Why do baby teeth fall out?
It was not by chance that nature provided for the replacement of a temporary set of teeth with a permanent one. Babies' first teeth appear at the age of 6-9 months, when in addition to milk, denser foods begin to be introduced into the child's diet. But at this time the maxillofacial apparatus is still very small, so the first teeth are smaller. Over time, baby teeth can no longer cope with the chewing load, and the jaw grows to such a size that it can accommodate the entire permanent set.
The first molars begin to appear at age 4
Typical problems.
NORMALLY, the permanent incisors are located “evenly” in the dentition without “protrusion” or “sagging” to the side. This indicates a harmoniously occurring process of physiological replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones.
If there has been early removal of baby teeth in children and, as a result, permanent chewing teeth are displaced forward, improper closure of the dentition occurs and crowding of teeth appears in the area of the frontal and chewing teeth.
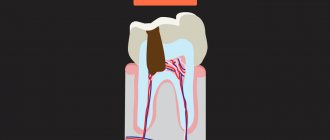
A common problem in the period from 9 to 12 years is poor oral hygiene, which is associated with the characteristics of the psychological development of children. As a result, caries develops in “young” permanent teeth. Most often, the 6th chewing teeth (1st molars) are affected in the area of fissures (natural depressions of the teeth located between the cusps of the tooth).
Fissure caries, remaining unnoticed, develops rapidly and is quickly complicated by inflammation of the nerve of the tooth (pulpitis).
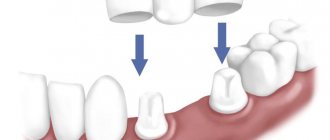
PHOTO: The child's lower permanent incisors erupted in the second row. In this situation, it is necessary to free up space by removing the mobile baby teeth so that the permanent teeth can take the correct position in the dental arch.
Normal shift times and sequence
Many parents believe that the change of baby teeth begins from the moment the child’s first tooth falls out, that is, at the age of 6-7 years. However, this opinion is somewhat erroneous. The replacement process begins several years before they begin to fall out. After four years, children develop third molars, which are already permanent. This is the starting point.
Around the same period, active resorption of the roots of baby teeth begins, which lasts up to two years. As the root tissues dissolve, the child’s tooth begins to wobble, and by the time the molars should appear, it is completely pushed out.
The order in which teeth change roughly corresponds to the pattern of their eruption. The front teeth on the lower jaw (central incisors) fall out first, then the teeth on the upper jaw are replaced symmetrically. Next, the lateral incisors, first (small) molars, canines and second (large) molars fall out in succession. The age at which the first tooth is replaced and when the last one falls out is individual and can vary among different children up to two years of age. Some experts note that in girls, teeth replacement occurs somewhat earlier than in boys.
The table shows an approximate schedule for replacing baby teeth with permanent ones.
| Temporary teeth | Beginning and duration of milk root resorption | Age |
| Central incisors on the lower jaw | After 5 years (for two years) | 6-7 years |
| Central incisors on the upper jaw | After 5 years (for two years) | 6-7 years |
| Lateral incisors on the lower jaw | From 6 years old (for two years) | 7-8 years |
| Lateral incisors on the upper jaw | From 6 years old (for two years) | 7-8 years |
| First (small) molars on the upper jaw | After 7 years (for three years) | 8-10 years |
| First (small) molars on the lower jaw | After 7 years (for three years) | 8-10 years |
| Fangs on the upper jaw | After 8 years (for three years) | 9-11 years |
| Fangs on the lower jaw | After 8 years (for three years) | 9-11 years |
| Second (large) molars on the lower jaw | From 7 years old (for three years) | 11-13 years old |
| Second (large) molars on the upper jaw | From 7 years old (for three years) | 11-13 years old |
How many baby teeth do children have?
So how many baby teeth do children lose? In a newborn, in the depths of the upper and lower jaws there are only 20 rudiments of temporary teeth - 10 follicles for each jaw. It should be noted that the formation of follicles begins already at 6-7 weeks of embryonic development, and when a child is born, the crowns of his baby teeth are already fully formed (although they have not yet erupted). But the formation of the roots of baby teeth continues to occur after the birth of the child.
