From this article you will learn:
- why is the gum around the tooth swollen,
- The gum is swollen and hurts - what to do.
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
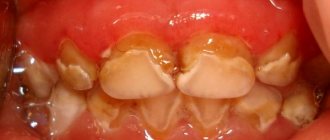
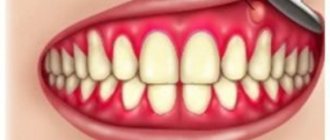
If your gums are swollen, what to do in this case will depend on the cause of the inflammation. There may be two main reasons. The first reason is associated with the development of periodontitis, i.e. inflammation at the apex of the tooth root (Fig. 1-3). The development of inflammation is associated here either with poor-quality dental treatment in the past, or with the lack of timely treatment. And in this case, you can always find a carious defect, filling or crown on the causative tooth.
The second reason that the gums are swollen and painful may be the development of localized or generalized forms of periodontitis in the patient. With these forms of gum inflammation, the attachment of the gingival margin to the neck of the teeth is destroyed - with the formation of so-called “periodontal pockets” between the gum and teeth (Fig. 4-6). In such gum pockets, good conditions are created for the growth of bacteria, which can also lead to the development of purulent inflammation in the gum pocket and the appearance of gum swelling.
Swelling of the gums due to periodontitis –
Swelling of the gums due to periodontitis -
A separate question in this article is what to do if the gums near the wisdom tooth are swollen. Most often this occurs in the lower jaw, and in this case the swelling of the gums is not associated with either periodontitis or periodontitis. This inflammation of the gums is called a special term - pericoronitis (which means inflammation of the “hood” over the wisdom tooth).
Causes and symptoms of periodontitis
Inflammation of the periodontium, the tissue that supports the tooth, often leads to swelling of the gums. This condition may be caused by the following reasons:
- Penetration of infection into bone tissue through the dental canal. This usually happens when caries is left untreated.
- Transfer of inflammation from other organs. This is possible with throat diseases or sinusitis.
- Damage to the periodontium as a result of a sharp physical impact, such as a blow to or near a tooth.
- Penetration of irritating substances into the periodontium. This is possible due to improper or unskilled dental treatment.
- An immunological reaction as a consequence of an allergy. Quite a rare occurrence.
Symptoms of periodontitis:
- Periodontitis
swelling occurs on the gum in the area of the problem tooth;
- pain is felt when pressing on or near a tooth;
- temperature rises;
- the tooth does not react painfully to sweets, as well as cold or hot water;
- the gum swells until a whitish fistula appears, followed by a breakthrough and leakage of pus.
Not all symptoms of this disease may appear at the same time. A decrease in gum swelling due to a breakthrough of pus is not a reason to ignore visiting a doctor. Inflammation of bone tissue is a very dangerous process that must be cured, otherwise it will cause serious complications.
The permanent course of the disease leads to constant intoxication of the body and can serve as a catalyst for diseases of the internal organs.
forums about dentistry on zub-zub.ru
Hello. The school installed seals. A few years later I decided to check what and how. I went to the dentist and they said that I have caries. When they opened the tooth, it turned out that it was also periodontitis (or something like that. I don’t understand this at all. And I don’t use medical terms. So I’ll apologize right away) The tooth was opened, cleaned and put on medicine (as I understand it, to kill the nerve ). Then they sealed it. They gave me a ticket for my next appointment.
And recently I noticed that the gums around this tooth became soft. I looked and there was a small white soft spot there. Looks like pus. Which starts right from the place where the tooth (filled) connects to the gum. This is exactly what interests me. What it is? How dangerous is this? And will they remove my tooth? And at least know roughly what awaits.
Lesya Chief Consultant Messages: 5457 Registered: Mon Apr 23, 2007 21:04 From: Moscow
Good evening. Let's take it in order. You correctly wrote the diagnosis - periodontitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the tissues at the apex of the tooth root, due to the fact that at one time the root canals were not filled. With this disease, before placing a filling, it is necessary to treat the canals. To do this, they need to be cleaned and often sealed temporarily with a special seal. medicine, and only then (after 10-30 days) can it be filled permanently. This is a generally accepted technique. I cannot say what was done in your case.
and there turns out to be a small white soft spot. Looks like pus.
