Forms of necrosis
Acid (chemical) necrosis of teeth develops in chemical industry workers and in people with chronic gastrointestinal diseases. In the latter case, the teeth are destroyed under the influence of hydrochloric acid coming from the stomach.
Post-radiation or radiation necrosis of teeth develops after radiation injury or as a complication after radiation therapy for some forms of cancer. A similar picture of tooth decay is observed in people who work at a computer for 8-10 hours a day. This form of dental necrosis is called computer necrosis.
Gingival necrosis can be of traumatic, toxigenic, ischemic or trophoneurotic origin. Ischemic necrosis of soft tissues develops when the blood supply to the affected area is disrupted, trophoneurotic - due to impaired innervation of tissues.
Pathogenesis
The reasons for the development of necrosis are most often the negative effects of chemical vapors saturated with acid solutions, improper diet or taking certain medications. In this case, decalcification is observed, that is, the loss of calcium salts by tissues, which reduces the strength of enamel and dental dentin, the formation of cracks, chips or destruction of a large area. Excessive sensitivity and increased abrasion appear. If treatment is not started, the lesion gradually affects the entire coronal part and pulp.
Symptoms:
- pigmentation, the appearance of dark spots on the surface;
- sticking of the lower and upper teeth when closing, which is caused by softening;
- the appearance of uneven contours, breaks and microcracks;
- the enamel surface becomes matte, slightly rough;
- the bite decreases, the gaps between individual units increase;
- dentin acquires a dark, pronounced shade;
- over time, increased sensitivity decreases and disappears;
- destruction gradually begins from the cutting edge to the neck;
- the root cavities are closed, the formation of a volume of replacement dentin is diagnosed.
Symptoms of necrosis
Tooth necrosis in the early stages can manifest itself in the form of loss of shine and pigmentation of the enamel, teeth become sensitive to temperature changes, the surfaces of the affected teeth become rough, and the chewing surfaces “stick” to each other. Calcium is gradually washed out of the enamel, the enamel is destroyed, exposing softer dentin. After this, the tooth is quickly worn away under the influence of normal chewing loads. Radiation necrosis is accompanied by radiation damage to soft tissues, dry mouth, and possible distortions of taste.
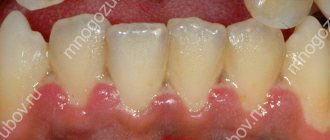
On the gums, necrosis appears as dark, painless spots. Over time, the gums completely lose sensitivity and the soft tissues die.
Causes
People whose work is associated with radiation or some kind of harmful production are at greatest risk of developing necrosis of hard tissues of the oral cavity. Main reasons:
- problems with the nervous system;
- hormonal surges (usually during adolescence or pregnancy);
- hypothyroidism – impaired functioning of the thyroid gland;
- regular intoxication of the body;
- genetics;
- regular exposure to acids in the oral cavity (work in hazardous industries, frequent vomiting, impaired acid-base balance in the body);
- high dose of radiation (for example, chemotherapy);
- taking certain medications that negatively affect tooth enamel.
Symptoms:
- excessive sensitivity, manifested by a painful reaction to cold and hot;
- causeless teeth set on edge, which usually occurs when sour fruits are consumed in large quantities;
- the enamel stops shining and becomes dull and pale;
- formation of chalk stains on enamel;
- the surface of the affected areas becomes rough;
- when using a probe to diagnose pathology, peeling of some areas of tooth enamel may be observed;
- sometimes the pathology is accompanied by constant aching toothaches;
- the cutting edges of the dental units are gradually destroyed, which leads to severe abrasion of the dentition and even malocclusion;
- at an advanced stage of the disease, the teeth are worn down so much that the distance from the edge of the tooth to the gum becomes completely insignificant.
Treatment of necrosis
Necrosis is an irreversible process and it is impossible to restore the viability of the affected tissues. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the factors that caused necrosis and stopping the pathological process.
The affected tissue is removed surgically. After the operation, the patient is prescribed a course of medication and physiotherapeutic procedures. Among the main goals of treatment: stimulation of cell regeneration, restoration of innervation and blood supply to the affected area, increasing local immunity.
