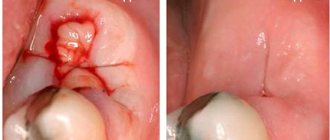
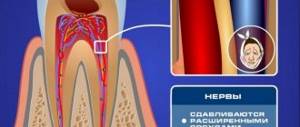
The Greek word "kystis", used to refer to a condition such as a dental cyst, is translated as "blister". This name most accurately reflects the essence of this disease. With it, a cavity is formed at the root of the tooth, which is filled with liquid (bacteria and dead cells), and the comparison with a bubble in this case is most appropriate.
The consequences of untimely treatment of a cyst in the gum of a tooth can be the most unpleasant - including tooth loss. The process may also involve neighboring teeth, which will also require professional dental treatment.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a dental consultation is 700
- The cost of an orthodontist consultation is 2,000
Make an appointment
Cyst symptoms
In the initial stages, the cyst is almost invisible. Unlike an abscess, it does not break out, but at the same time continues its development inside, affects healthy tissue of the jaw bone and leads to loosening of the tooth. As the inflammatory process develops, the following symptoms of a cyst in the tooth appear:
- pain in the affected area;
- swelling of the gums;
- increased body temperature;
- swollen and tender lymph nodes;
- flux.
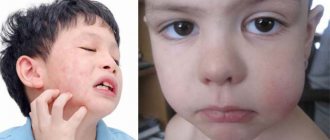
The pathology quickly develops into a chronic stage and is asymptomatic for humans. During an exacerbation, attacks of pain may occur when eating solid foods. Gradually, the tooth enamel becomes gray or yellow, and the tooth shifts. As soon as the immune system fails due to acute respiratory viral infections or exacerbation of chronic diseases, the growth of the cyst accelerates, so the appearance of a fistula, swelling, acute pain, fever and migraine is observed.
Indications
- Bite abnormalities.
- Periodontitis.
- Installation of orthodontic systems.
- Severe deformation of the ligamentous apparatus (tooth loosening).
- Hyperdontia.
Contraindications
- ARVI and weak immunity.
- Chronic and acute forms of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Nervous and mental disorders.
- Cancerous tumors.
What treatment methods are possible
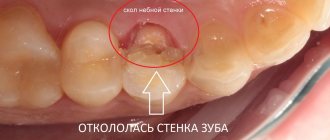
Until quite recently, doctors, in the presence of such neoplasms under a crown or without a crown, took drastic measures - tooth extraction. Today, in most cases, the tooth itself can be saved. And this can be done in completely different ways, depending on the clinical picture of the disease.
Conservative treatment
The use of antibiotics and medications is possible if the cyst is still very small and does not exceed 5-8 millimeters in diameter. In this case, you can do without surgery, and the doctor does not resort to removing the artificial structure and monitors the results of therapy over time. In this case, work with the cyst itself is carried out through a small incision in the mucous membrane near the root. Ideally, the cyst should gradually decrease in volume and disappear.
Also in modern dentistry today, depophoresis is used, i.e. medications (most often calcium and copper hydroxide) are injected into the root canals using current pulses. Naturally, before this procedure you will first have to remove the crown and unfill the tooth canals. This procedure is not considered a panacea for cysts, but in some cases (when the tumor is small and the situation is not advanced) it helps get rid of the problem without surgery.
If the listed conservative methods do not help or there is no point in them in the first place, then the specialist resorts to other, surgical measures, and, of course, must first remove the prosthetic structure.
"I am disappointed. I had an almost brand new zirconium dioxide crown. I received treatment six months ago and paid 25 thousand rubles. And then, during a routine examination, the doctor discovered a cyst on you, the reason for its appearance remained unclear, no one could clearly explain. The crown had to be removed and everything re-done. Naturally, then it is impossible to put it back; the doctor explained that it is fixed with special cement and it is simply unrealistic to remove it without damaging the material. After all the torment, I had to fork out for a new crown, I chose a cheaper one, a metal-ceramic one, but at least I saved the tooth, and thank you for that.”
Margo, comment from 32top.ru
Root apex resection
The doctor makes an incision in the gum, after which he performs micro-surgery on the root, removing only the damaged tip and the cyst. This operation is considered tooth-preserving and allows one to avoid extraction, but it is not suitable for patients with contraindications: if there are cracks in the tooth and if the roots of neighboring units are close together. After the resection procedure to restore tissue, the patient is also prescribed antibiotic therapy.
