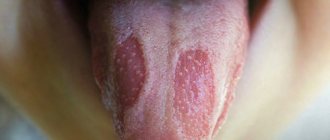
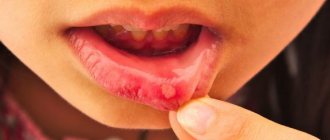
Oral stomatitis (mucositis) is a common dental pathology, especially in children. Under one name, a whole group of diseases of various etiologies is collected, which differ in cause and symptoms. What all these diseases have in common is inflammation of the mucous tissues in the oral cavity. Stomatitis can be either a separate ailment or a complication of another disease (for example, scarlet fever, influenza, etc.) It manifests itself in the form of ulcerations and is most often localized on the tongue (on the tip of the tongue and along the lateral edge), on the gums and mucous membranes of the cheeks, on the lips , on the hard palate.
In this article we will tell you by what signs you can recognize stomatitis, how to treat stomatitis on the tongue, how to avoid the disease and its dangerous complications.
Symptoms of stomatitis in adults and children
You can recognize a child’s illness by the fact that he begins to constantly be capricious, loses his appetite, and sleeps poorly. Symptoms of stomatitis are easy to detect with a careful examination of the oral cavity.
The following signs indicate the presence of the disease:
- inflammation of the mucous membrane (redness);
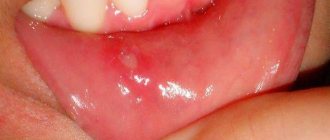
- the appearance of ulcers, rashes, wounds, erosion in the mouth;
- increased body temperature;
- hypersalivation (excessive salivation);
- white coating on the tongue and mucous tissues;
- unpleasant taste;
- discomfort, pain, in some cases burning;
- swelling, bleeding gums.
The clinical manifestations of the disease in an adult are mild, and the disease itself is not as acute as in a child. As a rule, small pockets of inflammation appear on the tongue, on the inside of the lips and cheeks, on the gums or on the palate (the mucous membrane in these areas becomes red), which may be accompanied by discomfort. The inflammation can be painful, causing the person to be unable to eat (chew food) normally.
Signs of stomatitis differ depending on the causes, stage of the disease, and individual characteristics of the body. However, regardless of the cause and form of the pathology, with stomatitis there is an increase in the lymph nodes located under the lower jaw.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is the most common lesion of the oral mucosa.
The mechanism of stomatitis is associated with the reaction of the immune system to irritants. It is believed that stomatitis occurs in cases where, for reasons that are not yet clear, the human immune system reacts to the appearance of molecules that it cannot recognize. The appearance of such molecules provokes an attack by the lymphocytes of the immune system (a type of white blood cell), in much the same way that the human immune system reacts, for example, to an organ transplant. The “attack” of lymphocytes on these unidentified molecules leads to the appearance of ulcerative formations in the mouth, which are called “stomatitis”. With stomatitis, patients complain of burning of the oral mucosa; pain when eating and talking; “ulcers” in the mouth. In some cases there may be an increase in body temperature, an increase in regional lymph nodes.
The causes of stomatitis also include:
Insufficient or excessive oral hygiene;
Thermal, mechanical, chemical injuries. Most often, minor injuries heal on their own. But under unfavorable factors, stomatitis may develop
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastritis, duodenitis, colitis, as well as helminthic infestation, can cause catarrhal stomatitis.
Various infectious disease agents have been implicated in the development of oral ulcers. Normally, opportunistic bacteria are constantly present in the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and do not cause irritation. For their reproduction, additional unfavorable factors are needed: mechanical or thermal damage to the oral cavity,
Dehydration caused by diarrhea, vomiting, insufficient water intake, prolonged increase in body temperature, increased urine output, large blood loss
Poorly made dentures
The use of medications that reduce salivation
Anemia
Vitamin deficiencies, lack of iron or folic acid
Malignant tumors in the neck, nose or throat
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, and adolescence.
Side effects of chemotherapy
HIV infection, tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma.
Toothpastes and mouth cleaners containing sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) This is likely due to the fact that SLS has a dehydrating effect on the oral mucosa. Therefore, it becomes more defenseless to various irritants.
Types of stomatitis
Allergic
Currently, many people have any allergic reactions to a wide variety of substances: food, medicines, pollen, animal hair, house and library dust, etc. This type of stomatitis is not considered as a separate disease, since it is only part general allergic manifestations. Treatment comes down to eliminating the allergen, taking antihistamines. An allergy to dental plastic may also occur if there are removable structures in the oral cavity. With this type of stomatitis (prosthetic stomatitis), adequate re-prosthetics is recommended.
