If there is swelling under the tongue, the first discomfort and unpleasant sensations should be an alarming signal. This may mean that inflammation has occurred.
Inflammation of the tongue is not the most common disease. The occurrence of which can be facilitated by a variety of harmless problems and serious pathological disorders. But, in the case of swelling, many people wonder what it could be and how to treat it?
What is located under our tongue?
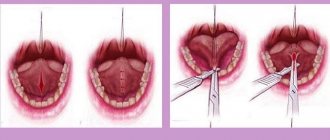
Remember that inflammation under the tongue can have serious consequences. Let's take a closer look at its structure. Doctors call what is in the area under our tongue the floor of the mouth. The floor of the oral cavity consists of:
- Large salivary gland.
- Enough powerful muscles.
- Nerves.
- Vessels
- Frenules under the tongue (this is a connecting fold).
- Hyoid bone.
All of these anatomical structures are extremely important and irreplaceable. They ensure the normal functioning of the language. If any pathology has occurred to them, this can be signaled by pain under the tongue and in the mouth. Therefore, if you have swelling under your tongue, see a doctor immediately. But pain under the tongue may not always be related to these structures.
White coating on the tongue
Absolutely every person can have a white coating on the tongue. And this does not always mean that there are some diseases in the body. But you should not worry only if there is a small amount of plaque on the tongue, in a thin layer. A coating on the tongue, determined by the level of humidity and temperature, is also considered normal. For example, in summer the coating on the tongue may be thicker than in the winter. This is due to the fact that as the weather changes, the body needs different vitamins.
The coating on the tongue reminds you of the needs of the body and is an indicator of its condition. It should be clarified that a coating on the tongue through which it is not difficult to see its natural color can be considered thin. If you suspect the presence of diseases in your body, but are not sure about it, take a look at your tongue. In this regard, the coating on the tongue will never deceive. If there is so much of it on your tongue that it is impossible to see the tongue itself, rest assured: this is not normal, which means your body needs help.
Drug therapy
If any form of inflammation under the tongue appears, both mild and moderate, it is not recommended to take any therapeutic measures without first consulting a specialist. A swollen area in the sublingual area may hide the formation of a malignant tumor. Therefore, differential diagnosis is required.
As a rule, therapeutic tactics to combat symptoms of inflammation in the oral cavity begin with the use of rinsing solutions:
- antiseptic
- Miramistin, Furacilin, Chlorophyllipt; - anti-inflammatory
- Iodinol, Rotokan, Potassium permanganate, Chlorhexidine.
It is better to carry out procedures for rinsing the mouth 4-6 times a day to prevent further proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
If the tumor in the sublingual area is caused by damage to the salivary glands of bacterial etiology, the doctor will select antibacterial therapy. Injections directly into the swollen area have proven themselves to be excellent. Penicillin drugs are used in combination with novocaine. If the patient is intolerant to medications of the penicillin subgroup, inject streptomycin.
In severe cases of pathology, antibacterial drugs are recommended for parenteral administration - intramuscularly or intravenously. The total duration of therapy is determined by the doctor individually.
Symptomatic treatment:
- antipyretics – Paracetamol, Ibuprofen;
- analgesics - as needed;
- detoxification therapy for severe cases - intravenous drip administration of glucose solution, Ringer.
Causes of pain
Discomfort in the sublingual area is very often associated with the following pathological conditions:
- The frenulum under the tongue was injured. The bridle itself is very thin and delicate. It is quite easy to damage if it is naturally short. Some people have a shorter frenulum than normal. In this case, she can easily get injured even during a conversation. But even with a normal frenulum length, injuries can occur. A common cause is stomatitis. Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral cavity. In this case, the infectious process covers the soft tissues of the oral cavity and tongue. Painful wounds and ulcers appear in the mouth. It can be caused by pain under the tongue and allergies, damage by any foreign object, hygiene errors, etc. During hygiene procedures, it is very important to move the toothbrush correctly. In this case, you will not be able to injure yourself.
- Angina. Since during a sore throat harmful microorganisms multiply on the mucous membrane, they cause an inflammatory process. The source of infection can grow, and the inflammation soon spreads to the area under the tongue. Acute sore throat is very dangerous. It can often cause pain under the tongue. A person begins to notice that he has difficulty speaking, swallowing, and chewing. It is difficult for him to even stick out his tongue.