Hemisection
Along with the cyst, the doctor removes part of the root and part of the crown. The procedure is considered the simplest in medical practice, but is used only in the initial stages of development of a cystic neoplasm.
Cystectomy
This is a type of surgical intervention that allows you to do without removing an artificial prosthetic structure. The procedure is carried out in a retrograde manner, which is why it involves a rather difficult rehabilitation period, suturing: the doctor first peels off the gum and gives himself access to the root system, after which he removes the cyst and the damaged part of the root, fills the canals virtually from below, and then applies sutures to the gum , which returns to its place. The patient recovers with the help of antibiotics and constantly visits the doctor for a thorough examination and X-ray control.
Cystotomy
This method is considered the most difficult to perform. It is used in the presence of large cysts. To save the tooth, the doctor makes an incision in the gum, removes the front wall of the tumor, and treats the cyst itself with medications. In this case, the specialist also necessarily removes the tip of the root, near which the inflammation is localized. Then everything goes according to the classical scheme: suturing, rehabilitation, taking antibiotics.
Doctors today can perform all surgical operations with a laser, which will make it easier to survive the intervention itself and the rehabilitation period. Therefore, you shouldn’t worry too much, because the main thing here is to preserve the natural tooth, and not to delay until the moment when there is no other choice but to completely remove it.
Why does a cyst appear?
The causes of the appearance of a dental cyst, a photo of which can be seen in this article, are injuries due to mechanical stress or infection, which leads to the development of inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth. A tooth inside the gum can be injured under a variety of circumstances, for example, when the tooth is hit or when chewing nuts. As for infection, it can get into the root canal if dental treatment is performed incorrectly, in particular, if the dental canal is incompletely filled. A cyst that arose as a result of sinusitis or another infectious disease is relatively rare. In this case, pathogenic microorganisms enter the gums along with the blood flow.
Why does pathology occur?
The culprit is infection of the root canals. But pathogenic microorganisms can get there in completely different ways:
- chronic periodontitis of neighboring teeth or a treated tooth, but if the inflammation has not been eliminated,
- violation of the technique of preparation and treatment of root canals before prosthetics: for example, the specialist used an unsterile instrument, injured the canals or root, used an allergenic material that caused irritation and inflammation of periodontal tissues. Also, the doctor could not complete the root canal, poorly disinfect it or seal it tightly enough, overlook incompletely cured caries, pulpitis, periodontitis,
- insufficiently high-quality prosthetics: for example, the doctor who initially installed the prosthetic structure for you could not fit it tightly enough to the gum, as a result of which you did not even notice how the smallest food debris and bacteria began to get under the crown, and, accordingly, the inflammatory process began ,
- chronic sinusitis: in this case, the infection from the nasal sinuses could have gotten not from the outside, but from the root, hematogenously, i.e. through lymph and blood,
- injury and inflammation of the gums,
- advanced diseases localized on adjacent teeth,
- eruption of adjacent (usually impacted) teeth: these are those that do not fully penetrate the surface and occupy an incorrect position in the bone. They can put pressure on neighbors, destroy them and thereby cause an inflammatory process around them,
- untreated systemic and chronic diseases: especially in the acute stage, they can reduce the overall immune status of the body and lead to the appearance of similar problems.
How does the disease develop?
The process begins with periodontitis, when the tissue located between the jaw bone and the tooth root becomes inflamed. As a result, the tissues located around the root begin to grow abnormally. Initially, the size of the neoplasm does not exceed five millimeters (it is called a granuloma). Growing and enlarging, it becomes covered with a membrane and transforms into a cyst.
There are cases when the cyst grows so much that it eats away the bone around the tooth. With the next exacerbation of inflammation, it opens, forming a channel to the outside through the gum mucosa. Such a channel is called a fistula or fistula tract.
It is worth noting once again the insidiousness of this disease, which not only negatively affects the condition of the roots of the teeth, but also affects the general condition of a person. At the initial stage, the pathology develops almost imperceptibly and can only be detected during a visit to the dentist. Pronounced symptoms appear in the later stages of the disease as a result of tumor growth and destruction of bone tissue.
The main danger of a cyst is the fact that, by corroding the bone, it deprives the patient of the opportunity to install an implant in place of a lost tooth without complex manipulations.