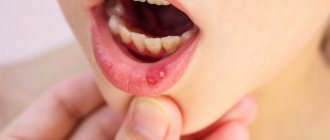
Aphthous
Aphthae are small superficial ulcerations of the mucous membranes of an oval or round shape. An inflamed red rim appears around this ulcer, a thin white film forms in the center, and the edges of the ulcer are smooth.
In addition to the ulcer itself, which is very painful, a person is bothered by increased salivation, bad breath and bleeding gums
Oral aphthae are accompanied by pain that makes chewing and speech difficult, excessive salivation, and enlarged submandibular lymph nodes. After 5-7 days they heal without scar formation.
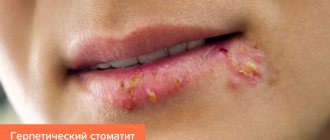
Herpetic
This type of stomatitis is caused by various viruses. This could be the chickenpox virus, the influenza virus, or adenoviruses. Among them, the herpes simplex virus is the leader in the frequency of lesions of the oral mucosa. The majority of the adult population is a carrier of the herpes virus. It remains in the body in a dormant state, without causing any discomfort or causing diseases.
But, if there is a decrease in the body’s defenses, stress, overwork, exacerbation of chronic diseases, the virus can become more active and manifest itself in the form of recurrent herpetic stomatitis,
With herpetic stomatitis in adults, there is usually no acute reaction of the body, such as an increase in body temperature, symptoms of general intoxication, etc.
Candida
This type of stomatitis occurs mainly only in very weakened people, in HIV-infected people, in patients with tuberculosis, in patients using steroid hormones. The causative agent of thrush in the mouth is the Candida fungus, which is always present in the oral cavity normally, but under unfavorable factors it begins to actively multiply.
A peculiarity of this stomatitis is that a cheesy coating first appears on the mucous membrane, which, when removed, forms a swollen, reddened inflammatory focus. Painful erosions can also form under the plaque film. Fungal stomatitis is characterized by dry mouth, catching, cracks in the corners of the mouth, burning and pain while eating.
Traumatic
This type of stomatitis is caused by traumatic factors that may be present in the patient’s oral cavity. Sharp edges of carious teeth and poorly made orthopedic structures can lead to the appearance of traumatic stomatitis.
Ulcerative.
Ulcerative stomatitis can be a complication of aphthous stomatitis. With a decrease in the general resistance of the body, with a deficiency of vitamins, stomatitis can be complicated by fusospirochetosis and proceeds as ulcerative-necrotic. In this form of the disease, the ulcers are covered with a greenish-gray foul-smelling coating. The patient's general condition worsens sharply, body temperature rises, and regional lymph nodes enlarge. This is a very severe form of stomatitis, which most often indicates serious health problems in an adult - immunodeficiency conditions, various types of leukemia, radiation...
Treatment methods
In most cases, stomatitis goes away on its own within a week. Depending on the type of stomatitis, treatment can be carried out with antiviral, antifungal or other drugs. If you have stomatitis, you must visit a dentist who will prescribe the correct treatment. Improper self-medication can lead to complications and generalization of infection. The patient is required to follow a gentle diet, hygiene and frequent and regular treatment of the oral cavity with drugs prescribed by the doctor.
When treating stomatitis, local painkillers are prescribed in the form of powders, gels, tablets, and sprays. For example, Hexoral-tabs, Lidochlor, Anestezin, Lidocaine Asept. Also, treatment of stomatitis should include antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity in the form of rinses and applications. Gargles with Miramistin, Stomatidin, Dentix, a weak solution of potassium permanganate, infusions of chamomile, calendula, and sage are used. The mucous membrane is treated with various dental gels; Kamistad, Cholisal Metragil denta gel. Agents that accelerate the healing of the epithelium are also used. For example, Solcoseryl dental paste, Vinylin, vitamin A oil solution, sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil. For ulcerative necrotic stomatitis, proteolytic enzymes are also used. Antibacterial therapy is often prescribed for necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis. When treating fungal and viral stomatitis, appropriate local and general specific treatment is prescribed. For candidal stomatitis, it is necessary to exclude from food products containing easily digestible carbohydrates - baked goods, confectionery, and sweets. Antihistamines are used for both allergic and other types of stomatitis.
Stomatitis in adults and children: causes of the disease
Factors that can provoke stomatitis can be divided into the following groups:
- local;
- internal;
- external.
Local include any causes that have a direct effect on the condition of the mucous membrane:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- use of poor quality hygiene products;
- smoking.
Internal are factors associated with internal disorders in the body:
- hereditary factor;
- dysfunction of internal organs (cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract);
- deficiency of a number of vitamins and microelements (B vitamins, selenium, zinc, iron or folic acid);
- metabolic disorders;
- allergy;
- hormonal imbalance due to diseases, during pregnancy;
- weakened immunity.
