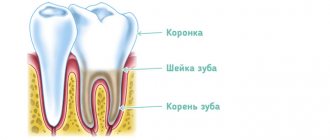
Dentist is a certified doctor who treats dental damage and eliminates inflammatory processes in them. In a broader sense, the doctor’s competence also includes the maxillofacial department, and depending on his specialization, the doctor has the right to engage in prosthetics, tooth extraction, and surgical operations on periodontal tissues.
In this article we will take a closer look at what a general dentist, as well as a dental hygienist, does.
The procedure for providing medical care.
The procedure approved by the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of December 7, 2011 No. 1496n determines that medical care for the adult population in the “dentistry” profile is provided for dental diseases of the teeth, periodontium, oral mucosa, tongue, salivary glands, jaws, face and head, including :
- carious, non-carious and other dental lesions;
- acute, chronic and specific inflammatory diseases, acute and chronic trauma, acquired defects and deformations, oncological diseases of the periodontium, oral mucosa, tongue, salivary glands, jaws, face and head;
- anomalies and defects in the development of teeth, jaws, face and head, their prerequisites and consequences.
This procedure is mandatory for organizations providing medical care to the adult population for dental diseases, regardless of their organizational and legal form.
Medical care in the specialty “dentistry” is provided in the form of:
- emergency medical services;
- primary health care;
- specialized, including high-tech, medical care.
The order specifically stipulates that medical care for adults with dental diseases and life-threatening conditions is provided in an emergency manner.
Next, we will consider the requirements for the procedure for providing medical care in the specialty “dentistry”, according to individual criteria.
Surgeon
The specialist deals with the following issues:
- removes diseased teeth if the therapist has given a conclusion that restoration is impossible;
- carries out extraction (removal) of healthy teeth that interfere with the normal growth of neighboring units;
- performs correction of dental anomalies, removal of impacted (unerupted) wisdom teeth, supernumerary units;
- the help of a dental surgeon will be needed if certain units grow incorrectly, for example, in 2 rows;
- The specialist's competence includes implantation and various types of prosthetics.
Who can provide medical care in the field of dentistry?
In accordance with clause 7 of the Procedure, primary health care for the adult population for dental diseases in an outpatient setting is provided:
- dentists (general dentists), dental therapists, dental surgeons, orthopedic dentists, orthodontists, maxillofacial surgeons (hereinafter referred to as dental doctors);
- dentists, dental hygienists, dental technicians;
- *paramedics and doctors of other specialties.
* If the medical workers specified in this paragraph identify signs of dental disease, after taking measures aimed at eliminating life-threatening conditions and eliminating pain, the patient is sent to a medical organization for medical care by dental doctors.
Qualification requirements are imposed on medical personnel.
Thus, a specialist of the corresponding dental profile is appointed to the position of a dentist in a specialized department (office) of a dental clinic, corresponding to the Qualification characteristics of positions for workers in the healthcare sector, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated July 23, 2010 No. 541n (hereinafter referred to as EKS) for a medical specialist.
The qualification characteristics for the position “Specialist Doctor” apply to positions of medical specialists for which the ESC does not provide for separate qualification characteristics. Dentist is one of these positions.
| Job responsibilities |
|
| Must know |
|
| Qualification Requirements | Higher professional education in the specialty “General Medicine”, “Pediatrics”, “Dentistry”, “Medical Biophysics”, “Medical Biochemistry”, “Medical Cybernetics”, postgraduate and (or) additional professional education and a certificate of a specialist in the specialty in accordance with the Qualification requirements for specialists with higher and postgraduate medical and pharmaceutical education in the field of healthcare, approved in the prescribed manner, without requirements for work experience. |
For other specialists providing medical care in the field of dentistry, we will consider only the qualification requirements:
| Job title | Qualification requirements in accordance with the CEN |
| Nurse | Secondary vocational education in the specialty “General Medicine”, “Midwifery”, “Nursing” and a specialist certificate in the specialty “Nursing”, “General Practice”, “Nursing in Pediatrics” without any work experience requirements. |
| Dental hygienist | Secondary vocational education in the specialty “Preventive Dentistry” and a specialist certificate in the specialty “Preventive Dentistry” without any work experience requirements. |
| Dental Technician | Secondary vocational education in the specialty “Orthopedic Dentistry” and a specialist certificate in the specialty “Orthopedic Dentistry” without any work experience requirements. |
It is also worth mentioning the Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated May 10, 2016 No. 227n “On approval of the professional standard “Dentist” (hereinafter referred to as Profstandard).