- Dental problems. It is very important to treat your teeth on time. An inflammatory process, for example, banal caries, can grow quickly. At the same time, it covers more and more healthy tissues. It is quite possible that there will be pain under the tongue. If you notice that dental problems have appeared, then get your teeth treated as soon as possible.
- A phlegmon or abscess has appeared at the bottom of the mouth. At the same time, a lot of pus accumulates at the site of inflammation. Very often it accumulates in the area under the tongue. This is often caused by some disease in the oral cavity. For example, periodontitis, acute periostitis, etc.
- The salivary gland is inflamed. Under our tongue there is a fairly large gland. Its task is to produce the required amount of saliva. Sometimes it gets infected. Through the numerous ducts of the gland itself, it easily penetrates its delicate tissue.
- If the symmetry of the hyoid bone has been broken. This happens as an anomaly even at birth. Or it could be the result of some kind of injury.
- Allergy. There are allergic reactions that occur at lightning speed. They are very dangerous and can be accompanied by pain and swelling in the sublingual area. This is observed, for example, with Quincke's edema. This is a very dangerous condition in which extensive swelling of the soft tissues develops, including in the mouth. In the absence of qualified assistance, a person may die. He'll just suffocate. Often this causes swelling in the tongue area. It is accompanied by quite severe pain.
- Various injuries. Due to trauma, soft tissues, nerves, and blood vessels are often damaged. Small and larger vessels rupture. As a result, blood begins to accumulate between the muscle fibers and nearby nerve fibers are damaged. This causes severe pain, including in the area under the tongue.
Recognition of internal diseases by the condition of the tongue
When diagnosing pathology, doctors pay attention to the condition of the taste organ.
Depending on the location of the sores, roughness or plaque, the sites of inflammation are determined. The upper part is responsible for the cardiovascular system and intestines. The right side is behind the stomach, the left side is behind the liver. The center is responsible for the functions of the pancreas and spleen.
You can recognize tongue diseases and at the same time identify pathologies in various organ systems using the following characteristics:
Shape change:
- swelling - problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- thinning - vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorder;
- thickening - liver pathology;
- changes in the median groove - diseases of the spine and bones;
- bulge - disruptions in the respiratory system.
Color change:
- white - infection with Candida fungi;
- yellow - problems with the gallbladder;
- black - advanced pathologies of the intestines and liver;
- blue - pus and the development of purulent processes;
- red - inflammatory processes, elevated body temperature;
- blue-violet - hypoxia.
Appearance:
- cracks - dental diseases;
- trembling - neuroses, stress;
- the presence of neoplasms - fungi, tumors, ulcers;
- inflammation of the papillae - dysfunction of the genitourinary system;
- dryness - intoxication.
Pathology can also be determined by the smell emanating from the oral cavity. For example, the smell of ammonia indicates dysfunction of the genitourinary system. The smell of rot appears in diseases of the stomach, multiple caries. The smell of acetone is a sign of the development of diabetes.
As a conclusion
You should not self-medicate if the situation gets out of control. At the slightest change in the condition of the tongue and mucous membranes, it is best to go to the hospital.
If the disease is chronic, such as a stomach ulcer, then to avoid complications you should take medications prescribed by your doctor and also follow a diet.
The tongue is an organ in the mouth that consists almost entirely of muscle tissue. Part of its surface contains taste buds, and it performs important functions in chewing, swallowing and speaking. Swelling of the tongue is a pathology in which its volume begins to exceed its standard dimensions.
If the swelling occurs instantly, it may be a sign of an acute anaphylactic reaction. Otherwise, there are a number of other factors, from illness to injury, that could cause a swollen tongue.
Causes of gray plaque on the tongue
The reasons for the appearance of a grayish layer on an organ can be varied.
Among them are the following:
- Diseases of the digestive system: stomach ulcers, bile duct obstruction, gastritis, enterocolitis, etc.
- Infectious diseases: sore throat, pneumonia, measles, scarlet fever.
- Inflammation of the oropharynx, for example, tonsillitis and pharyngitis, both acute and chronic.
- Dehydration of the body, in which additional symptoms include dry mucous membranes and skin, a tendency to constipation, and fatigue.
- Taking courses of antibacterial therapy and the development of dysbacteriosis against this background. Hormonal medications can also cause this condition.
