The treatment tactics for caries depend on the cause of the pathological process and its neglect. This is the most common dental disease, characterized by gradual tooth decay. The pathology goes through several successive stages; at first, the patient may not feel anything; in complex cases, complete loss of dental units is possible.
It is not difficult to detect the disease, because most of the symptoms are quite obvious. However, it is better to prevent the occurrence of carious lesions by following preventive recommendations, and then a snow-white smile will delight you for many years.
Caries - what is it?
More than 95% of the inhabitants of our planet face the disease. Thus, it can be called the most common dental problem. At the very beginning, the pathological process affects only the enamel, and in the absence of therapy it penetrates into the deep hard layers. Then the soft tissues with nerve fibers and blood vessels become inflamed.
The disease is insidious because in the earliest stages it does not manifest itself in any way, and the patient begins to sound the alarm only when acute pain and a large hole appear that cannot be eliminated by conservative methods.
What do the main bacteria that cause tooth decay look like?
We cannot see what the bacteria that provoke the development of dental caries look like. But visible changes on the teeth provide an understanding of what stage the pathological process is at.
First, a barely noticeable light spot forms on the enamel. At the second stage, the spot becomes darker, its size increases, and the formation of a carious cavity begins. At the third stage, the carious cavity covers not only the enamel, but also the dentin. At the fourth stage, the disease spreads even deeper and goes beyond the dentin.
Sources:
- bsmu.by
- kraszdrav.ru
- en.wikipedia.org
Causes of caries development
Oral disease develops under the influence of pathogenic microorganisms that multiply in a favorable environment. Dentists are of the opinion that the disease occurs due to changes in the acid-base balance on tooth surfaces. Fermentation of carbohydrates caused by pathogenic bacteria releases destructive amounts of organic acids.
The main factors that contribute to the formation of carious cavities:
- improper hygiene care;
- eating problems;
- systemic chronic or acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- reduced concentration of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- hereditary predisposition, etc.
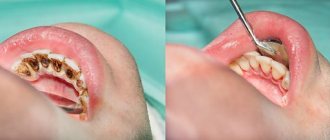
Bacterial plaque and tartar
Streptococci are microorganisms that live in organic acids, leading to the destruction of enamel and dentin. During brushing, soft structures are easily removed, but hardened structures cannot be removed. They also contain pathogens that cause destructive phenomena.
Poor nutrition
Every person knows from an early age that you can’t eat a lot of sweets. However, adults often ignore this rule and consume large amounts of carbohydrates, sugar, baked goods, and starchy foods. The enamel layer becomes thinner and more susceptible to external factors. Bacteria multiply better in a carbohydrate environment.
Decreased salivation
During the day, a person secretes about 2 liters of saliva. The secretion washes away food debris from dental surfaces and protects them from the negative effects of pathogenic microflora. If the salivary glands do not function well enough, a lot of food particles settle on the crowns, which the microbes feed on.
Violation of the mineral composition of enamel
This factor is directly related to diet. Demineralization is observed with a meager, monotonous menu, lack of calcium, phosphorus and fluorine. Seeds, cottage cheese, cheese, red beans, and buckwheat are rich in such microelements.
Genetic predisposition also influences mineralization. This means that the disease can be inherited from parents and other relatives.
The problem occurs in pregnant women at different gestational stages. The fetus takes all the useful minerals, and the expectant mother experiences a lack of them. Subsequent intervention is complicated by the inability to use anesthesia.
General diseases of the body
Systemic pathologies (especially chronic ones with periodic exacerbations) affect metabolic processes and, as a result, the proper absorption of vitamins and minerals. This applies to disorders such as hypoplasia and hyperplasia of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus, gastritis, stomach or duodenal ulcers, and hormonal imbalance. The body does not receive enough essential components, which contributes to the deterioration of the condition of hard tissues.
Poor environmental situation
This is not the main reason for the formation and development of caries in adults. However, there are cases when the patient is absolutely not predisposed to diseases of the oral cavity, leads a healthy lifestyle, eats right, regularly sees the dentist, but when moving to a locality with unfavorable conditions, he discovers deep damage to the dentition. This problem is typical for regions with hazardous production enterprises that emit heavy metal salts, acids, and alkaline vapors into the atmosphere.