External factors:
- violation of the antibiotic protocol;
- stress;
- severe hypothermia;
- any mechanical damage (for example, after tooth extraction) or permanent mechanical damage to the mucous membrane when wearing low-quality or improperly installed braces or dentures;
- radiation, chemotherapy.
Causes of stomatitis
The mechanism of stomatitis, unfortunately, has not yet been fully identified, so there are many causes of the disease:
- microorganisms that cause infection, acting directly on the oral mucosa;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- general weakening of the immune system;
- avitaminosis;
- metabolic disorders;
- nervous disorders;
- malignant tumors;
- hormonal fluctuations;
- various injuries in the form of abrasions of the oral mucosa;
- anemia;
- heredity.
Among the causes of stomatitis there are also local factors. Elementary lack of oral hygiene, caries, dysbacteriosis, poorly made or poorly installed dentures, the consequences of using medications, nicotine and alcohol consumption, as well as allergic reactions to products. Of particular note is the use of toothpastes containing sodium lauryl sulfate. Various studies have proven that they provoke the occurrence of stomatitis and its exacerbation.
Types of stomatitis: how to distinguish them from each other and why they are dangerous
Classification of stomatitis depending on etiology:
- bacterial - caused by various types of bacteria (streptococcal, syphilitic, tuberculosis, etc.);
- viral - occurs against the background of diseases such as herpes virus, influenza, enterovirus infection, measles;
- fungal - caused by the development of a fungal infection;
- radiation - the result of radiation (damages tissue during radiation sickness);
- chemical - acquired as a result of burns of the mucous membranes with aggressive chemicals (hydrogen peroxide, other alkalis or acid);
- medicinal - an allergic reaction of the mucous membrane to taking some medications.
Depending on the form, stomatitis in the oral cavity is divided into the following types:
- catarrhal;
- ulcerative stomatitis (ulcerative-necrotic Vincent);
- aphthous;
- gangrenous.
We will tell you in detail about the most common, as well as the most dangerous types of stomatitis.
Duration of the disease
It is impossible to say exactly how long stomatitis lasts. The duration of the disease depends on many factors:
- type of disease;
- timely contact with a specialist;
- correctness of the diagnosis;
- well-chosen means for treatment;
- compliance with doctor's recommendations;
- state of immunity.
It is important for patients to remember that the state of their health and the speed of recovery depend on the speed of contacting a specialist. The more advanced the disease, the longer and more difficult it takes to treat. There is a risk of the pathology becoming chronic.
This usually happens in the background:
- taking certain medications;
- vitamin deficiency;
- weak immunity, immunodeficiency;
- disruptions in the hormonal system;
- chronic stress;
- history of chronic diseases.
With proper and prompt treatment, the acute form of the pathology can be overcome within 3-7 days.
Herpetic stomatitis
The cause of this form of the disease is the herpes simplex virus (type 1). It is easy to become infected with this disease - it is transmitted through airborne droplets, as well as through contact with an infected person.
Another dangerous side of herpetic stomatitis is the ability of the virus to combine with the human genome. In this case, herpes remains with the person for life, that is, the disease becomes chronic.
Complications of stomatitis occur with decreased immunity or exposure to certain unfavorable factors. This could be stress, infection, oral trauma, antibacterial therapy, overheating or hypothermia, allergies, vitamin deficiency.
Herpes stomatitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- redness and inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- the appearance of blisters due to stomatitis on the gums, the inside of the cheeks and lips, and the tongue;
- painful sensations that increase when eating solid food;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes;
- increased salivation (not always);
- increased temperature (sometimes up to 40°C).
On the 2-3rd day of the disease, the formed blisters open. Erosion forms at this site and is covered with fibrinous plaque.
Symptoms of herpetic stomatitis can take up to 2 weeks to appear. How long stomatitis of this form is treated depends on the stage of the disease, usually a week.
To treat the viral form of the disease, antiviral drugs, immunomodulators, and vitamin complexes are needed. If the temperature rises significantly, antipyretic medications are used.
Catarrhal stomatitis
This type of disease is characterized by an intense inflammatory process in the absence of defects on the surface of the oral mucosa. This form of stomatitis is the most common.
The danger of catarrhal pathology lies in the mild manifestation of symptoms. Patients do not notice warning signs or pay attention to them late, when the disease is already advanced. The clinical picture of catarrhal stomatitis manifests itself:
- inflammation of the gums, teeth, inner surface of the cheeks;
- whitish coating on the affected area of the mucosa;
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness of the mucous membrane;
- bad breath;
- weakness and loss of appetite (more often in children).