The professional standard characterizes the labor function of a specialist and also fixes the qualification requirements for him. Thus, for a dentist, in accordance with the Professional Standard, the following requirements are imposed:
| Education and Training Requirements | Higher education – specialty |
| Requirements for practical work experience | — |
| Special conditions for permission to work | Passing mandatory preliminary (upon employment) and periodic medical examinations (examinations), as well as extraordinary medical examinations (examinations) in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation; Absence of a criminal record and (or) the fact of criminal prosecution or termination of criminal prosecution on rehabilitative grounds. |
| Other characteristics | Professional development of a specialist For professional growth and assignment of a qualification category, the fulfillment of criteria corresponding to the specialty is required Main ways to improve qualifications:
|
Professional standards are mandatory for use by employers in terms of the qualification requirements necessary for an employee to perform a certain job function, if they are established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), other federal laws or other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation (Part 1 of Art. 195.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
About the profession
A general dentist is a specialist in demand not only in Russia, but also in other countries. Medical and preventive institutions are interested in dentists with a specialization in “General Dentistry”. This is due to the fact that this specialist has quite extensive knowledge and skills, including a wide range of dental procedures. Thus, a general dentist provides care to patients with various dental pathologies.
Where can medical care in the field of dentistry be provided?
In accordance with the Procedure, medical care in the specialty “dentistry” can be provided in medical organizations and their structural divisions. The procedure provides for the following structural units:
| Structural unit | Characteristic | Functions |
| Dental clinic (requirements for organizing activities are set out in Appendices 1, 6, 11 to the Procedure) | is an independent medical organization or a structural unit of a multidisciplinary medical organization, organized to provide primary health care and specialized medical care |
and etc. |
| Dental departments (offices, laboratories) in medical organizations providing outpatient medical care (requirements for organizing activities are set out in Appendices 2, 7, 12 to the Procedure) | organized as a structural unit of a medical organization providing primary health care in an outpatient setting |
and etc. |
| Dental office in educational institutions, recruiting stations, enterprises and organizations (requirements for organizing activities are set out in Appendices 3, 8, 13 to the Procedure) | organized as a structural unit of a dental clinic or dental department of a medical organization or as a structural unit of an educational institution, organization, enterprise |
and etc. |
| Mobile dental office (requirements for organizing activities are set out in Appendices 4, 9 to the Procedure) | organized as a structural unit of a dental clinic or dental department of a medical organization |
and etc. |
Thus, the structural units in which dental services are provided must comply with the requirements of the Procedure in terms of general provisions, equipment standards and recommended staffing levels.
In addition, it is necessary to remember that the premises comply with the requirements of SanPiN. Thus, SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities”, approved by the Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated May 18, 2010 No. 58 (hereinafter referred to as SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10) establishes requirements for premises, in which medical services are provided. Among other things, SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 contains requirements regarding room ventilation, minimum areas, etc.
For example, in dental offices, the area for the main dental unit should be at least 14 m2, for an additional unit - 10 m2 (for a dental chair without a drill - 7 m2), the height of the offices - at least 2.6 m. Walls of dental offices, corners and The junctions of walls, ceiling and floor should be smooth, without cracks. The ceilings of dental offices, operating rooms, preoperative rooms, sterilization rooms and dental laboratories are painted with water-based or other paints. It is possible to use suspended ceilings if this does not affect the standard height of the room.
If there are several dental chairs in the office, they are separated by opaque partitions no less than 1.5 m high. The absence of a sterilization facility in a dental medical organization is allowed if there are no more than 3 chairs. In this case, installation of sterilization equipment is possible directly in the offices.
What does a general dentist treat?
A specialist in the field of general dentistry deals with many pathological processes that occur in the oral cavity and maxillofacial areas. The dentist treats:
Carious formations
- caries;
- pulpitis;
- periodontitis;
- periostitis.
Caries begins with demineralization of the enamel and ends with its subsequent destruction. The resulting cavities, if not treated in time, provoke the development of pulpitis and periodontitis. Thus, the connective tissue suffers and the pulp becomes inflamed.
Not carious diseases
- erosion of tooth enamel;
- enamel fluorosis;
- enamel hypoplasia;
- pathological abrasion of teeth;
- cancer formation in the gingival area;
- non-epidemic form of mumps;
- dental injuries.
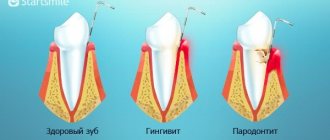
Diseases of the oral mucosa
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- cheilitis;
- gingivitis.
In what order is medical care provided in the specialty “dentistry”?
