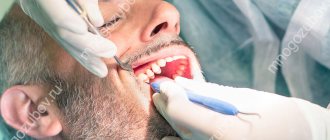
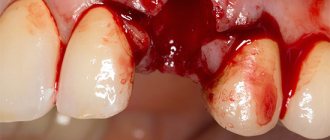
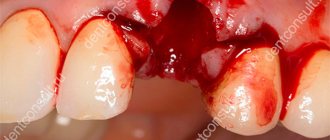
Tooth extraction surgery is probably the most common procedure in the outpatient practice of a dental surgeon. Like any surgical intervention, tooth extraction can be accompanied by various complications, even if everything is done perfectly. All local complications can arise both through the fault of the doctor and the fault of the patient himself, as well as for reasons beyond the control of either the doctor or the patient. Knowledge of possible complications after tooth extraction will help the dental surgeon prevent their development.
Content:
- Why does a fragment remain after tooth extraction?
- Symptoms
- What will the doctor do?
- Recovery after surgery
- Do not confuse a jaw bone with a root fragment
- If not deleted
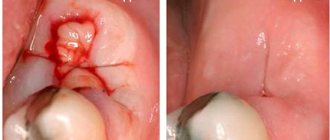
Extraction is a dental operation that is performed quite often. Her technique has been worked out to the smallest detail, so negative consequences are recorded in isolated cases. Sometimes it happens that after a tooth is removed, a fragment remains in the socket. Its presence cannot be ignored. You need to visit the dental surgeon again so that he can remove the forgotten fragment.
Is it possible to avoid
The success of the operation is largely determined by the experience and professionalism of the doctor. No dentist will remove a tooth without studying in detail the clinical picture of the condition of the oral cavity and the unit itself.
To exclude the possibility of complications developing during the operation and upon its completion, the specialist needs to know the characteristics of the root system, location conditions, find out the quality of the tissue and the degree of destruction of the supragingival part.
If a visual examination does not fully assess the complexity of the case, the patient is recommended to undergo one of the examinations - radiography, CT (computed tomography), orthopantomography or visiography.
If a complex removal is required, the entire range of these examinations is performed. Based on the results obtained, the dentist can clearly determine the number and structure of the root system, find out the direction of their growth and the degree of curvature, calculate the volume and duration of the upcoming manipulation, and prepare the appropriate tools.
An antibiotic sensitivity test is also performed which is very important if the amputation occurs against the background of alveolitis or gumboil.
If the dentist has removed a complex tooth and has some doubts about the cleanliness of the hole, he will definitely refer the patient for a repeat x-ray examination upon completion of the operation.
This is done in order to prevent the development of postoperative consequences associated with leaving a piece of root in the alveolus.
Important! A complete comprehensive examination of the patient before and after the extraction guarantees a safe and quick procedure.
Why does a fragment remain after tooth extraction?
Reasons why this problem may occur include:
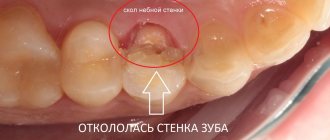
- A very difficult case. Many people do not go to see a doctor until the last minute. They endure pain and take analgesics. As a result, by the time they visit the dental clinic, an advanced inflammatory process is discovered in their mouth. Visualization of the unit in this case is significantly difficult. The situation is aggravated if the tooth is very tiny. Then, at the slightest pressure, it splits into several fragments. The bleeding that occurs at this moment makes it difficult for the doctor to understand whether all the particles have been removed. To prevent mistakes, the dentist should place all the elements of the tooth on a napkin. This will ensure that the gum tissue is thoroughly cleaned. If he has doubts about the quality of the work performed, radiography comes to the rescue. The image shows whether there are bone formations in the area of dental surgery.
- The root split into a large number of small particles. This is possible with a fracture, progressive inflammation, or malocclusion. Even a very small fragment remaining inside the gum will not allow regenerative processes to proceed normally. The patient will soon experience pain in the operated area and the appearance of bad breath. It is possible that other complications will join the inflammation progressing in the gums.
