Make an appointment
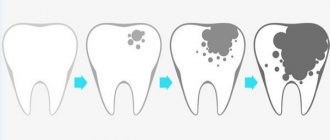
Initial caries is a pathology that is accompanied by demineralization and pigmentation of the surface layer of enamel. The pathology often occurs without symptoms, so many patients turn to the dentist for help when their teeth are constrained by pain.
The occurrence of pain in the area of the affected teeth indicates the active development of pathology and the transition from the initial stage to more complex conditions. The lack of relevant and adequate therapy provokes the development of serious concomitant pathologies. To avoid negative consequences when a patient has caries in the white spot stage, treatment should be aimed at suppressing the pathogenic process and remineralizing the enamel.
Causes of early stage caries
The initial stage of the disease is caused by microbes that live in the mouth, food debris stuck between the teeth, plaque and poor oral hygiene. All this is the reason for the contamination of the area with microorganisms.
Over time, calcium in the mouth is washed away from the tooth enamel, causing it to become brittle and porous. This process is called demineralization (loss of minerals), and the resulting spots are called areas of demineralization.
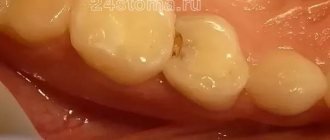
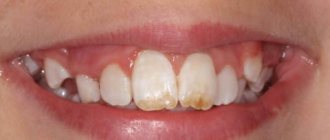
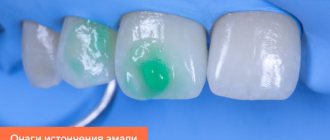
Quite often, these spots are located on the cervical area of the tooth, which is why they are practically invisible visually, and the person does not even realize that there is something wrong with the tooth. And in most cases, enamel caries in the stain stage is discovered only when the patient goes to the dentist with complaints about other teeth.
However, on the front teeth, both upper and lower, the onset of caries can still be seen even at home. To do this, you should brush your teeth, dry them and look in the mirror. If white spots are visible on the teeth, caries is present in the oral cavity.
A photo of the initial stage indicates that due to the similarity of shades of carious stains and tooth enamel, it is quite difficult to diagnose the onset of the disease. But if this succeeds, then with almost one hundred percent probability it can be said that the crystalline structure of tooth enamel can be restored with the help of mineral components coming from outside. If the carious spot has acquired a dark shade, then the enamel can be restored only if the process of destruction of hard tissues has not gone too far.
What complications can there be after treatment?
- Inflammation or even necrosis of the pulp - the tissue that fills the tooth cavity. Occurs after a long time due to inaccurate preparation of rotted tissue and excessive pressure on the pulp;
- secondary caries occurs due to the fact that during preparation some parts of the tissue affected by bacteria were not removed;
- inflammation of the gums due to injury;
- periodontitis, which occurs due to increased pressure on the tooth that occurs after the formation of an anatomically incorrect filling;
- loss of a filling due to insufficient strengthening or improper formation of a carious cavity.
Caries in the spot stage: diagnosis
The simplest diagnostic method consists, as already noted, in drying the enamel and visual inspection. On dry teeth, demineralized areas appear dull, while healthy parts of the tooth are shiny.
But the most effective and reliable diagnostic method is to check the condition of tooth enamel using various organic dyes. For this, modern dentists can use:
- methylene blue (most often used);
- carmine;
- methylene red;
- tropeolin.
To identify the presence or absence of the disease, as well as determine the stages of development of dental caries, you must first remove plaque from the tooth, rinse it with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, then isolate it from saliva. To do this, the dentist uses cotton wool rolls, a saliva ejector and a stream of air. After this, the doctor applies a dye solution to the surface of the tooth, waits for a while, rinses with water and evaluates the result. If the enamel in any area becomes discolored, it means that caries is beginning to develop on the tooth.
In addition, the dentist probes the patient’s carious spot. In this case, a rough surface on part of the tooth will indicate caries.
It is most difficult to detect the disease at the initial stage in hard-to-reach areas of the jaw, for example, between the teeth. Most often, the disease is diagnosed there only at the stage of formation of a carious cavity.
It is important to distinguish between caries in the white spot stage and endemic fluorosis, a disease associated with an excess of fluoride in the body. The main difference between these diseases, which are similar in their manifestation, is that the stain is usually single, but fluorous spots are paired (located on the teeth of the same name) or multiple. In addition, these spots are more typical for incisors and canines, and early caries can affect any teeth, especially in the cervical area, as well as in the fissure area. Endemic fluorosis is most likely to occur in those who live in areas where drinking water contains a lot of fluoride.