Risk factors for dental caries
Caries occurs when, as a result of negative factors, the integrity of the tooth tissue is disrupted, after which it becomes susceptible to the action of acids in the oral cavity. Factors influencing the emergence of this process are divided into local and general.
Local factors include:
- Insufficient oral hygiene.
- Bite abnormalities.
- Presence of braces or dentures.
- Diseases of the dental pulp.
- Low degree of enamel mineralization.
- Lack of calcium or fluoride in the body.
- Smoking.
- Plaque deposition.
- Violations of the composition of saliva or its properties.
- Remains of carbohydrate food in the oral cavity.
Common factors include:
- Stress.
- Radiation.
- Poor quality of drinking water.
- Lack of vitamins.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Genetic predisposition to the disease.
- The presence of somatic diseases in a person.
Varieties
Depending on the symptoms and causes of dental caries, localization, systemicity, frequency of relapses, as well as other characteristics, the disease is divided into types.
Classification by intensity of spread:
- single (not accompanied by additional symptoms);
- multiple (systemic) – affects the entire series, new foci quickly appear, the body’s immune defense is weakened.
Types according to developmental complexity.
- Uncomplicated. Additional disorders have not been diagnosed, and there are no negative consequences with timely dental intervention.
- Complicated. Pulpitis and periodontitis appear. Therapy takes a long time and is difficult.
By stage of the process
Depending on the degree of neglect of the pathological condition, the disease is divided into successive stages.
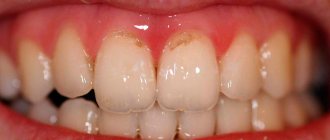
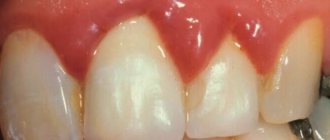
- Spot. Pale whitish or dark formations and stripes are visible on the surface. The patient is not in pain, he may not even notice any external changes when examining the oral cavity.
- Superficial lesion. The black or brown holes increase in size. Sensitivity occurs when consuming hot, cold, sour and sweet foods and drinks.
- Average caries. Dentin is destroyed. A person is in pain, unpleasant sensations are constantly present and do not depend on the time of day. Only installing a filling will help.
- Deep destruction. All layers rot, the pulp is affected. Experienced doctors can save the tooth by resorting to depulpation. It is often necessary to remove diseased units and subsequently install prostheses or implants.
By localization
This is a popular classification according to Black, according to which the disease is divided into classes depending on the location of the lesion and its depth.
- First. Erosion of the enamel occurs, the process reaches the dentin. At first, nothing is visible on the surfaces, but over time, slight pigmentation is visualized. In this case, you can do without preparation.
- Second. Chewing molars and premolars on both jaws are affected. The shade of the outer layer changes.
- Third. The front incisors and canines suffer. This problem is typical for those with a sweet tooth.
- Fourth. Dentin tissues are subject to severe destruction. Urgent medical intervention is required.
- Fifth. The most severe degree. All rows in the area of contact with the gums are affected. This is dangerous because the integrity of the dentin near the roots is compromised.
By frequency of occurrence
The disease may be detected for the first time. In some cases, an infectious process may develop directly under the filling material.
International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
Types of the disease, officially established:
- carious lesions of enamel;
- bacterial destruction of dentin;
- infection of the root system;
- suspended form;
- odontoclasia;
- other caries.
Prevention measures
As you can see, caries can be the result of many external and internal factors. You can reduce their effect on the body and prevent the development of the disease using preventive measures. Follow these guidelines:
- eat less sweets;
- brush your teeth at least 2 times a day;
- use oral irrigators;
- rinse your mouth after eating;
- Once every 6-12 months, carry out ultrasonic teeth cleaning;
- exercise and eat right;
- Visit your dentist every six months for a check-up.
Today, caries can be successfully treated, but if this disease is neglected, you can lose one or more teeth. Prevention should be practiced from childhood, and when the first signs of the disease appear, you should immediately make an appointment with the dentist.
Symptoms
The rate of growth of signs primarily depends on why caries occurs, holes are formed, and the inflammatory process develops in the neurovascular bundle. The most common symptoms of carious lesions:
- darkening of the enamel, the appearance of dots or stripes of a white or dark shade on it (typical of the initial stage);
- increased sensitivity when consuming certain categories of foods (sour, sweet, hot, cold, hard); pain when pressing on the diseased area or in the absence of mechanical action;
- deep black holes, cracks in hard tissues;
- bad breath;
- headache, shooting sensation in the ears.
