Home / Pulpitis
Back
Published: 06/14/2020
Reading time: 7 min
0
9
- 1 Main manifestations
- 2 Diseases of unknown etiology
- 3 Infectious lesion
- 4 Other pathologies
- 5 Which doctor should I contact?
- 6 What is the name of a specialist in the treatment of the oral mucosa, and how to make an appointment with him?
- 7 Treatment and prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa
- 8 Traditional medicine
- 9 Common diseases
- 10 General concepts
- 11 Oncology
- 12 Acute glossitis
- 13 You need to approach the problem with all seriousness
- 14 Causes of diseases of the oral mucosa
- 15 Prevention
- 16 Preventive measures
- 17 Symptoms of Oral Infections
- 18 Traumatic factor
- 19 How to treat at home
Main manifestations
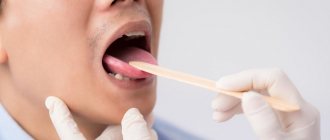
There is a common name for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa - stomatitis. When the pathological process is localized on the tongue they talk about glossitis, on the gums - about gingivitis, on the lips - about cheilitis.
A characteristic manifestation of stomatitis is the appearance on the oral mucosa of foci of redness, blisters, erosions (afts) or ulcers covered with plaque. These lesions are most often detected on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard palate, and tip of the tongue.
Often there is pain at the location of erosions and ulcers, enlargement of nearby lymph nodes, and sometimes an increase in body temperature. The average duration of the disease is 7-14 days.
Stomatitis can recur with decreased immunity, poor diet, hypovitaminosis, infectious diseases, and exacerbations are more common in spring and autumn.
Types of stomatitis
- Viral.
Infection with the Epstein-Bar virus or herpes simplex. It appears in the form of bubbles, in place of which erosion subsequently occurs. - Bacterial.
Caused by the proliferation of streptococci and staphylococci. It looks like pustules turning into wounds. - Fungal.
Decreased immunity and proliferation of Candida fungi. It looks like small foci of white plaque, after damage to which painful erosions remain. - Chemical.
Burns from acids and alkalis. Deep ulcers with the formation of scars and deformations of the mucosa. - Ray.
Arising as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation. Expressed in the form of erosions and tissue deformations. - Allergic.
Occurs as a reaction to medication or dentures.
Diseases of unknown etiology
Among the diseases observed in the oral cavity is lichen planus, an anomaly whose causes are not clear. The clinical picture of the disease has a number of features:
- In the initial stage, rashes appear on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity - small papules.
- The progression of pathology leads to an increase in affected areas and their merging.
- Stripes and plaques with a keratinized grayish-white surface form on the tissues, protruding above the level of the mucous membranes.
Treatment regimens for lichen are selected individually, taking into account the patient’s condition.
Infectious lesion
The intact mucous membrane of the oral cavity is immune to any infectious agents. However, when microtraumas appear, it becomes vulnerable to the following pathogens:
- Bacteria - cause inflammation with high fever, poor health, often with suppuration from the affected areas. Treatment requires antibiotics.
- Viruses, as a rule, are less severe, accompanied by redness of the mucous membrane, and sometimes by malaise. To get rid of them, antiviral drugs are prescribed.
- Fungi cause candidiasis: a white, dense coating on the mucous membrane, accompanied by dry mouth and burning. Candidiasis often occurs after uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
Determining exactly what type of infection has affected the mucous membrane of a particular patient should only be determined by a periodontist or dentist after consultation, examination and laboratory tests. Self-prescription of drugs by the patient will not only not help, but will also cause additional harm to his health.
Other pathologies
Among the ailments that change the structure of the oral mucosa are diseases resulting from allergic reactions. These include Reiter's syndrome, Lyell's syndrome, and exudative erythema. Provoking factors that cause abnormal conditions are microbial, contact and drug allergies. Treatment regimens for diseases include studying the allergological status and eliminating the source of negative impact.
The incidence rate of oral cancer varies from 2 to 4% of the total number of cancer pathologies detected in Russia. At an early stage, the disease proceeds hidden. Its further development is accompanied by the appearance of local pain, bleeding, and ulcers. In a later period, the discomfort intensifies and begins to radiate to the cheekbones, temples, and forehead. The outcome of oncological pathologies depends on the stage of the identified process and the general condition of the patient.
Which doctor should I contact?
Stomatitis must be treated, as otherwise serious complications and the disease becoming chronic are possible. Each type of disease is provoked by different pathogens, so for effective treatment it is necessary to identify the nature of stomatitis.
Who specializes in this area? The dentist diagnoses and treats stomatitis. If you notice the first symptoms, you should immediately go to the dentist.
Sometimes the disease is accompanied by additional, not entirely typical symptoms, which confuses the patient. In this case, the right decision would be to see your primary care physician or family doctor. After the examination, he will refer you to the necessary specialist.