Catarrhal stomatitis lasts about 5-7 days if treatment is started at the initial stage of the inflammatory process. At this stage, it is effective to use sage, chamomile, calendula, hydrogen peroxide (3%), and a weak solution of potassium permanganate for rinsing. Chlorhexidine is used for irrigation. Cholisal is often used as an antiseptic treatment.
If treatment is started late, ulcerative necrotic lesions may appear. There is a risk of developing concomitant pathologies. In this case, more complex treatment is necessary, which can only be prescribed by a doctor based on the characteristics of a particular case.
Video:
Medicines for stomatitis - TOP-11 drugs for treatment
Fungal stomatitis
This disease is often called candidiasis, candidal stomatitis or thrush. The cause of the pathology is the yeast-like fungi Candida. Children, especially those in the first year of life, are more susceptible to this form of pathology.
Read more about how candidal stomatitis appears and how to treat it on our website.
Fungal stomatitis usually affects adults with an extremely low level of immunity or after prolonged antibacterial therapy. The disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- redness of the mouth;
- the appearance of white cheesy deposits.
At the initial stage of pathology, deposits on the mucosa can be easily removed. In the future, this process becomes painful and leads to bleeding and erosive formations.
How long it takes to treat fungal stomatitis largely depends on the state of the immune system. In some cases, the disease will go away in a week, in others it may take a whole month.
Therapy for candidal stomatitis must include antifungal drugs, such as Candida drops. It is also necessary to strengthen the immune system.
Aphthous stomatitis
The inflammatory process in this form of the disease is accompanied by a violation of the surface of the oral mucosa. In this case, aphthae are formed.
Aphthous stomatitis, depending on the characteristics and severity of the disease, can be necrotic, fibrinous, deforming, glandular, cicatricial. The most severe form is deforming stomatitis, when the oral cavity is deformed due to large scars formed against the background of extensive ulcerative lesions.
In acute manifestations of aphthous stomatitis, the patient usually experiences an elevated temperature and increased salivation. The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and painful on palpation.
Chronic diseases are not characterized by changes in the lymph nodes. In this case, the patient periodically experiences single aphthae. They can occur on the inner surface of the cheeks, lower lip, and sides of the tongue. Read more about stomatitis on the lip on our website.
How long aphthous stomatitis lasts depends on the nature of the disease. It is possible to cope with acute pathology, subject to competent and timely treatment of aphthous stomatitis, in 1-1.5 weeks. Chronic manifestations of the aphthous form of the disease can lead to ulcerative stomatitis.
Ulcerative stomatitis
This form of the disease is difficult to cure, so the entire process must be supervised by a doctor. The inflammatory process in this case is accompanied by focal destruction of the mucous membrane. Ulcerated areas can grow and coalesce into large, painful lesions.
Attention! Before starting treatment for stomatitis in children at home, you should consult a doctor for a diagnosis.
With ulcerative stomatitis, the oral mucosa becomes red and swollen. This process is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- bad breath;
- increased temperature;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Patients at any age do not tolerate this form of the disease well, since the severe pain makes it difficult to eat or talk.
Treatment for ulcerative stomatitis should be comprehensive. It involves the use of anesthetics and antimicrobial agents. Additionally, antibacterial therapy, antihistamines, and vitamin complexes may be required.
A prerequisite that determines how long stomatitis is treated is sanitation of the oral cavity. It includes removing dead cells and tissues from the mucous membrane, cleaning teeth from plaque and tartar.
If all necessary measures are taken in a timely manner, ulcerative stomatitis can be cured within a week. If sanitation is not carried out, treatment may take 2 weeks or more. In this case, the risk of complications increases.
Allergic stomatitis
Inflammation of the oral mucosa in this case is caused by an immunopathological condition. The disease of this form manifests itself:
- swelling;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- bleeding;
- the formation of ulcers and erosions;
- burning;
- pain when eating;
- increased salivation;
- possible deterioration of general condition.
Penetrating into the human body, the allergen starts a chain reaction. Stomatitis is part of it. The body's reaction may vary. Stomatitis is usually part of the delayed type. The immediate type is characterized by Quincke's edema.
The duration of allergic stomatitis depends on many factors. The severity of the allergic reaction, timeliness and correctness of treatment are of greatest importance.
Under favorable conditions, stomatitis will disappear within 1.5-2 weeks. If the course of the disease is complicated, then its treatment may require much more time.
The duration of treatment for allergic stomatitis depends on the factor that caused the disease and the presence of contact with it. For successful treatment, it is important to eliminate the allergen, which can sometimes be problematic.