This is very similar to a fistulous tract through which pus is released. If this is the case, then you need to take a picture of the tooth and understand why this is happening. If your canals are filled with temporary paste, then it’s okay. This is a normal aggravation. This happens during the treatment process. You just need to see a doctor. And he will tell you what to do. If the canals have already been permanently sealed, the situation is worse. We need to look, everything will depend on the x-ray. But in any case, there is no need to remove the tooth yet. Treat anyway. If you are being treated at a local clinic, you will be offered removal. Do not hurry. In a good clinic, with modern materials and techniques, you can try to save this tooth. Something more specific can only be said by seeing your dental x-ray.
Lesya Chief Consultant Messages: 5457 Registered: Mon Apr 23, 2007 21:04 From: Moscow
Good evening. I had to zoom out your photo a little. At the same time, I showed with arrows the position of the filling in the canals. My personal opinion: the root canals (especially the anterior ones) are not passed along the entire length and are not sealed. This means the infection is still there. Even the image shows a widening of the periodontal fissure, which indicates chronic inflammation. For good measure, the canals need to be re-treated, preferably with the use of medicinal intermediate pastes. If this is not done, then the tooth will subside for a while, the fistula will close and everything will apparently be normal. But that's it until next time. If there were no signs of periodontal inflammation on the gums, then we could limit ourselves to such a filling. But this is not the best option. The canals are not sealed to the top. Any doctor will tell you this. What to do is up to you. Just one piece of advice: If they offer to put a crown, don’t rush. If a tooth starts to hurt with a crown, you won’t be able to get to the canals without knocking off the crown. Which will then be miscarried.
Read also: Gums bleed, how to treat them
Bronka Site Consultant Messages: 75 Registered: Mon Apr 23, 2007 22:24
Manifestation of acute gingivitis
If the gums are swollen, but the tooth does not hurt, then the patient is developing gingivitis or periodontitis. These processes are characterized by inflammation of only the tissue around the tooth. Periodontitis usually has a chronic course with periodic exacerbations, and gingivitis often occurs in an acute form. The reasons for exacerbation of pathologies and subsequent swelling of the gums are as follows:
Gum tumor due to periodontitissystemic inflammatory diseases of internal organs;
- colds;
- diabetes;
- decreased immunity due to illness or medications such as corticosteroids;
- entry of foreign bodies;
- presence of tartar;
- injuries, cuts and punctures of soft tissue.
Periodontitis in the picture
Pain can be present both near a certain group of teeth and throughout the jaw. Other symptoms of these diseases are:
- the gums swell, acquiring a bright red color with a bluish tint;
- the problem area hurts greatly with any pressure;
- there is swelling around the tooth with partial closure;
- Gums bleed at the slightest pressure.
With periodontitis, there are changes in the bone tissue, visible on an x-ray: the interdental septa become lower. It is also possible that the tooth root may be exposed.
With such diseases, symptomatic treatment of gum inflammation will not lead to recovery. To eliminate the problem, comprehensive measures are required under the guidance of an experienced dentist. In advanced cases, it can lead to the formation of an abscess.
Diseases leading to periodontal bleeding
If even the slightest signs of a disease appear in the oral cavity, you should immediately contact a dentist. The doctor will help you identify the problem in time and prescribe proper treatment.
Gingivitis
Catarrhal gingivitis
Inflammation occurs without destruction of the periodontium, due to the influence of local and general factors. A special role is played by bacteria that accumulate on the surface of soft tissues, causing swelling, soreness, unpleasant odor, itching and burning.
In case of catarrhal gingivitis, patients note a disturbance in the sense of taste. The pain reaction intensifies with exacerbation of the disease and during brushing. General health usually does not suffer, but in the acute phase, some develop low-grade body temperature.