What is the name of a specialist in the treatment of the oral mucosa, and how to make an appointment with him?
Most people do not know and often ask the question online: who to contact if problems appear in the oral mucosa, and what is the name of the doctor who treats them? The easiest way would be to contact a general dentist in a public clinic or in a private dental clinic.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with wounds on the gums: causes and symptoms, treatment with drugs, traditional methods, prevention, possible complications
It should be noted that sometimes damage to the oral mucosa is associated with the presence of another disease in the body (gastritis, diabetes mellitus, HIV infection, oncology), therefore, in addition to local treatment, it will be necessary to treat the underlying disease. In such cases, in addition to the dentist, the patient will be observed by a doctor of related specialization (gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist, oncologist).
What can stomatitis tell you?
The appearance of stomatitis may indicate the appearance of some more serious pathologies in the body. Sometimes stomatitis is a concomitant symptom of conditions such as:
- Received ionizing radiation or chemotherapy.
- Oncological diseases of the nasopharynx, mouth, neck.
- Disorders of the digestive tract, intestinal parasites.
- HIV infection.
- Prolonged dehydration.
- Hormonal disorders in women.
- Diabetes.
- Anemia.
- Bronchial asthma.
Treatment and prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa
In each case, the dentist will prescribe several drugs to treat the mucous membrane of the cavity.
- Painkillers (Cholisal gel, Lidocaine spray) - used for injuries and infections. As their name implies, they help relieve pain and achieve anesthesia of the mucous membrane.
- Antiseptics (chlorhexidine, miramistin, furatsillin) are used to prevent infection. Indications: trauma, oncology, diabetes.
- Antibiotics (Tsifran ST, Amoxiclav) are indicated for the treatment of bacterial infections. They must be prescribed by the attending physician.
- Antiviral (Anaferon, Acyclovir) - prescribed for viral infection.
- Antifungals (Nystatin, Levorin, Clotrimazole) – used for candidiasis.
- Healing agents (Metrogil-denta, Solcoseryl) - help improve the regeneration of the mucous membrane. Indications: injuries, infections, lesions in general diseases. Cannot be used for cancer without a doctor's prescription.
The prescription of drugs for the treatment of the oral mucosa from any of this group should be carried out only after an accurate diagnosis has been made and only by the attending physician.
It is unacceptable to take them independently or after an online consultation, since the patient does not have adequate knowledge about the disease, and the doctor cannot evaluate all the symptoms remotely and make an accurate diagnosis without additional examinations.
Prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa is primarily a timely visit to a general dentist. The specialist will examine the condition of fillings and dentures, adjust them if necessary, and be able to notice the first signs of oncology. If there is a general disease, the dentist will promptly refer the patient for consultation and treatment to a doctor of related specialization.
ethnoscience
Often, patients, in search of an effective remedy for stomatitis, decide to try folk remedies. But it is worth noting that they will not be able to help in all cases. So, for example, if the disease was caused by mechanical damage, then decoctions of various medicinal herbs (oak bark, sage, calendula, chamomile, and so on) will help.
But if stomatitis occurs as a result of the development of an infection or other diseases, then treatment with folk remedies will be at least unreasonable. Treatment of infectious stomatitis should be carried out exclusively with medication. Otherwise, you risk wasting valuable time on treatment that ultimately will not give the desired result.
Viral stomatitis and its treatment
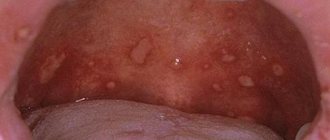
- Stomatitis – aphthous, chronic and catarrhal. In the first case, the affected areas are numerous white and round aphthae. These wounds are painful when pressed. Aphthous stomatitis in children can occur in 3 stages: mild, moderate and severe (with fever and symptoms of intoxication of the body).
- Pyoderma. Pathology occurs due to damage to the body by streptococcal infection. Pyoderma manifests itself as microcracks on the surface of the mucous membranes and lips. Babies with weak immune systems and children who do not receive adequate nutrition are especially susceptible to the disease.
- Thrush, or candidiasis. The problem is caused by yeast-like fungi. Most often, symptoms appear in infancy, when the mucous membranes of the baby’s mouth are not able to resist pathogenic flora.
In the complex treatment of inflammation of the mucous membrane, an important role is played by appropriate nutritional correction with the exclusion of foods that can irritate or injure tissues. Main rules:
- temporary refusal of solid or rough foods;
- excluding too cold or too hot foods from the diet;
- refusal of “food waste”: crackers, chips, spicy and spicy foods that can damage the palate, tongue and the inside of the lips, as well as pickles and smoked meats;
- exclusion of alcohol and smoking.
Which doctor treats stomatitis?
