Causes of oral abscess
The most common cause of an oral abscess is considered to be a history of severe dental disease, for example, when the patient has not been treated for periodontitis or periodontal disease for a long time. These diseases are considered the most dangerous due to the fact that as they progress, the gums and soft tissues located near the teeth suffer. The process consists of the destruction of these tissues and the formation of periodontal pockets (periodontal), which serve as a favorable environment for the activity of pathogenic microorganisms that produce toxins, poisoning of which leads to the development of the inflammatory process.
Another reason that can cause the development of an oral abscess is trauma to the mucous membrane. Trauma to this area can be caused by either poor-quality dental systems, for example, dentures, or caused by mechanical impact, for example, a wound left after some kind of injection.
Also, the inflammatory process can appear against the background of boils, especially when they are localized in the facial area.
As is known, the main causative agent of purulent processes is streptococci and staphylococci, which appear in sore throats. Influenza and viral diseases can provoke a purulent abscess, as a result of which the body’s protective function decreases.
Why does a scar appear on the gum?
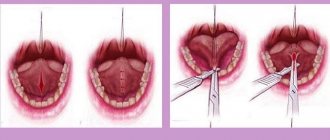
During any operation, the dentist has to make one or more incisions on the mucous membrane. This situation is inevitable with the formation of cones, purulent fistula or abscess at the roots of the teeth, with the accumulation of inflammatory fluid or other similar diseases. Sometimes only after opening the gums is it possible to get the “eight” or painful nerve. Once the stitches are placed, a healing process called scarring begins.
The mucous membrane consists of several types of cells. This is epithelial tissue that can recover and grow together. Under favorable conditions, the incision site is covered with a thin layer, gradually turns pale and merges with the surrounding tone. If the process is disrupted, a scar appears on the gum. It is formed during excessively active division of new collagen cells.
The main reasons for the appearance of such a defect:
- improper suturing;
- choice of coarse material (too thick thread);
- fusion of wound edges with displacement;
- inflammation of the incision with accumulation of pus.
Sometimes excessive formation of connective tissue is the result of a hormonal imbalance in the patient's body. Women during pregnancy or menopause, patients with diabetes mellitus and endocrinological pathologies are more prone to this problem.
Classification of oral abscesses
The classification of abscesses is based on their location in the oral cavity.
Thus, the following formations are distinguished:
- gum abscess.
- abscess of the floor of the mouth.
- abscess of the palate.
- cheek abscess.
- tongue abscess.
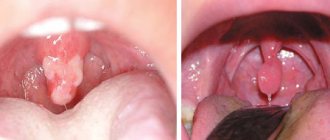
A purulent process that is diagnosed in dentistry more often than others. The main location of the abscess is the gum near a tooth. If treatment is not carried out for a long time, it can affect neighboring teeth and become chronic over time. With chronic gum abscess, the disease often worsens, pus flows out of a small hole at the site of the lesion, and a characteristic smell and taste appears in the mouth;
The main location of the abscess is under the tongue. With this localization, the patient feels discomfort and pain while eating. If the lesion ruptures, the pus that leaks from it can spread and create new foci of abscess, which will be located in the pharynx or neck;
It is a complication of previous or untreated periodontitis, it can become complicated and spread to healthy tissues of the palate, there is a possibility of developing osteomyelitis. Localized, as a rule, in the upper palate;
The purulent focus is located on the cheek, and it can be either external or internal. Has the ability to spread to neighboring healthy tissues;
This disease is characterized by an increase in the size of the tongue, which entails difficulties with eating and breathing. Dentists note that this process is the most dangerous.
Granuloma in the scar on the gum
Sometimes a small lump appears at the surgical site. The patient feels its mobility well and can move it by pressing the tongue. The scar on the gum seems to rise from the inside and resembles a convex tubercle. These are symptoms of a serious complication - granulomas. The disease causes various bacteria and microorganisms to enter the wound. The reasons are always related to poor hygiene:
- the patient did not properly treat the oral cavity after applying and removing sutures;
- the dentist used unsterile instruments or threads.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with how teething occurs in children.
The granuloma itself on the gum consists of phagocyte cells that surround the site of infection, preventing it from spreading to neighboring tissues. It occurs more often in people who have viral or bacterial diseases, rheumatism, tuberculosis or syphilis.