Diagnosis of dental caries
In some cases, the patient can independently diagnose himself, based on characteristic signs such as the presence of black holes and pain. However, there are situations when only a competent specialist can detect a lesion. This applies to the initial stage of the pathology in the absence of severe symptoms. At later stages, a thorough examination is also important in order to correctly differentiate the pathological process from other disorders.
The main methods used in dentistry:
- visual inspection using a mirror and other tools;
- computer images (panoramic, radiovisiography, CT, 3D study);
- functional diagnostics;
- thermal test;
- probing.
Dentik uses modern X-ray machines with safe radiation exposure and other equipment. We examine adult patients, women during pregnancy and lactation, and small children.
Social factors
Social factors in the occurrence of caries are:
- Nutrition. Frequent snacking on sandwiches, eating sweets and soda contribute to the formation of carious cavities in teeth.
- Profession. People who work in factories that produce alkalis, acids and other chemicals are more susceptible to tooth decay. This group also includes pastry chefs who taste their dishes while cooking.
- Age. The risk of caries in children from 2 to 11 years is 60% higher than in adults. This is due to low immunity and poor hygiene.
- Floor. Research shows that enamel deteriorates more often in women. Doctors attribute this to hormonal changes, pregnancy, lactation and other factors characteristic only of the female body. Thus, during breastfeeding, there is a decrease in calcium and fluoride levels, which can lead to caries.
- Racial origin. According to statistics, people with white skin are more likely to visit dentists with caries than representatives of the Negroid race. Moreover, this pattern persists even if they live in the same territory.
Social factors include the culture of food consumption. So, in the USA, people often eat incorrectly. In this country, tooth decay is a very common problem: 99% of the population suffers from it to one degree or another.
Methods of treating the disease
If the doctor was able to determine why a person has dental caries, he will be able to develop therapeutic tactics and help him recover quickly. In the early stages, the problem can be eliminated non-invasively, that is, without the use of a drill. If the lesions are deep, drilling and medical treatment cannot be avoided.
Traditional methods will not help in the fight against the disease. But home recipes show an excellent effect as part of complex therapy to consolidate the results and prevent relapses.
Conservative treatment without preparation
At the initial stage of infection, the dentist will not drill crowns. The doctor will carefully remove plaque and tartar, and then apply a special composition to mineralize the enamel. The procedure lasts about an hour. Procedure:
- visual inspection;
- gum isolation;
- removal of deposits;
- application of remineralizing solutions.
If all manipulations were carried out according to the rules, the pathological process will stop. No additional methods are required.
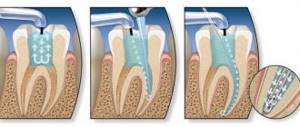
Treatment with preparation of hard tooth tissues
Severely affected dental units can only be cured by mechanical removal of the diseased areas. The stages of intervention depend on the stage of the disease, usually as follows:
- use of anesthesia or other pain relief option;
- drilling;
- application of medications (antibacterial, etc.);
- installation of a protective gasket;
- restoring the integrity of the crown (filling);
- correction of the shape of the filling;
- grinding and polishing.
With deep lesions, the risk of pulp involvement increases. It is better to take a targeted photograph of the dental unit and make sure that there is no or no inflammation.
In severe cases, depulpation (extraction of the nerve and cleaning of the canals) and extraction (tooth removal) are indicated. These are extreme measures that are resorted to at the very last moment.
Clinical researches
Asept toothpastes are distinguished by their clinically proven effectiveness - the products have been repeatedly tested. As part of the tests, it was found that:
- regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA ACTIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 60%, improve the overall condition of the oral cavity by 44% and reduce inflammation by 33% (research);
- Regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA SENSITIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 62%, reduce sensitivity of teeth and gums by 48% and reduce inflammation by 66%. (study);
- regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION after 4 weeks improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% (study);
- Regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA GENTLE WHITENING for a month allows you to lighten tooth enamel by 1.5 tones, increases anti-caries effectiveness by 3.4 times and increases enamel remineralization by 2.6 times (research).
