04.11.2019
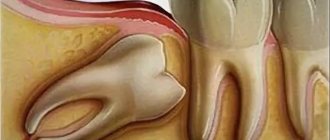
Purulent periostitis or flux is an inflammatory process localized in the periosteum area. A new growth appears on the gum, in which purulent secretion accumulates. This condition threatens a person’s health and even life, so when early signs of a problem appear, emergency intervention by specialists is required.
The key treatment method for gum flux in adults is taking antibiotics. Today, many effective drugs have been developed.
What is the essence of the problem
After the tooth was removed, flux formed. What it is? Scientifically, the disease is called periostitis. This is a purulent-inflammatory process that forms in the periosteum of the upper or lower jaw. Simply, a person who is faced with this disease has a swollen cheek, a rise in body temperature and signs of intoxication of the body such as weakness and malaise. But we will talk about the main symptoms of the pathology later.
It is generally accepted that periostitis (this is what gumboil is officially called) occurs due to the presence of diseased teeth in the mouth affected by caries, pulpitis and periodontitis. However, pathology can also develop when the main source of the problem is removed.
The principle of action of antibiotics
Antibiotics for dental flux are detrimental to pathogenic microflora, which acts as a key cause of the disease. Most medications have a broad spectrum of action. They are effective not only in the fight against gram-positive cocci and staphylococci, but also against other pathogens.
Antibacterial drugs kill bacteria, ultimately stopping the production of toxic waste products of pathogenic microflora. As a result, the symptoms of periostitis are relieved: body temperature decreases, pain is eliminated, and the size of the tumor decreases.
After a certain period of time, the medicine is eliminated from the body in the traditional way. Chemicals are adsorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and excreted along with feces and urine. To make this process easier, experts advise drinking medications before meals.
Why does pathology develop?
The development of a purulent-inflammatory process is provoked by bacteria that penetrate the tissue before the extraction procedure (i.e., tooth extraction), during or after it. Let's look at each scenario in more detail.
Advanced dental diseases before the extraction procedure
It often happens that the patient already had gumboil, his tooth was removed, but the tumor remained. That is, initially a person came to dentistry with an acute or chronic inflammatory process that arose against the background of advanced caries, pulpitis or periodontitis. Doctors carried out extraction, antiseptic treatment of the hole and its curettage (cleaning), opened the abscess, and prescribed antibiotics. And if the patient does everything correctly, in accordance with the recommendations, then the flux gradually goes away, but this does not happen instantly, because the inflammation has been present in the tissues for a long time.
If, after pulling out a tooth, you ignore medical recommendations, then the gumboil does not go away or even becomes larger.
2. Unprofessional actions of the doctor during extraction
If flux appears after tooth extraction, this may be due to a violation of asepsis during the surgical operation. The specialist could have carried out poor quality sanitation of the hole and introduced an infection inside. The problem can be caused by the presence of fragments or remnants of roots, filling material, or instrument fragments in the tissues.
Important! To avoid the formation of cheek flux after tooth extraction and other complications, it is necessary to monitor the work of a doctor. At the final stage of the surgical operation, professional dental surgeons must take an x-ray (especially if the extraction procedure was complex and it was necessary to use a bur, extracting the root in parts). An X-ray examination allows you to check whether there are any fragments left in the socket that can cause inflammation. For more information about whether you need to take an x-ray after extraction, read the feature article on the website.
Failure to comply with recommendations during the rehabilitation period
Flux is one of the common complications that arise due to neglect of the following recommendations in the first 2–4 days:
- active chewing of food on the side of the jaw where the intervention took place, eating irritating foods (hard, hot, spicy),
- direct impact on a socket that has not yet healed: active rinsing, damage with a brush, tongue, finger, or foreign objects. As a result, a protective clot disappears from the wound, which prevents bacteria from penetrating inside,
- drinking alcohol and smoking,
- refusal to take medications and antibiotics prescribed by a dentist,
- applying warm compresses, warming the cheeks, visiting the sauna and steam room, physical activity, long stays in the open sun,
- complete lack of oral hygiene.
Tumor after extraction of third molars
Flux often occurs after wisdom tooth removal. The fact is that the “eights” are located in the most remote place of the jaw, access to them is limited. They have long and winding roots. It also happens that they have not erupted completely or are completely located in the jawbone. The extraction of such elements is always difficult and traumatic; often in the process the doctor has to cut and peel off the gum and severely injure the mucous membrane1 of the oral cavity, and after this a large wound is formed, which takes a long time to heal and where bacteria can easily get into.
After extraction of third molars, many patients complain that their cheek is swollen. But this symptom does not always indicate gumboil. More often this is a consequence of complex surgical intervention, manifested in the form of physiological swelling of tissues. The swelling increases up to 3-4 days, and then sharply declines.
Characteristic symptoms of the problem
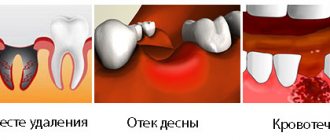
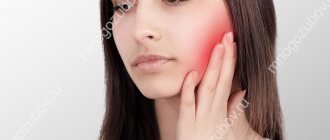
If flux has formed after tooth extraction, it is difficult not to notice. Firstly, the gums around the hole of the removed element swell and become inflamed, and a purulent sac can form here. Secondly, swelling of the cheek occurs, while the soft tissues harden, pulsate and may turn red. If the disease occurs in a very acute form, the tumor can spread to the lower eyelid, mouth, and nose. All this is accompanied by pain that spreads to the entire jaw, head, neck, and ears. The pain does not always go away after taking analgesics.
The patient usually has a fever of up to 38°C, enlarged lymph nodes, bad breath, loss of appetite and sleep. Some people report shortness of breath.
Important! After some time, the purulent sac on the gum can break through the fistula on its own, after which part of the pus comes out. This usually brings tangible relief. But you must not let your guard down: the symptoms will disappear only for a while, and the disease can worsen again at any moment and lead to life-threatening consequences.
Features of periostitis in children
Flux after tooth extraction in a child is a rather rare phenomenon, since the milk units have short roots, their extraction takes place without unnecessary trauma and difficulties, and after the operation a small and shallow wound remains, which heals very quickly.
More often it happens that parents bring their child to the dentist with a diseased carious tooth, due to which gumboil has developed. Doctors advise removing such elements, as they threaten the successful development and growth of permanent rudiments. After the operation, the tumor persists for some time, since there was an infection in the tissues for a long time, but if you follow the recommendations from dentists, all unpleasant symptoms disappear over the next 3-5 days.
Many parents are interested in whether it is possible to save a baby tooth that has developed gumboil? As mentioned above, removal is most often recommended, since the inflammatory process can affect the rudiments of permanent units. Also, preservation in most cases is not advisable, because in children periostitis quite often recurs with the slightest weakening of the immune system, overheating or hypothermia.
Flux and physiological edema: what are the differences
As mentioned above, swelling is a completely natural consequence of extraction, especially after the removal of third molars and complex manipulations, or against the background of some chronic diseases of the body (diabetes, hypertension). And this is not the same thing as flux.
What are the differences? With physiological edema, the patient’s general condition usually does not worsen, since there is no intoxication of the body. Temperature is normal. There is no putrid odor from the mouth. There is no abscess on the gum. Pain and discomfort are present, but they are not severe, and can be relieved with pills if necessary. After 2-3 days, all symptoms subside, and with each subsequent day the discomfort should become less and less.
What types of pathology are there?
Doctors distinguish two types of disease - acute and chronic. After extraction, an acute form usually occurs, accompanied by severe symptoms, sudden appearance and rapid development. The chronic type of the disease is sluggish; the patient may not be aware of its existence for six months or even several years, until the pathology worsens due to decreased immunity or other provoking factors (hypothermia, stress, physical and emotional overload).
How long does the swelling last?
When asked how long the gumboil lasts after tooth extraction, doctors answer this: if you start treatment on time, the inflammation and swelling of the cheek usually goes away after 3-5 days. But if the patient has a history of chronic diseases and weak immunity, or if seeking professional help was not timely, then the tissues take longer to return to normal; the rehabilitation process can take up to 2-3 weeks. That is, the sooner you see a doctor, the sooner you will find that your gumboil subsides after tooth extraction.
Effective drugs and tablets for pain after tooth extraction:
No. 1. Nise + Nurofen Express + Suprastin
- First, we drink 1 tablet of Suprastin, and after 20 minutes, a tablet of Nise and 1 tablet of Nurofen Express. The combination can be repeated after 4 – 6 hours
No. 2. solpadeine soluble + ketanov + suprastin
- First, we drink 1 tablet of suprastin, after 20 minutes, dissolve 1 tablet of solpadeine in water and drink, after another 15 minutes, drink 1 tablet of ketane. The combination can be repeated twice a day, every 6 hours, or take combination No. 1
Before taking pills, it is advisable to consult a specialist.
Just CALL US!
+7
We will answer any of your questions and will definitely help you!
What happens if you don't get treatment?
Have a tooth been pulled out, but the gumboil doesn’t go away? Need treatment. If this is not done, the infection will seep into the deeper layers of tissue and provoke the development of phlegmon (damage to the soft tissues of the face), abscess, and osteomyelitis (destruction of bone tissue). The infection can enter the bloodstream and lead to blood poisoning or sepsis, and even death.
The presence of infection in the body undermines the functionality of the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, brain, and heart. Immunity also drops sharply. If the disease is ignored for a long time, then you will no longer have to be treated in dentistry, but in a hospital. It is possible that other teeth that were located near the source of infection will subsequently have to be removed.
When is antibiotics required?
Therapy for periostitis should begin as early as possible, since there is a high probability of pus spreading into the tissue of the face, neck and chest. The result of this process will be death. A universal method of treating periostitis in adults is the use of antibacterial medications. They are used both in the initial phases of the disease and after surgical removal of the abscess.
Which antibiotics are preferable for a particular adult to take for dental flux depends on the state of his health and the phase of development of the disease. The state of the patient’s immune system also plays an important role. Taking antibiotics becomes advisable in the following cases:
- If the start of the inflammatory process is triggered by streptococcal or staphylococcal bacteria entering the body.
- In the presence of purulent formations.
- During therapy after surgery.
- To prevent complications.
The use of a drug prescribed by a doctor at the initial stage of the formation of periostitis allows you to avoid the formation of an abscess and quickly relieve inflammation. Self-medication in such a situation is dangerous and leads to the development of serious complications.
What treatment options are possible?
Let's talk about how to treat gumboil after tooth extraction. First you need to go to the doctor. Don’t be afraid of surgical intervention; if you have time to seek help before a purulent lump has formed on the gum, you can get away with conservative treatment methods. If you delay, you will not be able to avoid surgery, but surgical intervention for this type of pathology is still not as scary as for the consequences and complications of periostitis (osteomyelitis, phlegmon).
Conservative method
The specialist will prescribe antibiotics, which can only be purchased today with a doctor's prescription. To remove flux after tooth extraction, Lincomycin or Amoxiclav is usually prescribed. It is also necessary to take anti-inflammatory drugs (Nimesil, Diclofenac), as well as the use of antiseptics (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine). Applications with Metrogyl Denta gel or Levomekol ointment should be applied to the affected gum.
To combat such symptomatic manifestations of the disease as pain, take painkillers like Nurofen. Antihistamines help relieve swelling. It is also necessary to boost immunity with the help of vitamin and mineral complexes. Additionally, you may be prescribed physical therapy. The course of treatment is at least 7 days.
Surgical intervention
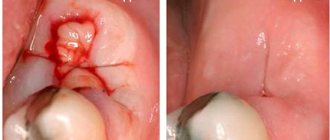
If after tooth extraction the flux has become larger and an abscess has appeared on the gum, then specialists perform periostomy - an operation during which the surgeon makes an incision in the gum, releases the pus and installs a drainage for its complete outflow. The drainage can be left for 2-3 days, during which the patient also takes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and rinses. After removing the drainage, the doctor places stitches on the gums, and the patient goes home and continues taking the prescribed medications until he is completely cured.
Important! At the stage of diagnosing the disease, the doctor takes an x-ray. If it turns out that the cause of inflammation was fragments of a root or instrument remaining in the hole, the specialist will curettage the hole, then put medicine into the wound and suturing it.
“After the tooth was removed, I still had gumboil, I noticed it about 2-3 days later. In the morning I woke up, and my cheek was swollen, and it felt like a stone, my jaw did not open, and there was severe pain. I took a painkiller pill, took time off from work and ran to the doctor. They cut my gum. I remember that anesthesia was injected before this, but still the incision was very painful due to inflammation and, as it turned out, due to the fact that I took the ill-fated pain pill at home. Drainage was not installed, because... the pus was only in one place and came out quickly. Then they sent me home with a warning that the swelling may worsen by night, and this is normal due to surgery. They prescribed all sorts of pills and rinses. Relief came almost immediately after the operation, the swelling did not get worse, everything went down within a day, but a small bruise appeared.”
