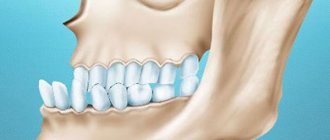
Gap between teeth occurs in almost twenty percent of people, and is most often observed between the two front teeth. In preschool children, gaps occur quite often, but over time, such a defect goes away on its own. In adults, the problem is not a death sentence, but it can signal the presence of certain pathologies or provoke orthodontic problems. If the patient is concerned about this large distance, the issue needs to be resolved, especially since modern dentistry offers a lot of techniques.
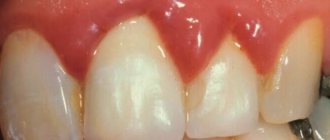
Gaps between teeth are considered natural to be 1 mm, and pathological - from 1 to 7 mm. It is normal when the side surfaces touch each other. If this is not the case, a diastema (another scientific name for distance) is diagnosed.
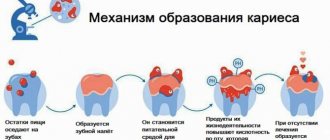
When the teeth touch each other, the chewing load is distributed evenly. Also, bacteria accumulate less in the interdental spaces, which means the risk of caries is reduced. Accordingly, if there is a distance, the dental units cannot cope with the loads and the risk of dynamic development of extensive caries is high.
What is the difference between a diastema and a trema?
Interdental gaps can appear not only on the front teeth, but also anywhere in the upper or lower jaw. In this case, empty spaces are called trems. Just like diastemas, they can arise due to various factors. Among the most common are malocclusion, premature tooth loss, and heredity.
The localization of trema depends on the cause that provoked it. Thus, trema in the lower jaw appear due to the mesial relationship of the dentition, and the spaces between the canines and lateral incisors are due to partial edentia.
Why do teeth come apart?
- due to genetic predisposition;
- if the patient has a short frenulum of the upper lip;
- due to artificial feeding of a child in infancy (using a pacifier);
- due to loss of teeth due to caries, periodontal disease;
- if the germ of an erupting tooth is located between the roots of adjacent dental units;
- for malocclusions;
- due to underdevelopment of the jaw, etc.
Note! A large gap between the crowns itself can cause malocclusion.
What types of diastema exist and why do they occur?
Diastemas, as well as tremata, come in different types. Experts divide them by etiology, location, and type of displacement. Doctors also distinguish between false and true diastemas separately. The latter are always a consequence of pathology, while false ones are found only in children and disappear as the teeth grow.
Symmetrical and asymmetrical diastema
Most often, the diastema is symmetrical, that is, the incisors are equidistant from the frenulum. An asymmetrical arrangement is much less common, and with it, only one incisor is displaced, the second is in the correct position.
Lateral deviation of crowns
With lateral deviation of the crowns, the roots are located correctly, the discrepancy begins only on the visible part of the teeth. Most often, this pathology is a consequence of supernumerary teeth. Also, a gap may appear due to bad habits.
Body lateral displacement
The peculiarity of this type of displacement is the complete deviation of the teeth along with the roots. It is provoked by congenital adentia, the lower attachment of the frenulum, and compaction of the middle suture on the bone tissue. In the latter case, the teeth cannot overcome the obstacle and take the correct position.
Medial inclination of central incisors
This type of diastema is the most difficult, since it simultaneously causes deviation of the teeth from the center and their rotation along the axis. The cause is almost always supernumerary teeth located between the first incisors or odontoma, a benign tumor growing in the jaw bone.
What it is?
The anomaly is expressed in the uneven growth of individual units in relation to the entire dentition.
Changes in size can be observed in fully formed single teeth or an entire group. But the second option occurs in rare cases.
The high position of the teeth is called supraocclusion, the low position is called infraocclusion.
How is it determined?
The main symptoms of the anomaly are the discrepancy between the height of the crown part of the tooth and the norm. Supraocclusion is identified by the excessive length of the tooth extending beyond the occlusal plane. In this case, the shape and width of the coronal part does not differ from normal bone organs.
The high position is often accompanied by lengthening of the arches in the dentoalveolar plane and displacement of the teeth in the vertical direction. One of the signs of pathology is an open bite, the degree of which will depend on the height of the abnormal unit.
Infraocclusion is determined by the insufficient height of the organ, which does not reach the occlusal line. In this case, the closure with the antagonist teeth is partially impaired or completely absent.