Traumatic stomatitis
The pathology of this form occurs against the background of trauma to the oral cavity. The cause may be accidental injury. In this case, catarrhal stomatitis is usually observed. Injuries to the oral cavity can occur multiple times. Usually this situation is observed against the background:
- large carious cavities;
- chipped teeth or fillings;
- frequent consumption of solid foods;
- malocclusion;
- constant biting of the lips or cheeks from the inside;
- smoking (including passive smoking).
The duration of treatment for traumatic stomatitis depends not only on the timeliness and correctness of the measures taken, but also on the elimination of the traumatic factor.
If you eliminate the cause of the pathology and start proper therapy at the first signs, you can be cured within 1-1.5 weeks. Otherwise, the disease may become chronic.
Aphthous stomatitis - inflammation of the oral mucosa
Herpes stomatitis
This is ordinary childhood stomatitis, since it affects mainly children, and in 80% of all cases of stomatitis in children, this type of disease is diagnosed.
Peculiarities:
- contagious, transmitted by airborne droplets;
- often occurs in an acute form, in which the child has a high fever, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea;
- stomatitis is located on the lip, on mucous tissues, and is often found on the palate, especially with infectious, chemical and mechanical damage to the tissues;
- due to painful sensations, the child refuses to eat, is capricious, and sleeps poorly;
- the lesions first look like blisters and then transform into ulcers, the healing time of which is 3-4 days;
- With effective treatment, herpetic stomatitis disappears in 7-14 days.
How long does stomatitis last in children?
In children, just like in adults, the speed of recovery directly depends on the type of disease. Approximate period: 7-14 days. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and start treatment immediately, this time is enough to cope with the disease.
Often recovery is delayed due to the fault of the parents themselves. For example, they did not monitor the timely taking of medications and the implementation of treatment procedures, ignored the doctor’s recommendation to take additional tests, or turned to a pediatric dentist only after long-term self-medication did not lead to a positive result.
But sometimes even the most responsible parents cannot cope with stomatitis for a long time. Alas, this happens. This disease is insidious and multifaceted, its course depends on many factors, and is often unpredictable even for an experienced doctor.
Catarrhal stomatitis
The mildest form of stomatitis. Most often it affects adults. Reasons: lack of necessary hygiene, dental disease, gingivitis, mineral deposits on teeth, helminthic infestation, gastrointestinal problems.
- the oral mucosa hurts and swells;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- Individual foci appear in the form of grayish spots.
For catarrhal stomatitis:
How to treat catarrhal stomatitis? How many days does it take for the disease to go away completely? At the initial stage, you can quickly get rid of the problem: if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, after 10 days there will be no signs of the disease. If the patient has a related disease, specialized specialists prescribe general treatment, and the dentist writes a local treatment plan.
If you ignore the symptoms of the disease for 10-14 days, severe complications are inevitable.
How to understand that stomatitis has passed?
The fact that the disease is a thing of the past is indicated by the complete return of dental health to the level that preceded the disease. This:
- disappearance of ulcers and aphthae;
- stop bleeding gums;
- extinction of the inflammatory process;
- no pain when talking or eating;
- getting rid of bad breath.
Despite the fact that recovery is obvious to the patient, only a doctor can put an end to treatment. As a rule, this does not require additional tests. Treatment regimens have been verified over years of experience, and a routine examination is quite sufficient to confirm a cure.
Often the patient’s well-being returns to normal after 2-3 days, the ulcers heal, and the pain recedes. It is important not to stop treatment at this point. Antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal drugs are taken in courses for a reason. Their duration directly depends on the life cycle of pathogens. To completely destroy some it will take 5 days, others – 20. And only a doctor can determine the duration of treatment!
If you ignore the prescriptions and stop taking the medications, stomatitis will return at the first slight decrease in immunity. And it will be more difficult to cure him.
Ulcerative (necrotizing) gingivitis
This is nothing more than an advanced form of catarrhal stomatitis in adults, in which most of the oral mucosa is affected by ulcerative and erosive foci, redness, swelling and bleeding of the gums, a slight increase in temperature to 37.5°, pain in the gums. In more severe cases (in the absence of timely effective treatment), stomatitis on the cheek can develop into extensive ulcers (up to 6 cm in diameter), deep tissue necrosis (mucous and even muscle), temperature rise to critical values, transition to the chronic stage, loss teeth.
How many days it takes to treat ulcerative stomatitis depends on the severity of the disease and individual factors. With the use of modern methods and remedies against the disease, you can quickly get rid of the disease (in 5-10 days).
Aphthous or recurrent stomatitis
A very common form that affects both adults and children (the incidence rate among children is slightly higher). A sign of pathology is the formation of round ulcers with a red outline, which look like a cold. Aphthous stomatitis spreads on the gums, lips, and cheeks from the inside, that is, in any part of the oral cavity. It can occur in both acute and chronic forms. The chronic form is more common, of allergic or infectious etiology, develops against the background of systemic diseases and weakened immunity.
