is no direct threat in the procedure. However, radionuclides can accumulate, so diagnostics are prescribed if necessary. After the session, the radiologist must write down how many sieverts the patient received, this will make it possible to calculate the next dosage with minimal harm to the person. After the examination, it is advisable to eat more carrots, apples, radishes, beans and citrus fruits. These products will help remove radionuclides from the body.
How often can it be done
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
The type of x-ray and its frequency depends on the condition of the oral cavity and the complexity of the treatment. It is better to do CBCT no more than 3 times a year. Bitewing film photographs are prescribed no more than 7 times a year; the new technology uses lower radiation doses, so there may be more digital diagnostics. The acceptable norm is 7 diagnostic studies per year. When changing dentists, it is not necessary to take new photographs; it is enough to take the ones you already have with you to the appointment. If digital data has been lost, it can be requested from the clinic that conducted the examination. CBCT results are stored for up to a year in the archives of medical centers.
Restrictions
There are no complete restrictions on conducting targeted X-ray examinations. The doctor always weighs the possible danger for the patient against the benefits of the procedure.
Contraindications to radiography include:
- early pregnancy. Dental treatment is not recommended for a pregnant woman. Initially, when planning a child, it is recommended to undergo an examination by a dentist to exclude the possibility of further therapy;
- infancy (from 0 to 2 years).
The lactation period in most cases is not considered a contraindication to radiography.
Pros and cons of the diagnostic method
The procedure performed by a digital radiovisiograph has several advantages:
- obtaining a clear image of the tooth and tissues;
- safety;
- carrying out several procedures without the risk of adverse effects of x-ray radiation on the human body;
- convenient storage of sequential images on a computer or electronic media;
- the ability to print images;
- better conditions for assessing the clinical picture (the picture can be enlarged several times).
Among the disadvantages of the described method, it is worth noting the release of images from only one angle and the small coverage of the study area.
Where to get an x-ray, how much the procedure costs, video
The targeted radiography service is available in almost every specialized clinic. The cost varies around 400-450 rubles.
Some clinics provide the practice of booking several x-ray procedures (2-4) as part of dental treatment - the patient has the opportunity to save money.
A targeted dental image is a highly informative and safe procedure that allows you to identify a dental problem and monitor the effectiveness of the therapy. It is successfully carried out for both adults and children. X-rays are used with caution in pregnant women and infants.
Reviews
A targeted image is considered in dentistry to be one of the highly informative studies, safe and popular diagnostic options, which make it possible to detect even a hidden problem and monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.
You can share your feedback, impressions and advice about the necessity and effectiveness of this procedure by leaving a comment on this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags toothache diagnostics
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Universal trainer I-3 for the correction of malocclusions in children
Next article
The first signs of diffuse pulpitis and two treatment scenarios