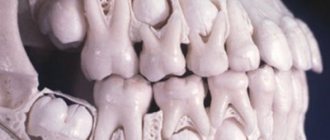
Studies have shown that a baby tooth begins to erupt when its root is 25-50% formed. One of the theories of eruption says that the developing root, as it were, pushes the baby tooth out of the jaw. Normally, the process of teething in the primary occlusion begins at 5-6 months, and in completely healthy children it ends by 24 months (the last to erupt are the temporary fifth molars). In diagram No. 1 you can see how many baby teeth children should have depending on their age.
Scheme of teething in children without pathology (scheme No. 1) –
→ Eruption of baby and permanent teeth
In diagram No. 1 you can see the timing of the eruption of baby teeth - in completely healthy children who do not have any pathology. These data are taken from the National Guide to Pediatric Dentistry. But if there is (for example, any somatic pathology), the timing of the eruption and loss of baby teeth can shift by 3-5 months. Below in the article we will tell you at what time children’s baby teeth fall out and what leads to this.
Nutritional features during this period
When permanent teeth erupt, their enamel is not yet fully formed. This maturation process continues for several more years. During this period, high-quality and nutritious nutrition plays an extremely important role for children:
- Every day, your baby’s diet should include foods rich in calcium: cottage cheese, hard cheeses, milk.
- Twice a week you need to eat dishes made from fish, a source of phosphorus. For children, it is better to use low-fat varieties: hake, pike perch, pollock.
- Eating fresh vegetables and fruits, some of which should be in solid form. This is necessary to stimulate the resorption of the roots of baby teeth and the eruption of permanent teeth.
- Refusal of white pastries, chocolate and sweets. Sweet carbonated waters pose a particular danger to fragile enamel.
- Sometimes, when a child refuses dairy products, it becomes necessary to take multivitamin complexes containing calcium.
During the period of teeth change, too hard or sticky foods should be prohibited: nuts, candies, toffees. They can cause premature loss or injury of a baby tooth, which will lead to impaired growth of the molar. It is also undesirable for children to include in their diet foods containing active dyes, which can ruin the color of the enamel for the rest of their lives.
Replacing baby teeth with permanent ones: what should parents pay attention to?
The process of replacing children's milk teeth with permanent ones requires increased attention from parents. It is necessary to monitor the child’s adequate nutrition and oral hygiene, and if there are deviations from the norm, immediately contact a dentist
Every person in childhood goes through a period when temporary teeth are replaced with permanent ones. In most cases, this process does not cause any problems. However, parents should still know what exactly to pay attention to when a child’s baby teeth fall out and permanent teeth appear.
Causes of loss of baby teeth
There are very specific reasons for the process of changing a set of teeth after a certain age. The fact is that children erupt their first teeth before they reach the age of one, when more dense foods than milk appear in the diet. However, the child’s jaws at this time are still quite small, and the first teeth that grow have a corresponding size. And milk teeth themselves, which have weak enamel, are not very strong.
Gradually, as the baby grows up, the chewing load on the teeth increases due to the intake of increasingly solid foods. This requires the formation of an appropriate masticatory apparatus. By this time, the growing child's jaws are just large enough to accommodate the entire set of permanent teeth. Therefore, the process of loss of milk teeth and the appearance of stronger molars, necessary for a full future life, begins.
At what age do baby teeth change?
Parents often mistakenly believe that the process of changing primary teeth begins with the loss of the first milk tooth. As a rule, this occurs at the age of 6-7 years. However, doctors take as a starting point the appearance of the first permanent teeth - third molars, which are absent in the “deciduous bite”. This process is observed at the age of 5-6 years. It is at this time that the process of resorption of the roots of temporary teeth begins, which lasts approximately 2 years. Gradually, baby teeth begin to loosen, and by the time the molars appear, they fall out.
The age at which teeth change varies from person to person, and the time difference is sometimes up to 2 years. Experts note that this factor may also depend on the region of residence: in warmer climates, permanent teeth appear earlier. It is also known that girls replace their baby teeth with molars a little faster than boys.
What to pay attention to during the period of teeth change?
Proper nutrition
The process of final formation of enamel during the eruption of permanent teeth takes several years. And during this period, proper nutrition becomes extremely important, thanks to which the child must receive all the substances necessary for the body.