If the patient has been diagnosed with aphthous stomatitis, treatment will be complex (general + local therapy). How long it will last and what medications will be used depends on many factors, including the causes and nature of the disease.
Candidal stomatitis
The most famous type of disease (often called “thrush”). The cause of the pathology is a fungus of the genus Candida. It is believed that candidal stomatitis is a disease of infants, but this is not so. Even adults can “catch” it, especially women in old age (when the body’s resistance is weakened) through hypothermia, contact with carriers of the infection, or treatment with antibiotics.
Symptoms of candidiasis: a cheesy white coating on the tongue, on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and palate. When plaque is removed, areas of inflammation may bleed. The duration of the incubation period for candidal stomatitis can reach 20 days. Treatment is carried out using anti-inflammatory, antifungal drugs, as well as nutritional correction.
Types of stomatitis
- Herpetic. The mucous membrane becomes irritated and bubbles filled with liquid form. The temperature may rise, your head will feel dizzy, you will begin to shiver, or other signs of ARVI will appear;
- aphthous is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers ranging in size from five millimeters to a centimeter. A maximum of three ulcers can form on the sides of the tongue, inside the cheeks or lips;
- fungal occurs due to Condida fungus. A persistent white coating appears because breast milk promotes the growth of the fungus. Children under one year of age become ill;
- allergic. The tongue and gums turn red, there may not be a fever, but after a while this type can develop into another more serious type of disease;
- bacterial occurs during teething in children. It can also occur when causing injuries to the oral cavity. Injuries can be either mechanical or thermal. With poor hygiene, the risk of this disease is also high.
Gangrenous stomatitis (noma)
This type of pathology is very dangerous. Severe form of stomatitis belongs to the category of wet gangrene. With this disease, there is damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity, progressive destruction of the tissues of the cheeks, tongue, gums (mucosa, submucosa), and face. The etiology is not fully understood, but there is an assumption that anaerobic infection influences the development of pathology. Most often, gangrenous stomatitis occurs in children with weakened immunity after infectious diseases. A huge number of cases are observed in African countries.
The disease develops rapidly: inflammation, formation of a bubble with hemorrhagic fluid - blue spot stage - swelling and hardening of the affected tissues (vitreous edema) - formation of a rotting wound. From the appearance of the first signs of inflammation to large-scale damage and the beginning of the process of rejection of necrotic tissue, only 3 days can pass. The disease occurs against a background of high temperature, the inflammatory process can affect large areas, involve the maxillary sinuses, jaw bone, gums, lead to tooth mobility, severe intoxication, and death.
The treatment is complex, aimed at fighting infection, intoxication, general strengthening of the body, in parallel with taking medications, local treatment is prescribed (antiseptic treatment, rinsing, ointments).
Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of a large number of aphthous stomatitis on the oral mucosa. These are round or oval ulcers covered with plaque. The causes of this disease are as follows:
- past infectious diseases: influenza, measles;
- lack of vitamin B12 and microelements in the body;
- oral injuries;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
For the most effective treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children, our specialists pay special attention to identifying the cause that caused it. Treatment of acute stomatitis in children is simply necessary, since the disease itself is very difficult. Its characteristic feature is unpleasant pain symptoms, which intensify when the ulcers are touched with hot or sweet food.
Treatment of purulent stomatitis in children requires an integrated approach. It consists not only in local treatment of ulcers with medications, but also in proper diet, frequent drinking and regular oral hygiene.
Prosthetic stomatitis
If an adult who has had dental prosthetics develops stomatitis, then most likely the disease is associated with wearing the prosthesis.
Symptoms of prosthetic stomatitis:
- the tissue under the crown is inflamed;
- soft tissues become painful;
- an ulcerative or necrotic focus of inflammation has formed (in rare cases).
The main cause of the pathology is bacteria that get under the orthopedic structure, as well as an allergy to the orthotic material. Treatment is antiseptic and anti-inflammatory and can last up to 2 weeks.
Stomatitis and treatment at home
Treatment of stomatitis at home primarily involves the use of various herbal decoctions and infusions with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effects. For example, even doctors recommend rinsing with calendula - it has a strong antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect and promotes healing. Chamomile is an excellent antiseptic - it is one of the most popular remedies that is widely used in folk and official medicine.
Stomatitis is treated using folk remedies not only for rinsing, but also for oral administration. For example, rosehip decoction is a real storehouse of vitamins and other substances necessary for the human body. It improves immunity, prevents the development of inflammatory processes, and also helps destroy harmful bacteria. Despite the miraculous power of herbs, it should be remembered that candida and herpetic stomatitis will not be eliminated by such folk treatment, since fungi and viruses are not affected by antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and immune-modifying agents.
