Not every person worries about the condition of their gums as much as they worry about the condition of their own teeth. However, gum problems can cause serious problems, including deterioration of dental health. A fairly common situation is when the gum has moved away from the tooth. Let's try to figure out how serious this condition is and what can be done to correct this pathology.
Why can gums recede from teeth?
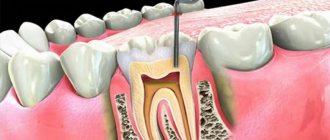
The gum is the soft tissue that surrounds the tooth. Healthy tissue securely holds the teeth and does not allow the tooth to become loose. If its function weakens, the development of periodontitis is immediately assumed.
The causes of gums receding from the teeth are divided into local and general.
Local ones include:
- Over time, inflammation of the tissues surrounding the teeth develops into periodontitis and other dental pathologies of soft tissues
Insufficient and improper oral care. Poor oral hygiene leads to the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms that cause the development of gingivitis. Over time, inflammation of the tissues surrounding the teeth develops into periodontitis and other dental pathologies of soft tissues.
- Mechanical injury to the gums. An example of this would be: Using a toothbrush with very stiff bristles.
- Presence of a high filling.
- Inaccurately selected prosthesis.
All these factors lead to irritation and injury to the gums with the subsequent development of periodontitis.
Diseases in which the gums recede from the teeth
In addition to the main reasons that provoke the gums to recede from the teeth, there are a number of pathologies that also affect the development of this condition.
Such reasons include:
- Signs of recession directly depend on the etiology and prevalence of the provoking disease
Diseases of the endocrine glands. It is especially evident in cases of hormonal imbalance of the gonads in women and dysfunction of the entire endocrine system.
- Immunodeficiency pathologies. I contribute to the development of capillary dysfunction, which leads to insufficient enrichment of the gums with blood.
- Diabetes mellitus of any type.
- Circulatory dysfunction in soft tissues. They are provoked by pathologies of the kidneys and liver or spinal cord. With such diseases, a disorder occurs in the hematopoietic system, and the amount of oxygen and nutrients entering the body decreases. The elasticity of the mucous membranes of blood vessels also decreases.
- Dental pathologies: gingivitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis, large localized tartar, as well as neoplasms of any etiology on the gums.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Long-term use of diuretics.
Important! Correctly identifying the cause that causes the gums to recede from the teeth will significantly reduce the time of treatment for this pathology.
Types and stages of periodontitis
Depending on the lesion, the following types of periodontitis are distinguished:
- generalized (affects the tissue around each tooth);
- localized (spreads to one or two adjacent teeth, most often as a result of injury).
Stages of the disease:
- Easy.
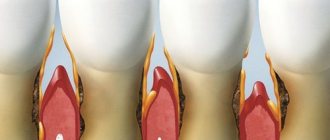
The gums bleed after eating hard and hard foods, brushing, and tartar appears. Periodontal pockets (gaps between the edge of the gum and the crown) up to 4 millimeters deep are formed.
- Average.
The gums bleed profusely and hurt, the crowns of the gums are exposed by 5-6 millimeters, and pathological mobility is not very pronounced.
- Heavy.
Gingival bleeding is accompanied by suppuration, pockets deepen to 7-8 millimeters, and pathological mobility of teeth leads to their displacement.
Symptoms
Signs of recession directly depend on the etiology and prevalence of the provoking disease. The disease can manifest itself locally or in a generalized course.
Most often, this pathology is accompanied by the following external signs:
- At first, bleeding gums appear only when eating or brushing teeth.
Soft periodontal tissues bleed.
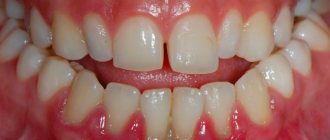
- The gum lags behind the tooth, is inflamed and hurts.
- A gap has formed between the tooth and the gum (it does not fit tightly).
- The presence of an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
- Suppuration of gum pockets.
- The gum mucosa swells and becomes a deeper red color.
- The gums expose the necks of the teeth.
- The teeth become exposed and begin to loosen.
At the initial stage of recession, a person feels minor discomfort associated with the gums moving away from the teeth.