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” COFFEE and TOBACCO Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky. First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Table of contents
- Causes
- Clinic
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
Causes
The hard tissues of the tooth are unable to recover, or this ability is very limited. There are no living cells in the enamel; they die immediately after the crown is formed, immured in the dense products of their vital activity. This is due to the amazing hardness of the enamel, which is superior to the cortical substance of the bones. Dentin is able to partially recover because it contains tubules - processes of pulp cells that supply the tissue with nutrients. The dental cement surrounding the root regenerates less well, but also receives nutrition by diffusion from the periosteum.
Considering the above, it is clear that it is easy to destroy a tooth, and you should not hope for natural regeneration. But teeth can last for decades with proper care and consumption of healthy foods. Fluorides play an important role in protecting against damage. Tiny fluoride ions are packed into dense structures. Any material containing them benefits from resistance to physical and chemical influences. For example, fluoroplastic is the strongest and most refractory type of plastic. In dental tissues, fluoride is combined with calcium and phosphorus, forming microscopic enamel prisms. The functions of “reinforcement” are performed by collagen fibers, once formed by living cells.
Under the influence of aggressive substances, especially acids, fluorine is gradually lost. Toothpastes contain fluorides, which replenish the deficiency of this element. Fluoride saturation is an even more important task when brushing teeth than mechanical plaque removal. Modern formulations also include antiseptics, so the paste has a “three-component” effect. And you can’t skimp on its quality.
Acids are found both directly in food and are formed by bacteria that have settled in the oral cavity. Some types of microorganisms and their combinations are more harmful than others. Microbes feed mainly on sugars, so sweet foods lead to rapid growth of microflora in the mouth. It may be enough to chew sweets for a few minutes to feel how noticeably the thickness of plaque on your teeth increases. It consists mainly of bacteria. People with a sweet tooth put their teeth at great risk. The proliferation of microbes in the periodontal pockets of the gums can also cause periodontal disease.
The surface layer of enamel depleted of fluoride is vulnerable to acids and enzymes. The tissue irreversibly loses its protective properties, softens, bacteria settle in it, and the damage spreads deeper. The flow of fluoride into dentin through the blood vessels should also be sufficient, although an excess of this microelement is harmful and causes fluorosis.
The hereditary factor is important in the occurrence of caries. Some people have naturally stronger enamel than others. Its characteristics are determined genetically and are inherited.
The condition of teeth is influenced by the endocrine and immune systems. In particular, excess corticosteroids are harmful. Many patients experience emotional upheaval, which is accompanied by the release of adrenaline into the blood.
IMPORTANT: If you have a congenital tendency to caries, you should protect yourself from unnecessary emotions and try not to get nervous in difficult situations.
Clinic
The earliest stage of caries is a spot, or precaries. The damaged area is better visible with special lighting or under a microscope. The enamel changes color, becomes dull and matte. Instead of a smooth glossy surface, a rough area appears. At the stage of a carious spot, the disease is easiest to stop. Even a complete cure is possible, without replacing the defect with a filling.
The spots are white and pigmented, but there is no clear sequence in their color changes. The color of the grooves on the surface of the tooth depends more on the diet and composition of the microflora. Darkening is not necessarily a sign of tooth decay. On the other hand, even the deepest and most aggressive caries can be completely white. With the rapid progress of the disease, a color change will most likely not have time to occur.
As the damage progresses, a “hole” or caries itself appears. Based on the depth of tissue damage, dentists distinguish between superficial, medium and deep. The superficial affects only the enamel, the middle penetrates into the dentin, the deep reaches the pulp with the formation of a through channel.
Dental classifications also distinguish different types of caries according to the location of the carious cavity in the tooth. It can be located on the chewing surface, on the side - buccal or lingual, and also between the teeth. In the latter case, the prognosis is the worst: it is impossible to reach the cavity from the outside with instruments; food is packed in there, which is difficult to remove with a brush. The patient does not see caries in the mirror, does not feel it with his tongue, and consults a doctor late.
Dentin is sensitive, and when “rotting” (as caries is translated from Latin) reaches the processes of the pulp cells, a person feels pain. Painful sensations intensify at night, when there are fewer other irritants. The tooth hurts from the cold, and later hot drinks or food painfully “go” deep into it. Sugar and acid are very irritating to dentin.
With caries, a persistent unpleasant odor from the mouth appears early. The quality of life deteriorates noticeably. If you do not get rid of the disease in time, serious complications are possible: pulpitis, purulent damage to the tissues surrounding the tooth, and even sepsis (blood poisoning).