Sasha, fragment of review from otzovik.com
When swelling is not dangerous
Swelling of the gums or cheeks is not always pathological. There is no need to panic or worry if:
- general condition is satisfactory;
- swelling is not accompanied by an increase in temperature (if it was not there before removal);
- swelling is in one place (usually in the gum or cheek area) and does not spread to the face;
- the pain is tolerable and lasts no longer than 2-5 days;
- the swelling of the cheek is hardly noticeable, goes away in 3-4 hours and is not accompanied by increased pain;
- no redness on the skin or mucous membranes;
- there is no suppuration, as evidenced by the absence of severe pain, bad smell and taste in the mouth.
If the temperature before removal was elevated, then on the first day after the intervention it may increase slightly (37-37.5 degrees).
Pain after removal is always present to some extent when the effect of anesthesia wears off. The so-called “background” aching pain can occur in the first days after removal. After complex removal, discomfort may persist for 2 weeks. The main thing is that the pain gradually decreases.
If there are no alarming symptoms, then at first it is enough to simply observe the swelling. The main thing is a gradual reduction in swelling and pain.
What is prohibited: actions that lead to worsening symptoms
- warming up the inflamed area: you should also not wrap your cheek with a scarf or warm bandage, rinse your mouth with hot decoctions and solutions,
- self-medication, especially with the help of folk recipes,
- taking blood thinning pills (Aspirin),
- hypothermia or overheating of the body, physical activity,
- drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking, drinking too much strong coffee: this leads to increased blood pressure, increased blood supply to inflamed tissues and the likelihood of bleeding,
- You should not sleep on the side where the swelling is located.
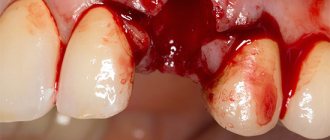
What and how to stop bleeding after tooth extraction?
As a rule, the dentist already during the operation sees that the bleeding from the tooth socket is profuse and he himself carries out an intensive tompanade of the socket using gauze swabs soaked in hydrogen peroxide and hemostatic sponges. A tight tomponade for 20 minutes is guaranteed to stop bleeding in 99% of cases. Additionally, cold is applied to the surgical area, which leads to spasm of the arterioles and also helps stop bleeding. If at home there is suddenly bleeding again from the hole of an extracted tooth in the gum, you need to do the following:
- soak gauze or a clean handkerchief in hydrogen peroxide and roll it in several layers
- rinse your mouth with cold water and pour hydrogen peroxide into the dental socket
- press the gauze swab tightly to the hole and hold for 30 -40 minutes
- take a semi-lying position and apply ice in the tissue to the cheek for 1 hour
- sleep on raised pillows at night
- visit the dentist the next day
Treatment at home
The first step is going to the dentist. The second step is to follow medical recommendations at home. What you need to do at home: take medications prescribed by your doctor, carry out antiseptic treatment of the inflamed area. At home you need to follow a certain diet: exclude solid and hot foods from your diet. After the obvious manifestations of the disease have passed and the course of treatment has been completed, you must again see a doctor who will conduct a follow-up examination.
Is it possible to use folk recipes at home and will the flux go away after tooth extraction? It is permissible to use some folk recipes, namely applying cold compresses to the cheek and rinsing the mouth with herbal decoctions, as well as a soda-saline solution. These remedies are good as an additional measure to the treatment prescribed by your doctor.
It is important for people with chronic diseases, such as hypertension, to take medications that will keep their blood pressure normal and prevent it from increasing.
How to prevent the temperature from rising?
Prevention of a hyperthermic reaction consists of:
- antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity after surgery (it is recommended to make baths/lotions using the drugs Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Iodinol, Betadine);
- regular hygiene procedures (brushing your teeth twice a day, rinsing your mouth after eating);
- refusal to visit public places for swimming (beach, water park, sauna, bathhouse) and sunbathing;
- careful choice of food (it is better not to eat solid food in the first days);
- alcohol taboo.
If other preventive measures have been prescribed by the doctor, these must also be followed strictly.