At first, bleeding gums appear only when eating or brushing teeth. Then tooth and gum sensitivity appears. If treatment is not timely, the symptoms increase and a purulent taste appears in the mouth.
Important! If you experience the slightest symptoms, you should immediately seek qualified help from a dentist.
What to do if the necks of teeth are exposed?
To eliminate increased sensitivity and prevent the development of cervical caries, you can cover the exposed necks of the teeth with a composite material, composite materials or veneers.
Watch the video , which demonstrates the technology of closing the neck of a tooth with COMPONERS (direct composite veneers).
We talk more about the technology of dental restoration with COMPONERS in the article What are COMPONERS and will they solve my dental problems?
Now you know the causes and consequences of gum recession and can do more to prevent gum disease
Diagnostics
Only a dentist can determine the exact cause of periodontal tissue recession and prescribe appropriate treatment.
At the appointment with this specialist, a visual examination of the oral cavity will be carried out and a modern diagnostic examination will be prescribed.
For these purposes, patients are prescribed:
- Radiography.
- Orthopantomogram.
- Measuring the depth of the periodontal pocket.
Important! To accurately determine the etiology of the disease, the dentist may prescribe additional examination to exclude provoking systemic pathologies. This will make it possible to carry out complex therapy and achieve rapid recovery dynamics, eliminating the development of relapse.
What can be done to prevent and prevent the development of gum disease:
- Visit the dentist regularly so as not to miss the first signs of the disease, and if detected, determine the true causes of gum recession and carry out the prescribed treatment.
- Take proper care of your teeth at home.
- As prescribed by your doctor, do professional hygiene and remineralizing therapy to strengthen your teeth enamel. Read more about these procedures in the articles Why do you need professional dental hygiene and What causes tooth sensitivity and will remotherapy help me?
First aid at home - what to do?
Important! Experts warn that self-treatment of gum recession at home is unacceptable. Such therapy will not bring positive results, but will only worsen the condition of the soft periodontal tissues and can lead to partial or complete loss of teeth.
But, as a last resort, such manipulations can and should be carried out at home as first aid for this pathology.
What to do:
- Irrigation of the oral cavity with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic dental rinses or herbal decoctions.
- Applying applications of aloe leaves, sea buckthorn oil or soda slurry to the affected areas of periodontal tissue.
- Taking antibacterial pharmacological drugs.
- When brushing your teeth, use floss and soft toothbrushes.
- Rinse your mouth with an anesthetic solution made from a decoction of chamomile and sage with the addition of propolis.
Surgical intervention
Based on the general picture of the situation, the specialist may resort to surgical treatment. Thus, at an early stage of the pathological process, when the periodontal pocket does not exceed 5 mm, subgingival deposits and granulation changes in the gum are removed (closed curettage).
In advanced cases, you will have to make an incision in the gum, and then remove the mucous layer by layer; the doctor will also implant synthetic materials into the gum, and finally apply sutures. Sometimes a flap operation is used to eliminate foci of prolapse: an incision is made in the gingival margin, exfoliated tissue is removed, and a flap of tissue from another place in the oral mucosa is pulled in its place.
Important! Traditional methods of treatment involve rinsing with various medicinal decoctions from oak bark, chamomile, strawberry leaves, St. John's wort, and calendula. However, you should not self-medicate, because... Traditional medicine can only weaken the symptoms, but not eliminate the cause of the pathology.
The postoperative stage usually lasts several months and ends with complete healing of the damaged tissue.
How is dental treatment performed?
When the gums recede from the teeth, treatment should be extremely comprehensive and consistent.
At a dentist’s appointment for periodontal tissue recession, a therapeutic complex is performed, consisting of the following manipulations:
- Treatment must be exclusively comprehensive and consistent
Professional teeth cleaning. Removing supragingival and subgingival deposits and dental plaque eliminates pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity. Depending on the condition of the teeth, the following methods can be used:
- Ultrasonic cleaning.
Instrumental technique.
- Sandblasting method.
- Anti-inflammatory treatment. It consists of treating soft periodontal tissues and gum pockets with antiseptics, taking broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs, and local treatment of the mucous membrane with anti-inflammatory gels.