Catarrhal process is more common during teething or due to abundant dental deposits in the form of stones. This form can be complicated by ulcerative lesions.
In this case, the following symptoms are revealed:
- swelling of the gums;
- hyperemia;
- the presence of ulceration on periodontal tissues;
- bleeding and inflammation;
- severe pain, especially when brushing teeth and eating;
- increase in body temperature to 37-38 degrees.
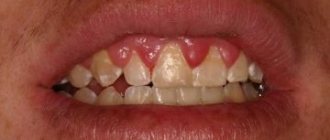
Periodontitis
Periodontitis on the upper and lower jaw
When gums bleed and become swollen, it may be a sign of a more serious condition than gingivitis. With periodontitis, so-called periodontal pockets are formed.
They are a specific formation between the root of the tooth and the marginal gum. Their sizes range from small depressions to large-scale destruction. Upon examination, discharge of purulent exudate is usually detected.
As the process progresses, the teeth begin to loosen, and the lack of further treatment leads to their loss. The shape and color of the gums in this disease are greatly changed, the pain is significant even without exposure to irritants. There is a sharp unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
Periodontal abscess
Sometimes, when examining the problem area, it is clear that the gum is not completely swollen, but there is a semicircular formation, often pale in color. By comparing the appearance of the tumor with a classic photo of an abscess, you can easily identify it.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of an abscess, but it usually occurs during periodontitis, when pus cannot break through the area of inflammation for a long time. Also, local inflammation can be caused by a festering deep wound on the inside or outside of the gum.
A diagnosis of an abscess is made with the following symptoms:
Periodontal abscessthere is a characteristic semicircular formation with an elastic, stressed surface;
- red swelling of the surrounding soft tissue;
- when pressed, fluid movement inside the inflammation zone is felt - a symptom of fluctuation;
- the cheek was swollen and the palate was swollen;
- temperature rise is possible.
Treatment of an abscess is carried out by opening the abscess and prescribing a number of analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs. The procedure itself is not too complicated and painful (taking into account anesthesia), but you cannot do it yourself at home. This is due to the need for high-quality disinfection of the resulting wound. The doctor must also determine the cause of the accumulation of pus and, if periodontitis or periodontitis is detected, treat it.
If treatment is delayed or after it is carried out unqualifiedly (on your own in unsanitary conditions), complications may develop. The formation of phlegmon as a result of pus breaking through the skin or into the intermuscular space will lead to the need for a serious surgical operation, including removal of pus through facial incisions on the outside.
Other causes of inflammation
In most cases, prolonged swelling is caused by the factors described above, but there are other reasons why gums may become swollen. The easiest way to identify the dental prerequisites for the problem is:
- Stomatitis. In advanced cases, swelling appears before the appearance of ulcers.
- Eruption of wisdom teeth in adults and molars in children. A gum tumor forms above the tooth.
- Incorrect installation of fillings, veneers or braces. Constant exposure to the tissue quickly causes it to swell at the site of irritation.
- Physical injury in the form of a puncture or cut. Inflammation of the wound may not begin immediately, but at a time when the patient may no longer remember its existence.
- If the gums near the tooth swell after treatment, this may be the result of physical damage or an allergic reaction to medications or an anesthetic injection.
It is much more difficult to determine the reasons why your gums are swollen if they are not directly related to dental problems. Inflammation in the mouth here is only an indicator of a serious problem in the body. Diseases such as AIDS, hepatitis and diabetes reduce the body's immune response to bacteria, which causes inflammation at the slightest tissue damage.
The cause of gum swelling can be the herpes virus. With an atypical course of sore throat, the infection can also spread to the gum tissue and cause it to swell.
A severe lack of vitamin C can also cause swelling. Although now it is difficult to imagine the development of vitamin deficiency to such an extent, given the availability of fruits, vegetables and multivitamins on the open market.