When treating dental necrosis, the patient is prescribed remineralization therapy, fluoride-containing medicinal pastes, and damaged teeth are restored through prosthetics or implantation.
Classification and diagnosis
Depending on the causes of the development of problems, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- household (improper diet, taking certain medications, gastrointestinal diseases, unfavorable environment);
- professional (develops under negative conditions in industrial premises).
According to the degree of severity, they are distinguished:
- first - only the enamel is affected;
- second – the lesion concerns the dentin;
- third – secondary dentin is formed;
- fourth - necrosis of pulp tissue, the appearance of inflammatory processes, pain.
When diagnosing, it is important to distinguish necrosis from similar problems such as multiple caries, hypoplasia, fluorosis, and amelogenesis imperfecta. They all have some similar characteristics, such as rough enamel or pigmentation. But when exposed to acidic vapors or substances, the intensity is higher, progression is observed, a decrease in the level of occlusion and severe abrasion.
Price
The approximate cost of treatment, taking into account the regional average, is as follows:
| Name of procedure | Cost in rubles |
| Consultation with a dentist | Free in most clinics |
| Professional cleaning | From 250 |
| X-ray examination | From 300 |
| Orthopantomogram | From 750 |
| Enamel restoration | From 1250 |
| Consultations with relevant specialists | From 200 |
It is worth noting that this list does not include the cost of medications and auxiliary products used in the treatment process. They must be paid separately.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Sources:
- https://spas-dent.ru/zuby/kislotnyj-nekroz-tverdyh-tkanej-zubov.html
- https://DentConsult.ru/desna/nekroz-desny.html
- https://anZub.ru/novosti/nekroz-desny/
- https://dental-area.com/statyi/nekarioznie-porojeniya-zubov/kislotniy-nekroz.html
- https://DentConsult.ru/lechenie-zubov/nekroz-tverdykh-tkaney-zubov.html
- https://implant-expert.ru/poleznye-stati/nekroz-desny-prichiny-lechenie-i-profilaktika/
- https://spas-dent.ru/drugoe/kislotnyj-nekroz-emali.html
- https://dr-zubov.ru/lechenie/zuby/nekroz-sereznym-problemam.html
- https://MikDent.ru/stomatolog/bolezni/nekroz-tverdyh-tkanej-zubov.html
- https://DesnaZub.ru/zabolevaniya/nekroz-desny
- https://mnogozubov.ru/nekroz-desny-prichiny-lechenie-i-profilaktika/
Causes of necrosis
Table 1. Causes of gum structure destruction
| Causes of necrosis | How it manifests itself |
| Insufficient oral hygiene | Plaque forms, which leads to the development of gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontal disease. |
| Injury to the gums due to malocclusion or ill-fitting dentures | This disrupts blood flow and blood circulation stops in certain segments. |
| Hormonal disbalance | During pregnancy, adolescence, with diseases of the endocrine system and blood. |
Sometimes the disease can occur due to prolonged exposure to cold, high temperatures or arsenic, which is part of the dental pastes used in root canal treatment. For example, if a temporary filling does not close the dental canal tightly, the paste can come out, causing tissue necrosis.
Prevention of the development of gum necrosis
Interventions are often based on maintaining oral health and preventing dental diseases.
- Regular teeth cleaning and professional hygiene.
- Quitting bad habits (smoking, alcohol).
- Timely correction of the bite to prevent trauma to the mucous membrane and accumulation of dental plaque.
- Balanced diet, taking vitamins if necessary.
- Timely treatment of diseases of teeth and gums, gastrointestinal tract, endocrine diseases, etc.
After treating necrosis, it is important to prevent its reappearance. Proper oral care and mandatory visits to the dentist once every six months will help with this.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of gum necrosis directly depend on the stage.
- Early. Signs of tissue necrosis are weak. You may notice loss of enamel shine, roughness of teeth, and pale gums.
- Average. The interdental papillae swell. A gray coating forms on the oral mucosa. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- Heavy. The gum tissue swells greatly, becomes black, and numerous ulcers appear on it. Appetite disappears, body temperature rises to 39 °C.