- Dietary disorders, in particular, consumption of excessively salty, spicy or fried foods.
- Respiratory diseases. In particular, such pathologies include bronchitis, tracheitis, and pneumonia. After the human body copes with the infection, the tongue returns to its original pink color.
- Lack of basic hygienic skills for oral care. Not only regular brushing of your teeth, but also proper care of your tongue and gums will help you cope with this problem.
- An increase in body temperature can cause a gray film to form on the tongue.
What is the treatment based on?
Of course, at the first symptoms of pain in the area under the tongue, you should seek qualified medical advice. He must quickly determine the cause of the pathology and prescribe the correct treatment. It will depend on what exactly provoked the appearance of pain in the tongue area. As practice shows, most often this happens due to an inflammatory process or injury to soft tissues. Quite often the frenulum becomes inflamed. This problem is especially relevant for those who have pathologically short periods. With a short bridle, it is easy to injure it, since it experiences more load than a normal-length bridle. If the doctor has determined that the main reason lies in the fact that the frenulum was injured or inflamed, then rinsing with antiseptic agents will help you. They will help eliminate pathogenic bacteria from the oral cavity and relieve inflammation. These are the simplest and most affordable drugs. For example, furatsilin, a soda solution, is suitable. There are also herbal-based preparations. They are perfect even for treating children. Let's take a closer look at these mouthwashes. Most often, doctors prescribe the following mouth rinses in this situation:
- Stomatophyte. You need to dilute 10 ml of this product in 50 ml of water.
- Romazulan. This is an infusion of pharmaceutical chamomile, just more concentrated than we usually brew. For a whole liter of water you will need only 2 tablespoons. This drug is safe even for children.
- Chlorophyllipt. This drug is an alcoholic infusion of eucalyptus. Dissolve a tablespoon of the product in 300 ml of water and rinse your mouth with the resulting solution. It is also suitable for children.
- Tincture of calamus (alcohol). 5 ml of the substance must be diluted in 100 ml of water.
- Hexoral and Stomatidin. These drugs are no longer herbal. These products are based on a synthesized substance – hexidine. It has proven itself to be an antibacterial and antiseptic agent. It doesn't get divorced. These drugs are often prescribed for stomatitis. And they do their job perfectly. Even severe forms of stomatitis are not scary for them.
- Iodinol. This drug also does not require dilution. It is initially ready for use. Doctors often prescribe it for wiping the delicate oral mucosa.
In order for all these solutions to work as efficiently and safely as possible, you should take into account simple rules:
- Rinse your mouth after every meal.
- Never swallow even a small amount of the solution.
- For the rinse to work. After it, you should not eat or drink for at least half an hour.
- Also rinse your mouth in the morning and before bed.
For pain under the tongue, not only pharmaceutical rinsing solutions help. Traditional medicine is no less effective.
- The most affordable of them is to use a solution of table salt and baking soda as an antibacterial rinse.
- Cabbage juice is also the most effective. It should be diluted in half with water.
- Wipe areas where there is inflammation with regular parsley juice.
- For the same purpose, you can use carrot or beet juice. It is diluted half and half with water.
All of these folk remedies have pronounced antiseptic properties, that is, they are able to destroy pathogens in the oral cavity.
Pain under the tongue may not be caused by inflammation of the frenulum. Contact your dentist or physician for a diagnosis. Pay attention to where exactly under the tongue the sensation of pain is localized. If you feel it on the right or left, then there is reason to be wary. There may be several reasons for this localization: purulent inflammation, dental problems, inflammation of the lymph nodes or salivary gland. With such a symptom, you need to rush to the doctor. He should quickly prescribe treatment and carefully monitor the general condition of the patient. It is unacceptable to self-medicate! Traditional medicine can only be a light addition to the main treatment. There are the most complex cases that even require hospitalization or urgent surgery.
In any case, contact your dentist at the first sign of pain under your tongue. Perhaps, thanks to the timely assistance of a specialist, you will avoid serious and dangerous complications.
Blue tongue
Some people notice that their tongue has a blue tint
Naturally, this attracts attention and an explanation needs to be found as to why this happens. A blue tongue in a person, if it is not colored by berry juice or other dyes, is a fairly important signal of serious health problems
Why can the tongue turn blue? This coloration may appear as a result of any serious problem in the functioning of the cardiac system. This most often occurs in heart failure. Cardiopulmonary failure with circulatory problems is especially clearly indicated by the localization of cyanosis on the lower parts of the tongue. In this situation, it is advisable to analyze the general condition, summarize all unpleasant sensations and contact a medical specialist for examination.