The x-ray shows underdevelopment of the alveolar process. According to its clinical picture, infraocclusion is similar to semi-retention.
Infraocclusion of several adjacent teeth, in most cases, is combined with a deep bite.
Meaning of symptoms
These symptoms not only determine the degree of the anomaly, but also distinguish it from diseases with similar symptoms.
Supraocclusion must be differentiated from the Popov phenomenon. A high position is characterized by maintaining normal shape and size. With the Popov phenomenon, the coronal part significantly exceeds the anatomical standard dimensions. In this case, it is observed to move out of the alveolar socket due to bone tissue deposits at the bottom of the socket and excessive development of the alveolar process.
When diagnosing infraocclusion, it should be distinguished from incomplete retention. The main difference will be the underdevelopment of the alveolar part of the tooth with a low location.
Otherwise, it will not differ from nearby normal bone organs.
Why is an unclosed diastema dangerous?
The large distance between the teeth cannot be ignored. You need to visit an orthodontist, who will tell you what caused the pathology and whether it needs correction. At ORTHODONT CENTER clinics, the first consultation is free. If the doctor suspects serious changes in the structure of the jaws, he will conduct a detailed examination using X-ray equipment or a CT scanner.
If the situation is unfavorable, the specialist will offer various types of correction that can remove the cleft and at the same time eliminate the problems associated with it. Untreated diastema can lead to gum disease, the formation of “pockets” in the periosteum, and premature tooth loss. Due to the diastema, incorrect pronunciation of hissing and whistling sounds may occur.
Types of distances between teeth
- Trema between teeth - spaces between dental units, with the exception of incisors. In this case, the pathology may not bother the patient for a long time, but it will be determined by the dentist during the examination;
- Diastema is a gap between the upper and lower incisors, which can lead to problems with pronunciation and speech in general, as well as with the aesthetics of the smile.
The distance between the front incisors, if it is not pathological, may not be treated. The most famous owners of diastemas are Vanessa Paradis, Madonna, Katy Perry and many others.
Ways to eliminate gaps between teeth
Surgical plastic surgery
Surgical methods for correcting diastema can be used either alone or in combination with other measures. In childhood, sometimes it is enough to reduce the tension of the frenulum so that the teeth take the correct anatomical position. If the cause of the diastema is the supernumerary of teeth, their removal alone is not enough - alignment is required with braces or orthodontic caps.
Surgical intervention is also required for various types of disposition, when teeth erupt outside the dentition. In this case, the incorrectly located tooth is removed and orthodontic movement of the adjacent teeth is carried out.
Implantation
Braces
Implantation
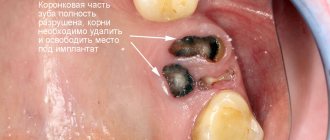
Unfortunately, with diastema, teeth cannot always be straightened. Particular difficulties arise with medial inclination of the incisors. If the rotation of the tooth is too great, the specialist may decide to remove it and replace it with an implant. Since the procedures are carried out over a short period of time, the process of bone loss does not have time to begin, and implantation does not cause difficulties.
Braces
Braces are the most popular way to correct orthodontic problems, including those that cause the formation of diastema. Their main advantages are high efficiency and the ability to be used in patients of all ages. Braces are installed for both children and adults. But due to the nature of the growth of the dental system, which continues until the age of 18-20, correction requires less time in younger patients. Treatment after this age, depending on the severity of the pathology, can last two to three years.
Wearing braces requires a conscious approach - you should not skip scheduled visits to the orthodontist, nor should you remove the installation yourself. After completion of the main treatment, a retention period begins, during which the doctor prescribes the use of mouth guards or plates. If they are neglected, the teeth may return to their original position and the correction will have to be done again.
Crowns and veneers
Crowns and veneers can be used as primary and additional correction methods. With lateral deviation, when the roots of the teeth are located evenly and do not need to be turned, the gap is simply closed with crowns. Veneers, in this case, are installed on adjacent teeth to hide the increased transverse size of the central incisors.
The doctor may also recommend using veneers on the front teeth if, after eliminating the diastema, it turns out that the crowns are not in the best condition. It is important to understand that if the cleft is a consequence of malocclusion, overcrowding, disposition or other dental pathology, it makes no sense to install veneers until the problem is eliminated.