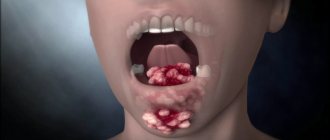
Symptoms of an oral abscess
An oral abscess can present with a variety of symptoms. Quite often the disease is accompanied by tooth pain (as with periodontitis). If the abscess affects the gum, then the pain syndrome can spread only in the area of the affected tooth, and the feeling of pain intensifies during the process of pressing on the tooth, for example, when eating. If you do not respond to the first signs of the disease, then the affected area subsequently swells and becomes very painful when touched. If a cheek abscess develops, localized in its inner part, then during the examination the dentist may notice that the affected area has redness and swelling.
In combination with obvious symptoms, the patient feels a general deterioration in his condition, body temperature rises, sometimes insomnia is present, and appetite decreases.
If you do not consult a specialist, then as the disease progresses, a breakthrough of the lesion may occur, while the patient feels a decrease in pain, a decrease in the tumor, body temperature normalizes, and the general condition can be assessed as satisfactory. Most often, with this outcome, patients refuse to visit the dentist, which is completely in vain. This phenomenon only indicates that the likelihood of the abscess becoming chronic has increased.
Why is it necessary to treat a scar?
Mucosal tissue recovers much easier and faster than the epithelium on the skin. Therefore, the postoperative scar on the gum in most cases heals imperceptibly and practically without traces. If a granuloma or lump has formed near a tooth, a noticeable scar may remain. You should immediately contact your dentist or therapist if alarming symptoms appear:
- temperature rises to 38–40°;
- the gums swell, itch and burn;
- a tugging pain appears inside the roots of the teeth;
- the seal turns white and may acquire a yellow tint.
These are signs of accumulation of pus and exudate in periodontal tissues. It can enter the body through the circulatory or lymphatic system and accumulate in the kidneys, liver or heart. The problem is fraught with sepsis or inflammation of internal organs.
Diagnosis of oral abscess
To diagnose an oral abscess, a visual examination by a dentist is necessary, during which the doctor will determine the condition of the mucous membrane. It is strictly not recommended to delay the start of treatment for the disease. Self-medication by taking antibacterial medications can only lead to a worsening of the patient’s condition and complicate the course of the disease. At the first symptoms, you should contact a specialist: it is important to do this before the spontaneous opening of the abscess occurs; you should also not open the detected lesion yourself or forcibly. The only thing a patient with symptoms of an oral abscess is allowed to do is take painkillers that will help relieve severe pain; you can also rinse your mouth with antiseptic medications.
Therapy for the disorder
Inflammatory processes are not only dangerous, but also bring significant discomfort to a person. In order to get rid of inflammation of the palate, you need to find out the cause of this disease. In this case, the doctor will be able to decide on the goals and method of treatment.
What can be done if the palate is inflamed and hurts:
- If the source of the inflammatory process is injury, then it will be enough to use traditional medicine. And to enhance the effectiveness of their action, you can use folk remedies in combination with local medications. They will help not only relieve pain, but will help create a protective barrier against the penetration of infections and bacteria.
- If there are dental problems of an inflammatory nature, the main goal will be to eliminate not only pain, but also the cause of its occurrence. So, with inflammation of the tonsils and nerves, you cannot do without the use of antibiotics to relieve swelling and pain. This treatment method will help within 1-2 weeks.
- In case of stomatitis, damage to the mucous membrane can be caused by a fungus, so it is necessary to use antifungal drugs for internal use. In this case, local treatment with ointments, sprays and gels is prescribed in compliance with the necessary hygienic measures and a special diet.
- If the palate is inflamed, affected by caries or pulpitis, it is necessary to visit a dentist. Initially, it is necessary to treat diseased teeth, which are a source of infection. If the source of caries is a virus, then the affected areas are treated with antiseptics and painkillers.
- If the cause of pain is a tumor, it is necessary to undergo an examination to identify the nature of its occurrence. You can only get rid of malignant tumors or benign formations through surgery.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Blisters on the lips of newborns
Treatment of oral abscess
If symptoms are detected that indicate purulent inflammation in the oral cavity, the patient should be immediately taken to the hospital for treatment. The main method of treating an abscess is surgery. In a hospital setting, the patient undergoes an opening of the abscess. After this, the accumulated purulent fluid is emptied. At the last stage, drainage is installed to prevent the formation of a new purulent focus. As an additional therapy, the attending physician prescribes the patient to take medications that reduce and suppress the inflammation process. Immunity enhancing drugs and a complex of vitamins are also prescribed.