Average caries
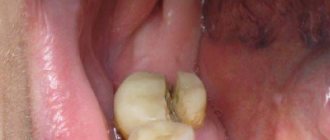
This is not a death sentence for the tooth, but it is the first sign that an infection has entered inside. The upper layers of dentin are subject to carious lesions.
Dentin is a hard tissue that makes up the main part of the tooth, but its structure is still softer than that of enamel. However, despite the fact that enamel is considered the hardest fabric, it is quite fragile and can crack. Through these microcracks, bacteria penetrate into the dentin, where in more fertile soil they multiply much faster, which will lead to the formation of a carious cavity. On the surface, the diameter of the lesion is small. But even a tiny dark point in depth can extend to the pulp.
This stage is not the easiest, but still, with timely contact with a specialist and proper treatment, you can avoid the worst and keep the tooth alive.
Treatment of caries in the spot stage
There are several treatment methods for the initial stage.
- Treatment with solutions of calcium and sodium - the Borovsky-Leus method. This method of combating incipient caries was very common several years ago; today it is used less frequently, primarily due to its toxicity. The technique includes cleaning the tooth from plaque using a professional abrasive paste, treating it with hydrogen peroxide and special solutions. First, use a solution of calcium gluconate, and then make lotions with a solution of sodium fluoride. You need to repeat the procedure 15-20 times. It is advisable to treat the tooth every other day.
- Gel applications. Damaged teeth are cleaned, after which a special heated gel containing agar-agar and sodium fluoride is applied to them. It hardens on the teeth in the form of a film and saturates the enamel with minerals. The course of treatment includes 5 applications. Recently it has also been used infrequently.
- The use of special calcium phosphate-containing gels, fluoride-containing varnishes (fluoride varnishes) and other preparations for remineralization of enamel.
- Filling. The dentist cleans the tooth surface from plaque, prepares the enamel by drilling, isolates the tooth from saliva, applies acid and a special adhesive to ensure reliable adhesion of the tooth surface to the filling, and only then fills the tooth and grinds the filling.
In addition, the dentist teaches the patient proper oral hygiene: he tells how to properly care for his teeth, how to clean them and how to eat. And he strongly recommends visiting the dental clinic in a few months.
Other drugs for remineralization at home -
Below we have listed a few more decent medications that you can use to remineralize weakened tooth enamel.
- Remineralizing gel ROCS Medical Minerals –
This Russian-made gel contains increased dosages of easily digestible calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. After its use, a thin film is formed on the surface of the teeth, from which microelements gradually penetrate into the tooth enamel. The gel should be used immediately after brushing your teeth (an important point - to brush your teeth before directly using the gel, you need to use fluoride-free toothpastes).
ROCS Medical medicated toothpaste – this Russian toothpaste contains a combination of amino fluoride and sodium fluoride; total fluoride content – 5000 ppm. You can apply it to your teeth using applications, or brush your teeth with it (for 3-4 minutes).- Elmex gel (Germany) – highly effective fluoride gel for teeth cleaning, containing a combination of amino fluoride and sodium fluoride; total fluoride content 12,500 ppm. To consolidate the effect of the ROCS remineralizing gel, you just need to use Elmex-gel only 2 times a week, brushing your teeth with it before going to bed for 3 minutes.
Caries in the spot stage: treat at home
Unfortunately, carious lesions cannot be cured with folk remedies. To eliminate them, you need to contact your dentist. Caries in the spot stage can be cured with the help of professional hygiene and special remineralizing therapy.
An effective assistant in the fight for dental health will be remineralizing gels, pastes with fluoride and calcium, which must be alternated. For example, ASEPTA PLUS REMINERALIZATION paste will satisfy the enamel’s need for calcium, slowing down the development of carious processes.
Popular traditional methods of treatment can rather be attributed to measures to prevent this problem.
- Onions are considered an effective remedy with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Freshly squeezed juice from this vegetable can be used both to prevent caries and to get rid of toothache. To do this, you need to get juice from onions, moisten cotton wool with it and apply it to the sore tooth for several hours. If you don’t like the taste of onion juice, you can use a decoction of onion peels. To do this, you need to pour boiling water over the husk, let it brew and rinse your mouth three times a day.