- The last one. The epithelium dies. There is severe pain in the gums. The necks of the teeth are exposed, and the dental units begin to loosen.
Necrosis of hard dental tissues.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the disease. The issues of etiology and pathogenesis of the disease are not sufficiently clarified today. The disease is associated with exposure to endogenous and exogenous factors. Currently, there is an increase in the incidence of the disease, the emergence of new types of necrosis (computer, environmental, etc.) The presence of diseases of the endocrine and central nervous system, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, chronic intoxication, work in chemical and other industries associated with exposure to toxic substances are important. factors. Necrosis of hard dental tissues also occurs in pregnant women, especially often when a pathological pregnancy is combined with increased thyroid function.
Clinical picture of necrosis of hard dental tissues. At the beginning of the disease, chalky areas with a smooth, shiny surface appear on the vestibular surface in the cervical region of the incisors, canines, and premolars. The size of the chalky spots gradually increases, the surface becomes dull and the surface becomes rough. After the loss of enamel, smooth, shiny, light brown dentin is exposed, and the defect takes on a grooved shape.
Changes in the subsurface layer of enamel, detected during electron microscopic examination of dental sections, are similar to the carious process, which allowed some authors to regard necrosis of hard dental tissues as rapidly progressing caries.
Differential diagnosis of necrosis of hard dental tissues . Necrosis of hard dental tissues is differentiated from erosion of hard dental tissues. What these diseases have in common is the presence of a defect. The difference is that the walls of erosion are dense and shiny, while with necrosis, against the background of a dense shiny surface, there are areas of softened tooth tissue.
.
Treatment of necrosis of hard dental tissues . Patients with necrosis of hard dental tissues require careful examination. Particular attention should be paid to the functional state of the thyroid gland. General treatment should include treatment of general somatic pathology, oral administration of calcium-containing medications and multivitamin complexes. Local treatment consists of remineralizing therapy. If there are areas of softening, the defects are prepared and then filled.
Necrosis of hard dental tissues is also associated with the intake of hydrochloric acid for gastritis with low and zero acidity of gastric juice, acid-containing foods, and the intake of certain medications. In chemical production, acid necrosis of hard dental tissues occurs under the influence of acids and their vapors. Necrosis of hard tissues associated with exposure to acids and their vapors is called chemical or acid necrosis. The impact of acids and their vapors on dental tissues leads to damage to the organic matrix and dissolution of the mineral components of dental tissues. General intoxication leads to disruption of the functioning of organs and systems of the body, a decrease in the immunological reactivity of the body. The pH of the oral fluid decreases to critical values (5.8-6.2), the remineralizing ability of the oral fluid decreases. A pathomorphological examination of thin sections of teeth reveals thinning of the enamel, disruption of the structural organization of the enamel, deposition of replacement dentin, obliteration of the tooth cavity, pulp-vacuolar degeneration and reticular atrophy.
Clinic of acid necrosis of hard dental tissues. Patients' complaints about
a feeling of teeth on edge and “sticking” of the teeth of the upper jaw in the teeth of the lower jaw, the appearance of sensitivity to the effects of irritants. It is characteristic that the teeth of the frontal group are affected first. Upon examination, dullness and roughness of the affected area are revealed; subsequently, a progressive loss of hard tooth tissue occurs in the direction from the cutting edge to the neck of the tooth. There is a thinning of the cutting edge, a decrease in the height of the crowns of the teeth, the appearance of gaps between the teeth, and a decrease in the height of the bite. Once the enamel is lost, areas of pigmented dentin are exposed. Depending on the extent of acid necrosis, four degrees of damage are distinguished.
Classification of acid necrosis:
first degree – loss of enamel only;
second degree – loss of enamel and dentin;
third degree – loss of enamel and dentin with the formation of secondary
dentin;
fourth degree – loss of enamel and dentin, accompanied by
pulp damage. Pulp necrosis occurs painlessly, but with the rapid development of the process, pulpitis may occur.