- Removing the "eight" This tooth is considered the most capricious. It is located in a hard-to-reach place, has long winding roots and a large crown part. It is always difficult to remove it efficiently, so it is important to choose a doctor with extensive experience. It happens that individual elements of the roots grow together with the jaw bone. Then it is very difficult to remove them. After extraction of the figure eight, it is recommended to take x-rays. This simple examination will help avoid complications.
- Anatomical features of the human oral cavity. It happens that the “back” units are very far away. They are difficult to reach.
- During the operation, the adjacent tooth crumbled. If there are two damaged units in a row and you need to remove one of them, the roots of the second may split during extraction. This is important to note. Otherwise, the problem cannot be avoided.
Treatment and care of the oral cavity after removal of splinters
Important! On the first day after the procedure, you should not rinse your mouth or brush your teeth. Violation of this point provokes subsequent complications. If repeated complications occur, it is recommended to immediately consult a dentist.
Chipped teeth are a serious complication, accompanied by many pathological symptoms. Therefore, oral hygiene and following the dentist’s instructions are mandatory. To eliminate a pathogenic infection, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. Oral sanitation is performed using dental antimicrobial agents. In the first three days, instead of rinsing, baths are used: the drug is kept in the mouth for some time.
Slight aching pain, slight swelling and a temperature within 37° are a normal condition after removal of fragments. If the unpleasant sensations gradually increase and are accompanied by a clear pathological process, emergency help is necessary. If it is impossible to get to the dentist on the first day after the onset of unpleasant sensations, a number of urgent preventive measures are carried out:
- treat your mouth with an antiseptic several times during the day, holding it in your mouth for 3-5 minutes;
- take any antipyretic or anti-inflammatory drug.
Do not apply hot compresses or intensively rinse the pathological area. The next day, be sure to urgently visit the dentist to identify the causes of the pathology and eliminate the consequences.
Symptoms
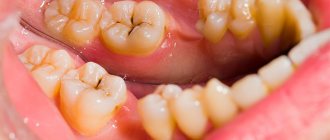
You can understand that a tooth fragment remains after extraction by the following symptoms:
- the gums remain swollen, red, and painful for a long time;
- elevated body temperature persists for 3-4 days;
- worried about joint pain, weakness;
- there is a foul odor coming from the mouth;
- purulent exudate began to separate;
- regenerative processes are slowed down.
Inflammation after extraction normally lasts up to five days. Then the gums should actively recover. If this does not happen, you need to see a doctor. Most likely, serious complications arose after the manipulations.
What will the doctor do?
If you suspect the presence of a fragment, the doctor:
- Conducts a visual examination of the mouth, assesses the condition of inflamed tissues.
- Writes a referral to the patient for x-rays. Examines the resulting image. Any bone formations and particles are clearly visible on it.
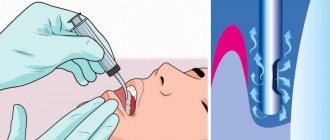
- Based on the characteristics of the localization of fragments and their sizes, the tactics for their extraction are determined. If the particles are close to the surface of the gum, they are removed using a special tool. If they are deep, you have to cut through the soft tissue. In any case, the dental surgeon uses anesthesia so that the patient does not feel pain.
- Removes root particles and treats the wound with an antiseptic solution. Puts an antibacterial drug in it.
Soon after the operation the situation returns to normal. Now the tissues can calmly heal and recover.
Specialist actions
If you suspect that there is a piece of tooth left in the hole, you need to make an appointment with a dentist, and if for a number of reasons this is impossible, you need to contact emergency room specialists.
In each of the options, the doctor’s actions take place in the following order:
- Visual examination of the oral cavity.
- Referring the patient for an x-ray.
- Detection of the presence of fragments from the image, determination of location and quantity.
- Selection of debris removal technique.
- Extraction from the gums.
- Rinsing the hole with an antiseptic.
- Placing an antibacterial drug.
In this case, radiography is the fastest and most convenient way to detect the presence of tooth fragments. The method of performing the procedure for extracting them depends on how many there are and in what place they are located.