Difficulty performing simple tasks such as choosing the right clothes or bathing. Spatial disorientation to follow known paths or locate in places. Behavioral change: Agitation is the most common, but aggression can also occur. A person may have illusions, such as thinking that someone has stolen them or been stalked. Less commonly, but still quite common, there may be hallucinations where the patient sees people or hears voices. These changes can happen at any time, but are often more intense or only noticeable in the middle and late afternoon.
If cyanosis appears on the upper plane, then this is almost accurate evidence of the onset of progression of cardiovascular failure, while the remaining symptoms (pain, weakness, feeling of heaviness behind the sternum) may not yet appear. Timely response and implementation of a set of medical measures can often prevent a heart attack.
Another common change is the tendency to walk aimlessly. Changes in appetite: in general, with a tendency to overeat. Sleep disturbance: insomnia and restlessness at night. To diagnose the disease with absolute certainty, it is necessary to test brain tissue through an autopsy or brain biopsy, which can lead to serious complications. So the diagnosis is clinical: several tests are done to rule out different types of dementia so that you can conclude that Alzheimer's disease is likely.
How should clinical evaluation follow for Alzheimer's disease? It is not difficult to diagnose Alzheimer's disease in someone with obvious memory loss and behavioral changes. The problem is to diagnose it at the beginning, when usually there is only a complaint of memory difficulty, which may also have other causes. Neurological examination alone is not enough
A well-conducted examination of memory, orientation, language and other mental functions is important because, despite the absence of a complaint, if, for example, language impairment appears on the exam, the likelihood of Alzheimer's disease is very high
The tongue may also have a bluish tint. In addition to some disruption of blood circulation, this may reflect the development of the initial stages of scurvy. If a blue plaque suddenly appears in the area located directly in front of the pharynx, then the cause must be sought in a violation of renal activity. Normalization of the functioning of the adrenal glands (proper production of hormones) usually leads to the disappearance of such spots.
Unfortunately, this assessment requires training and is not performed in many places. Many cases of dementia are only eventually diagnosed with the most advanced disease. What tests should be ordered to diagnose Alzheimer's disease? A person with more advanced disease has a good history and a good examination. At an earlier stage, the diagnosis may be more difficult.
The following tests may be ordered to rule out other causes of dementia. Imaging or nuclear magnetic resonance of the skull to rule out multiple ischemia, hemorrhage, or tumors; thyroid hormone dosage and blood test to check for changes in liver, calcium and phosphorus metabolism, vitamin B deficiency, etc.
The orders to be ordered depend on the history and clinical examination, further highlighting their importance
Quite rare, but sometimes occurs, a bluish tint appears due to poisoning with heavy metals, for example, mercury. Only a specialist can identify such a lesion after conducting a serious examination.
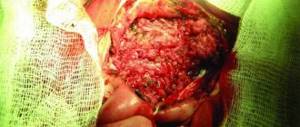
Treatment of tongue tumors: strategies and methods of combating malignant tumors
In order to choose the right treatment method, it is imperative for a specialist to conduct a series of diagnostic and biochemical studies. To determine the type, shape, type and stage of cancer, a biopsy is done, after which the resulting biopsy is examined histologically, finding out which treatment method can kill these particular cancer cells. You can see how much tissue is affected and how deeply the metastases have grown using CT.
Radiation therapy
The main treatment for tongue cancer is still radiation therapy. In particularly advanced cases, when there is a need to prescribe combination therapy, treatment with medications is resorted to. In the first and second stages of cancer of the lower and lateral surfaces of the tongue, radiation therapy is used using the contact method; in later stages, a remote type of exposure is used.
Surgery
Surgery is indicated only as a radical method of treatment. Since excision of tissues in the mouth will inevitably lead to their subsequent scarring, and therefore to a sharp deterioration in the patient’s quality of life. With extensive metastasis, invasive interventions do not make sense, since it is not possible to completely remove the affected tissue. When predicting a favorable outcome, the following manipulations are performed: partial resection of the tongue, cheeks, palate, mouth and jaws.