- A vodka tincture of calamus root can also help in the fight against the initial stage of caries. To prepare it, you need to grind the root of the plant, add vodka and let it brew for a week. It is better to rinse with this solution before going to bed for one to three minutes. To enhance the bactericidal effect, you can add alcohol tincture of propolis to the calamus tincture.
- Chinese lemongrass also has an antibacterial effect. You can drink tea with this plant after holding it in your mouth, or you can rinse your mouth with it.
- Sea salt, a solution of which you need to rinse your mouth, can also prevent development.
- But, perhaps, propolis is considered the most effective remedy. A piece of it can be placed on the tooth, pressed with a cotton swab and held for thirty minutes.
- It’s a good idea to brush your teeth with laundry soap. To do this, you need to prepare a fresh soap solution, brush your teeth and rinse thoroughly with water.
- Fir oil will not only stop the development of caries, but also relieve aching pain. It is necessary to moisten a swab with oil and apply it to the tooth.
- Camphor alcohol has a similar effect, which is used to lubricate the tooth or moisten a tampon and apply it to the diseased area.
If dental caries is in the white spot stage, during this period the disease is still practically undetectable. But at the same time, it responds well to treatment, so it is important to visit the dental clinic as often as possible in order to detect it in time.
Deep caries
It is at this stage that the tooth begins to react and sends us SOS signals - sharp aching pain. However, they are temporary; unfortunately, patients can endure these moments or help themselves with painkillers and delay going to the doctor. It’s not worth the effort to guess; this has never ended in anything positive. Medium caries that is not treated in time slowly and quite difficultly turns into deep caries. The rate of damage varies from compensated to decompensated, which in turn is more dangerous, because in a short period of time it can cover even two teeth. It is important to prevent infection from entering the pulp chamber and to prevent complications - pulpitis and periodontitis.
Prevention
How to protect yourself from caries?
- rinse your mouth after eating with Asepta Fresh (you can use chewing gum, but always without sugar);
- use dental floss, forgetting about toothpicks;
- choose the toothpaste wisely and change the brush more often;
- strengthen your immunity;
- take vitamins;
- take care of a balanced diet;
- no smoking;
- avoid stress.
Sources:
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” COFFEE and TOBACCO Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky. First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
Preventive measures for multiple dental caries
L. A. Skorikova
Doctor of Medicine, Professor, Head of the Department of Propaedeutics and Prevention of Dental Diseases, KSMU
G. N. Osadchaya
Assistant at the Department of Propaedeutics and Prevention of Dental Diseases KSMU
For many years, the main focus in domestic dentistry was filling existing carious defects. Insufficient attention was paid to primary prevention, that is, preventing the development of caries and reversing its initial manifestations.
Prevention of dental caries and related complications, early detection of dental diseases form an integral part of general medical prevention. The most important role in the prevention of dental diseases is given to oral hygiene [2]. Hygienic training and education is a basic and accessible measure for the primary prevention of dental diseases and includes health education aimed at teaching methods of individual oral hygiene [7].
A correct and thoughtful integrated approach to health education among children gives the best results and is most effective in instilling healthy skills for life. Four main groups of stakeholders must be involved in this work: medical workers, teaching staff, parents and the children themselves.
According to the law, every dentist must carry out primary prevention in the form of planned activities, using the allotted working time budget - four hours per month. This work should be carried out under the direct supervision of the administration of preventive departments of dental clinics.
Practice, however, shows that dentists are busy with medical work and do not have enough time to carry out primary prevention. As a result, the intensity of dental diseases increases. The real way to increase the effectiveness of dental prevention is to improve the organizational structure, that is, transfer a significant part of the dentist’s workload to the shoulders of specially trained nursing staff [1].
Expanding the functions of nursing staff allows the dentist to focus his attention on key positions in the planning and implementation of preventive measures and thereby significantly increase the coverage of the population and increase the effectiveness of prevention.
At the current level of health care, an important aspect of the implementation of prevention is its financing. Without funding, preventive work is doomed to failure.
Due to the fact that dental caries has a high prevalence among the population, sanitary and educational work on the prevention of caries, hygienic education of the population are of great importance, but we should not forget about the pathogenetic direction of preventive measures.
Dental caries is a pathological process that occurs after teething, during which demineralization and softening of the hard tissues of the teeth occurs, followed by the formation of a cavity.
Dental caries should be considered a social problem. First of all, we should point out its high prevalence. Secondly, caries and especially its complications affect the condition of the body due to disruption of chewing function and the occurrence of focal diseases. The concept of “carious process activity” is widely used in the literature, which determines the tactics of treatment.