Article checked by doctor
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa that affects the inside of the lip, tongue, gums, or palate. According to statistics, approximately one in five suffers from this disease. Depending on the causes of occurrence, there are several forms of stomatitis. As a rule, young children most often suffer from the disease, although adults can also develop erosions, ulcers or blisters that affect the oral cavity. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor, regardless of the patient’s age. You will find out which doctor treats stomatitis in this article.
Which doctor treats stomatitis?
Causes
There are certain factors that can lead to stomatitis. Let's look at the most common of them:
- frequent consumption of foods prepared with serious violations of sanitary standards or without pre-treatment. This also applies to unwashed vegetables or fruits;
About the reasons for the development of stomatitis
Exposure to poor ecology, as well as hormonal imbalances during pregnancy or breastfeeding can also aggravate the situation. Some medical professionals claim that eating too much sweets can also result in stomatitis, but this is most likely only the consequences of caries or other dental problems caused by these sweets. In order to be able to recognize the disease at an early stage of development, it is necessary to become familiar with its characteristic symptoms. This will allow stomatitis to be detected promptly and treated at an early stage.
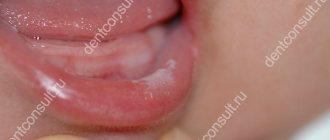
Stomatitis on the tongue
Characteristic symptoms of stomatitis
In most cases, stomatitis occurs suddenly. Even in the evening the patient may not even suspect the disease, but the next morning he notices slight redness of the mucous membrane. After some time, the affected area swells and swells, and along with the enlargement of the resulting ulcer, painful sensations appear.
What does stomatitis look like?
Stomatitis may also be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the formation of white plaque on the affected areas;
- redness of the gums;
- unpleasant sensations in the affected area, which often turn into aching pain.
Incorrect treatment or its complete absence leads to the fact that the disease begins to progress. Small ulcers that appear in the patient’s mouth gradually spread and increase in size. Often they move to the patient’s upper palate or to the tonsil area. They can also appear under the tongue, which causes a lot of discomfort, so many patients are worried about which specialist they should contact with this problem.
Stomatitis in a child
Which doctor should I contact?
Specialists at the dental department study diseases of the human oral cavity, therefore, when the first symptoms of stomatitis appear, you should contact a dentist. This does not depend on the age of the patient, be it a small child or an elderly man. When the baby reaches the age of 3 years, he is examined by a dentist, although all this happens under the supervision of another doctor - a pediatrician.
In cases where, in addition to stomatitis, the patient has other diseases of the oral cavity, during the treatment the following doctors may feel:
- gastroenterologist, because pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract often lead to stomatitis;
- allergist. Various food additives consumed by the patient along with food can also trigger the development of the disease as a result of allergic manifestations;
- immunologist When the body is exposed to external irritants, the immune system activates a special defense. Accordingly, if the patient’s immunity is weak, then relapses of the disease may occur;
- endocrinologist As noted earlier, hormonal imbalances can also cause stomatitis, so endocrinologists may be involved to eliminate this factor.
Help from an endocrinologist may also be required
Treatment of the disease
The choice of the doctor to whom you should contact has already been sorted out. But how is stomatitis treated? In fact, quick relief from pain, itching and discomfort can be achieved using a set of procedures. During treatment, it is extremely important to prevent the disease from progressing and becoming chronic. Treatment can be carried out using different methods - for example, drug treatment, the use of a laser, or traditional medicine recipes. Let's consider each of these methods separately.
Medications
Medicines are used to treat stomatitis, usually if test results confirm the presence of infection. In such cases, the doctor may prescribe several medications, including an anesthetic and a restorative. Depending on the chemical composition that has an effect on the body and the type in which it is produced, drugs may differ from each other. Below are the most effective medications used to treat oral diseases.
Table. Review of the best medications for stomatitis.
| Drug name | Description |
| An anesthetic agent available in tablet form. To use, you need to crush several tablets into a powder, which is applied to the affected area. | |
| A dental preparation produced in the form of a gel. Has anesthetic and antiseptic properties. The active substances are chamomile and lidocaine. | |
| Another dental product that has anesthetic properties. It has an analgesic and antimicrobial effect on the body, which occurs within a few minutes from the moment of application to the inflamed surface. | |
| An effective remedy for the treatment of various diseases of the oral cavity. Has anti-inflammatory and wound healing properties. Effectively used for herpes, various ulcers and skin lesions. | |
| This is an oil-based solution intended for external use. The composition includes useful substances and vitamins, due to which the body has an antioxidant effect. | |
| One of the few dental drugs used for stomatitis, which is available in the form of a paste. The product has regenerative and stimulating properties, which accelerates the healing process of ulcers and wounds on the mucous membrane. | |
| A highly effective combination product with analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Available in gel form. |
Rinse for stomatitis
Laser Application
More and more dental clinics are using laser to treat stomatitis. With the help of such a device, you can cure the disease as effectively and painlessly as possible. Moreover, during the operation, the adjacent layers of the epithelium, to which the ulcer has not yet spread, remain undamaged. The treated area of the mucous membrane is disinfected, which prevents the penetration of infection.