Parents should pay attention to the following points:
- the child’s daily diet should include foods with a good calcium content - milk, cottage cheese, cheeses;
- the diet should be supplemented with fresh fruits and vegetables to obtain the required amount of vitamins and microelements;
- at least 1-2 times a week, to obtain a sufficient amount of phosphorus, you need to include fish dishes in the menu;
- Until the final formation of the enamel of the molars, it is advisable to give up sweets, chocolate and sweet pastries. Sweet soda is also extremely dangerous for young enamel;
- The child should eat some food, such as fruits and vegetables, in solid form. The load on the teeth will stimulate the resorption of the roots of baby teeth, helping the eruption of molars;
- in some cases, for example, if a child does not eat dairy products well, the baby’s diet should be supplemented with a multivitamin complex with calcium.
It is better to exclude the hardest or most chewy foods, such as nuts or toffees, from the diet completely during the period of teeth change. Their use can lead to injury or early loss of primary teeth, which will interfere with the proper growth of permanent teeth.
Oral hygiene
As already mentioned, permanent teeth appear with weak, not yet fully formed enamel. Therefore, oral care to prevent tooth decay is very important.
Proper oral hygiene in a child involves morning and evening brushing of teeth using children's toothpastes that have an optimal content of calcium and fluoride. To avoid injury to the gums, it is better to choose a toothbrush with soft bristles. It can also be helpful to teach your child how to use children's dental rinses. Ideally, it is advisable to rinse your mouth every time after eating - this will optimally prevent the formation of plaque.
Visiting the dentist
Special attention should be paid to the medical prevention of dental diseases during the period of teeth change. For preventive purposes, dentistry for children should be visited at least 2 times a year. And if there is a need to treat a child’s teeth, then you need to go to the doctor as quickly as possible. After all, caries in children with teeth with still weak enamel can develop very quickly.
Early and late change of primary teeth
Sometimes situations arise when the replacement of temporary teeth with permanent ones in children occurs in violation of the deadlines. Let's consider what parents should do in such cases.
Early tooth loss
The loss of baby teeth can be called early if it occurs before the age of 6 years. As a rule, such situations arise due to injury, dental disease, or intentional loosening of a tooth. The main problem here is that when a baby tooth disappears, free space appears in the dentition. And if the permanent tooth does not begin to grow after the loss of the temporary one, then gradually the neighboring milk teeth will begin to move, filling the resulting volume. In the future, this will lead to the fact that the molars will not have enough space for normal eruption, and the dentition will be uneven.
With the early loss of a temporary tooth, pediatric orthodontics comes to the rescue. Currently, modern techniques are available to doctors to prevent the displacement of adjacent teeth. Therefore, in case of early loss of a baby tooth, it is advisable to immediately go for a consultation with an orthodontist. After all, correcting cosmetic defects and correcting the bite will bring much more trouble in the future.
Late replacement of primary teeth
There are two possible scenarios here. The first is when molars do not appear in a timely manner, even if the milk teeth have already fallen out. There may be several reasons for this anomaly, from a physiological delay in the appearance of new teeth to incorrect positioning of the tooth inside the jaw apparatus. The second scenario is when the molars began to erupt before the baby teeth fell out. The result can also be the formation of bite defects.
If a child shows signs of a delayed change of teeth, it is necessary to contact a dentist to identify the causes of the deviations. As a rule, the doctor will be able to tell about the causes of the anomaly after an X-ray examination, after which appropriate treatment will be prescribed.
Features of care
Since the enamel is not fully formed when permanent teeth erupt, an important point during this period is high-quality oral hygiene and caries prevention.
- In the morning and evening, it is necessary to brush your teeth with a brush with soft bristles that cannot injure the gum tissue. For a child, it is advisable to choose special children's toothpastes containing optimal concentrations of fluoride and calcium. This procedure should be carried out under the supervision of parents, since children often shorten its duration and cannot fully clean all surfaces.
- You should teach your child to rinse his mouth after every meal. For these purposes, children's dental rinse, chamomile decoction or plain clean water are suitable. This will prevent plaque from accumulating on the surface of the teeth and reduce the risk of developing gum inflammation in the area of the erupting permanent tooth.
- Twice a year, every child needs to visit the dentist’s office not only for a preventive examination, but also for timely treatment of caries and professional hygiene.