Differential diagnosis of acid necrosis is carried out with hereditary dental lesions, initial, superficial and medium caries, with hypoplasia, erosive and destructive forms of fluorosis. Clinical signs of hereditary dental lesions similar to acid necrosis of hard dental tissues, such as multiplicity of lesions, changes in their color, rapid loss of hard dental tissues with a decrease in bite height, necessitate differentiation with amelogenesis imperfecta, marble disease, Stanton-Capdepont syndrome. Distinctive features include the time of onset of the disease, since hereditary lesions occur before teething; there are other common clinical signs of these hereditary diseases. With acid necrosis of hard dental tissues, there is a clear connection with the etiological factor. The difference between hypoplasia and fluorosis, which are also characterized by symmetry and multiplicity of lesions, is that these non-carious lesions are formed before teeth erupt; upon probing, the tooth tissue is dense and shiny. Common to multiple caries and acid necrosis are uneven edges of the resulting defects, dullness of the affected areas, roughness during probing, a progressive course, and the occurrence of pain from irritants. Distinctive features include the localization of necrosis not only in areas of the crown typical for caries, the extent of the lesions, and the combination with increased abrasion of tooth tissue. The diagnosis can also be made by medical history, in particular, the presence of occupational hazards. Clinical signs such as localization, shape of the defect, and course of the process make it possible to differentiate the disease from a wedge-shaped defect and erosion.
Treatment of acid necrosis of hard dental tissues. In the treatment of acid necrosis of hard dental tissues, the elimination of the etiological factor is of paramount importance, namely the cessation of the effects of acids and their vapors on dental tissues, the use of preventive measures in chemical industries associated with the use of these chemical agents.
Calcium-containing drugs and multivitamin complexes are prescribed internally. Remineralizing therapy is applied locally. In case of significant defects in the crowns of the teeth, restoration work is carried out using modern photopolymer composite materials; in case of a decrease in the bite, orthopedic treatment is used.
Dental hyperesthesia.
Dental hyperesthesia is an increased sensitivity of dental tissues to mechanical, chemical and temperature stimuli. The disease occurs not only when the structure of hard dental tissues is damaged (carious process, increased wear of dental tissues, enamel erosion, wedge-shaped defects, gum recession in periodontal diseases), but also in their absence, which allows us to classify these two forms. Hyperesthesia without morphological changes in the dental tissues is called essential. According to prevalence, a distinction is made between localized hyperesthesia, in cases where increased sensitivity is observed in a small number of teeth (from 1 to 6), and generalized. The most common (63-65%) is generalized hyperesthesia; localized hyperesthesia has a lower frequency, reaching 35-37%. The causative factors of generalized hyperesthesia include dysfunctional conditions of the nervous system, previous and concomitant somatic diseases (psychoneurosis, menopause, endocrine diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, etc.).
Clinic of hyperesthesia. Patients with hyperesthesia complain of severe short-term pain under the influence of various irritants (sour, sweet, salty foods, cold drinks and air, reaction to tactile stimulation, etc.). Characteristic is the varying intensity of pain, which can vary from a slight feeling of discomfort to severe pain. During examination, structural changes in the hard tissues of the tooth and periodontal pathology are often detected. With gum recession associated with periodontal diseases, a wedge-shaped defect, erosion, and increased abrasion of tooth tissue, the exposed dentin is hard, smooth, shiny, and sometimes slightly pigmented. When probing exposed dentin, short-term pain occurs, in some cases quite intense. A short-term painful reaction is also observed to a temperature stimulus and exposure to a sour or sweet stimulus. There is a discrepancy between the size of the exposed area of dentin and the intensity of pain. Electrical excitability of the pulp is within normal limits (2-6 μA).
The mechanism of pain during hyperesthesia is not clear enough; there are various hypotheses. The most recognized explanation is the sensitivity of not only dentin, but also enamel from the perspective of Brannstrom's hydrodynamic theory. The sensitivity of enamel and dentin is explained by the movement of enamel cerebrospinal fluid and dentinal fluid with changes in intrapulpal pressure and capillary forces. Since the amount of enamel liquor is insignificant, the sensitivity of enamel is less pronounced than dentin. When dentin is exposed to irritants, dentinal fluid moves, resulting in displacement of odontoblasts and irritation of the nerve fibers of the pulp. The nerve fibers of the pulp form a powerful plexus under the layer of odontoblasts and end on the vessels or freely, reaching the predentin and entering the dentin almost to the enamel-dentin junction. Free nerve endings are detected in the dentinal tubules.