Reasons: why the gums near the wisdom tooth become inflamed when it comes out
Remember the symptoms with which a six-month-old baby starts teething for the first time. Things are somewhat better for five- and six-year-olds. But in both cases, the same painful process occurs - the dental plate literally tears, injures the mucous membrane in order to erupt and come out. All this can cause pain, inflammation, and itching. Children are prepared for this procedure, while an adult experiences everything much more difficult, because over 20-30 or more years of life a person could have suffered many dental diseases, which only add to the difficulties.
In addition, the oral cavity is more likely to contain pathogens that spread due to food debris and bad habits. And bacteria can cause suppuration and intensify the infectious process.
The main reasons why gums hurt due to wisdom teeth are:
- Physiological structure of the jaw plate.
- Various diseases and pathological conditions.
Let's take a closer look at the factors and possible pathologies.
Atypical growth of the third molar
Most often, doctors encounter a situation where the figure eight erupts in the wrong direction. That is, it tends with its upper end not upward, but to the side. Thus, it “squeezes” the closest neighbors, and also pinches the nerve endings, leading to a shift in the entire row and even to malocclusion in cases where no measures were taken.
There are two types:
- Sloping location. During this process, the bone formation compresses the facial nerve and irritation occurs not only of the mucous membrane, but also of the cheeks or even the neck. The patient may mistakenly localize the pain as throat pain or confuse the symptom with an ENT disease.
- Horizontal. Even more dangerous, since the molar can compress the root system of the nearest “seven”, causing damage to the nerve endings and cutting off blood flow. All this will most likely lead to the destruction of the 7 and major inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth.
The occurrence of pericoronitis
This term refers to the appearance of a gum “hood” that covers part of the bone tissue. Food particles accumulate under the formed fold, creating an ideal environment for the development and spread of bacteria. Suppuration forms in the lesion, which leads to swelling, swelling of the area, bad breath and the release of purulent exudate when pressed. The latter does not always happen, since often the fold remains tightly closed.
There are several reasons for the occurrence of pericoronitis, including:
- Not enough space on the jaw plate.
- The dental sac is very dense, making it difficult to cut through.
- Thick mucous membrane, which also prevents successful rupture.
Additional symptoms include pain when chewing and swallowing food. With such a pathology, but the correct direction of growth, dentists most often make an incision in the skin fold and sanitize the area with the complete elimination of pus and other signs of infection.
Inflammation of the tissues of the wisdom tooth due to gum disease
Often the “eight” erupts painfully. The back of the jaw begins to hurt and bleed. The most common diseases that occur in patients:
- Gingivitis – the marginal area of the gum, as well as the entire mucous membrane, is subject to an inflammatory process.
- Periodontitis – the surrounding tissue structures are destroyed, which leads to poor stability of the dental plates. They may begin to loosen, and if the disease is serious, they may even begin to fall out.
- Periodontal disease is a severe lesion of the periodontium, which is located near the root.
In all of these cases, the most common symptoms are:
- Swelling.
- Bleeding.
- Pain.
- Redness.
The nearby third molar begins to grow, affecting the affected mucous membrane and nerve endings, provoking even greater pain, which can be accompanied by the appearance of a tumor and even suppuration. When treating, it is necessary to first pay attention to the root cause.
The gums under the wisdom tooth hurt due to caries
In this context, we are not talking about the teething itself, but about the further development of the “eights”. They, like other rows, can be subject to carious changes. This is a long process that develops due to the action of pathogenic microorganisms and additional unfavorable factors. It passes slowly and leads to disruption of the integrity of bone tissue. Cavities are formed, the expansion of which can cause a lot of inconvenience, as well as expose nerve endings. Therefore, caries-prone molars are usually removed. They are healed only in cases where they are planned to be used in the future to install implants.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Its structure is branched and literally covers the entire face, dividing into three bundles:
- ophthalmic;
- maxillary;
- mandibular.
During the eruption of the 8, pinching or squeezing, or irritation may occur. This also happens when the dentition moves apart (horizontal atypical growth), and at the time of extraction. Usually the pain is very strong, shooting. And its localization depends on what exactly was pinched.