- Advice on proper oral care after therapy. Hygiene products are determined and a schedule for a preventive examination with the attending physician is assigned.
Important! This type of therapy is used in the early stages of periodontal tissue recession. At an advanced stage, this technique will not reveal any dynamics of recovery.
Other treatments
There are several methods for treating gum separation from a tooth:
- Surgical treatment methods include open and closed curettage. They are carried out when the gums recede strongly from the tooth or in the presence of severely damaged bone tissue. The principle of such manipulations is to dissect the gums and then cleanse it of purulent exudate, granulation, and the like. After cleaning, stitches are placed and pain medications are prescribed. In addition to curettage, as a last resort, if indicated, flap surgery or transplantation is performed.
- Therapeutic treatment is carried out with the aim of influencing the source of the inflammatory process. For this purpose, antibacterial, antiseptic, immunostimulating, and hormonal medications may be prescribed. Their selection is carried out taking into account the etiology of the pathological condition. A course of physiotherapeutic procedures is also prescribed, which, in combination with medications, significantly influence the dynamics of recovery.
- Traditional methods are mainly based on irrigating the oral cavity with anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and strengthening herbal decoctions . For their preparation, chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, oak bark, tea tree and eucalyptus essential oils are most often used. Applications of fir or sea buckthorn oil, as well as wiping the gums with propolis, are effective.
- Diet plays a major role in the gum treatment process. The diet must include a large amount of food products containing ascorbic acid: kiwi, rose hips, black currants, dill, Brussels sprouts. At the initial stage of pathology, it is recommended to eat solid food.
Important! Periodontal tissue therapy must be comprehensive and must be prescribed by a doctor.
Self-medication increases the risk of worsening gum health.
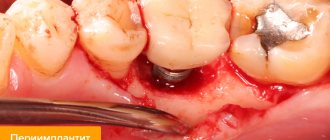
What is the essence of the problem
Gum receding is called “recession” in dentistry. This pathology is most often associated with abrasion and detachment of the gingival margin and exposure of part of the tooth. With periodontitis, bone tissue is destroyed. In this case, the gums in relation to the tooth recede or form a pocket, which contributes to the accumulation of microbes and the appearance of various inflammations in the oral cavity. In this condition, the tooth is surrounded by its own root with a dense pathological coating, which does not strengthen it, but threatens inflammation and pathological mobility. As dental-gingival pathology progresses, the connection with the gum is disrupted and it recedes. In addition, in addition to destroying periodontal tissues, some pathogens also release acidic poisons that destroy enamel. This causes demineralization of teeth and the development of carious micro-foci, which further increases the fertility of pathogenic microorganisms in the mouth and involves the gum mucosa in the pathological process. Moreover, in cases of delayed treatment, a person may even lose several teeth.
Basically, the initial manifestations of a recession are:
- increased sensitivity of diseased teeth;
- visual lengthening of the affected tooth.
Such signs require a visit to the dentist to begin eliminating this pathological condition as quickly as possible.
Special cases
There are other cases in which the gums move away from the teeth:
- If you experience the slightest signs of recession, you should immediately seek qualified dental help.
Exposure of teeth during pregnancy is a fairly common problem, especially if a woman has previously had gingivitis or periodontitis. Physiological changes in the body characteristic of this period contribute to the deterioration of gum health. Therefore, if the slightest signs of recession appear, you should immediately seek qualified dental help and prevent the development of complications of this pathology.
- The gum has receded from the wisdom tooth. Exposure of wisdom teeth occurs immediately during their eruption. This phenomenon is considered normal, and the use of alternative methods of therapy is allowed to alleviate the condition. If the cause of the recession in this case is an infection, urgent medical attention and antibacterial therapy are required.
- Gum receding in a child is extremely rare. It can be caused by injury to the gums, improper care, or hormonal imbalances in the body. Vitamin deficiency due to poor nutrition or a hereditary factor may also be the cause. It requires immediate treatment as it provokes the rapid development of inflammatory periodontal tissues. This leads to destruction of dental tissue or tooth loss.