Classification of hyperesthesia (Fedorov Yu.A. et al., 1981).
A. By prevalence:
I. Limited form in the area of individual or several teeth with
the presence of single carious cavities and wedge-shaped defects, as well as
after preparing teeth for artificial crowns.
II. The generalized form appears in the area of the majority or
all teeth, more often when the necks and roots of teeth are exposed due to diseases of steam-
dont, pathological abrasion of teeth, with multiple caries, with
multiple and progressive forms of dental erosion.
B. By origin:
I. Dentin hyperesthesia associated with loss of hard tooth tissues:
a) in the area of carious cavities;
b) arising after the preparation of tooth tissue for artificial
crowns, inlays, etc.;
c) accompanying pathological abrasion of hard dental tissues and
wedge-shaped defects;
d) with erosion of hard dental tissues.
II. Dentin hyperesthesia not associated with loss of hard tooth tissue:
a) hyperesthesia of dentin of exposed necks and roots of teeth during steam
dontosis and other periodontal diseases;
b) hyperesthesia of dentin of intact teeth (functional), associated
causing general disorders in the body.
B. According to the clinical course:
I degree – tooth tissues react to temperature (cold, heat) changes
jellyfish; the threshold of electrical excitability of dentin is 5-8 μA;
II degree – tooth tissues react to temperature and chemical (co-
flaxseed, sweet, sour, bitter) irritants; electrical excitability threshold
dentin 3-5 µA;
III degree – tooth tissues react to all types of irritants (including
tactile); the threshold of electrical excitability of dentin is 1.5 - 3.5 µA.
Differential diagnosis. Hyperesthesia of hard dental tissues
differentiate with acute and chronic forms of pulpitis. What these diseases have in common is the occurrence of intense pain in response to stimuli and the irradiation of pain. The difference is the duration of the pain; with pulpitis, the pain continues even after the irritant is removed. Acute forms of pulpitis are characterized by spontaneous, paroxysmal pain, intensifying at night, which is not observed with hyperesthesia. The electrical excitability of the pulp decreases with pulpitis, but with hyperesthesia it remains within normal limits (2-6 μA).
Treatment of dental hyperesthesia.
General treatment includes oral administration of calcium-containing medications and multivitamin complexes. Sedative therapy is prescribed according to indications. It is recommended to use toothpastes containing mineral components and fluoride. Local treatment consists of using various methods of remineralizing therapy.
Method of remineralizing therapy:
The teeth are isolated from saliva, plaque is removed from the surface of the enamel, dried, then a 10% solution of calcium gluconate or a 3% solution of Remodent is applied for 15-20 minutes. After two applications of the remineralizing liquid, on the third visit after the remineralizing solution, apply a 1% sodium fluoride solution for 3-5 minutes or cover the teeth with fluoride varnish. After 5-7 such sessions, hyperesthesia decreases, and after 12-15 procedures it disappears. After 6-8-12 months, when hyperesthesia appears, the courses are repeated. It is recommended to use toothpastes containing minerals and fluoride. Remineralizing drugs can be administered via electrophoresis. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes, the course of treatment consists of 7-10 sessions. Fluoride varnishes with sodium fluoride (fluoride, vernident), varnishes containing ammonium fluoride (fluramon), varnishes containing sodium fluoride and calcium fluoride (fluoridine, bifluoride -12) are used. When using fluoridine and bifluoride-12, the flow of fluoride into tooth tissue is 1.5 times greater than when using varnishes containing only sodium fluoride.
Knappvost A. proposed deep fluoridation of dental tissues using two liquids, liquid No. 1 is a fluorosilicate complex containing copper and liquid No. 2, which is highly dispersed calcium hydroxide.
Treatment tactics
Regardless of the degree of damage and subsequent treatment tactics, the first thing that needs to be done is to take measures to prevent the effects of acid on the teeth.
Subsequent treatment depends on the stage of the disease. It usually begins with remineralizing therapy - local and systemic.