So, if the pieces are located close to the gum surface, they are removed using a special dental instrument. If they settle very deeply, the doctor cuts the gum. Both procedures are quick and painless under local anesthesia, and in special cases, general anesthesia is given.
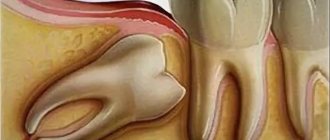
It happens that a person confuses a dental fragment with a jaw bone. After extraction, usually of molars, a small, pointed edge of bone may actually be visible from the gum.
Its appearance is explained by the peculiarities of the anatomy of the jaw. In this situation, the dentist grinds down the edge or it gets pulled over by gum tissue over time.
Today, the likelihood of developing such a complication is very low. If the doctor still has doubts about leaving a tooth fragment after a complex extraction, the patient is sent for an x-ray immediately after the operation.
The video shows a diagram of the extraction of fragments remaining after the removal of a wisdom tooth.
Recovery after surgery
When the hole is cleaned, you need to create optimal conditions for its speedy healing. To do this you need:
- Take an antibacterial drug prescribed by a dental surgeon. The standard course duration is 5-7 days.
- Carry out therapeutic rinses. For this purpose, you should use Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, etc.
- Drink painkillers. Its use is indicated only if the gums hurt very badly.
- Do not touch the wound with your hands. A blood clot will form on its surface. Under no circumstances should you remove it, lift it, or feel it. If it falls off prematurely, an infection may enter the gum tissue.
- Apply cold compresses to your cheek for the first 24 hours. You can keep them for 10-15 minutes. Warming your face is prohibited!
- During the entire rehabilitation period, do not eat anything spicy, sour, or salty. Such products irritate damaged mucosal tissues and have a bad effect on the course of recovery processes.
- In the first three days, refrain from performing intense sports exercises and heavy physical work, and do not drink alcohol.
Rehabilitation period
If a secondary surgical intervention occurs, the duration of the postoperative period increases significantly. When you get home, be sure to apply ice to your cheek. This will help relieve swelling and finally stop the bleeding. You should try not to consume any food or water for 4 hours. Rinsing the mouth can only be done after consulting a doctor.
Remember not to drink alcohol, take a hot bath or engage in strenuous exercise during the week. Neglecting these tips can lead to heavy bleeding, which cannot always be stopped at home.
Complications
The human body always tries to cleanse itself of dangerous substances and particles, so it is possible that over time the unremoved root element will “come out” on its own. But it is unreasonable to hope that this will happen. If the image confirms the presence of a fragment in the hole, it is necessary to remove it surgically. Otherwise, you may encounter dangerous complications, including:
- Acute inflammatory process in the root area. A large amount of pus is released, the tissues become severely inflamed. The roots of neighboring units or even the entire dentition may be damaged. It is possible that the abscess will spread to the periosteum.
- Osteomyelitis. Damage to the jaw of an infectious nature. Pathogenic microorganisms actively multiply in the unhealed hole. As a result, osteonecrosis develops - the jaw tissue begins to die. Pathology can occur in acute, subacute and chronic form. The patient feels weakness and headaches. The oral mucosa turns red, the lymph nodes become enlarged. If osteomyelitis is not stopped in time, it can develop into meningitis, meningoencephalitis, sepsis, or brain abscess.
- Inflammation of the periosteum. The gums swell, and when pressed, a sharp pain appears. The roots of units located on both sides of the inflamed hole may be affected. Treatment involves eliminating the root cause of the disorder and carrying out long-term antibiotic therapy.
- Sharp pain radiating to the neck. It is neurological in nature. It is the result of an inflammatory lesion of the jaw.
- Phlegmon. The gums swell and hurt. Purulent exudate is released from it. The neck and cheek become swollen. The patient's general well-being worsens.
All consequences of a root element not removed from the hole are dangerous. Therefore, if you suspect that your tooth has not been completely removed, be sure to take a photo and consult with an experienced dentist. This way you will avoid many health problems.