When to see a doctor
If your gums are swollen and it hurts a little, you don’t have to see a doctor right away. This is especially true in cases where the cause can be clearly determined independently. If the gums are slightly swollen in the first 3 days after treatment or tooth extraction, then this is a normal reaction of the body. The same applies if the gums are swollen and hurt at the site of the eruption of the wisdom tooth.
There is no need to urgently treat the gum if its area is swollen as a result of injury from a toothpick, fish bone, or other sharp object. But this all applies to “clean” wounds without complications.
Urgently seek medical help in the following situations:
There is a smell from the mouth, there are taste sensations characteristic of purulent discharge.- The gums are swollen so much that there are problems with eating, or the cheek is apparently swollen.
- When there is a rush of blood, a feeling of heaviness occurs as a result of tilting the head.
- The gums are slightly swollen, but this condition lasts longer than three days. It is better not to wait for suppuration to occur.
- The color of the tumor differs from the color of healthy tissue located near the swelling. Burgundy and bluish color indicates stagnation of blood, yellowish and whitish - a purulent process.
- The temperature has risen.
- It is not possible to relieve the pain, or it is pulsating.
- It is not possible to establish the reason why the gums are swollen or the cheek is swollen.
If your gums are swollen, then you need to go to the dentist for treatment. If the causes of swelling are not related to diseases of the oral cavity, then symptomatic treatment will be prescribed to relieve pain and exclude the development of complications, and the therapist will determine the etiology of the disease.
Reasons for using a temporary filling
The main reason is treatment or removal of the nerve. In the center of the dental bone there is a small collection of nerves, which is a connection between bone tissue and blood vessels. Inflammation of this collection of nerves is called pulpitis. Inflammation occurs due to advanced caries, which has “reached” the nerves. Severe pain and infection of other adjacent tissues in the oral cavity are the consequences of this disease if treatment is refused. The treatment concept involves removing the nerve, installing a temporary filling, and replacing it with a permanent one a few days later.
Treatment concept in removing a nerve from a tooth
Deep caries is another important point. Caries is an iceberg that looks like a small black dot from the outside, but when excavated you can find a fairly large affected area. After removing caries and diseased tissue, a temporary filling is placed, because it is almost impossible to determine immediately whether the dentist has gotten rid of the entire problem. Therefore, temporary filling is done. A week or two later, the patient comes to the clinic for a recheck, because a relapse is possible. If everything went well and no further infection is observed, a permanent filling is placed.
If a cyst is found. When infected foreign bodies enter the soft tissue of the root area, a cyst is formed. In order to penetrate the cyst, it is necessary to remove the accumulated fluid in this place and thoroughly disinfect the affected area. If this is not done, after some time the appearance of a new cyst is inevitable. Treatment occurs in several ways. Several stages of treatment include the introduction of a temporary filling, which at the last stage is replaced with a permanent one.
Drug treatment
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of inflammation. Depending on the type of problem, the dentist may perform dental treatment, open the abscess, or perform other surgical procedures in the mouth. He will also prescribe medication using antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
An antiseptic fights pathogenic organisms that lead to inflammation. Since gums swell as a result of exposure to various bacteria and microbes, an effective drug can only be prescribed by a qualified specialist.
It is not recommended to treat yourself with antiseptics; you may make a mistake. Choosing the right remedy is difficult due to the existence of restrictions on the combined use of certain drugs. This is especially true for antibiotics.
Anti-inflammatory drugs quickly remove swelling, which helps get rid of pain and improve a person’s general condition. These drugs are classified as symptomatic treatment, so you can choose them yourself. The only condition is the absence of an allergic reaction to the components of the medicine.
Since the local area is susceptible to inflammation, ointments are usually used to relieve it. They are applied around the tooth where the gums are swollen 3 times a day after meals.
Stomatitis
If the white spot on the gum has a dense coating that cannot be removed, then it is more likely that it is stomatitis, when the oral mucosa becomes inflamed. The mechanism of occurrence of the disease has not been reliably established, but most doctors attribute it to an immune reaction to irritants that affect the oral mucosa.