User Questions
QUESTION My dentist found a cyst in my front tooth under the crown. She says that while she is small, she can be treated with antibiotics. But he said it was better to remove the crown. Why can't you leave her? Alexei
ANSWER Hello, Alexey. It is likely that your doctor wants to reduce the chewing load on the tooth. To prevent you from accidentally biting something hard or pushing the infection deeper, it is better to remove the tooth from the bite. Another option is to remove the crown. Don't worry, after treatment it will be put back in place. During the treatment process, the tooth will be covered with a temporary filling.
1Epifanov E.A. Medical rehabilitation for diseases and injuries of the maxillofacial area, 2021.
Author: Vasin Yu. A. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
What complications does a dental cyst lead to?
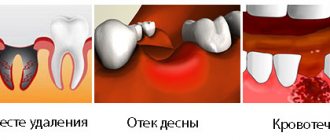
Untimely treatment or removal will lead to the following complications:
- Periostitis.
- Swelling.
- Abscess.
- Phlegmon.
- Temperature increase.
Usually the cyst does not make itself felt in any way, so complications may appear unexpectedly. To exclude serious consequences, you need to be examined by a dentist at least once every six months. The appearance of a capsule with pus can occur against the background of deep caries or severe inflammation of the gums, so do not delay a visit to a specialist.
The lack of results with conservative treatment leads to the fact that the cyst has to be removed along with the tooth.
Consequences and complications of the disease
Why is a tooth cyst under a crown dangerous? If the pathology is left unattended, then eventually even a slowly developing neoplasm will provoke any of the following complications:
- spread of inflammation to the roots of neighboring teeth: they may change color, begin to hurt, become loose or fall out,
- tooth loss,
- spread of pus to the jaw and soft tissues: this can result in osteomyelitis, abscess, phlegmon, sinusitis, etc.,
- spread of infection throughout the body through the bloodstream: can cause damage to the brain, lungs, liver, kidneys and other organs,
- “degeneration” into a malignant neoplasm,
- sepsis.
Treatment of consequences and complications is much more difficult, longer and more expensive than treatment of a cyst. In many cases, the patient will additionally require rehabilitation1, and, for example, jaw bone augmentation after osteomyelitis. By the way, with this disease you can lose all your teeth in a row.
Complex on 4 OSSTEM implants with delayed loading - 150,000 rubles.
Complex implantation Osstem (South Korea) with delayed loading after 4-6 months.
Doctor's work guarantee - up to 5 years (under an agreement on the provision of medical services) Call now or order a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Types of dental cyst
The type depends on the place of occurrence. A cyst forms in the maxillary sinus, gum, root or under the crown. To determine the type of capsule with pus, the specialist examines the medical history and assesses the client’s general health. There are 5 types of dental cysts:
- Follicular - formed when the tooth was unable to grow unhindered and most of it remained inside.
- Keratocyst - develops against the background of pathological processes during the growth of the body (the growth of the neoplasm is stimulated by the pharynx-forming tissue).
- Radicular - appears from a granuloma and is a serious complication of deep caries.
- Retention – is formed during the eruption of molars in children.
- Residual – appears due to complications and inflammatory processes after tooth extraction.
Diagnostic measures
Here, the most effective diagnostic method to this day remains x-ray examination. After all, it is with the help of an image that the doctor can best assess the extent of the inflammatory process and confirm the diagnosis. In the photographs, the cyst appears as a black, rounded spot located near the apex of the root.
“Many patients panic, suspecting a cyst under the crown. After all, in their minds they immediately begin to replay a situation in which in any case they will have to get rid of the prosthetic structure, remove it, treat it, and then install a new one. All this costs significant costs, and no one wants to pay twice. It is important to emphasize here that the less the inflammatory process, the greater the chance of getting by with therapeutic measures, medications, and even in some cases you may not have to remove a previously installed crown. Therefore, it is important for patients not to delay treatment, but to immediately consult a doctor at the first suspicion. This is a real chance to save money and nerves,” says dentist-therapist O.A. Belyaeva.
Cyst on the root of a tooth
This species grows in the alveolar area and can appear in any area of the gum. There are no symptoms except for tingling when eating or touching. Pain appears in later stages of development. A cyst on the root of a tooth is divided into 3 types:
- Peri-root - appears in the upper part of the root.