- Receding gums between the front teeth can occur if there is a short frenulum on the upper lip. Also, this condition indicates the development of periodontal disease, periodontitis or gum recession. Depending on the etiology of the pathology, the method of therapy is selected.
- Gum rupture due to apical displacement of the gingival margin can be caused by mechanical trauma or consumption of hard foods. Also, this condition can be a negative consequence of poor-quality dental services. In this case, it is possible to restore the condition of periodontal tissue through surgery or the use of medications with an antiseptic effect.
ethnoscience
During a recession, traditional methods of treatment must be agreed with a doctor and do not have the right to replace qualified treatment.
Traditional treatment of periodontal disease often includes the use of rinses based on various medicinal decoctions. Oak bark, chamomile, strawberry leaf, St. John's wort or calendula are often used for this. Often, folk healers recommend chewing (in the summer) or rinsing your mouth with a decoction of St. John's wort 2-3 times a day for 3-4 days.
Sea salt is an excellent disinfectant and decongestant. A solution of 1 tsp. salt per glass of water is used after each meal. This product destroys bacteria and accelerates the restoration of the gum mucosa.
If the gum has moved away from the tooth, it is unpleasant, but not scary. The main thing in such a situation is not to bury your head in the sand, pretending that everything will “go away on its own” or that “the neighbor had the same thing.” In the initial stage, this condition can be easily treated, so do not forget about regular and obligatory visits to your dentist. Health to you and your teeth!
Sources used:
- Periodontal diseases / V.S. Ivanov. - Moscow
- Treatment of diseases of gums and teeth using traditional and non-traditional methods / E.L. Isaeva
- Diseases of the endodont, periodontium and oral mucosa: monograph. / Edited by A.K. Jordanishvili. — M.: MEDpress-inform
Forecast
With apical displacement of the gingival margin, in most cases the prognosis is positive.
Timely and adequate therapy allows you to restore the structure and integrity of periodontal tissues. This helps prevent the destruction of periodontal tissues and tooth decay.
Gum recession requires mandatory treatment. It is strictly not recommended to ignore it. Advanced stages of pathology contribute to the rapid development of complications and partial or complete loss of teeth.
Types of gum injuries
- Mechanical injury. The most common type of damage. The cause is usually external physical influence. Most often such injuries occur during a fall or from an external blow.
It is possible that injuries may occur during sports activities in strength martial arts - boxing, freestyle wrestling, judo, karate and other sports. Mechanical injuries are easier to diagnose, since in most cases they are accompanied by external injuries, such as bruises, bruises, and even skin tears.
- Chemical injury. Such gum injury may be the result of exposure to chemically active drugs. For an inattentive or in a hurry person, it is quite acceptable that he can confuse externally similar liquids, for example, vinegar and water, or a concentrated solution of manganese and currant juice. After such an impact, the gums receive extensive trauma.
Possible complications
There is a misconception that the separation of periodontal tissue from the gums is not a significant pathology.
But, experts argue and warn that with untimely or incorrect treatment, this condition contributes to the development of numerous complications in the form of:
- Lymfodenitis.
- Infectious lesions of the bone tissue of the jaw apparatus.
- Periostitis.
- Periodontitis.
- Pathologies of the heart muscle.
- Development of endocrine diseases.
- Respiratory diseases of infectious etiology.
Important! If the pathology in which the gums move away from the teeth is not addressed in a timely manner, the likelihood of both partial and complete tooth loss increases.
Preventive measures
Recession prevention consists of the following manipulations:
- Strict adherence to oral care rules.
- Correction of the daily diet, which should be balanced.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Elimination of bad habits.
- Preventing gum injury.
- Carrying out self-monitoring of oral health.
- Systematic medical examinations with dentists.
- If any dental pathologies are present, provide immediate treatment.
Important! Compliance with preventive measures will prevent the development of gum recession, thereby preserving not only the health, but also the beauty of the dentition.
The receding of the gums from the teeth can be caused by a number of factors, the correct determination of which can be carried out by a doctor.
Therefore, if the slightest signs of periodontal soft tissue recession appear, you should immediately visit a doctor.