Types of curettage
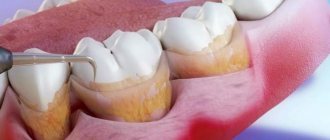
There are open and closed curettage. The open curettage technique is more difficult because a small piece of gum must be removed to reach and clean hard-to-reach areas. Upon completion of the procedure, sutures are placed on the treated area, and the surface is treated with a wound-healing solution. The open method is rarely used if the gums have peeled off by more than 5 millimeters.
Closed curettage is used if the pockets are no more than 3 millimeters deep. The procedure is carried out “blindly”, since there is no way to inspect the roots and thoroughly clean out food debris. If there is no inflammation, then it is possible to use a laser, which destroys tartar without causing discomfort to the patient. Upon completion of the procedure, the enamel is polished, and areas of inflammation are treated with antiseptic solutions.
Indications for curettage
Indications for curettage:
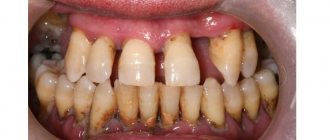
- Gingivitis. For high-quality treatment of gum inflammation, the main cause of its development is removed - subgingival dental deposits, which irritate tissues and cause pathological reactions.
- Plaque and tartar on the surface of the teeth or in spaces covered by the gums. Curettage is indicated to prevent the development of inflammatory or allergic reactions.
- Periodontal pockets in diseases of the dental ligament apparatus of mild or moderate severity, when the depth of the cavities does not exceed 4-5 millimeters.
- After tooth extraction. To remove possible fragments or remaining material, the dentist additionally uses a curette.
Curettage of periodontal pocket
| CONTENTS Curettage Methods of implementation Indications Contraindications Recommendations for care Pros and cons Patient reviews |
Dental plaque is one of the main factors that prevents the effective treatment of periodontitis. After all, they are a constant environment for the growth of pathogenic microorganisms, which further irritate the gums. Curettage, also known as periodontal pocket curettage, is one of the most effective methods of treating periodontitis.
Stages of dental curettage
Procedure steps:
- Diagnostics, development of treatment tactics. The dentist determines the depth of the pocket and the volume of intervention. This is done by examining the oral cavity, visualizing the bone using X-rays or computed tomography.
- Preliminary treatment. Before performing curettage, all concomitant diseases of the oral cavity are eliminated to prevent side effects or complications.
- Curettage. The dentist cleans the gum pockets or subgingival space.
Tips during the rehabilitation period
After surgery, the oral cavity is very vulnerable. To prevent the spread of infection, you need to follow some recommendations:
- Do not eat solid foods for the first few days, protect yourself from additional damage to soft tissues;
- stop brushing your teeth for the period recommended by your doctor;
- do not rinse your mouth with medicinal herbs and antiseptics, this can damage soft tissues;
- Visit your doctor promptly for a routine preventive examination to avoid additional complications.
Professionals at the KRH-Medical clinic perform a painless and effective curettage procedure to prevent and eliminate gum disease.
We use various technologies taking into account the individuality of each patient. You will not feel pain or discomfort thanks to the latest generation of effective pain relief. The professional work of our specialists will contribute to the speedy healing and restoration of the integrity of the gum tissue. The result of curettage at KRH-Medical is predictable, and the risks of complications are minimized.
How is curettage performed?
Techniques:
- Closed cleaning is needed to remove deep dental deposits and granulations in pockets. Since the doctor is not able to visually assess the effectiveness of the process, pathological agents often remain in place.
- Closed dental curettage is effective for mild periodontitis. At the moderate or severe stage after the procedure, the condition of the gums temporarily improves, but later the disease progresses.
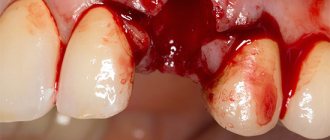
- First, the mucous membrane of the gums peels off from the places of attachment to the teeth. To do this, the dentist makes an incision around the neck of the affected tooth.
- Flaps of gum are peeled off to expose the roots and bone defects. All periodontal pockets and subgingival deposits become visible to the doctor. Using a scaler and curette, unwanted elements are removed and granulations are scraped out.
- After this, treatment is carried out with antiseptic solutions. Synthetic bone tissue is “implanted” onto the cleaned surfaces of deep pockets, which is necessary for adequate bone restoration. This allows you to reduce periodontal pockets and speed up reparative processes.
- Upon completion of the operation, sutures are placed in the area of the papillae between the teeth. The wound is covered with a gum bandage on top to promote protection and healing. After 10 days, the stitches are removed.
- After ensuring hemostasis, the doctor removes tooth fragments and filling particles.
- The hole is sanitized with the removal of damaged tissue and potential foci of inflammation. Areas injured before or during removal are scraped out to prevent complications.