After a successful operation using the Krail method, patients have the opportunity to live for at least another five years. And if for objective reasons, for example, if the patient refuses surgery, resection cannot be performed, then the patient is prescribed a course of dosed chemotherapy. In any case, the type and method of treatment will depend on the patient’s age, stage, shape, rapidity of growth, abundance of metastasis and general health of the patient.
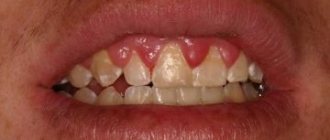
If inflammation of the salivary gland begins
Our body is designed very thoughtfully. There is practically no process for which only one organ is responsible. Most of them complement and support each other's work. At the same time, a number of organs are responsible for one function at once, forming an entire system. For example, not just the stomach, but the entire digestive tract is responsible for digestion. Digestion of food begins from the moment it enters the mouth.
The salivary glands are responsible for the process of secreting saliva, which is so important for us. There are as many as three pairs of them in our mouth. Saliva is very important for digestion of food, normal swallowing and maintaining the alkaline balance in the mouth. The salivary glands can be susceptible to various diseases. Doctors consider the parotid gland to be the most vulnerable. Inflammation can also affect the sublingual and submandibular glands. Do not underestimate the danger of such inflammation. The inflammatory process in the tissues of the salivary glands is dangerous both due to its symptoms and severe complications. These can result from untimely or incorrect, delayed treatment.
Complications of inflammation of the salivary glands are extremely dangerous. It could be:
- Nephritis.
- Neuritis.
- Myocarditis.
- Meningitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Encephalitis.
This is why it is so important to start treatment as soon as possible. It must be intensive and systematic. Then the disease will pass quickly and without complications.
And it is best not to bring the salivary gland to a state of inflammation at all. Follow simple rules of prevention.
Often, inflammation of the salivary glands begins due to the closure of the excretory duct. There is simply a colossal amount of bacteria in our mouth. If the duct is closed and saliva is not excreted. Then these bacteria quickly penetrate inside the ducts themselves and infect them. A focus of the inflammatory process develops.
If you have undergone surgery in the oral cavity or have had severe flu, encephalitis, typhoid, or pneumonia, your risk of inflammation of the salivary glands increases. Be as attentive as possible to your health and consult a doctor at the first warning signs. In these diseases, the glands under the tongue are often involved in the inflammatory process. An important role is played by what pathogen led to the disease, as well as how it progresses. In this case, inflammation can be gangrenous, purulent, catarrhal.
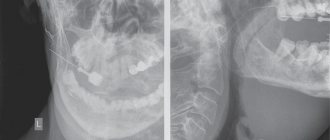
Diagnosis of the disease
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis of varicose veins after all the necessary diagnostic procedures. An important place in the diagnosis of varicose veins is given to ultrasound examination, which will show the state of blood flow in the vessels. Another diagnostic method is angiography. With this method, a contrast agent is injected into the vessel and then an x-ray is taken. This method allows you to clearly determine how the vessels function. The specialist will also refer you for a special blood test to identify a tendency to thrombosis and, if necessary, prescribe medications to thin the blood and prevent this complication of the disease. Therefore, at the first symptoms of the disease, you must immediately consult a doctor. This will help to start treatment on time, if necessary, and prevent unwanted consequences of the disease.
Possible consequences
If the swelling is not eliminated in time, then negative consequences will not keep you waiting. They may appear as follows:
- chronic or acute respiratory dysfunction;
- violation of a person’s aesthetic appearance (almost constantly open mouth with tongue hanging out);
- psychological discomfort;
- speech distortion;
- malocclusion;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- copious amounts of saliva;
- tooth decay and loss.
How not to miss such inflammation?
The first alarming signal is the appearance of obvious swelling in the area where the salivary gland is located. It becomes painful almost immediately. This area quickly becomes inflamed, the skin above it becomes shiny, red and tense, and acquires excessive elasticity. In the mouth, where the exit of the duct of this gland is located, swelling and inflammation begin to develop. This zone is clearly defined and difficult to miss. Cloudy saliva begins to be released from the duct, and in the most advanced cases, pus. The temperature rises sharply. It can rise to 39 degrees. The patient's condition deteriorates very quickly. New alarming symptoms appear every day. Swelling increases rapidly. Soon the patient may even have problems opening his mouth because of it. The pain syndrome is growing. At this stage, it is extremely important to take appropriate comprehensive treatment. If it is absent, serious complications develop due to the fact that pathological processes worsen. If enough time has passed since the inflammation process began, and treatment has not been prescribed, then dangerous complications may arise. For example, salivary fistulas.