- Interroot – formed between the roots.
- Radical - appears near the root canal and over time can cause the growth of a malignant tumor of the jaw (if not properly treated).
Types of neoplasms under the roots
In the dental classification, there are 3 types of cysts under the crown; let’s look at them in more detail:
- root or radicular: located in the apical part of the root. Appears due to infection during preparation before prosthetics or due to injury,
- primary or keratocyst: most often located near the lower molars - large chewing teeth. It does not appear in any way for a very long time; it is discovered by chance on an x-ray - in the corner of the jaw, on its body or branch. The bone tissue is greatly sparse,
- follicular or tooth-containing: develops from the tooth germ of a canine or wisdom tooth on the upper or lower jaw. Can cause ameloblastoma, a benign tumor
- residual: we can say that this is a secondary cyst, since it develops on the site of a previously poorly removed one,
- paradental or retromolar: most often located between the dystopic wisdom tooth and the roots of the adjacent one, on which the “figure eight” presses.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS ON 6 IMPLANTS - 290,000 rub.
The price includes all manipulations for installing Osstem implants (South Korea), manufacturing, installing and fitting the prosthesis, including anesthesia and diagnostics.
Save RUB 30,000. >> Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Conservative and surgical treatment of cysts
In the early stages, in the absence of complications, a conservative method is acceptable. The root canal is drilled and cleaned. The capsule with pus is opened and cleaned, and a composition with an antibiotic is poured inside. Next, a bone tissue regeneration paste is applied and a filling is installed. A control check after 6 months demonstrates the absence of a cyst on an x-ray in 80% of cases
Surgical treatment is prescribed if there is no result. With the help of cystectomy, the affected part of the tooth and the capsule with pus are completely removed. Cystectomy is an operation that not all dental surgeons can do. Hemisection is often used, which gives a 100% result and is prescribed for severe root damage. All affected tissue is removed, and the appearance of the tooth is restored with a crown or composite composition.
Cyst under the crown: how to recognize, treat and prevent complications
If you have recently had a tooth treated and restored with a prosthetic structure, then very soon or after a few years it may come as a complete surprise to you that there is a cyst under the crown. Unfortunately, it is sometimes impossible to insure against this pathology even for those who have undergone expensive treatment. Despite the fact that the situation is quite common in medical practice, it is considered one of the most insidious, difficult to diagnose in the early stages and, in the absence of timely treatment, can harm the patient.
In order not to miss a tumor under the crown and know what to do, be sure to continue reading today’s useful material.
Do you really have to put up with this?
Making dentures is quite a complex job, in some ways even comparable to art. Working in tandem, the orthopedic surgeon and the dental technician put a lot of effort into making an accurate and as comfortable prosthesis as possible. But in most cases, after putting it on and wearing it, it turns out that it needs some adjustment to the patient’s gums.
To regain lost comfort, you need to walk with the installed structure for 3–4 weeks. During this time, you can get used to the initially interfering prosthesis and get rid of the unpleasant sensations. If you simply remove it when discomfort appears, then you will have to describe all the inconveniences experienced in words, and the doctor will not be able to understand what exactly caused them. Do you want the correction to be effective? Be sure to come to your appointment wearing a prosthesis that causes discomfort.
Correction of dentures is carried out within 15–20 minutes. As a rule, it is possible to restore the patient’s comfort in one or two visits to the dental clinic.
Dental prosthetics with ceramics
The modern choice for dental prosthetics is ceramics. Ceramic crowns have long become affordable; they have excellent biocompatibility - they do not cause allergies, do not change the sense of taste, and support healthy gums. Ceramic crowns are quite durable, and their aesthetic properties are much higher than those of metal ceramics.
After the implant has been implanted, a gum former is installed on it, which models the shape of the gum around the crown, like around natural teeth.
A ceramic abutment is installed on the implant - the basis of the crown, replacing its own tooth. The crown was made in the Dial-Dent laboratory from E.max ceramics.
The crown fastening is screw. With this type of fastening, the crown can be easily removed if any treatment is suddenly required, since the site of the cyst remains under the supervision of specialists for some time until complete recovery.
The place where the crown is fixed is covered with filling material.
A panoramic photograph 4 months after implantation showed good condition of the bone around the implant:
The cavity where the cyst was was overgrown with bone tissue, and the spread of the cyst was stopped.
Video about screw-retained crowns: