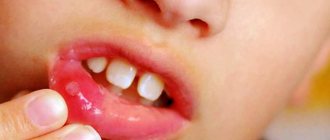
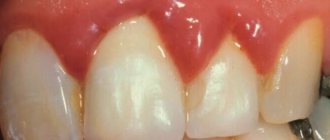
Stomatitis is a disease of the oral mucosa.
It can be caused by various reasons:
- Traumatic (burn, injury).
- Symptomatic (cardiovascular diseases, diseases of the endocrine system and gastrointestinal tract).
- Infectious (scarlet fever, measles, diphtheria, influenza).
- Specific (syphilis, tuberculosis, fungal infections).
- Dental (carious lesions of teeth, dental plaque, non-compliance with rules of oral hygiene, microtrauma during dental procedures).
Many dental institutes cited sodium lauryl sulfate, contained in toothpaste, as the main cause of stomatitis.
Changing toothpaste reduced the incidence of stomatitis by more than 80%. Stomatitis is divided into several types:
- Catarrhal.
- Ulcerative.
- Aphthous.
Causes of catarrhal stomatitis
The main reasons for the development of stomatitis are tissue microtraumas from the sharp edges of dilapidated teeth, old fillings or as a result of using a too hard toothbrush. In infancy, catarrhal stomatitis often accompanies the process of teething. The presence of a large number of bacteria in the mouth creates a favorable environment for subsequent infection of wounds and inflammation of the entire oral cavity. Catarrhal stomatitis often occurs against the background of chronic internal processes or after viral infections.
How to treat herpetic stomatitis?
Herpetic stomatitis
The form develops against the background of cold complications, gingivitis and other inflammatory processes in the body. The symptom is the appearance of multiple small rashes on the tongue, gums and inner surface of the cheeks. The pain, as a rule, is much stronger than from aphthous ulcers, but it is not the discomfort itself that is scary, but the consequences - fever and weakness.
Herpes lesions are primarily treated with a course of medications:
- Acyclovir - from 1 to 3 tablets per day.
- Viferon-gel - topically, twice a day, and only after the approval of the attending physician.
- Solcoseryl - temporary pain relief, 15 minutes before and immediately after meals.
- Rinsing with soda creates an additional alkaline environment in the mouth against bacteria.
Symptoms of catarrhal stomatitis
The most common symptoms accompanying catarrhal stomatitis include the following:
- hyperemia and severe swelling of the tissues of the oral cavity, and sometimes the larynx;
- a whitish coating forms in places where cracks or abrasions become infected;
- gums begin to bleed, oral hygiene becomes more difficult;
- increased or, conversely, decreased salivation;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- in rare cases, body temperature rises.
In advanced cases of the disease, ulcerative necrotic lesions may appear in the mouth, which significantly complicates the treatment process.
Stomatitis
Cold
HIV
Fungus
Scarlet fever
Gastritis
5562 24 September
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Stomatitis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Stomatitis is a collective name for diseases of the oral mucosa, manifested by its redness, swelling with the formation of areas of erosion, ulcers or blistering rashes. Stomatitis affects approximately 20% of the population, most often children. Stomatitis can be either an independent disease or a complication or manifestation of other diseases (for example, scarlet fever, influenza, measles, etc.).
Causes of stomatitis
There is no single factor that is the sole cause of oral inflammation. With stomatitis, bacteria or viruses are detected, especially in ulcers on the mucous membrane. However, a diverse microflora is always present in the oral cavity, but stomatitis makes itself felt only when there is a strong additional impact on this microflora.
These impacts include:
- trauma to the mucous membrane caused by overzealous brushing of teeth, rough food, etc.;
- decreased immunity due to colds, vitamin deficiencies, chronic diseases, stress, poor nutrition, as well as more serious diseases (anemia, cancer and autoimmune diseases, HIV);
- entry of a large number of pathogenic microorganisms into the oral cavity through dirty hands, unwashed foods, etc.;
- conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora due to the presence of caries, tartar and plaque, lack of proper teeth cleaning, etc.;
- uncontrolled use of drugs that affect the quantity and quality of saliva and reduce its antimicrobial potential;
- inhibition of normal microflora by antibiotics;
- dehydration of the body with a decrease in the amount of saliva;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, pancreatitis, etc.).
Classification of the disease
Due to its occurrence:
- traumatic stomatitis
occurs as a result of the influence of physical (wound, burn from hot food, etc.) or chemical (burn of the oral mucosa with caustic substances, etc.) factors on the mucous membrane; - infectious stomatitis
occurs as a result of a viral, bacterial or fungal infection; - specific stomatitis
occurs as a result of a specific infection (tuberculosis, syphilis); this group includes radiation, drug, and stomatitis due to occupational diseases; - symptomatic stomatitis
develops against the background of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular, nervous, endocrine systems, and blood diseases; - allergic stomatitis
develops upon contact with allergens.
According to the clinical picture:
- catarrhal stomatitis;
- ulcerative stomatitis;
- aphthous stomatitis.
With the flow:
- spicy;
- chronic.
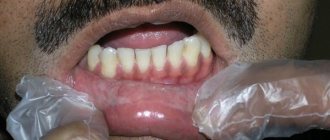
There are stomatitis associated with dental problems - for example, denture stomatitis occurs due to damage to the mucous membrane by dental structures, due to poor care of removable dentures, and the patient’s failure to comply with oral hygiene.
Symptoms of stomatitis
In children, the disease is more severe than in adults: body temperature may rise significantly and intoxication may be present.
In adults, oral stomatitis, as a rule, is not accompanied by fever, except in cases of deep damage to the mucous membranes in the ulcerative form of the disease.
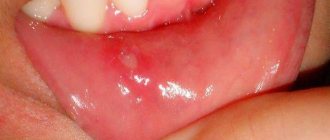
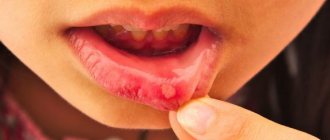
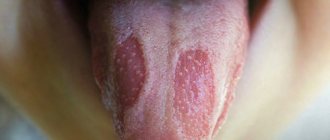
The most common is catarrhal stomatitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa without the formation of deep defects (ulcers). For those around you, catarrhal stomatitis manifests itself as “stale breath”, for the patient himself – pain, swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. Gingival papillae are easily injured and bleed.
In persons with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as with inadequate treatment, catarrhal stomatitis tends to progress to the next stage - ulcerative with the formation of defects throughout the entire depth of the mucous membrane. It is accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the mouth, even putrefactive, the ulcers are covered with a gray coating, and eating any food leads to increased pain. Ulcerative stomatitis is more severe than catarrhal stomatitis and can cause a slight increase in temperature and enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Aphthous stomatitis manifests itself in the form of small (3-5 mm) single or multiple defects of the mucous membrane of an oval or round shape, surrounded by a thin bright red border and covered with a yellow-gray fibrin coating. Aphthae do not form simultaneously, so you can see different stages of their development. Healing of aphthae begins after the fibrin plaque peels off on its own and ends with the complete disappearance of the defect.
Allergic stomatitis in the mouth occurs against the background of an exacerbation of the underlying disease - allergies. Increased sensitivity of the body can occur to food, medications, pollen, animal hair, cosmetics and care products, and even clothing. Most often, stomatitis is provoked by toothpastes that contain flavorings and chemical components.
Among viral stomatitis, the most common is herpetic stomatitis, which worsens against the background of ARVI. The disease begins with general malaise and lasts 7-10 days.
The oral mucosa becomes red and swollen, and regional lymph nodes become enlarged. After a few days, a blistering rash appears on the tongue and inner surface of the cheeks, and inside the rash there is a translucent liquid. After the bubbles open, small erosions appear, which are covered with a yellowish film.
Diagnosis of the disease
Adequate treatment of stomatitis can be prescribed by determining what caused it - bacteria, fungi or viruses.
If a fungal infection is suspected and to assess the effectiveness of therapy,
Candida albicans
in an oropharyngeal scraping and culture is performed for yeast-like fungi of the genus
Candida
and
Cryptococcus to determine sensitivity to antifungal drugs.
Diagnosis and treatment of catarrhal stomatitis
Diagnosis of stomatitis is carried out by visual examination of the oral cavity, as well as on the basis of a microscopic examination of a smear from the oral cavity. First of all, the treatment will be aimed at reducing inflammation in the tissues, and secondly at anesthetizing the oral mucosa during the treatment process. Rinsing with antiseptic solutions or special dental compounds may also be prescribed.
To relieve pain, anesthetics are used in sprays or as applications to the affected areas. Along the way, the dentist identifies carious areas and sanitizes them. Vitamin complexes are also prescribed for oral administration, which helps increase the body's resistance to infections.
With timely detection of catarrhal stomatitis, relief from the painful condition occurs quite quickly. If this does not happen, then in the future the cause of stomatitis is sought among the patient’s chronic diseases.
Causes of stomatitis
The main cause of stomatitis is infection: viral, bacterial or fungal. But viruses and bacteria themselves are not dangerous to the body; the disease develops only under certain conditions:
- damage to the mucous membranes: biting the inside of the cheek, burns, injuries from the sharp edge of a chipped tooth or hard dry food, etc. A small wound that gets infected is enough for the disease to develop;
- poor oral hygiene, hard plaque;
- deficiency of vitamins B, zinc, folic acid, iron;
- smoking: causes an imbalance in the microflora of the oral cavity and a constant negative effect of hot smoke on the mucous membranes, which over time can lead to the so-called “smoker’s stomatitis”;
- decreased salivation: occurs due to the use of certain medications, dehydration, stress and a number of diseases;
- Using toothpastes with sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) and brushing your teeth too often;
- incorrectly installed dentures or their low quality;
- hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, and adolescence.
At the PROPRICUS clinic in Moscow, treatment for stomatitis is prescribed only after a thorough diagnosis and identification of the cause of the disease. This allows you to select the most effective therapy depending on the type of stomatitis.
Prevention of catarrhal stomatitis
Very often, due to mild symptoms of catarrhal stomatitis, patients neglect medical help. This leads to the development of severe ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa, and significantly complicates the treatment process. The course of the disease is complicated by the fact that eating becomes painful, and brushing your teeth sometimes causes fear, so you should not neglect painkillers before daily hygiene procedures.
Keeping your mouth clean significantly reduces the risk of recurrent inflammation and speeds up recovery. Preventative dental examinations reduce the risk of recurrent inflammation to almost zero. An excellent prevention of all types of stomatitis is to quit smoking and maintain proper oral hygiene.
Risk factors and causes of pathology development
With catarrhal stomatitis, damage to the mucous membrane occurs, but bleeding or wounds do not occur. It can develop against the background of various infectious diseases that reduce the body's protective functions.
Diet for stomatitis
Stomatitis often worries children, becoming a consequence of insufficient immune forces of the body, weakened by some disease.
However, the main reason for its development is poor oral hygiene. Stomatitis can also occur as a result of:
- caries;
- dental plaque, which is an optimal environment for the development of pathogens;
- tartar , which causes injury to the gums and tooth enamel;
- mechanical damage;
- acute infectious disease;
- chronic inflammatory processes of the oral cavity;
- pathologies of endocrine and other body systems;
- infections ;
- allergic reaction;
- hormonal imbalance caused by pregnancy or puberty;
- poor quality treatment in a dental clinic;
- teething .
There are factors that can increase your chance of developing the disease. These include:
- Childhood . The point is not only a weak immune system, but the fact that the child constantly puts his hands, toys and other objects in his mouth. In addition, children brush their teeth poorly and eat too many sweets. Therefore, an optimal environment is created in the oral cavity for the proliferation of fungi, bacteria or other pathogens.
- Stress. Nervous stress leads to a decrease in the protective properties of the body, as well as local immunity of the oral cavity.
- Injuries. Any trauma to the mucous membrane is a prerequisite for the occurrence of catarrhal stomatitis. They create an acceptable environment for the proliferation of microorganisms, especially with insufficient oral hygiene.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Poor nutrition. If the body does not receive enough nutrients, the diet is irregular, and the diet consists of a large amount of sweets, spicy foods and fast food, the likelihood of developing stomatitis will be higher.
- Allergic reaction. Occurs when food enters the oral cavity, to which an allergic reaction occurs.
For effective therapy, the doctor first of all determines the cause of the development of catarrhal stomatitis, the elimination of which facilitates rapid treatment.
Treatment of stomatitis
Many patients are interested in how to quickly cure stomatitis? Which doctor treats stomatitis in adults and children?
Most often, local treatment of all types of stomatitis is carried out by a general dentist or periodontist. Treatment of stomatitis in adults and children is carried out mainly symptomatically, but with mandatory consideration of the main cause of its occurrence. Medicines for stomatitis in adults are aimed at relieving swelling, pain and inflammation.
Local treatment of stomatitis begins with the removal of dental plaque, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory rinses of the mucous membranes, as well as anesthetic ointments and gels for the treatment of aphthae and ulcers are prescribed. Limit food, exclude hot, spicy and hard foods. If candidiasis is detected, then antifungal drugs are prescribed; if there is herpes, then antiviral drugs are prescribed. If necessary, antibiotics are also prescribed to prevent infection of large oral ulcers. At the final stage of treatment, keratoplatic preparations from sea buckthorn and rose hips, as well as propolis, are prescribed. On average, the treatment period for stomatitis lasts from 7 to 14 days.
The main common root cause of stomatitis, gastrointestinal diseases, immune diseases, etc. are always identified and treated. It is clear that this is not done by dentists, but by their colleagues - specialized doctors. However, the first person who can detect and pay attention to this and send the patient for examination to colleagues is the dentist.
The most pressing question from many patients is: “How much does it cost to cure stomatitis? Where can stomatitis be treated inexpensively and efficiently?”
The price for turnkey treatment of stomatitis in dentistry in Moscow and other large cities of Russia is determined by the causes of stomatitis. The cost of local treatment of oral stomatitis on a turnkey basis starts from 2000 rubles and can reach 20 thousand rubles or more. Prices for general treatment of stomatitis depend on the main pathogenic factor and concomitant diseases, such as systemic herpes, the presence of Crohn's disease, enteritis and other health problems.
0%
Installment plan without overpayments
Start treatment today!
Take advantage of interest-free installments for 2 years without a down payment
Find out more
8
Payment by installments is possible without bank participation
Home treatment for stomatitis
Home treatment of stomatitis using folk methods is aimed at solving two problems:
- For antiseptic and anti-inflammatory rinses.
- For these purposes, you can use herbal decoctions of calendula, chamomile, plantain and antiseptic ointments based on propolis, sea buckthorn and vitamin A.
- To stimulate the immune system by drinking solutions of rose hips, sea buckthorn, taking amaranth oils and other means.
- However, before home treatment, it is necessary to consult a dentist, because very often it is necessary to eliminate not only local, but also general causes of stomatitis, such as the Candida fungus or the herpes virus, not to mention more serious diseases.
Just CALL US!
8
We will answer any of your questions and will definitely help you!