From this article you will learn:
- why does bleeding occur after tooth extraction,
- If a tooth is pulled out, the blood won't stop - quick help at home.
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
Situations where blood bleeds after tooth extraction most often occur when the patient has high blood pressure (due to hypertension or severe stress), as well as if a large vessel was damaged during surgery.
Most often, bleeding develops while still in the dentist’s chair (immediately after tooth extraction), but sometimes bleeding can be delayed, i.e. develops only a few hours or overnight after removal. In the latter case, patients often passively wait for the bleeding to stop on its own, and this can sometimes lead to significant blood loss and weakness.
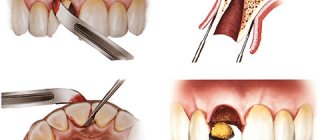
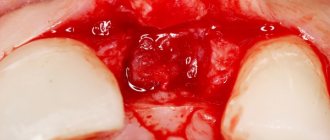
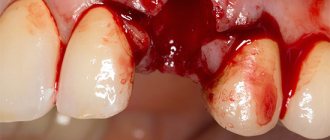
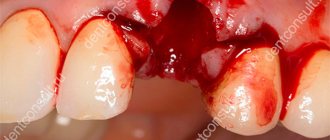
Bleeding after tooth extraction: before and after photos
How long does bleeding occur after tooth extraction (normal) - normally, bleeding should stop within the first minute after extraction, as soon as the hole fills with blood. However, during the first time, ichor may be released from the wound (do not confuse it with blood), and do not be alarmed if the saliva turns reddish at first - this is normal.
Top 5 practical tips
Method No. 1
Change the tampon that the doctor placed on the tooth. Take a sterile piece of bandage, fold it in several layers, cover the hole and press firmly, closing your jaws. To be on the safe side, you can moisten a new tampon with a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution. A clean bandage should be held with your teeth for 15-20 minutes; if you used peroxide, do not overdo it, hold for no more than 5 minutes.
Method number 2
Apply a hemostatic sponge; you can buy it at any pharmacy. The product has hemostatic properties, so it almost always helps. Cover a piece of sponge with a cotton swab and place it on the wound - after a few hours it will disappear without a trace.
Method number 3
Cold will help stop bleeding. Apply a piece of ice or a cold bottle of water to your cheek, after wrapping them in a napkin or towel. Leave for 4-5 minutes, then remove. Apply cold objects 3-4 times at intervals of 5 minutes.
Method number 4
Tea leaves have tanning properties, so you can try to stop the bleeding by placing a tea bag soaked in warm water in the tooth socket. You need to act very carefully so that the bag does not rupture and grains of tea leaves do not get into the wound.
Method number 5
Suitable for those who suffer from high blood pressure. Measure your blood pressure - if the readings are elevated, take “your” medicine that you always use.
Professional assistance in dentistry
If you could not stop the bleeding at home on your own, then you need to go to the dentist. The doctor will examine the hole, clean it if necessary, and treat it with an antiseptic. Further, depending on the clinical situation and indications, iodoform turunda or a hemostatic sponge can be applied to the wound.
A specialist can also cauterize the vessels with an electric current using a procedure such as electrocoagulation. Another effective measure to stop bleeding and minimize possible complications is suturing the edges of the wound and applying sutures. If large blood vessels were damaged during the extraction process, the doctor will compress and bandage them.
If the bleeding has not stopped for too long, the doctor will definitely prescribe you medications and antibiotics to avoid further complications. Additionally, the dentist may prescribe hemostatic drugs that promote rapid clot formation (for example, Dicynone), but only if you have no contraindications (thrombosis, thrombophlebitis).
“I once returned home from dentistry after a planned operation, and my extracted tooth was bleeding, quite heavily. It's good that I'm on the phone with my doctor. She advised me to take a Tranexam tablet if there are no contraindications. I quickly read the instructions on the Internet and sent my husband to the pharmacy. I took it at home, the bleeding stopped after 20 minutes and there was no more…”
Vera, review from otzovik.com
What drugs increase bleeding?
- If bleeding is accompanied by severe pain, then there is a natural desire to get rid of it as quickly as possible. Drinking Aspirin and Ketanov is strictly prohibited, especially during pregnancy, as they thin the blood and increase blood flow. When the effect of the analgesics wears off, the situation may repeat itself, so if the pain is “not fatal”, it is better to be patient.
- It is not recommended to take a hot bath, drink hot or alcoholic drinks, that is, perform activities that can provoke a jump in blood pressure.
- For 48 hours you should not eat solid food or check the socket with your tongue. You can damage the formed clot, and the blood will flow with renewed vigor.
- If there is no inflammation, do not rinse your mouth. The liquid washes the “plug” out of the wound, so the process repeats.
Signs of normality
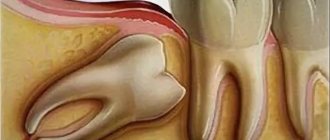
It is quite normal that after you have a tooth pulled out, the wound that forms in its place begins to bleed. This is natural, because the doctor performed a surgical operation, during which he acted on living tissues penetrated by many vessels and capillaries. As a result of the injury, a physiological reaction such as bleeding occurred.
Immediately after removing the root, a hole forms in its place, which should fill with blood. The oozing blood should not be spit out; you must wait until it thickens and stops. The resulting clot is necessary for our body, as it performs a protective function and prevents infection from entering damaged tissues.