Aligners (aligners)
Orthodontic plate
Records
Plates are mainly used to treat diastema in children when the jaws have not yet formed and less effort is required to correct the irregularities. Plates are removable structures that can be installed on one or two rows of teeth at once. They consist of a palatal part and arches, which are located in such a way as to exert pressure on the teeth and, thereby, help them move into the desired position.
The plates are removable and non-removable. The latter, like braces, are installed for a long time, and, at certain intervals, the doctor adjusts their position and changes the tension force. When treating with removable structures, several devices may be needed per course of treatment.
Plates are the best solution when it comes to correcting diastema in children. They do not cause severe discomfort even at the initial stage of treatment, they can be removed while eating, plus, the devices themselves are inexpensive.
The disadvantage of the plates is the impossibility of their use as the main method of treatment in adult patients and in complex clinical cases.
Mouthguards
Mouth guards are removable structures that are placed over the teeth in the form of a cover. Despite the softness of the material, it puts enough pressure on the teeth to return them to their correct position. Several trays are made for the entire treatment period, and the size of each subsequent design is reduced. Thanks to this, the movement takes place without pain and discomfort. Another important advantage of mouth guards is transparency. When worn, they are practically invisible to others. Among the disadvantages are the inability to use for complex cases and the rather high cost.
Cosmetic correction and artistic restoration
These methods are very similar - the gap between the teeth is closed using filling materials. If phosphate cements are used during the work, this is considered a cosmetic correction. The use of modern photopolymer materials allows us to talk about artistic restoration. The difference between the methods is in the external result and durability. Artistic restoration allows you to achieve better aesthetics, and thanks to the strength of filling materials, the result lasts several times longer.
However, these two methods are purely cosmetic and do not solve the problem itself. They are only suitable in cases of lateral deviation of the crowns. At the same time, no matter what materials are used, the patient will have to forget about solid foods such as seeds, crackers or nuts.
Big teeth or not: how to determine?
The normal physiological size of teeth has clear boundaries. The central upper incisors, which most often seem too large to their owners, should be from 9 to 13 millimeters in length in an adult, depending on height. The lateral incisors are usually 2 millimeters shorter. As for the ratio of the width and height of the dental crown, ideally it is 1.25%, and the lower this figure, the larger the teeth are considered. However, do not panic if your parameters differ from ideal ones: macrodentia is diagnosed when the size of the teeth exceeds the norm by at least 1.5 times.
Macrodentia can be absolute or relative (individual). The absolute sum of the width of the crowns of the four upper incisors reaches 35 millimeters, and the lower ones – 27 millimeters. If this number is 1 - 2 millimeters less, then the pathology is relative.
Prevention of recurrence of diastema
Relapses in orthodontic treatment, unfortunately, occur frequently. This is especially frustrating considering how much time and money is involved in fixing the problem. In the case of diastema, its appearance can be caused by various reasons. The most common are incorrectly selected treatment and neglect of the orthodontist’s recommendations during the retention period.
Sometimes patients refuse the necessary surgical treatment or wearing braces, and insist on “simple” correction methods, for example, installing crowns or masking the gap with composite materials. But since the problem remains unresolved, the diastema will return.
Likewise, she will not keep you waiting if, after treatment, the patient decides to ignore the orthodontist’s recommendations and does not wear retention devices.
Causes
The main cause of infraocclusion is the fusion of the root system of the tooth with the jaw bone. The anomaly develops only if the fusion occurs during the period of complete tooth eruption.
The main factors provoking the process include:
- periodontitis;
- incorrect location of the primordium;
- presence of supernumerary teeth;
- abnormal shape of the alveolar socket;
- underdevelopment of the premaxillary bone;
- disruption of the process of resorption of the roots of milk units.
Among the main factors that result in the formation of supraocclusion are the following:
- earlier removal of milk antagonists;
- pathological development of the rudiment;
- disruption of biological processes due to a lack of microelements and vitamins.
These anomalies are provoked by various groups of causes. But, regardless of this, both disorders of dental development require timely correction, as they can provoke a number of certain complications.
What is dental hypodontia and what methods are used to correct it?
We will discuss here the methods of treating partial secondary adentia.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/kolichestva/giperdontiya.html see photos of hyperdontia in people.
Is it possible to fix a hole between teeth at home?