To avoid inflammation, it is important to take timely care of high-quality prevention. Good oral hygiene is very important. You should take good care of your oral cavity. Brush your teeth thoroughly twice a day, rinse your mouth with special balms. If you notice that saliva flow from the ducts has become worse, use special medications that promote its outflow. It is useful to wipe the mouth with a solution of citric acid (1%). A special kind of food will also help. If everything is fine with your gastrointestinal tract, you can consume more spices and juice products. This special diet perfectly stimulates saliva production.
Also, for patients who have impaired salivation, doctors recommend taking a saline solution of pilocarpine (about 6 drops) every day (3-4 times). It can be replaced with potassium iodide (2%). You need to take it 1 tablespoon 2-3 times a day. If a diagnosis of “inflammation of the salivary gland” has been made, the doctor will immediately need to prescribe effective antibacterial treatment. The inflamed area of the gland can be injected around with a solution of novocaine (0.5%). This blockade is quite effective. Antibiotics are prescribed intramuscularly.
To support such therapy, the doctor also prescribes a number of physiotherapeutic procedures to the patient. If purulent foci appear, surgical intervention will be necessary. There is no need to be afraid of such an operation. Remember that the inflammatory process in the salivary glands is much more dangerous than surgery. The surgeon will only free the cavity from accumulated pus. This will immediately bring relief, relieve pain, and your general condition will noticeably improve.
It also happens that the duct of the salivary gland closes the stone. In this case, you need to remove it as soon as possible. Doctors call this pathology sialolithiasis. As it develops, stones begin to form in the ducts or parenchyma of the gland itself. Most often they are single, but in some cases the formation of a whole group can be observed. Their sizes can be completely different - from a small grain of sand to a stone the size of a chicken egg. The reason for this striking pathology lies in a violation of mineral metabolism.
Sialolithiasis does not make itself felt immediately. The person feels quite healthy, but tiny stones are already beginning to form in the ducts, which can soon block them. It is at the moment when the normal outflow of fluid stops that a person begins to feel the symptoms of the disease. They begin with a sharp pain, which has the character of colic. Further, in the place where the pain syndrome appears, swelling and edema forms. Such symptoms may periodically subside and then intensify again.
The inflammation process progresses rapidly. As the disease progresses, its manifestations become stronger. The main key to successful treatment is the removal of the culprit of the disease - a stone or a group of stones at once. If the process has gone too far and the stones themselves cannot be removed, the entire salivary gland must be removed. The salivary gland under the tongue does not often become inflamed. But if such inflammation occurs, it makes itself felt with bright and rapidly developing clinical manifestations. If this pathology is not treated, the consequences can be disastrous.
Types of raids
The plaques that occasionally form on the surface of the tongue are very diverse. They differ in color, outline, and localization. Moreover, the color of the tongue and the disease are often directly related. In infectious pathologies, a dense whitish coating is usually observed that covers the entire surface. There is almost always a simultaneous increase in temperature.
If white deposits appear on the middle part of the tongue, and cracks form on the sides, then some pathological lesions of the stomach or intestines can be suspected. Having noticed the first manifestations, it is recommended to change the diet to a more easily digestible one, limiting salt and fat. The appearance of pain indicates the need for emergency examination by a doctor.
White deposits that appear on the front of the organ are evidence of problems with the respiratory system, with the most common cause being tobacco smoking. At the same time, sometimes a person’s speech changes tonality. Developing dysbacteriosis often leads to a fungal infection, manifested in particular by the appearance of whitish spots on the entire surface. Quite often it develops as a result of improper treatment with antibiotics.
An alarming signal is the appearance of a red and white spotted coating. This is what the symptoms of scarlet fever look like. Having noticed such formations, you should immediately seek medical advice; a timely and effective treatment method will allow you to quickly get rid of the pathology without any consequences.
If your tongue turns yellow, you should pay attention to the amount of deposits. A small amount of yellowish plaque should usually not cause concern
However, the intensive formation of a thick layer allows one to suspect the presence of foci of inflammation inside the gallbladder. In this case, you should pay attention to the presence of unpleasant sensations under the ribs on the right side. These are the signs of developing cholecystitis.