Lymphocytes attack unidentified particles, which is why first areas with a white coating appear in the mouth, and then painful ulcers in their place. Swelling of the mucous membrane is also observed. Hyperthermia and pain are likely to occur. \
White spots can appear from:
- bacterial or viral infection;
- mechanical damage to the mucosa;
- vitamin deficiency;
- poor quality or poorly installed dentures.
Due to stomatitis, salivation decreases: due to dehydration, taking specific medications, or excessive oral hygiene. Stomatitis requires treatment prescribed by a doctor, only then will you be able to get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
Treatment at home
By using traditional medicine together with drug treatment, you can quickly relieve swelling at the site of inflammation, get rid of severe pain and better perform antibacterial and antimicrobial treatment of the oral cavity. If the gums are swollen, treatment at home is carried out in the following ways:
Gargling with herbal decoctions. Usually they use calendula, sage, lemon balm, St. John's wort, and chamomile. The main contraindication is allergic reactions to specific herbs. The purpose of the procedure is to disinfect the affected gum area.- Rinse your mouth with diluted propolis tincture. This method of treatment has a complex therapeutic effect in the presence of accompanying diseases of the ENT organs, such as sinusitis or tonsillitis.
- Rub honey into the gums around the tumor using a soft brush. This relieves pain, softens the tissue and prevents the formation of scabs.
- Lubricating the gums with vegetable oils using a soft brush or bandage. Olive and fir oil are used. Effective for inflammation of the gums above the wisdom tooth.
If your gums are swollen, you can rinse your mouth with a solution of salt and soda . To prepare it, dissolve one teaspoon of each component in a standard glass of water. You need to rinse your mouth after eating. The product gives a good effect when it is necessary to heal wounds and stop bleeding.
It is strictly forbidden to heat the gum, both when it is slightly swollen and when it is very swollen. This reduces the level of pain, but contributes to the intensive reproduction of pathogenic organisms.
Using an irrigator to combat swollen gums
To reduce swelling, using an irrigator is effective . This device is gradually coming into user use despite the fact that it was created back in 1962.
The irrigator supplies water under high pressure, which allows not only to clean hard-to-reach surfaces of teeth, but also to influence soft tissues. This device was originally designed to clean interdental spaces. But, at the same time, massaging the gums with a stream of water can restore blood circulation in the affected area. This will promote rapid regeneration.
Indications and contraindications for use
An irrigator is recommended for almost every person; it is the same hygiene product as toothbrushes and toothpastes. The device is an addition to basic oral care. For people suffering from gingivitis and periodontitis, irrigators are the best choice, especially if there is pain and using a toothbrush becomes impossible.
Among the contraindications, doctors identify:
- Acute forms and exacerbations of chronic forms of gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Conditions after surgical intervention on oral tissues. Irrigation with water prevents the formation of a blood clot, and accordingly, wound healing is very slow.
How to use an irrigator for gum swelling
Before use, you must clean your mouth with a toothbrush and paste. Fill the tank only with filtered water. Then start cleaning with an irrigator.
The device must be held at a right angle. Starting with the least pressure, treat the gums near each tooth; it is better to start with the teeth of the upper jaw. The total procedure time should not exceed 10-15 minutes.
If bleeding occurs after using the irrigator, contact your dentist, he will help you choose the mode that suits you.
Which irrigator is best for getting rid of tumors in the gums?
For those who are still thinking about purchasing, you should pay attention to irrigators from the German brand ACleon . The devices produced are quite simple to use, so they are convenient to use even for beginners. The reasonable price makes them accessible to absolutely everyone. In addition, German quality guarantees a long service life of the irrigators.
The company produces two types of irrigators:
- Stationary (ACleon TF600);
- Portable (ACleon TF200).
Stationary irrigators of this brand have a number of advantages:
- They have a built-in ultraviolet lamp, which is designed to disinfect nozzles.