On a note! The use of a laser device allows you to completely remove all nerve endings from the affected area of the mucous membrane, due to which the pain that accompanies stomatitis instantly goes away. In this case, the recovery period is reduced to a minimum.
Laser dentistry in action
The peculiarity of this method is the complete absence of any contraindications, but, despite the large number of advantages, the use of a laser has its disadvantages. First of all, this concerns the cost of the procedure, which, depending on the prestige of the clinic or the city in which the patient will be treated for stomatitis, can vary from 500 to 5,000 rubles. Other factors can also influence the cost - for example, the brand of equipment used, and so on.
Stomatitis on a child's lip
ethnoscience
Often, patients, in search of an effective remedy for stomatitis, decide to try folk remedies. But it is worth noting that they will not be able to help in all cases. So, for example, if the disease was caused by mechanical damage, then decoctions of various medicinal herbs (oak bark, sage, calendula, chamomile, and so on) will help.
Folk remedies for stomatitis
But if stomatitis occurs as a result of the development of an infection or other diseases, then treatment with folk remedies will be at least unreasonable. Treatment of infectious stomatitis should be carried out exclusively with medication. Otherwise, you risk wasting valuable time on treatment that ultimately will not give the desired result.
Treatment of stomatitis at home
Do I need to contact a specialist?
For a quick recovery from the development of oral diseases, including stomatitis, you should immediately consult a doctor after the first suspicious symptoms appear. Treatment of stomatitis occurs regardless of the patient’s gender or age.
At the dentist's office
Ignoring the symptoms of stomatitis can result in the following complications:
- active proliferation of bacteria in the patient’s oral cavity, which will lead to exacerbation of the disease and pain;
- damage to gums and teeth, which in severe inflammatory processes can lead to their loss;
- severe pain when chewing food or when talking, which causes discomfort to the patient;
- self-medication can lead to the fact that you not only do not eliminate all the symptoms of stomatitis, but also significantly aggravate the situation, thereby exacerbating the inflammatory processes in your body.
Catarrhal stomatitis on the tongue
On a note! The further functionality of the patient’s oral cavity will directly depend on how quickly he seeks help from a doctor. The structure of the teeth also depends on this, damage to which can occur as a result of improper preventive measures.
Prevention measures
Any disease is much easier to prevent than to cure. This also applies to stomatitis, the prevention of which consists of maintaining oral hygiene, giving up alcohol and smoking. Many experts argue that stomatitis most often occurs as a result of poor personal hygiene, calling it “the disease of dirty hands,” so all products must be washed thoroughly before eating. You also need to be careful when in contact with sick people so as not to pick up the bacteria that causes stomatitis.
Strengthening the body will help protect against this disease. To keep your immune system strong, you need to exercise regularly, eat right, and avoid stressful situations. It is no secret that stomatitis can also occur as a symptom of another disease, so it remains extremely important to promptly treat all ailments, especially those of an infectious nature.
General diseases
This includes diseases of other systems and organs of the body that directly or indirectly affect the condition of the oral mucosa. For example, in diabetes mellitus, a characteristic symptom is poor healing of injuries, the addition of a bacterial infection, and oral candidiasis.
We suggest you read: Sore gums: what to do and how to treat them at home
If you have problems with blood clotting, when brushing your teeth in your mouth, you often experience increased bleeding from the gums. The peculiarity of this group is that treating only the mucous membrane without treating the underlying disease is useless and pointless.
Therefore, the periodontist will definitely prescribe the patient a consultation with a related specialist - an endocrinologist, therapist, gastroenterologist.
Treatment of stomatitis
You can undergo treatment at the paid dentistry of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The approach to the process depends on the nature of the disease and the cause of its occurrence:
- If stomatitis is catarrhal, that is, arising as a result of non-compliance with hygiene standards, it can be cured quite simply, within a week at home. To do this, it is necessary to exclude irritating foods from the diet - sour, hot, spicy, salty, etc. The mouth should be rinsed with solutions that fight germs.
- If there are more serious manifestations that indicate an infectious lesion, contacting a dentist or therapist is a prerequisite for properly combating the disease. At a consultation with a dentist, after examination and questioning, the doctor will prescribe treatment. These are measures to relieve pain, relieve inflammation, and fight infection. Both rinses, local preparations, and general medications in the form of tablets are used.
- Stomatitis resulting from allergies is not considered an independent disease. Treatment is based on identifying the object that caused the allergy and taking antihistamines.