In the presence of single tooth lesions localized in the fissure area, treatment is reduced to filling them. In the presence of multiple carious lesions, and especially in the case of carious lesions of smooth surfaces, in addition to filling, preventive treatment should be carried out in the form of remineralizing therapy, which is carried out comprehensively before treatment and some time after it [3].
One of the most effective anti-caries remedies is fluorides. They slow down the development of caries by changing the structure of the enamel, making it stronger and more resistant to acids.
In addition, fluorides have an inhibitory effect on the growth and metabolism of oral microflora.
Fluorides can reach the tooth in two ways:
- with drinking water, food, medicines (endogenous route, another name for it is “communal method of prevention”);
- directly to the surface of the enamel (exogenous route).
Preventive effects in communal methods of prevention occur regardless of the subject of prevention - the population. People consume water, salt, and milk with added fluorides, which provides a preventive effect regardless of the will and desire of the population. This is a serious advantage of communal methods of prevention.
All communal methods provide for certain rules and approaches to their implementation. Firstly, they are necessary only in areas where the content of fluoride ions in drinking water does not exceed 0.5 mg/l. Secondly, it is necessary to study the dental morbidity of the population using epidemiological indicators that confirm the need for communal methods of prevention.
In Krasnodar, the prevalence and intensity of caries in permanent teeth is: at the age of 6 years - 22%, at the age of 12 years - 95%, at the age of 15 years - 100%, at the age of 35-44 years - 100%. Thirdly, an administrative decision of the local authorities together with the health committee on the implementation of one or another method of communal prevention is mandatory. Fourthly, it is necessary to allocate financial resources for the purchase, installation and operation of appropriate equipment, hiring of labor and monitoring of morbidity, control of the fluoridation process. It is necessary to develop reliable methods for controlling the intake of fluoride in quantities that are effective for the prevention of dental caries and at the same time safe for the health of patients.
Local fluoride prophylaxis agents are used to prevent caries in temporary and permanent teeth [6].
Dental care with fluoride-containing toothpaste provides a lasting preventive and therapeutic effect, which results from a reduction in the amount of plaque and strengthens the tooth structure. Today, toothpastes based on amino fluoride are very effective.
Fluoride-containing varnishes and gels are used for a prolonged period of exposure to fluoride on the enamel. They form a film adjacent to the enamel, remaining on the teeth for several hours, and in fissures for several days. Dental effectiveness from the use of fluoride varnishes averages about 40% (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1a. Individual mouthguards for remineralizing therapy. Rice. 1b. Individual mouthguards for remineralizing therapy.
Fluoride-containing gels.
Gels containing fluorides are used for application to teeth in order to increase the intensification of mineralization, remineralization and increase the resistance of enamel to acids. Often the gels are acidified, since the incorporation of fluoride into the enamel occurs more actively in a slightly acidic environment. They can be intended for individual use at home or for use in a dental office. Thus, these means of local caries prevention relate to both personal dental care and medical dental prophylaxis.
In some European countries, topical gels are used as part of mandatory dental brushing programs (6-12 times a year) or are recommended for weekly home use in persons over 8 years of age. The concentration of fluoride in self-administered products is lower than that in products intended for professional use.
Applications are usually carried out not daily, but at certain intervals. To carry out applications, the gel is applied to the teeth using a toothbrush or applicator for several minutes, after which the mouth is thoroughly rinsed. Application with gel applied to the impression tray is more effective and safe.
It is convenient to use individually made spoons. Apply 2.5 ml of gel onto a spoon. The duration of the application should not exceed 4 minutes. Before applying the gel, you must brush your teeth, 30 seconds after application, rinse your mouth with water and do not drink or eat for 30 minutes.
With regular use of solutions of sodium fluoride and amino fluoride for rinsing, the formation of dental plaque slows down and the hygienic condition of the oral cavity improves. This method does not require large time and material costs and at the same time is quite effective.
The dental effectiveness of rinses is on average 30-40%. For multiple caries, we can recommend an anti-caries rinse from the Elmex anti-caries series, the fluoride content is 250 ppm, does not contain alcohol and dyes. It should be used once a day after brushing your teeth, preferably in the evening.
To form a complete enamel structure that is resistant to acids, not only fluorides are needed, but also microelements such as calcium and phosphorus. Quite often, a child’s diet does not meet the physiological needs of the growing body for these minerals. In this regard, children during the period of growth and development can be recommended a new drug GC Tooth Mousse, or “Liquid Enamel”. The composition of “Liquid Enamel” is CPP-ACP complex (casein phosphopeptide amorphous calcium). The carrier of the active ingredients is milk casein, which freely binds to enamel, biofilm, and plaque, delivering calcium and phosphorus to where it is most needed.