- A clean hole is treated with antiseptics, and a turunda with an antibiotic is placed.
- The procedure helps reduce complications and prevent gum and bone diseases.
Curettage of the uterine cavity (curettage) - how to prepare?
Curettage of the uterine cavity, or in other words, this procedure is called curettage, as well as gynecological cleansing. During curettage, the patient undergoes removal of the upper (superficial) layer of the uterine mucosa.
Please note: in order to remove the top layer from the uterine cavity, you must first undergo several medicinal and instrumental procedures. This is necessary so that the cervix dilates.
Why is curettage needed?
Gynecological cleansing is carried out both for the purpose of treating gynecological diseases and for diagnosing serious pathologies.
Most often, the patient is offered not only curettage, but also a study called hysteroscopy.
This is necessary in order to completely examine the uterine cavity, and if necessary, then clean the mucous membrane of the organ again, but in those places that were not noticed.
Rules for preparing for the procedure
The procedure for curettage of the uterine cavity must be carried out before the onset of the next menstruation, preferably several days before. These conditions must be met in order to:
- Reduce possible blood losses (and, they will definitely occur when performing curettage);
- Ensure restoration of the uterine mucosa in the most natural way (as is known, during menstruation, the uterine mucosa exfoliates and then, after menstruation, is restored again).
Curettage is not an ordinary gynecological procedure, but a real surgical intervention on the female body. That is why, in order to avoid possible consequences and complications after this procedure, the patient must undergo a series of procedures and studies.
Necessary research before cleaning the uterus
- General blood analysis;
- Vaginal flora smear;
- Analysis for urogenital infections, including syphilis, HIV.
Important!
Before curettage, the patient must refrain from using any medications (antibiotics, contraceptives, and even homeopathy (medicines based on plant extracts). The exception is those medications that the doctor may have specifically prescribed for the gynecological cleansing procedure.
Why is this so important?
A number of medications can cause the patient’s blood clotting rate to drop during cleansing of the uterine mucosa. As a result, there is a risk of heavy blood loss.
Also, 3 days before curettage, the patient must refuse sexual intercourse; It is not recommended to eat or drink anything 12 hours before surgery. It is very important! Since the operation is performed under anesthesia, this condition must be observed for its safe operation.
Curettage technique
The ultimate goal of curettage is the complete removal of the upper mucous layer of the uterus. It is worth noting right away that this procedure can be quite painful and unpleasant for a woman.
That is why, in the vast majority of cases, curettage is performed under anesthesia.
The only exception is the case when the patient’s cervix is already dilated so much that it makes it possible to remove the top layer of the mucous membrane - this happens only after childbirth.
The gynecological curettage procedure itself is carried out as follows:
- The patient is given anesthesia and waits for a certain time;
- Afterwards, a special dilator is inserted into the vagina. This is necessary so that the gynecologist can fully examine the cervix;
- A probe is inserted into the cervix (its diameter depends on how much it is necessary to dilate the cervix for cleaning);
- The doctor uses a special video camera to examine the cervix (hysteroscopy procedure);
- A procedure is carried out to scrape the mucous membrane with a device called a curette (visually it resembles a spoon);
- The curettage process lasts about 40 minutes;
- The scraped tissue of the cervix is sent for histological examination.
What is histological examination?
After the mucous membrane has been scraped off the cervix, all these tissues are sent for histological examination. This is necessary so that under a microscope in the laboratory, doctors can determine which tissues from the cervix are healthy and which are malignant, that is, cancerous. This analysis is carried out for 2 weeks.
Diagnostic curettage
Curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervix may be prescribed for such purposes as:
- To determine the cause of irregular menstruation in a woman or menstrual dysfunction;
- With heavy bleeding from the vagina;
- For painful menstruation, requiring the administration of painkillers;
- During menopause;
- For female infertility;
- At risk of developing a malignant tumor on the uterus.
Indications for curettage
Serious gynecological indications for uterine curettage in a woman may include:
- Postpartum curettage, which is necessary to completely remove the placenta, as well as blood clots;
- For the purpose of terminating pregnancy according to indications or at the discretion of the patient;
- In case of frozen pregnancy;
- In case of miscarriage at any stage of pregnancy;
- With an ectopic pregnancy.
How to recover after the procedure?
Most patients think that after cervical curettage they will have a long recovery period in the hospital. But that's not true.
Contraindications
Contraindications for curettage:
- Acute systemic infectious diseases.
- Osteoporosis.
- Oncological diseases.
- Allergic reactions to the drugs used.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular or hematopoietic systems.
- Chronic endocrine diseases at the stage of decompensation.
- Tuberculosis.
- Uncorrectable bite pathology.
- Ulcerative diseases of the oral cavity.
- Poor oral care.