IMPORTANT: You need to contact a dentist when caries is first noticed visually or tactilely. You should not expect any pain to occur.
Diagnostics
The first examination that the doctor conducts is an examination of the patient in the dental chair. Given the superficial nature of the disease, almost all carious cavities are revealed. It is more difficult to determine how deep they extend. Even rarefied hard tissues do not allow the probe to pass through, and the patient’s sensations are not enough for diagnosis. Therefore, X-rays are now almost always taken. Only obvious superficial caries allows you to do without x-rays.
Any serious clinic has its own equipment. Pictures are usually taken in a lateral view. Only part of the patient's head is exposed to minor radiation; other organs are often covered with a lead vest just in case. Teeth contrast well with soft tissues, so long exposure to a radiation source is not necessary.
The photographs determine the number, shape and location of defects, and evaluate the condition of adjacent tissues (presence of inflammation, mineral deposits). In people with “bad” teeth, it is necessary to determine which of them is affected - the one pointed out by the patient, or the neighboring one. Tapping on the tooth also helps in differential diagnosis; the patient experiences unpleasant sensations. It is most difficult to detect caries that are hidden under a filling, or that have developed in a dead tooth with the pulp removed.
Treatment
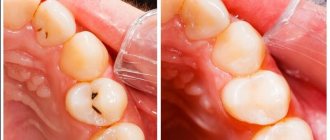
At the stain stage, the enamel is remineralized with a special solution. It works faster and more reliably than regular teeth cleaning, the effect is almost 100%. Another treatment method used in children is fissure sealing. Deep grooves in teeth are covered with filling materials. On permanent teeth, you can subsequently remove the excess layer if it interferes with the correct formation of the bite.
If there is a pronounced defect, it must be replaced. For this, filling is used. There are no drugs yet that stimulate the growth of natural tissues, although developments in this direction are underway. For fillings, substances are used that are foreign to the human body, but mechanically adhere well to dentin, cement and enamel.
Several generations of popular filling compounds have changed. Simpler mineral and synthetic ones have been replaced by ultraviolet-curable ones. The filling hardens quickly when a beam of light from a UV lamp is directed at it.
But first you need to remove the softened dental tissue. They are no longer viable, the filling will not hold well on them, and a relapse of the disease is possible. Superficial caries is usually prepared without anesthesia. For medium and deep cases, conduction anesthesia is performed - with access to the nerves passing in the jaw canals through natural openings in the bones.
The tooth is drilled with a metal or diamond bur. Having prepared the walls of the cavity, it is washed with antiseptics, dried, and filled with a filling compound. When it hardens, no liquid (saliva) should come into contact with the surface. You will have to sit very carefully in a chair with your mouth open for several minutes. The doctor covers the mouths of the salivary glands with cotton swabs. To avoid excessive drooling, it is advisable to come to the doctor on a full stomach. People who are prone to excessive salivation can, on the advice of a dentist, take a medicine that blocks the parasympathetic nervous system.
In severe cases, the pulp is removed from the living tooth, the root canal is prepared and pins are inserted. If the crown is excessively damaged, dentures are attached to pins. If there is still a lot of enamel and dentin left, you can restore the shape of the crown using a filling made of a special material. In any case, pulling teeth due to caries is an outdated and barbaric method. After this, only implantation or bridge installation is possible, which is much more difficult and expensive.
IMPORTANT: If the patient has experienced allergic reactions to injection anesthetics, the dentist must be informed about this in advance.
Prevention
Caries will not affect teeth if:
- reduce consumption of flour, sweet and sour foods;
- end the meal with foods that “clean” your teeth;
- rinse your mouth thoroughly after each meal;
- brush your teeth 1-2 times a day, depending on your diet;
- choose the right toothpaste and change your brush more often;
- remove tartar in a timely manner and seal fissures;
- visit the dentist for preventive maintenance every six months.
Children should not be deprived of sweets. Glucose is important for brain development, connections between cells of which are most intensively formed at 5 years of age. In addition, babies' baby teeth will still fall out. But you need to teach them to clean them early. Fruits and vegetables should be introduced into the diet as soon as the child is ready to chew them. Parents should lead by example and gently encourage their children to eat healthy foods.