With the latter, medications containing glycerophosphate or calcium gluconate are taken orally. The daily dose of 1.5 g should be taken in 3 divided doses. The standard duration of treatment is 1 month.
Multivitamins are prescribed simultaneously with calcium. For example, Kvadevit, which contains a large amount of vitamins and microelements necessary for the regeneration of dental tissues.
2% sodium fluoride is used as a means for local remineralization.
A swab moistened with it is applied to the teeth, the surface of which is isolated from the soft tissues with cotton rolls. Tampons and insulation are removed after 5 minutes, after which the mouth is rinsed. The use of fluoride-containing toothpastes is also recommended.
If the degree of damage is significant and worsens the aesthetics and/or functionality of the teeth, after remineralization, the teeth are filled with glass ionomer cement and, if necessary, prosthetics are used.
Treatment of avascular necrosis using MBST
One of the acute problems facing orthopedists around the world is the difficulty of treating aseptic necrosis of bone tissue, in particular when the head of the hip joint is affected. The pathology lasts for 2-5 years, the disease ends either with recovery with preservation of all functions of the joint, or with complete destruction of the joint with shortening of the limb and disability.
A favorable prognosis is possible only with timely detection, adequate treatment and comprehensive orthopedic measures. The individual characteristics of the body are of great importance - good physical condition, absence of chronic diseases, age under 60 years, healthy bones without osteoporosis, uncomplicated heredity. Of course, the patient’s personal characteristics also play a role – patience, conscientiousness, the desire to quickly cope with the disease and trust in the doctor. Only if the doctor and patient work as one team can success be achieved.
Thanks to modern diagnostic capabilities, the disease can be identified in the early stages of manifestation and measures can be taken to help cope with the disease.
One of the new techniques that can effectively combat aseptic necrosis is MBST therapy. Nuclear magnetic resonance is used as a therapeutic factor. High-speed pulses are consistent with the oscillation frequencies of the hydrogen nuclei of osteocytes, and through their energy saturation, autoregenerative processes in the bone are stimulated.
This technology has been actively used in Germany since 2001 as a treatment for degenerative skeletal diseases. During this time, numerous studies have been conducted at prestigious universities around the world and research institutes, which have confirmed the regeneration of bone and cartilage thanks to MBST therapy.
After the course, the patients received a significant improvement in their condition, pain relief and an expansion of the orthopedic regimen. Recovery was observed, and improvement occurred regardless of the location of aseptic necrosis. The MBST method was combined with osteotropic and vascular therapy.
Capabilities of bone tissue
Relatively recently, the amazing ability of bone tissue to regenerate when damaged was discovered. Moreover, the restoration of the defect occurs not due to the scar, but due to full-fledged bone tissue. The head of the femur, which is distinguished by its high regenerative abilities and plasticity, has proven itself especially well in this regard. Moreover, according to Wolff's law, when the functional load on it changes, the bone can adapt to it, internally restructuring and taking into account the new needs of the body. Therefore, if adequate treatment and the correct orthopedic regimen are prescribed, one can expect adequate restoration of the head and the return of all functions of the joint.
Until recently, there was no effective conservative treatment for aseptic necrosis; it was impossible even to reduce the focus of necrosis; in the end, it all came down to endoprosthetics. But today an alternative to surgery has appeared - this is Multi Bio Signal Magnetic Resonance Therapy. This innovative technology eliminates the root of the problem, which is its advantage over other methods.
MBST therapy is currently considered one of the most promising areas of orthopedic therapy.
Mechanism of action of MBST therapy
Physiological regeneration of bone tissue is regulated by certain flows of electric and magnetic fields. But with pathology, this ratio changes and the recovery processes are disrupted. For normal functioning they must be activated. The role of an external activator of biophysical processes, but at the expense of its own resources, is performed by MBST therapy. Due to a certain magnetic resonance effect, a specific electrochemical environment is created in the bone tissue during the session. The installation's impulses affect the hydrogen of bone cells, the hydrogen atoms absorb this energy and return it to their own cells. This energy activates the regeneration of new cells, restores impaired microcirculation, removes damaged cells and clears the space for replenishment with new and healthy osteocytes. In addition to healing internal processes, bone tissue can, if necessary, receive the necessary substances from the outside due to parallel drug therapy (which is minimized with this method) and good nutrition, which further improves regeneration.