- Each area has its own specific nozzle. There are 7 of them in the set.
- 17 modes allow you to select the optimal jet pressure.
- The water tank has a capacity of as much as 600 ml.
This type of device is convenient to have at home, because it works from the network.
Portable irrigators, in turn, are attractive because:
- They take up little space and are convenient to take with you. Their weight is only 250 grams. The manufacturer took care of the buyer and also included a case in the set.
- Compared to other portable devices, this one has a power of up to 750 kPa!
- Work occurs without a network connection. The battery capacity lasts a long time.
- The water tank has a capacity of 200 ml.
Swollen gums after tooth filling, gums and cheek become swollen and inflamed
2 April — 17:37 #2
If your gums (cheek) are swollen, there is redness or pain, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible to use an x-ray to check whether the canal (or canals, depending on which tooth) has been refilled, i.e. whether the filling mass went beyond the apex of the root when filling it. If this happens and the reaction described above occurs, then you need to correct the situation immediately, because in the future, an abscess may form (in other words, a flux), which will need to be opened by cutting the gum and drainage installed for some time. In addition, you will have to open and clean the canals, treat the inflammatory process and fill them in a new way. In your situation - the inflammatory process, apparently, has already begun - run to the dentist#33;
4 April — 13:11 #3
This is an inflammatory reaction to the filling material. It is necessary to urgently remove the irritating factor and sanitize the tissues by rinsing with a local antiseptic solution, and after the inflammatory phenomena have subsided, fill the tooth using another method.
4 April — 13:18 #4
And there are also cases when doctors, due to inexperience or carelessness or due to the lack of a dental X-ray machine, do not find one or two canals in a multi-canal tooth (since the number of canals in certain teeth is not always standard). They fill only those canals that they find, then they fill the tooth and send the patient home, at best, warning him about possible phenomena and the possibility of contacting their clinic again if something happens. Meanwhile, bad bacteria multiply in the unsealed canal, which leads to the accumulation of pus in the tissues of the tooth and gums, which can manifest itself with the symptoms described above. There is only one way out - go to the dentist (possibly another one) - find and eliminate the cause.
5 April — 23:41 #5
Today, the most advanced method for checking and diagnosing problems with canals is computed cone beam tomography, which provides a three-dimensional image of the tooth. It is advisable to find a clinic where a 3-D tomograph is installed and be examined.
Most likely you treated a tooth in which the pulp (nerve) had long since died. As a result of long-term chronic exposure to microflora, inflammatory tissue has formed, which, with therapeutic intervention, can aggravate the process. In the future, a fistula may form. If this situation is true, then the tooth must be treated and the canals filled in a new way. It is also possible that there is a significant resorption of the root and removal of the filling mass outside the root (beyond the apex). Most often this happens with the fourth or fifth tooth. Know that there should be no teeth with inflammatory lesions in the child’s oral cavity. The teeth should be re-treated.
1 people are reading this topic 0 users, 1 guests, 0 hidden users
The information published on the website WWW.DENTIST.UA is not a medical diagnosis or a guide to action, and is intended for informational purposes only. We strongly recommend that you do not test methods of diagnosis, treatment, prevention, etc. on yourself. without consulting a dentist. This may be dangerous to your health! For a complete and reliable consultation, contact the dental clinic by phone: +38 044-570-71-72, 044-572-37-71, 095-849-06-06, 068-870-53-61.
The information published on the website WWW.DENTIST.UA is not a medical diagnosis or a guide to action, and is intended for informational purposes only. We strongly recommend that you do not test methods of diagnosis, treatment, prevention, etc. on yourself. without consulting a dentist. This may be dangerous to your health! For a complete and reliable consultation, contact the dental clinic by phone: 044-570-71-72, 044-572-37-71, 095-849-06-06, 068-870-53-61.
Preventing gum disease
Prevention can prevent many serious oral problems. Main recommended activities:
- Brush your teeth regularly. If you don't have a brush, you can use dental floss or rinse your mouth with salted water.