A burgundy coating over time turning into a brown crust often indicates food poisoning. If it is small and passes quickly enough, then coloring can occur due to the use of food (natural) dyes, for example, chocolate or coffee. The prolonged presence of such deposits usually indicates dysbacteriosis.
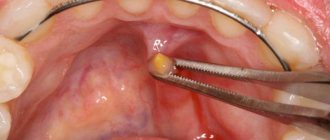
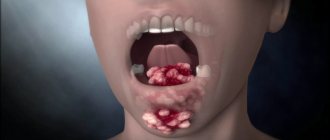
If your child has an abscess under the tongue
If an abscess appears, it means that an infection has entered the body. Most often it is streptococcus or staphylococcus. Then an abscess develops, pus forms, and the site of infection begins to break out. If the mucous membrane in the mouth has been damaged, germs can get deeper. This is often how abscesses form under the tongue. As soon as microbes penetrate deep into the tissues, an inflammatory process develops. The abscess grows over time and its breakthrough is possible. If it breaks through on its own, recovery occurs. But this doesn't always happen. Most often, such purulent inflammation in a child requires timely and intensive treatment. Also, the abscess can break into the tissues surrounding it. This only contributes to the spread of inflammation. That is why it is best if the abscess is opened by a doctor. He will carefully empty the cavity, treat it with an antiseptic and prescribe effective comprehensive treatment for the child.
How inflammation develops
To prevent such inflammation, teach your child to follow simple hygiene standards. It is very important to brush your teeth regularly. If a child finds a wound in his mouth, it should be immediately treated with brilliant green or iodine. Invite your child to rinse his mouth thoroughly with a decoction of chamomile, calendula, sage, a weak solution of potassium permanganate or soda. All these products have an antibacterial effect. If swelling or painful redness appears, take your child to the doctor immediately. He will recommend how to proceed further. Don't risk your child's health and don't waste time on self-medication! Under no circumstances should this swelling be rubbed, iced, or heated. Because of this, the abscess can burst inside.
How to treat an abscess in children
To identify an abscess, a puncture is often performed. This will make it possible to find out which specific pathogen caused the abscess. Also, the doctor will immediately determine which antibiotic is most effective against it. Most often, treatment is surgical. The doctor opens the abscess, cleans it, treats it with antibacterial agents, prescribes antibiotics and other drugs. Physiological procedures support the treatment. For a superficial abscess, the doctor will administer anesthesia with novocaine. Once the autopsy is performed, treatment will be the same as for normal wounds.
As a result, we emphasize once again that it is easier to avoid such inflammation than to treat it later. Just don't forget about basic hygiene. Well, if symptoms of the disease appear, immediately go to the doctor.
Most explanations for why skinks have blue tongues are related to the behavioral aspect.
It is generally accepted that the tongue of skinks is used in a complex of defensive reactions. Typically, skinks, when threatened, inflate their bodies and turn their heads towards the source of concern. Then they open their mouth wide, stick out their tongue and begin to hiss. At this moment, the skink may even move towards the predator, attack it or bite it.
This behavior has two main functions. Firstly, the hissing skink, turned head towards the predator and having a coloration of transverse stripes (Tiliqua occipitalis, Tiliqua scincoides), is very reminiscent of the spiny-tailed echidna (Acanthopis antarcticus) - a very dangerous venomous snake that lives in Australia and New Guinea.
Secondly, a predator may simply be frightened by the sight of a bright blue tongue, which sharply contrasts with the pink color of the mouth. This explanation, unlike the first, explains why the skink has a blue tongue. This theory finds some support in the fact that during such a demonstration, the skink’s hyoid apparatus moves the tongue as far forward as possible and visually enlarges it. And, since red and blue are contrasting colors, the skink looks really scary.
However, although this theory has indirect support, there is no direct evidence that skink language plays a role in defensive behavior. For example, it does not explain why one species of the genus Tiliqua has a pink tongue. If tongue coloration is fundamentally important for protection against predators, Gerard's tiliquas should be more susceptible to predation than other members of the genus. On the other hand, it can be assumed that the blue tongue is important for defense only for young lizards, which are more susceptible to attacks by predators.