- Treatment of herpetic stomatitis is similar to the elimination of other types of stomatitis. It consists of taking medications for swelling and pain, application of medications and rinses, antiviral, antihistamines, as well as agents for restoring immunity.
- Stomatitis caused by Candida fungi is treated with oral antifungal drugs and local application of antifungal agents. To increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is recommended to exclude or minimize the consumption of simple carbohydrates, since sugars are the main food for mushrooms.
Oncology
This includes all lesions of the oral cavity directly or indirectly associated with malignant neoplasms of the oral cavity:
- Oncology itself – it develops quite quickly in the oral cavity and has the appearance of a painless ulcer. A characteristic sign is enlargement of the lymph nodes on the affected side; they have a dense consistency and are immobile. It is important to remember that if the damage in the mouth does not heal for more than 2 weeks, you need to make an appointment with the dentist.
- Mucositis of the oral mucosa - occurs after radiation therapy in the head and neck area. Irradiation significantly reduces the secretion of saliva in the mouth, as a result of which the mucous membrane dries out, cracks, and poorly healing ulcers appear on it. In addition, saliva has a bactericidal effect, so a decrease in its quantity leads to the easy addition of a secondary infection to any microtrauma of the mucous membrane in the mouth.
Doctors answer that in the last 10-15 years there has been a rapid increase in the incidence of cancer, even among people under 30 years of age (young age).
Early detection of tumor precursors or diagnosing it at an early stage allows for maximum health preservation and improved survival.
Therefore, it is necessary to visit the dentist every six months, including for the purpose of preventive cancer examination of the mucous membrane.
Causes of stomatitis
There are several reasons that provoke stomatitis:
- The addition of infection is viruses and bacteria, which very quickly colonize, revealing damaged areas of the mucous membrane.
- Poor nutrition – if the diet is too poor, the body does not have enough strength and resources to fight the pathogens attacking it.
- Wounds and other injuries in the mouth - these can be scratches from sharp edges of teeth with carious cavities, bitten cheeks, cracked lips, burns.
- Improper oral hygiene - insufficient cleaning leaves plaque on the tooth and tongue, in which bacteria multiply very quickly.
- Insufficient hygiene in general - dirty hands, unwashed fruits, which become sources of bacteria.
- Consequences of dental intervention performed in violation of norms.
- Using pastes with sodium lauryl sulfate, which reduces salivation. In such a situation, the epithelium may dry out and, as a result, not be sufficiently resistant to bacteria.
- Alcohol and smoking.
- Chronic diseases of a general nature that affect the state of the body, digestion of food, and other vital processes.
Acute glossitis
Here you need to explain in more detail which symptoms require urgent medical attention. There are many types of glossitis, and often their symptoms are similar.
- Catarrhal glossitis is manifested by inflammation of the mucous membrane with swelling and redness. Caused by bacteria, a complication of candidal stomatitis, smoking, acute respiratory infections, influenza, alcohol, caries, and can signal gastrointestinal diseases.
- Ulcerative: It can be recognized by a dark gray plaque, bleeding ulcers and an unpleasant odor from the mouth. It signals ulcerative necrotic stomatitis and especially develops with decreased immunity.
- Abscess: develops in case of injury to the tongue, it swells, turns red, becomes painful, breathing may be difficult, and swelling increases.
- Mycotic: if a white cheesy coating appears on the back of the organ, this indicates mycotic glossitis; it appears when immunity is reduced.
- Desquamative: signals problems with the circulatory/digestive system, kidney disease, dysbacteriosis, metabolic disorders. It manifests itself as itching and burning, mild soreness, and red polishing spots.
- Herpetic glossitis: against the background of acute respiratory infections, hypothermia and stress, it is visually manifested in the appearance of bubbles on the mucous membrane, which, when bursting, turn into painful ulcers. The temperature rises, the head hurts, joint pain torments.
With glossitis, the tongue hurts and burns, tissues swell, speech becomes difficult, salivation is impaired, and it becomes difficult to chew food.
The problem must be approached with all seriousness
Inflammatory processes that occur in the oral cavity are called stomatitis in the professional language of dentists.
It is important to remember that this disease combines several problems that cause a similar reaction from the oral mucosa, that is, a whole group of diseases falls under the definition of stomatitis.
The mucous membrane becomes inflamed most often due to the fact that certain changes occur in the body, sometimes of a serious nature. In any case, it is necessary to pay attention to the characteristic redness.
It is important to understand here that the causes of inflammatory processes can be different - from a simple burn from hot food to diseases that require professional help.
Oral candidiasis
Treatment of oral candidiasis
Treatment of oral candidiasis in adults can be local or general. General treatment focuses on medications that affect the entire body. Taking antifungal drugs in this case allows you to destroy Candida fungi throughout the body.