It is impossible to remove diastema at home. To carry out effective correction, specialists use a whole range of diagnostic measures, as well as devices that are manufactured specifically for the patient. It is naive to believe that the problem can be eliminated simply by tying the two front teeth with floss. Moreover, such manipulations are dangerous, as they can damage the gums or the teeth themselves.
Sometimes you can hear stories about how a child's teeth were bandaged and the cleft disappeared. But, in this case, we are talking about a false diastema, which goes away on its own without any intervention.
Consequences of malocclusion
If the defect does not create physical inconvenience, then you can ignore it. This is a misconception held by many people who experience protruding front teeth. In fact, this is not only an aesthetic flaw.
Incorrect bite leads to very disastrous consequences, various kinds of complications affecting all organs and systems.
Here are some of them:
- 1. Accelerated tooth decay. Uneven chewing load leads to grinding of incisors, formation and development of caries.
- 2. Deformation of the facial part of the skull. An aesthetic defect that affects the beauty of a smile, the appearance of the profile.
- 3. Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. With an incorrect bite, chewing food is not of sufficient quality, which leads to diseases of the digestive system.
- 4. Development of periodontal disease. Inflamed gums cause physical discomfort. In addition, they can cause tooth loss.
- 5. Impaired functioning of the temporomandibular joint. If the problem is ignored for a long time, neuralgia and arthritis develop.
Protruding front teeth are the tip of the iceberg, underneath which lies a huge number of problems. The consequences of malocclusion worsen over the years. They concern not only the oral cavity, but the whole body. With protruding front teeth, beautiful diction and correct articulation are impossible. In addition, they can make breathing difficult. If the bite is incorrect, prosthetics become more difficult.
How to prevent diastema in a child
If diastema is a common occurrence among relatives, the parents of a small child should inform the dentist about this when the child is 2-3 years old. The specialist will observe the dynamics and, if necessary, offer age-appropriate types of correction.
Among the general recommendations on how to prevent gaps between teeth in children, the main one is to ensure that the child does not develop bad habits, such as biting nails, pencils and pens, and sucking fingers.
Symptoms and signs of abnormal growth
It is extremely rare for eights to appear without any complications. This is due, first of all, to the fact that wisdom teeth grow in adulthood, when the jaw is already formed. Even with proper teething, discomfort may still be present for several weeks or months. If a wisdom tooth grows incorrectly or has an abnormal location, then certain symptoms indicate this.
Let's take a closer look at the types of pathologies and symptoms associated with the growth of wisdom teeth.
- Retention is a pathology in which the third molar is located under the mucous or bone tissue. The main symptoms are severe pain in the gums, as well as the development of an inflammatory process in the gum pocket.
- Dystopia or abnormal position of the tooth. It manifests itself as severe pain, affecting adjacent teeth, and the development of inflammation, including phlegmon or osteomyelitis.
The initial alarming symptoms that a patient may identify when a wisdom tooth grows are:
- Swelling in the cheek area.
- When swallowing, severe pain occurs, radiating to the throat or ear.
- Purulent or bloody discharge.
- Injury to the mucous membrane.
If you detect at least one of the above symptoms during the eruption of figure eights, you must seek the help of a dentist as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct an x-ray and determine whether the wisdom tooth is growing correctly.
Symptoms
The diagnosis of “uneven teeth” includes many different defects. They can hardly be called diseases; rather, they are cosmetic problems. Only in rare cases is there a serious impairment of chewing function. Usually the teeth “grind” against each other, and contact is established between them, sufficient for confident chewing.
There may be violations:
- location of teeth;
- growth directions;
- tooth sizes;
- dental crown shapes.
Humans are mammals, and their teeth are very different. But for each tooth there is a fairly accurate version of the norm, and small deviations make the dentition unsightly. Large or small teeth, protruding forward or backward, displaced to the side, not corresponding to their intended purpose (incisors, canines, molars) - patients turn to the orthodontist with such a wide range of defects.
Normally, crowns fit tightly to adjacent ones, or the gaps are minimal. Expanded ones, which are popularly called “birdhouse”, look unimportant and can cause damage to the gums when chewing.
The symptoms of malocclusion are usually obvious; an experienced orthodontist does not require additional research to clarify the diagnosis. In some cases, radiography is useful. Teeth (usually fangs) can shift due to the growth of excess teeth nearby, which normally should not be there. On an x-ray, the location and angle of inclination of the roots of teeth “number 1” and “number 2” are determined, and how healthy they are is assessed. Then they decide to keep or delete some of them.