Important! Don't confuse blood with ichor. Ichor is a yellowish liquid with a slight admixture of blood, which is released from damaged tissues and promotes their healing. You may notice how saliva is stained with it within 1-3 days after extraction (removal), which is also a sign of normality.
What to do if nothing helps
If none of the methods help, blood continues to accumulate in the socket, dizziness, weakness, chills or headache appear, call the doctor and go for a follow-up appointment.
If food gets into the wound after wisdom tooth removal, the gums may become inflamed. Use a folk remedy: rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile or oak bark. If the inflammation intensifies or the temperature rises, go to the dentist immediately. He will examine the wound and decide on the spot which agent to use to stop the bleeding.
Cases in which we are talking specifically about pathology
Some patients even at home notice that blood continues to ooze. Sometimes the bleeding stops at the dentist's office, and then, at home, it starts again. An unpleasant symptom may make itself felt again a few days after the operation. All these are signs of pathology.
What else says about the pathological process:
- the bleeding is severe and cannot be stopped by any acceptable home remedies (we will talk about them later),
- weakness and dizziness appeared,
- body temperature has risen,
- pus is released along with the blood,
- there is severe pain that is not blocked by analgesics,
- there is severe swelling of the soft tissues of the oral cavity and face.
In all of the above situations, immediate consultation with a doctor is required.
Important! Pathological bleeding is dangerous because the clot that protects the wound is washed away, and the hole remains dry and becomes defenseless against pathogenic bacteria. This situation is dangerous for the development of the inflammatory process, alveolitis, gumboil, and osteomyelitis. In addition, heavy and prolonged blood loss can lead to a general deterioration in health, weakness, dizziness, and anemia.
What measures will help prevent bleeding after tooth extraction?
- Before visiting the dentist, take a tincture of motherwort or valerian. This way you will get rid of fear, calm the nervous system, and normalize blood pressure.
- Buy hemostatic drugs at the pharmacy in advance, for example, Dicynon. Such drugs accelerate thrombus formation, so a clot forms faster. Ask your pharmacy about contraindications.
- The day before your appointment, do not take blood thinners. Blood clotting disorders can lead to complications during surgery.
Folk recipes
Of course, herbal decoctions and juices are not able to completely cure gums that bleed when brushing your teeth. However, natural compounds can become excellent therapy assistants, reduce pain, reduce bleeding, and most importantly, significantly speed up treatment.
The most popular remedies for bleeding gums are:
- A decoction of blueberries will help quickly get rid of even severe bleeding.
- A decoction of oak bark is effective for almost all gum diseases.
- Sage decoction provides antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Chamomile has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. A decoction of this plant helps with gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontal disease, and for the prevention of gum inflammation.
- Lemon and black radish will provide reliable protection of teeth from plaque and gums from inflammation.
- An effective means of preventing gum inflammation is water pepper tincture. This healing composition increases the density of the walls of blood vessels, increasing blood clotting.
- Onion and aloe juice are also used to prevent and treat inflammation. These plants (in equal parts) can be applied as applications to the gums twice a day.
To prevent bleeding and inflammation of the gums, it is necessary to eat raw carrots, apples, celery, pears, radishes and other hard fruits and vegetables. Such food will not only enrich the body with vitamins, but will also provide excellent natural massage of the gums and cleanse the enamel of plaque.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
Myths about complications after tooth extraction
The bleeding should stop within half an hour
In practice, in most patients, the period of clot formation takes from 2 to 12 hours. This is due not only to the characteristics of blood clotting, but also to how accurately the doctor’s recommendations are followed.
Prolonged bleeding is a sign of alveolitis
If there are no signs of inflammation, then there is no reason to panic. Manifestations of alveolitis are strongly expressed, as a rule, by several signs simultaneously. This is a gray coating on the hole, bad breath, purulent discharge from the wound.
Why do my gums bleed?
In fact, bleeding gums is a symptom that accompanies many different diseases. The reasons for this unpleasant manifestation may be:
- Inflammation in soft tissues
. Due to inattention to oneself and improper oral hygiene, plaque and tartar gradually form on the teeth. Deposits between the teeth and on the enamel sooner or later lead to inflammation: the patient begins to develop gingivitis and the gums bleed. Without proper treatment, the problem can develop into a very dangerous disease for teeth – periodontitis. - Mechanical damage.
Sometimes we don’t notice that at lunch we chewed a stalk of celery that was too hard or enjoyed a cup of roasted coffee. As a result, the gums are injured, tissue integrity is compromised, and bleeding begins. By the way, often when brushing our teeth, our gums begin to bleed precisely because we choose toothbrushes that are too hard. Incorrectly selected dentures, braces, crowns and other structures can also scratch tissue. - Chemical irritants
. Smoking and inhaling harmful fumes have a detrimental effect on the health of gums and teeth. The tissues begin to react to even the softest brushes and bleed. - Taking blood thinning medications
can also cause gum sensitivity and then bleeding gums. - Stomatitis
is a common cause of bleeding. Ulcers in the cavity can bleed when brushing your teeth or chewing hard food.
Moreover, bleeding gums are also caused by various diseases, for example, acute leukemia, hemophilia, vitamin deficiency and others. This problem is especially common in pregnant women: women's hormonal levels change, tissues become more susceptible to irritants and begin to bleed.