Taking antifungal drugs
Polyene antibiotics (levorin and nystatin) are considered effective antifungal drugs, which are recommended to be taken for two weeks. A few days after starting to take these tablets, the patient’s well-being returns to normal, erosions heal and the white plaque disappears. Imidazoles such as econazole, clotrimazole, and miconazole have also shown their effectiveness in the treatment of candidiasis. The duration of their use and dosage are prescribed depending on the severity of the disease and the age of the patient.
Restoration of protective functions
Since oral candidiasis often occurs against the background of suppressed immunity, drugs to restore the body’s protective functions occupy a special place in the treatment of the disease. For this purpose, vitamins B, C, and PP are usually prescribed. To restore iron metabolism, which is significantly impaired due to the disease, it is advisable for the patient to take Ferroplex or Conferon. Despite the effectiveness of general treatment, it can also have a negative effect on the human body, as it has side effects.
Local treatment
Local treatment is safer than general treatment for the reason that it allows you to act directly on the source of inflammation. In addition, doctors prescribe drugs that are not absorbed into the blood, which eliminates possible complications after using antibiotics. Local preparations can quickly and effectively stop the proliferation of fungi, relieve symptoms of the disease and eliminate damage caused by candida.
For local treatment, doctors usually prescribe various aniline dyes: methylene blue, brilliant green, fucorcin solution. Iodine is used for application. Drugs such as Lyzac and lysozyme have a bactericidal effect. To eliminate white plaque, which is localized in the corners of the mouth, levorin and nystatin ointments are prescribed. During treatment of the disease, it is extremely important to pay special attention to eliminating all possible inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
For more effective treatment of the disease, rinsing the mouth with special solutions of borax, boric acid, and baking soda is recommended. This procedure will help cleanse the oral mucosa of white plaque, eliminate inflammation, remove fungal colonies and speed up the healing of erosion. You should rinse your mouth with solutions three hours after eating.
Special diet
Diet is of great importance in the treatment of the disease. Excessive consumption of foods that contain yeast, as well as confectionery products, leads to the creation of good conditions for the proliferation of candida. Spicy and sour foods, which irritate the oral mucosa, also have a bad effect on the body.
During treatment, it is worth limiting the consumption of sweet fruits, coffee, tea, alcohol, carbonated drinks, ketchup, mayonnaise, mushrooms, fatty meats, smoked meats, and confectionery. The diet for candidiasis provides for the predominance of cereals, lean meat, herbs and vegetables, herbal teas, natural juices, coconut, flaxseed and olive oils, seeds, nuts, and fermented milk products in the patient’s diet. After recovery, the list of products can be expanded. However, it is advisable not to consume prohibited foods for a year in order to avoid a recurrence of candidiasis.
Causes of diseases of the oral mucosa
Diseases of the oral mucosa occur throughout life in an average of 5-10% of the population.
Their cause may be:
- Traumatic damage to the tissues of the oral cavity and other traumatic effects (chemical, thermal, etc.) with the development of traumatic erosion, ulcers, leukoplakia or leukokeratosis (keratinization of an area of the mucous membrane capable of malignant degeneration).
- Infectious diseases that affect the oral mucosa due to the penetration of viruses, spirochetes, bacteria, and fungi.
- Quite often, the occurrence of pathological changes in the oral mucosa is associated with disruption of the functioning of various organs and systems of the body: allergies, dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, endocrine disorders, systemic connective tissue diseases, blood diseases, dermatoses, tuberculosis, AIDS and some other conditions.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the dangers of viral stomatitis in children and the subtleties of its treatment
It is often quite difficult to identify the true cause of pathology of the oral mucosa - a lot of experience, high professionalism, and the ability not only to carefully collect information, but also to interpret it correctly and draw appropriate conclusions are required. Experienced medical dentists will quickly understand the intricacies of the existing manifestations of the disease in relation to a specific patient, determine the cause of the disorder and prescribe highly effective treatment.
The oral mucosa is constantly exposed to a variety of irritants - chemical, mechanical, thermal, numerous microbial agents and toxins. In addition, the oral cavity is a sensitive indicator, showing the state of the internal organs and promptly signaling the presence of problems in one or another body system. If at least one protective factor is weakened, there is a risk of developing inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa. The most common of them are stomatitis and glossitis.
The cause of diseases of the oral mucosa can be: traumatic damage to the tissues of the oral cavity and other traumatic effects (chemical, thermal, etc.) with the development of traumatic erosion, ulcers, leukoplakia or leukokeratosis (keratinization of an area of the mucous membrane capable of malignant degeneration).
Infectious diseases that affect the oral mucosa due to the penetration of viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Quite often, the occurrence of pathological changes in the oral mucosa is associated with disruption of the functioning of various organs and systems of the body: allergies, dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, endocrine disorders, systemic connective tissue diseases, blood diseases, dermatoses, tuberculosis, AIDS and some other conditions. It is often quite difficult to identify the true cause of pathology of the oral mucosa - a lot of experience, high professionalism, and the ability not only to carefully collect information, but also to interpret it correctly and draw appropriate conclusions are required.