Complications
The loss and eruption of new teeth occurs without any problems, but sometimes unforeseen circumstances occur that require immediate intervention :
Shark teeth . This phenomenon occurs when permanent teeth erupt before baby teeth fall out. It turns out that they grow in two rows, in parallel. This does not affect the bite and further development of the jaw. Dentists must observe the situation for three months, and then the baby teeth are simply removed.
Increased pain . Often the exit is painful, the gums swell and the temperature even rises. It does not rise high, but the baby feels the stress on the nervous system and, as a result, he sleeps poorly and gets tired quickly. Inflamed gums cause diarrhea. You can eliminate all problems at once with the help of the drug Dentokind, it relieves pain and inflammation, calms the nervous system and restores sleep.
Hematomas . This complication rarely manifests itself as a small purplish-red or bluish bubble along the edge of the gum. It hurts a lot, interferes with eating and causes discomfort. The hematoma goes away on its own after the permanent tooth comes out after a couple of weeks. You can help your child by lubricating the sore spot with Solcoseryl ointment or Kalgel gel.
Attention! These complications require the participation of a dentist; you cannot take any action on your own.
Violations of deadlines
Although the period allotted for replacing baby teeth with permanent ones is quite long, sometimes there are situations when all the time limits go beyond normal limits and a dentist’s consultation is required.
Early loss
Early tooth loss refers to the loss of teeth before the age of 6 years. This can be the result of injury, caries, or intentional loosening. And if a baby tooth falls out long before the permanent one begins to grow, then a free space is formed in the oral cavity, into which the rest will eventually move. This will lead to the fact that when the permanent teeth come due, they simply will not have enough space, and they will erupt crookedly.
If primary teeth are lost early, an orthodontist consultation is necessary. Nowadays, in pediatric dentistry, prosthetic techniques are increasingly used to replace defects in the dentition in order to prevent the displacement of other teeth. In the future, this helps to avoid problems with bite and cosmetic defects.
Late shift
Sometimes it happens that permanent teeth are already emerging, but milk teeth are still firmly in place. This is also fraught with improper growth of molars and the formation of dental defects. In this case, you need to visit the dentist to remove the temporary tooth.
Another option for late teeth change is cases when permanent teeth do not erupt in a timely manner. In this case, milk can either remain or fall out. This may happen when:
- Physiological delay in eruption, when tooth germs are formed correctly, but due to the individual characteristics of the child’s body they grow somewhat more slowly.
- In case of partial primary adentia, when during the period of intrauterine development the baby did not develop the correct formation of tooth germs or they died due to inflammatory diseases.
- With retention of permanent teeth, when the tooth germs are formed correctly, but the molar tooth has an incorrect location inside the bone tissue of the jaw.
Only a dentist can identify such defects and determine why teeth do not fall out after an X-ray examination, which will show whether all tooth germs are forming correctly. If defects in the development of the dental system are detected, then children are indicated for temporary prosthetics for the period of jaw growth. After the child grows up, he will need restoration of dental defects with permanent dentures.
Delayed loss of primary teeth
Many factors influence the timing of the emergence of temporary teeth, so there is no need to worry right away.
Doctors allow deviations of 1-2 years from the prescribed deadlines. The presented process is influenced by the following factors:
- hereditary predisposition;
- gender of the baby – in girls the process begins earlier;
- complications during pregnancy;
- duration of breastfeeding;
- child's diet;
- the presence of chronic diseases in the child;
- quality and chemical composition of drinking water;
- the climate where the family lives;
- endocrinological problems in a child;
- previous infections.
Teeth fall out later than expected for the following reasons:
- unbalanced diet leading to nutrient deficiencies;
- stressful state;
- presence of chronic infections;
- rickets in a baby;
- genetic predisposition.
If at least one of the listed factors is present, it will provoke a shift delay. The task of parents is to eliminate negative aspects in a timely manner.
Another video on the topic:
Hair loss begins earlier than usual
Early tooth loss is considered to be removal before the age of 5.
This can be done for the following reasons:
- injury from a fall or blow;
- development of a tumor in the mouth;
- the presence of advanced caries that cannot be treated;
- malocclusion – a tooth grown in the wrong place can put pressure on the neighboring one and force it to fall out;
- if the baby deliberately loosens it.
Often a tooth is removed early due to the displacement of the dentition, causing the permanent units to emerge crookedly.
Should a baby tooth be removed?