Why is stomatitis in the mouth dangerous? Methods of transmission of the disease
There are many types of stomatitis, but not all of them are contagious. The most common methods of infection:
- airborne and contact (through kissing, sharing dishes, sneezing, etc.) - characteristic of bacterial and viral stomatitis;
- Candidiasis is also transmitted through hygiene items, household items, and toys;
- types of diseases such as chronic, aphthous, chemical, allergic, etc. develop independently (under the influence of unfavorable factors).
Children most often become infected through toys, fruits, dirty hands, dishes, that is, through contact. Babies put everything in their mouth and can get candidiasis after playing with a dirty toy or from an untreated pacifier.
What negative consequences can stomatitis lead to?
- inflammation and bleeding of gums;
- tooth mobility and tooth loss;
- secondary infection;
- tonsillitis;
- with long-term treatment, voice changes (hoarseness, hoarseness) and the development of chronic laryngitis are possible.
But in most cases, stomatitis does not pose a health hazard under one condition - if a visit to the doctor is not postponed, effective treatment is prescribed in a timely manner and the patient follows the recommendations of doctors for treatment and oral hygiene.
Reasons for development
Stomatitis often occurs in people with reduced immunity and impaired microflora. If these 2 conditions are observed simultaneously, then even opportunistic microorganisms can cause severe inflammatory processes. Many other factors also influence the development of the disease.
Inflammation of the oral mucosa can occur in the following cases:
- mechanical, chemical, thermal injuries - hot burn, injury from solid food, cheek bite, etc. leads to tissue damage, penetration and spread of infection;
- poor nutrition, lack of vitamins, especially C, group B, minerals - zinc, iron and others;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules, eating unwashed fresh berries, vegetables, fruits, dirty hands while eating;
- treatment with medications that reduce salivation, antibiotics that destroy beneficial microflora, and a number of other medications;
- Frequent brushing of teeth with a paste containing sodium lauryl sulfate leads to a decrease in saliva secretion and dry mucous membranes, which become more susceptible to aggressive substances;
- poor-quality prosthetics and dental treatment due to which the gums are constantly injured;
- smoking, drinking alcohol;
- dehydration with prolonged diarrhea, vomiting.
Stomatitis often occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal imbalance. At risk are patients with diseases of the heart, blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, pathologies of the immune and endocrine systems, and those with helminthic infestation. In diabetes mellitus, the aphthous form is diagnosed. People who use hormone inhalers to relieve asthma attacks suffer from candidiasis.
To answer the question whether stomatitis is contagious or not, differential diagnosis is necessary. Bacteria, viruses, and Candida fungi can be transmitted from person to person. The most contagious is the viral form of the pathology. However, with good immunity, the infection will not necessarily develop. It is also important how stomatitis is transmitted. If this is direct contact, for example a kiss, then the risk of getting sick is higher.
Diagnosis of stomatitis
Effective diagnosis allows you to accurately determine the form of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment, which speeds up the recovery process as much as possible. Since stomatitis has quite eloquent symptoms, in many cases a general clinical picture is enough for a doctor to make a diagnosis. An examination and anamnesis are taken.
In addition, laboratory diagnostic methods are used:
- general blood analysis;
- bacterial sowing;
- viral culture;
- cytological studies;
- PCR diagnostics;
- tissue biopsy;
- subcutaneous tests with yeast allergen.
There are many types of stomatitis, and some of them may require additional diagnostic tests:
- immunological;
- serological reaction;
- gas chromatography for fungal metabolites;
- molecular biological diagnostics;
- immunofluorescence method, etc.
Features of the manifestation of stomatitis in the mouth during pregnancy
The main causes of stomatitis in pregnant women are hormonal changes and decreased immunity, and these are ideal conditions for any inflammatory processes.
Stomatitis during pregnancy manifests itself in the form of redness on the tongue, palate, buccal mucous membranes and gums. In the area of inflammation, ulcers and erosions appear in the form of white spots with a red outline. If stomatitis occurs in an expectant mother, treatment should be carried out immediately, since each ulcer is a source of infection that can cause intoxication of the body, lead to serious problems in bearing the fetus and complications during childbirth.
Babies are more susceptible to the disease.
Firstly, because they love to taste everything. As a result, any thing can be in a child’s mouth (toys, someone else’s pacifier, an apple uneaten by another child), covered with a million unfriendly bacteria that can cause inflammation.
Secondly, even the slightest cold can affect the condition of the mucous membrane. Dry mouth leads to a decrease in the protective function of the mucous membrane.
Thirdly, during the period when the baby is teething, he can injure his cheek or lips on the inside during sleep. Inflammation forms at the site of injury, and then stomatitis develops.