Dentists will quickly understand the manifestations of the disease in relation to a particular patient, determine the cause of the disorder and prescribe highly effective treatment.
MAIN CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
There is a common name for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa - stomatitis. When the pathological process is localized on the tongue, they talk about glossitis, on the gums - about gingivitis, on the lips - about cheilitis. When the mucous membrane of the mouth thickens, becomes horny and peels, they speak of a special type of disease - leukoplakia. A characteristic manifestation of stomatitis is the appearance on the oral mucosa of foci of redness, blisters, erosions (afts) or ulcers covered with plaque. These lesions are most often detected on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard palate, and tip of the tongue. Often there is pain at the location of erosions and ulcers, enlargement of nearby lymph nodes, and sometimes an increase in body temperature. The average duration of the disease is 7-14 days. Stomatitis can recur with decreased immunity, poor diet, hypovitaminosis, infectious diseases, and exacerbations are more common in spring and autumn.
DIAGNOSIS OF ORAL CAVITY DISEASES
Diagnosis of stomatitis and other diseases of the oral cavity is based on a thorough clinical examination of the patient by a dentist, which makes it possible to determine the stage of the pathological process and its prevalence, and the presence of a general reaction of the body to inflammation. It is very important to establish the true cause of the disease (trauma, infection, allergy, pathology of internal organs, hypovitaminosis, etc.), because the effectiveness of treatment and the absence of exacerbations in the future will depend on this.
PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT OF DISEASES OF THE ORAL MUCOSA
Etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease (antiviral, antibacterial therapy for the infectious nature of stomatitis, glossitis, cheilitis, vitamin therapy for hypovitaminosis, treatment of the underlying disease that caused the appearance of a pathological process on the oral mucosa); Local treatment aimed at eliminating local traumatic factors, the main symptoms of the disease and the rapid healing of existing erosions and ulcers; A general strengthening treatment that stimulates the body's defenses. An early visit to a dentist when identifying the first signs of pathology in the oral mucosa is the key to a speedy recovery!
STOMATITIS
Stomatitis is a general concept of inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa. This pathology usually occurs against the background of a general and local decrease in immunity. Depending on the cause of occurrence, the following types of stomatitis are distinguished: • Chronic recurrent aphthous • Herpetic • Ulcerative-necrotic • Candidal
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis - manifests itself in the form of characteristic painful aphthae on the mucous membrane of the lips, cheeks, palate or tongue. The main causative agents of this disease are viruses and bacteria. The disease manifests itself against the background of an imbalance in the body of vitamins such as B1 and B12. Most often this can be observed in chronic diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract).
Herpetic stomatitis
The causative agent of herpetic stomatitis is the common herpes virus. Herpetic stomatitis most often occurs in children aged 1 to 3 years. At the same time, in children, at the very beginning of the disease, general symptoms of intoxication begin to appear: • General malaise occurs • Body temperature rises • Lymph nodes enlarge • Nausea and vomiting • Diarrhea
Then, on the oral mucosa, as well as on the red border of the lips, peculiar bubbles begin to form, which quickly open and form erosions with characteristic so-called scalloped (uneven) edges. After about 8-10, healing occurs.
Necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis is characterized by necrosis of the gingival margin. More often, inflammation begins with the interdental papillae and adjacent mucous membrane, namely the cheeks. Then painful, easily bleeding ulcers form, which very quickly merge and form quite large defects in the mucous membrane. As a result of the active process of necrosis, a characteristic putrid odor occurs from the mouth. This picture can be observed with poor oral hygiene. This type of stomatitis is most common in adults aged 17 to 30 years. Necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis can be associated with diseases such as influenza, tonsillitis, acute respiratory infections, various blood diseases, AIDS, tuberculosis and give quite unpleasant and serious complications. In addition to rashes, with this pathology of the mucous membrane, general symptoms of intoxication are also noted - increased body temperature, general malaise, as well as enlarged and painful lymph nodes. Candidal stomatitis
Candidal stomatitis
Candidal stomatitis is a fairly common disease of the oral mucosa, caused by fungi of the genus Candida. In the oral cavity, the following manifestations are noted: • Dryness • Burning • Formation of a white cheesy coating (when this plaque is removed, the mucous membrane bleeds profusely)
Treatment of stomatitis
First of all, at the first symptoms of one or another type of stomatitis, you need to contact a dental clinic. In this case, you should not self-medicate! Indeed, depending on the type of disease, the doctor prescribes a specific treatment for stomatitis. Therefore, the main task of the dentist is, firstly, competent diagnosis, secondly, elimination of the cause of the disease, and only, thirdly, symptomatic therapy for the complete and final treatment of stomatitis. The main prevention is, of course, high-quality and regular individual oral hygiene and careful attention to your health.