Results of MBST therapy
The patient feels the effect of therapy after the first sessions - pain decreases, range of motion increases, and stiffness disappears. The patient adapts to new loads more easily, the gait becomes normal, and the patient returns to his usual lifestyle. The results of therapy will depend on age (for example, in older people the results are better), the patient’s sports activity, the stage of the process and the degree of damage to the head. Sometimes, in advanced cases, courses have to be repeated several times during the year.
In addition to subjective data, the improvement is also confirmed by objective studies. The x-ray shows improvements in the structure of the head, tissue compaction, bone formation parameters change for the better, cartilage tissue is completely regenerated, good dynamics of blood, urine, mineral and fat metabolism can be seen.
Thousands of patients have already undergone treatment and are convinced of excellent results, and clinical examinations have confirmed that the effect after therapy lasts for more than 5 years!
Advantages of MBST therapy
- Minimum contraindications and absence of complications.
- Quick tangible results.
- Impact at the cellular level, eliminating the immediate problem using your own resources.
- Outpatient treatment and comfortable painless sessions.
- Long-term preservation of the increasing effect for several years.
- Clinically proven 100% restoration of cartilage and bone tissue.
- Possibility of use not only in adults, but also in children.
- Excellent combination with other types of therapy.
How does MBST therapy work?
After consultation, questioning, and medical history, the doctor prescribes therapy sessions. Each session lasts approximately 60 minutes. Their number and frequency depend on the recommendations of a specialist. Usually these are 6-8 daily sessions (sometimes every other day).
The MBST therapy device consists of a magnetic coil into which the affected joint is placed. The space is not enclosed, so the patient feels quite comfortable. The patient can take a comfortable position - read, watch a movie, listen to music.
The doctor adjusts certain parameters (time, field strength, resonance frequency). To form the necessary therapeutic environment in the coil, three different fields are used - the main magnetic field, radio pulse and electromagnetic alternating field. External influence activates internal energy, strengthening it, and when combined they produce the desired effect.
The session lasts about an hour. The patient is in constant contact with the doctor. Some patients are worried - can they drive a car after the session? Of course they can. The procedure does not affect the patient’s well-being in any way; he can lead a normal life. The improvement will be noticeable already in the 2-3rd session - patients note a decrease in pain and stiffness in the joint.
Contraindications to magnetic resonance therapy
Doctors do not recommend the method if you have:
- pregnancy;
- acute infectious diseases;
- mental disorders;
- oncology;
- working electronic implants;
- cardiovascular emergencies
MBST therapy - an alternative to surgery
Surgery is a last resort. Any operation is traumatic and has side risks. Only when the disease is advanced and the doctor sees no other way but radical intervention, one has to choose surgery. But, if aseptic necrosis is detected in the early stages, total endoprosthetics can be dispensed with or postponed for many years. Bone tissue has the property of self-healing and today, thanks to the innovative technology of MBST therapy, it is possible to save the joint and return the patient to their normal lifestyle in a few sessions. At least to date, there is no more worthy and effective conservative treatment with proven results.
MBST therapy is:
- recovery without pain;
- preservation of the joint without surgery;
- the opportunity to live without pain, without using medications and without injections;
- full movement in the joint;
- return to normal lifestyle.
The technique has been actively used in many clinics around the world for 10 years. Orthopedic centers in Israel, Germany, Switzerland and other countries have assessed the effect of this technology and adopted it as an effective method of treatment for many diseases. In Russia, magnetic resonance therapy is just beginning to gain credibility, so only a few centers have unique equipment. If you experience pain, limited mobility of the hip joint, changes in gait, or suspect aseptic necrosis, contact our Center! If treatment is timely, the likelihood of a full recovery is very high, and positive dynamics are always expected! Don't neglect your health, we only have one life!
Diagnosis of gum necrosis
Often the problem is identified during an examination by a dentist, without any complaints from the patient. In some cases, symptoms are present: pain, bleeding, flushing, bad breath.