Amorphous calcium phosphate complex is a perfectly balanced combination, identical to the components of tooth enamel, providing free calcium and phosphorus ions to tooth enamel. We conducted research on the effectiveness of using “Liquid Enamel” in 80 children from 3 to 14 years old. The enamel was applied to the teeth after brushing them for 10 days every month. The increase in the KPU indicator over the year was 0.19 ± 0.3 per child, and the increase in carious cavities did not exceed 0.25 ± 0.5. Some lightening of the teeth was noticed. In the comparison group, the PCI indicators increased by 0.75 ± 0.10, and the increase in carious cavities by 1.11 ± 0.10.
Thus, the use of “Liquid Enamel” in the form of GC Tooth Mousse significantly affects the rates of dental caries in children and makes teeth stronger and lighter.
In this regard, the data obtained give grounds to recommend the wider use of “Liquid Enamel” in comprehensive programs for the prevention of dental diseases. Particular attention is drawn to the ease of use of the drug: patients can use the mousse for teeth on their own, it has good taste, and no special skills are required.
To prevent and treat multiple dental caries, you can use New Pearl toothpaste. Calcium" produced (St. Petersburg) on individual mouth guards (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2a. The use of individual trays in the oral cavity. Rice. 2b. The use of individual trays in the oral cavity.
The trays are used for application to the teeth for 20 minutes once a day for 30 days after individual oral hygiene (Fig. 3). After using trays with toothpaste, tooth enamel is strengthened and teeth are somewhat lightened.
Today, for the treatment of multiple caries, it is important to carry out remineralization therapy using calcium preparations [5].
Remineralization is possible only with a certain degree of damage to dental tissues. The limit of damage is determined by the integrity of the protein matrix. If the protein matrix is preserved, then, due to its inherent properties, it is able to combine with calcium and phosphate ions through diffusion and adsorption of these elements from saliva. Subsequently, hydroxyapatite crystals form on it. Thus, during initial caries (white spot stage), with partial loss of enamel minerals (demineralization), free microspaces are formed, but a protein matrix capable of remineralization is preserved.
The dynamic balance of demineralization and remineralization processes in the oral cavity ensures homeostasis of dental tissues; disruption of this balance in the direction of demineralization and a decrease in the intensity of remineralization processes are considered as an important link in the chain of pathogenetic mechanisms of caries development.
Remineralization therapy for dental caries is carried out using various methods, resulting in the restoration of the surface layer of the affected enamel.
These can be the Leus-Borovsky, Vinogradova, Leontyev and Suntsov methods, and the electrophoresis method.
Due to the high incidence of caries on the chewing surface of molars in children and adolescents and the rapid progression of the carious process, it is advisable to seal fissures. This method ensures that your teeth remain healthy. It is advisable to seal fissures of the first permanent molars at 5-6 years, first premolars - at 9-10 years, second premolars - at 12-13 years, second molars - at 12-13 years. In order to seal blind pits and fissures of teeth, sealants belonging to three classes of materials are used: composite materials, compomers and glass ionomer cements [4].
The use of glass ionomer cements as fissure sealants is advisable in newly erupted teeth with extremely low fissure mineralization. Composite sealants based on UDMA have slightly higher fluidity, lower viscosity and, at the same time, higher shrinkage. Filled composite sealants are more resistant to wear and abrasion, but unfilled ones penetrate better into narrow fissures and pits.
Transparent sealants allow one to judge the changes occurring underneath them (for example, the development of caries, the appearance of pigmentation). Therefore, their use is advisable in persons with a severe cariogenic situation. Colored (usually chalky white) sealants allow the patient or his parents to control the retention of the material on the tooth surface. Opaque tooth-colored sealants are the most aesthetically pleasing, but their durability is difficult to control because they blend with the color of the surrounding tooth surface.
The use of all these drugs in combination with other preventive measures gives good results. Today, there are two methods of fissure sealing - invasive and non-invasive. The choice of technique depends on the type of fissure.
Consequently, an integrated approach to the treatment of patients with multiple caries is a whole series of activities that should be implemented in the system of dispensary observation of the population. At the same time, the active participation of the population in this work should play a significant role; every citizen should personally contribute to the implementation of preventive measures.
.