Doctors recommend that parents regularly examine the child’s mouth, especially in the area behind the lower lip, where foci of inflammation are almost always localized during stomatitis. Childhood stomatitis is very painful, and early detection of the disease will help get rid of it in a matter of days.
How to cure stomatitis in a child? Under no circumstances use tips from the Internet and do not try to treat your baby with folk remedies yourself. If you suspect that your child has stomatitis, contact a pediatric dentist at Amel Dental Clinic for a consultation. He will conduct an examination, draw up a treatment plan and give professional recommendations.
Treatment of stomatitis in children of different ages
Stomatitis in children is a kind of profuse inflammation of the oral mucosa. It is necessary to treat the baby immediately and avoid extensive lesions. The child needs to be provided with special hygiene products with which he can regularly rinse his mouth.
If the baby is still very small, then he should treat his mouth with special napkins, on which a special solution - an antiseptic - is applied. Children over one year old can easily learn to rinse their mouth after eating, clearing it of dirt. This rinse will allow the sores to gradually heal as all bacteria and infections are destroyed. If stomatitis is not treated promptly, ulcers can spread throughout the entire oral cavity. In the future, this will lead to diphtheria, which is much more serious than stomatitis.
If an infant gets stomatitis, it means that nipples and bottles need to be carefully treated. Also, before each feeding, the mother’s nipples need to be treated, since various infections can be transmitted through them. Everything must be clean and sterile. If the child eats independently, then you need to ensure that the temperature of the food is equal to body temperature. In this case, he will use it without whims and stubbornness. Sour foods or particularly spicy foods should be excluded from the diet. If it is too painful for your child to eat, you can offer him food through a straw. This can be broth or liquid puree.
If a child with stomatitis refuses to eat, it is possible that he experiences severe pain while eating. In this case, you can use special gels that reduce the sensitivity threshold, and the child can eat little by little. If stomatitis is detected in a child, treatment must be started immediately. Nowadays, childhood stomatitis can be successfully treated, and the treatment itself can be completed in just a few days if you regularly rinse the mouth and monitor hygiene.
Sometimes there are situations when stomatitis is accompanied by the appearance of another disease - periodontitis. Here, home treatment is not enough, since periodontitis in children is treated in a specialized dental clinic or hospital. These diseases can be treated by the staff of the Dent Prestige dental clinic. Experienced specialists will always come to the aid of children and their parents.
How to treat stomatitis: treatment in adults and children
The sooner the problem is detected and the patient consults a doctor, the easier and faster the healing of inflammation occurs and recovery occurs. How to cure stomatitis in the mouth in adults and children?
The treatment regimen is always individual, and it is prescribed by the dentist based on the results of anamnesis and research.
However, in each case, complex therapy is used, which necessarily includes:
- 1
Improving the quality of hygiene and choosing gentle oral care products (soft brush, non-aggressive pastes). - 2
Changing eating habits. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that can injure the mucous membrane (sour, spicy, cold, hard, etc.)
- 3
Antiseptic and anti-inflammatory measures - to fight bacteria, the doctor will recommend rinsing your mouth regularly with a special balm, herbal infusion or other antiseptic agents, and applying medicinal ointments.
Depending on the cause and form of the disease, you may need to:
- undergo drug treatment aimed at combating viruses, fungal or bacterial infections (if they are the cause of the disease);
- scrape out and treat areas of inflammation;
- have your teeth professionally cleaned;
- undergo a laser treatment procedure (excision of necrotic tissue);
- regularly treat dentures, and in some cases, reinstall the denture;
- undergo a course of immunotherapy, etc.
How to treat stomatitis in the mouth, which treatment methods are most effective, how many days (weeks) treatment should last, the doctor will decide after examination and (if necessary) laboratory diagnostics. You can sign up for a consultation at Amel Dental Clinic on our website by choosing a doctor and a time convenient for visiting the clinic.
Stomatitis, treatment: the best remedy is prevention
Fighting a disease is always more difficult than preventing it. By following simple rules of oral care, you can maintain the health of your gums, teeth, and even protect your children from transient (contagious) stomatitis.
For effective prevention of stomatitis, doctors at Amel Dental Clinic recommend:
- follow the rules of hygiene - brush your teeth regularly and effectively, rinse with balm after each meal;
- have your teeth professionally cleaned to remove plaque every 3-4 months;
- change your toothbrush on time;
- rinse the mouth after taking liquid antibiotics;
- Get regular dental check-ups;
- take care of a balanced diet;
- take care of your health - maintain a healthy lifestyle, receive timely treatment for gastrointestinal pathologies, cardiovascular and infectious diseases;
- strengthen the immune system.