Other signs of the disease may include:
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- digestive problems;
- problems with swallowing;
- deterioration of health.
During diagnosis, the doctor does an X-ray examination and conducts an instrumental examination. The image allows not only to identify the necrotic process, but also to determine the stage, possible complications, etc.
Tooth sensitivity
Dental hyperesthesia
– a special disease associated with increased sensitivity of teeth to temperature, chemical or mechanical stimuli. The disease is accompanied by pain that does not allow one to lead a normal life, loss of teeth whiteness, and can lead to dire consequences if treatment is not treated in time.
Forms of the disease
The disease can affect both part of the teeth (limited form) and all teeth (generalized form). The second form occurs in 60-65% of cases, since hyperesthesia is usually associated with common causes. Limited hyperesthesia is ensured by more “narrow” factors, the action of individual exposed nerve endings and areas of worn enamel. Most often, the disease occurs in people with non-carious diseases.
Causes
There are many reasons for hyperesthesia of hard dental tissues. This could be an overly hard toothbrush, exposure of the cervix, periodontitis, or a whitening procedure. Using toothpaste that is oversaturated with abrasives, as well as frequent consumption of carbonated drinks, can also lead to the destruction of the dental structure. Foods with a high acid content have a negative impact on enamel and bone tissue; hyperesthesia is caused by erosions, enamel damage, wedge-shaped defects and dental caries. Pathological abrasion and periodontal disease can also lead to the destruction of enamel and its sensitivity.
Stages of the disease
Conventionally, dental hyperesthesia is divided into three stages. The first stage is characterized by increased sensitivity of teeth to temperature factors, the second - to chemical and temperature factors. The third, in addition to the first two stimuli, also implies a mechanical one. Stages of development are distinguished by the degree of electrical excitability of dentin. The threshold in the first stage is 5-7 µA, in the second stage – 3-5 µA, and in the third stage the dental tissues respond to a current of 0.5-2 µA.
Treatment of hyperesthesia
There are many methods of treatment, as well as the causes of the disease. The first stage of therapy is to identify and eliminate the cause of the pathology. Complete and high-quality treatment can only be carried out by a specialist, so you should not waste time on self-medication.
Usually, to eliminate dental hyperesthesia, a complex of drugs is used to restore enamel. A professional dentist will help determine the root cause of the disease and work on solving the problem. The usual course of treatment (you can find out where to cure your teeth by contacting us) includes the use of medicinal varnishes and toothpastes containing potassium salts, fluoride compounds, strontium, citrates, phosphorus and calcium. A schedule for taking medications is determined for the patient, and special recommendations for dental care are given. There are products that provide exceptional results and excel in the restoration of dental tissue. The action of the selected drugs is aimed at compacting dentin, healing dentinal canals, reducing the excitability of the network of nerve endings, and normalizing the process of restoration and nutrition of enamel.
Treatment of generalized hyperesthesia requires a special approach. The dentist must identify: where to treat teeth and analyze the symptoms in order to establish a connection between dental lesions and disorders in the body systems (central and peripheral nervous systems, endocrine system, etc.). Eliminating the cause of extensive dental disease will give an excellent impetus to the healing process.
Dental varnishes, which are based on sodium and calcium fluorides, act quickly and effectively. To ensure better effectiveness, the varnish is applied to teeth that have already been cleaned and dried, and measures to normalize phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the body will guarantee the preservation of dental health.
Acid necrosis
The acid form of necrosis is caused by the aggressive effect of certain alkalis and acids on tooth enamel. At enterprises, acidic fumes accumulate in the air, which penetrate into the mouth, making saliva sour, resulting in the leaching of calcium from tooth enamel and its further destruction.
Acid necrosis causes increased sensitivity of tooth enamel to increases and decreases in temperature and mechanical stress. There is often a sensation of teeth stuck together or locked together.
As the disease progresses, the enamel becomes gray, rough, gradually wears off, and the crowns are destroyed.
Treatment of acid necrosis involves minimizing exposure of teeth to aggressive substances. In addition, remineralization is carried out, and in the presence of caries, fillings are placed. With timely access to a dentist, the disease can be largely overcome.