- Carry out regular preventive examinations with your dentist. You should also immediately treat sore teeth and seek medical help if you suspect other serious problems.
- Try not to injure your gums with hard foods and sharp objects. It is better not to eat hard candies, crackers, unpeeled seeds, and it is strictly forbidden to use your teeth to open traffic jams, bite small wires, hold nails and other similar actions.
- Massage the gums. This can be done with a soft brush or chewing gum. You can also chew comb honey.
- Maintain a nutritious diet with calcium-containing foods. This element is found in high concentrations in dairy products, beans, meat and eggs.
- Stop smoking.
It's easy to follow these recommendations. Their benefits extend not only to the oral cavity, but to the entire body. If the gums are swollen or the cheek is swollen, then poisoning of the body often occurs due to intoxication. Therefore, it is better to take measures to prevent this problem.
There are many reasons for gum swelling, and the treatment method depends on the factors that led to this phenomenon. If the case is not entirely obvious, then only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis, perform the necessary procedures and prescribe medications. It is necessary to seek professional help in a timely manner to avoid the development of complications.
Causes of pain in teeth with temporary fillings
The main thing you need to know is that pain in teeth with such a filling is not a critical moment, and this is not a reason to urgently contact a dental center. It is worth remembering that this is an intermediate stage, and the final step is yet to come.
Temporary filling fell out
As written above, the cause may be a relapse. An incompletely treated problem can cause an unpleasant, aching pain. But the dentist is just a person, and an error could have occurred during the procedure. If this is not a continuation of the illness for which the patient went to the dentist, the reasons may be different.
- The seal was not made to the level. If the nerve is completely removed, this complication may occur. The places where the nerves were located are canals. Recently, a method has emerged to avoid this complexity. The channels are closed with an elastic soft font, and then only the filling occurs. But not all clinics have the opportunity to obtain this special material, and a filling is placed on the tooth. After filling the canals, it goes beyond the level of the top of the root. Next, the filling material may get on the surface of the mucosa. The body immediately begins to fight foreign bodies, and pain is one of its ways.
- Foreign bodies. This can only happen through the fault of the dentist. If the instruments are used incorrectly, a small chip of some instrument may occur, and this part will remain inside the tooth. If the doctor did not notice this during the procedure, this threatens inflammation with all the ensuing consequences. Pain in a filled tooth, itching, swelling of the gums, fever, etc. Before you decide to fill a tooth, you should work hard and find a professional.
- Root damage. Using a dental hammer requires special care. One uneven movement and the root may be broken. Neither the patient nor the doctor will notice this during the procedure, since there are no visible symptoms other than the damage itself, which may be tiny. But when the effect of the painkiller wears off, pain appears, and by the evening the gums swell.
- Incomplete nerve removal. When treating pulpitis, this mistake is very common. Nerves have long branches with many branches. And sometimes it is not possible to remove it completely. Part of the nerve remains in place. Pain comes almost immediately after filling a tooth. This nagging pain can continue for a long time. At the stage of replacing fillings, it is necessary to inform the dentist about the pain that has arisen so that he can check whether there are any nerve residues left in the tooth.
- Allergy. It’s trite, but for some reason it is always forgotten that a person may be allergic to any substance included in filling materials. This is manifested by the fact that this substance presses on the nerves of the soft tissues, which causes pain and may cause swelling of the gums. It seems that the tooth hurts, but it is the gums. After visiting the doctor, you need to ask to replace the filling with another one.
- Damage to the seal. The main recommendation when wearing a temporary filling is not to touch it with your tongue, finger or other household items, including a toothbrush. A temporary filling is a fragile thing that can be easily damaged or even lost altogether. When pain appears, the first thing you need to do is look in the mirror at the sore tooth and check for integrity and the presence of a filling.
- Negligent attitude to doctor's recommendations. Having received a prescription from the dentist, most patients believe that the job is done, and the drugs specified in the prescription are not such a necessity. But, these may not just be painkillers, but medications that act against the recurrence of infection, or special disinfecting gels.