In accordance with the Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated March 11, 2013 No. 121n “On approval of the Requirements for the organization and performance of work (services) in the provision of primary health care, specialized (including high-tech), emergency (including specialized emergency), palliative medical assistance, provision of medical care during sanatorium-resort treatment, during medical examinations, medical examinations, medical examinations and sanitary and anti-epidemic (preventive) measures as part of the provision of medical care, during transplantation of organs and (or) tissues, circulation of donor blood and (or) its components for medical purposes” (hereinafter referred to as Order No. 121n), medical care in the “dentistry” profile is divided into the following types:
- Primary pre-medical health care in an outpatient setting (dentistry, orthopedic dentistry; preventive dentistry);
- Primary specialized health care in an outpatient setting (general dentistry, orthopedic dentistry, therapeutic dentistry, surgical dentistry);
- Primary specialized health care in a day hospital (pediatric dentistry, orthopedic dentistry, therapeutic dentistry, surgical dentistry);
- Specialized, including high-tech, medical care (pediatric dentistry, orthopedic dentistry, therapeutic dentistry; surgical dentistry);
- Medical assistance during sanatorium-resort treatment (pediatric dentistry, orthopedic dentistry, therapeutic dentistry; surgical dentistry).
When providing medical care in the field of dentistry, medical personnel must maintain medical documentation, including primary, accounting and reporting.
Paid dental services must be provided in accordance with the Rules for the provision of paid medical services by medical organizations, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 4, 2012 No. 1006. This Decree sets requirements for the mandatory conditions of the contract for paid medical services, informing patients, etc.
Dental Treatment Options
- Fillings. The doctor restores the voids formed after cleansing using filling materials. In his practice, he uses amalgam, porcelain, gold or rubber-based composite material. Each substance has its own advantages and disadvantages. Before installing a filling, the doctor discusses this information with the patient in order to determine what to choose.
- Treatment of dental canals. In this case, the damaged pulp is removed, and the tooth itself is filled with an antibacterial filling, after which it is isolated from external factors by covering it with a crown.
- Bonding. The essence of this cosmetic procedure is to apply a composite to the front or back of the tooth in order to restore it. This way you can improve its appearance, give it a healthy color, lighten stains, hide chips and uneven surfaces.
- Orthodontics. Long-term treatment of crooked teeth using retainers and braces to give your smile an aesthetic appearance.
Orthodontist
Most people encounter a specialist in this category during their lifetime. Bite anomalies, according to statistics, are observed in 80% of residents of different countries. Some studies suggest a higher percentage of patients who are candidates for orthodontic treatment.
The main task of an orthodontist is to restore the beauty of a smile. According to scientists, bite defects not only worsen aesthetics, but also provoke serious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, cause headaches, and severe diseases of the gum and bone tissue.
What does an orthodontist do:
- aligns the dentition;
- eliminates wide interdental spaces, removes diastema - the gap between the “units” in the center of the dentition;;
- corrects the growth of milk and permanent units;
- gives recommendations for the prevention of malocclusions;
- controls the formation of the jaw in childhood.
Take note:
- the specialist draws up a treatment plan, takes impressions, sends the jaws for x-rays, sends the collected materials to the dental laboratory;
- after receiving the finished product, the doctor installs the design, gives recommendations for care and correct correction;
- During the entire period of treatment, the patient is observed by a doctor who installed braces, retainers or other special devices;
- The duration of correction is calculated in months, often years (especially in adults).
Removable and non-removable orthodontic structures help correct bite defects:
- stretching plates;
- bracket systems;
- veneers;
- lumineers;
- orthodontic devices;
- lip bumpers;
- retainers;
- trainers;
- aligners;
- orthodontic aligners;
- clasp devices.
Orthopedist
Patients who have lost one or more units of dentition turn to this specialist. The doctor will help people who have ugly stumps sticking out instead of teeth, causing injuries to the mucous membrane.
What does an orthopedic dentist do:
- performs full or partial prosthetics;
- restores the beauty of a smile;
- selects the optimal method for normalizing chewing function.
Important! Before consultation with a prosthetist, it is mandatory to sanitize the oral cavity and eliminate inflammatory processes of various etiologies. A visit to the dentist or dental therapist is the first stage of orthopedic treatment.
Preventive measures
For oral health, it is necessary, first of all, to regularly prevent caries. This consists of high-quality teeth cleaning with toothpaste, floss and other means. A proper diet and constant consultations/examinations with a doctor are necessary.
Some cases of caries can develop without symptoms, and can only be detected with certain examinations. This allows you to stop the development of a destructive disease and postpone the removal and drilling of infected tissue for some time!