If the process is acute, then severe pain must be removed before transporting the patient to the hospital. For this purpose, taking analgesics is allowed. Disinfection of the oral cavity is performed by rinsing with antiseptic drugs (for example, furatsilin, chlorhexine) or herbal decoctions (chamomile, sage or St. John's wort). To relieve swelling, cold compresses can be applied to the external affected side.
Types of Scar Tissue
There are two main types of scars: hypertrophic and keloid. The first ones are slightly increased in size, but gradually “deflate” and cause practically no discomfort to the patient. Over time, they resolve and become noticeably pale. The second type is considered more problematic for humans. Its characteristic features:
- a dense white scar appears on the gum, which can follow the outline of the seam;
- a person feels constant squeezing or stretching;
- Some patients lose sensitivity at the incision site;
- The color of the scar may change to dark red or bluish.
If such tissue has formed during the healing process, it may contain very thin capillaries. Sometimes the area bleeds and becomes very painful when brushed with a toothbrush or touched with the tongue. If after removal of the fistula or drainage there is a deep scar in the gum, the photo will resemble a small dense tumor. If you do not treat this problem, the scar will turn into a painful atrophic one and it will be too difficult to remove it.
Prognosis and prevention of oral abscess
In general, with timely treatment, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Depending on the severity and extent of the process, the duration of the recovery period will vary. Considering that the surgical intervention will be performed at the required time and will take place without complications, as well as provided that the patient’s immune system is relatively stable, complete recovery will occur within 7-14 days.
The main preventive measure is regular oral hygiene and visiting the dentist for a preventive examination at least once every six months. Trauma to the mucous membrane should be avoided as much as possible, caries, gum disease and periodontal tissue should be treated in a timely manner.
Kinds
| Classification | Description |
| By location | Aphthae can form on the mucous membranes of the palate, the inside of the cheeks, the tongue, lips in the throat |
| To size | Small sores with a diameter of 3-5 mm, large wounds with a diameter of up to 1 cm |
| By variety | Fibrinous stomatitis is characterized by the presence of erosive changes on the mucous membrane of a gray color. Duration 2-3 weeks. Necrotizing stomatitis resulting from infectious or inflammatory diseases. Cells of the oral mucosa die, the resulting lesions gradually increase and cause severe discomfort to the patient. The duration of the healing process is 2 months. Grandular stomatitis affects the salivary glands. Aphthae cause severe pain, and the risk of recurrence is quite high. Cicatricial stomatitis is manifested by the presence of large ulcers, which after healing leave visible scars. This process takes place over 3 months. Deforming stomatitis, as one of the most severe forms, is characterized by the formation of very large ulcers, leaving behind huge scars. There is a high probability of changes in the structure of the oral mucosa. Healing occurs very slowly and takes a long time. Herpetic stomatitis is observed mainly in infants who were infected from their mother. The sizes of the afts are small, but there are a lot of them. The baby has a high body temperature, the mucous membrane is severely inflamed and the membranes of the eyes and skin are affected. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis is often diagnosed in the adult population. The ulcers (aphthae) connect with each other and form large wounds that are covered with a white coating. The disease causes pain when eating food and while talking. Acute stomatitis is observed in children under three years of age and in some situations occurs against the background of whooping cough, measles, diphtheria and other pathological conditions characteristic of this age. |
How to distinguish a boil from other formations in the mouth
A furuncle, as medicine defines it, cannot form in the mouth due to the absence of hair follicles in this cavity, in which the infectious process begins during furunculosis. Abscesses in these places are abscesses due to local tissue inflammation.
Abscesses occur on:
- gums;
- sky;
- tongue and in the area under it;
- cheek tissues.
The danger lies in the possible breakthrough of the boil into the oral cavity.
Differential diagnosis allows the dentist to evaluate symptoms and separate non-odontogenic processes from formations of odontogenic origin. The main difference between boils and carbuncles and odontogenic abscesses and phlegmons is the purulent-necrotic core. With sialadenitis, suppuration is noted, the presence of a stone in the duct of the major salivary glands, which is determined by palpation or x-ray. Suppurating soft tissue cysts are anamnestically preceded by a soft elastic formation. The puncture shows the presence of fluid. An odontogenic source of inflammation in the mouth cannot be detected.