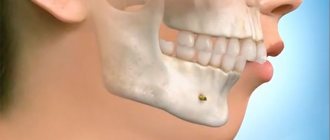
Sometimes, in the way of the miracles created by modern orthodontics (for example, if it is necessary to regroup the teeth in order to correct the bite or for another reason), an obstacle arises in the form of excessive density of the jaw bones, in such cases a compactosteotomy comes to the aid of a specialist.
This is the name of the surgical method of thinning the structure of the compact zone of the jaw bone. Technically, the procedure looks like a destruction of its integrity - perforation of the jaw bone (drilling a series of holes in it in a checkerboard pattern in the area of intersocket partitions, apexes of roots and buttresses).
Description of the disease
Tortoanomaly or otherwise tortoocclusion is a pathology in which the tooth is placed in an abnormal position. "Tortuosus" is translated from Latin as "twisting, curved."
The element with this pathology is indeed bent, or rather, rotated around its axis, and the angle of rotation can be insignificant - from 20 to 45⁰, and quite large - more than 45⁰, which experts attribute to a severe degree of anomaly.
More often, torto-occlusion affects the lateral canines and incisors of the upper jaw , less often the lower and molars. In most diagnosed cases, one unit has an unnatural position, but sometimes pathology can develop on several elements at once.
Goals of the intervention
If previously, to reduce the density of bone matter and facilitate the process of moving teeth, they resorted to removing part of the compact (cortical) layer, but now they are limited to minimal intervention, the result of which is the development of an inflammatory reaction in the bone in response to its damage.
Partial demineralization and the launch of reparative mechanisms facilitate tissue reconstruction under the influence of pressure from orthodontic devices used at the second stage of the operation.
Indications for surgery are severe deformations of the dental system:
- anomalies in the structure of the jaws (microgeny, progeny);
- either a prognathic bite with the lower jaw moving forward, or a retrognathic bite with the upper or lower jaw moving back;
- open bite.
Reasons for development
Abnormal torsion results from the following circumstances:
- hereditary predisposition;
- excessively large units;
- narrowing of the dentition;
- untimely loss of baby teeth. In this case, the permanent elements grow, forced to change their natural position;
- falls and impacts during the development of permanent dentition;
- deviations in the development of rudiments in the embryonic period;
- congenital underdevelopment of jaw bones;
- hyperdentia;
- cutting through eights.
In addition, malignant and benign formations and bad habits can lead to tortoanomaly.
Contraindications and restrictions
Along with the indications for intervention, there are also contraindications for it, including the presence of disorders:
- blood clotting;
- mental;
- hormonal (of various origins), including diabetes.
Obstacles to the operation are also:
- the presence of an active or chronic infectious process;
- the patient’s age is less than 18 years (due to the incomplete development of the jaw bones at this age);
- peculiarities of the location of the teeth in the form of a high degree of crowding (due to the high probability of damage to the dental roots).
Symptoms
At a small angle of rotation (less than 45⁰), tortoocclusion causes only aesthetic discomfort.
However, when the turning angle exceeds 45⁰ and the cutting surface is unnaturally positioned, the following symptoms may be observed:
- the oral mucosa is injured, and as a consequence relapses of stomatitis;
- Tremas and diastemas develop;
- problems with diction and difficulty biting food appear;
- teeth become loose;
- the natural bite deteriorates.
Often the patient complains of microtraumas of the tongue and cheeks due to the incorrect position of the canines and incisors.
What is a deep bite and how can it be corrected? Evaluate the results of open bite treatment here using before and after photos.
At this address https://dr-zubov.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/podrobnoe-opisanie-distalnogo-i-metodov-korrekcii.html all the most interesting things about the methods of treating distal occlusion in adults.
Diagnostics
Typically, a doctor diagnoses the disease during an examination, but other research methods are also used to obtain more accurate information:
- Radiography. The patient is given a targeted photograph, with the help of which the position of the root and its position relative to other units are determined;
- An orthopantomogram allows you to obtain a panoramic image to determine the quality and structure of bone tissue;
- Anthropometric study. To do this, impressions are taken and a plaster model of the patient’s jaws is made, which is studied, measured, and the data obtained is analyzed.
Treatment methods
Torto-occlusion is corrected using orthodontic, surgical and orthopedic methods. Depending on the angle of rotation, the following can be used:
- plates and braces – if the rotation is from 10 to 20⁰;
- arches and structures with springs - when turning up to 40⁰;
- surgical intervention - when turning more than 40⁰.
If the specialist has correctly selected the technology for treating the torsional anomaly, then minor reversals are corrected within 4 months. Serious cases will take at least a year and a half.
When choosing the optimal method of correction, the doctor takes into account the patient’s age, the cause of the pathology, narrowing of the jaw arch and a number of other factors.
Elastic positioners
The products are used if there is a slight degree of rotation. The devices are effective during changes in the primary dentition.
They are vinyl-silicone mouthguards that have special channels for the teeth and labial arches that press on the abnormal surface.
Trainers help stabilize muscle function and eliminate myofunctional deficiencies. The main time of action of elastopositioners is at night, when a person is sleeping; during the day they are worn for no more than 2 hours.
Braces
They are used during the period of completion of the mixed dentition, as well as in permanent dentition. At the beginning of treatment, the doctor prescribes wearing a thin round arch made of nickel and titanium alloy.
Then it is replaced by a thicker arc with a rectangular cross-section. At the end of treatment, the arch is replaced by an elastic chain.
Cofin Loop
The system is indicated for narrowed jaws. The expansion does not occur uniformly, but in the direction in which the spring is open.
The design is formed by 2 arcs, the shape of the corrective arc is semicircular. One part of the device is positioned on the outside of the dentition, the other on the inside.
The curved part acts on the protruding surface of the anomalous units, promoting their natural orientation. The straight ends of the arch are placed on the alveolar process, which leads to jaw expansion.
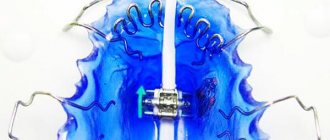
Engle's apparatus
An orthopedic design is indicated to expand the jaw and normalize occlusion. This is an arch made of titanium or steel with screw threads on the ends and rings that are installed on the first molars.
Loops and microhooks are attached to fragments of the frontal zone and the most remote area of the abnormal tooth.
The spring is attached with these hooks and fixed on artificial crowns. The traction force of the spring helps to correct the position of abnormally located units.
The main signs of mesial occlusion and treatment used in modern orthodontics. In this material we collect truthful reviews about surgical correction of malocclusion.
Here https://dr-zubov.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/primenenie-miogimnastiki.html a detailed description of myogymnastics exercises used in orthodontics is presented.
Removal of a tooth
It is carried out both with milk and permanent dentition. In the first case, the fang is removed, in the second, either the affected fragment or the first molar.
Extraction is carried out using an elevator. It penetrates into the upper part of the root and tears the ligamentous tissue. The tooth is then loosened and removed from the socket.
Compactosteotomy
To correct elements whose position has been changed due to a narrow jaw, two types of compactosteotomy are used:
- lattice. Holes are made in the root of the problem unit using a ball-shaped bur. The holes are spaced 4 mm apart in a staggered pattern;
- tape. A section of bone up to 3 mm wide is removed. The bone at the root apex is not affected.
Fibrotomy
The operation helps to reduce the resistance force of the ligamentous apparatus. For these purposes, the periodontium is incised from the area where the ligaments exhibit maximum traction force.
The instrument in this case is a narrow scalpel. It is inserted into the periodontal cavity (cleft) and the tissue around the problem area of the root is cut.
The successful movement of fragments into a normal position is facilitated by the combination of fibrotomy with hardware treatment.
Incomplete dislocation
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The problematic element is moved to the correct position using forceps. Stability is ensured by applying tires using classical technology.
The procedure can be carried out under the following conditions:
- there should be enough space in the general row;
- the root should be smooth and fully formed.
Retention period
During the final period of treatment of torto-occlusion, the following methods are used as fixing manipulations:
- orthodontic. The arc is fixed on the corrected units. Ribbon fiber tape and metal arc are used. Despite all the aesthetic appeal of Ribbon tape, this method has a drawback - the dentist will need to prepare the enamel. The use of custom plates and trays may be indicated as an alternative;
- surgical. Used only for mature occlusion in adults. The retention effect is long-term, lasting at least 6 years. The doctor dissects the gingival papilla;
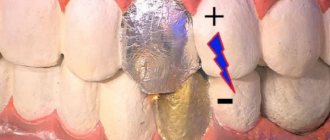
- physiotherapeutic. Stable retention is achieved using vibration stimulation. The teeth are permanently exposed to low-frequency (up to 50 Hz) vibration vibrations. This effect stimulates the vascular-motor reaction and, as a result, bone tissue is restored.
About possible complications
Excessively intense impact on the bone during its perforation can lead to undesirable consequences - a more protracted course of the inflammatory process than required for treatment with further necrosis of individual bone segments due to a disorder in their nutrition.
At the second retention stage of the operation, the ultra-long (over 2.5 months) impact of the orthodontic apparatus on the “softened” tissue of the alveolar process, with an insignificant degree of tooth mobility, also supports the process of inflammation in it, subsequently leading to complications in the form of:
- bone osteoporosis;
- reduction in the height of the alveolar process (due to atrophy of its ridge) with a decrease in jaw height.
Other complications include damage to the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw due to the thinness of the spongy layer between the compact layer of bone and the wall of the tooth socket, as well as infection of the periodontium due to a loose fit of the interdental papillae, which opens the gates to infection.
However, thanks to the existence of many modifications, this technique can lead to success in the most difficult situations that require moving large groups of teeth (along with their cells).
Prevention
It is almost impossible to prevent pathological tooth orientation, but you can reduce the risk of an anomaly. To do this you need:
- visit the dental office periodically. For the first time, you need to show the child only once before reaching the age of one year. But then, such visits should occur more often - at least 3 times a year. The dentition is actively forming and the orthodontist can easily detect the initial stages of pathology. A five-year-old child should be examined by an orthodontist up to 2 times a year;
- monitor how baby teeth grow and fall out in children , consult a doctor if a baby tooth prevents the appearance of a permanent one. Treat carious formations;
- consult a geneticist and orthodontist if there is a genetic predisposition;
- correct myofunctional habits , fight bad habits.
- perform a special set of myogymnastic exercises for minor anomalies.
The pathology responds well to treatment during the period of change in the primary occlusion.