Clinical manifestations of stomatitis According to clinical features, the following types of stomatitis are distinguished: catarrhal, ulcerative, aphthous.
Catarrhal stomatitis is the most common lesion of the oral mucosa. The cause of its occurrence is considered to be local factors: poor oral hygiene, dental disease, dental plaque, oral dysbacteriosis. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastritis, duodenitis, colitis, can also cause catarrhal stomatitis. The cause of catarrhal stomatitis may be helminthic infestation. With this disease, the oral mucosa becomes swollen, painful, hyperemic, and may be covered with a white or yellow coating. Hypersalivation (increased salivation) is noted. Bleeding gums and bad breath may occur.
How is catarrhal stomatitis treated?
Treatment comes down to eliminating local causes - removing tartar, treating dental diseases. The mucous membrane is treated with antiseptic rinses - 0.05% and 0.1% chlorhexidine solution. During the day, you can rinse your mouth with a warm solution of chamomile and calendula decoction. A gentle diet is required. With this treatment, the symptoms of stomatitis disappear after 5-10 days. If the symptoms of stomatitis do not disappear, then it is necessary to establish a common cause - as a rule, these are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or helminthic infestation. In this case, local treatment should be combined with general treatment.
Ulcerative stomatitis is a more severe disease than catarrhal; it can develop either independently or be an advanced form of catarrhal. Most often, this disease develops in patients suffering from gastric ulcers or chronic enteritis. It also often occurs in patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system and blood, infectious diseases and poisoning. Unlike catarrhal stomatitis, which affects only the superficial layer of the mucous membrane, with ulcerative stomatitis the entire thickness of the mucous membrane is affected. The initial symptoms of catarrhal and ulcerative stomatitis are similar, but subsequently with ulcerative stomatitis there is an increase in temperature, weakness, headache, enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes. Eating is accompanied by severe pain. If such symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of single or multiple aphthae (ulcers) on the oral mucosa. Aphthae are oval or round in shape, no larger than a lentil grain, with clear boundaries in the form of a narrow red border and a grayish-yellow coating in the center. The causes of this variant of stomatitis are considered to be diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, allergic reactions, viral infections, and rheumatism. The disease begins with general malaise, increased body temperature, and the appearance of pain in the mouth at the site of aphthae formation. This disease should be treated by a doctor.
Leukoplakia is a chronic lesion of the oral mucosa, which is based on increased keratinization of the epithelium (hyperkeratosis). It affects mainly men after 40 years of age and is localized on the mucous membrane of the cheek, in the corners of the mouth and the lateral surfaces of the tongue. The causes of leukoplakia can be mechanical injuries to the mucous membrane: cuts from hooks from a denture, burns from hot or spicy food, etc. This disease most often does not have pronounced symptoms, only sometimes the patient may feel mild itching and burning. But the danger of the disease is that it can develop into malignant forms, so the patient needs to consult an oncologist.
GLOSSITIS is an inflammation of the tissues of the tongue. It can be superficial or deep. Most often, glossitis is a symptom of some general disease of the body, but it can also occur independently.
The main causes of glossitis are: carious teeth, difficult teething, tartar, injuries to the mucous membrane of the tongue and oral cavity, smoking, alcohol abuse, poor oral hygiene, poisoning with heavy metal salts, burns, too hot food, hot spices, allergic reactions etc. Superficial glossitis is often a sign of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and infectious diseases. It is characterized by the presence of plaque on the tongue, its swelling, hardening, and limited mobility. The tongue becomes bright red, there is a burning sensation in the tongue, pain, loss of taste, and excessive salivation.
Treatment of superficial glossitis is based on the use of local anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs. For oral administration, multivitamins, desensitizing agents (antihistamines), and immunostimulants are prescribed. Oral debridement (the process of cleaning an open wound by removing foreign material and dead tissue from it so that nothing impedes its healing) is of great importance.
With deep glossitis, everything is much more complicated. The inflammatory process in this form of the disease is localized in the thickness of the tongue and manifests itself in the form of an abscess (a limited accumulation of pus that occurs during acute or chronic focal infection). Deep glossitis can spread to the floor of the mouth and cause inflammation in the chin and neck. For this form of glossitis, surgical treatment is indicated.
In addition to the above, there are also non-inflammatory forms of glossitis, namely:
— desquamative glossitis (geographical tongue) This form of the disease occurs during pregnancy, damage to the gastrointestinal tract, blood diseases, metabolic disorders, some infectious diseases, helminthic infestations, and rheumatism. Desquamative glossitis is characterized by focal destruction of the red epithelium on the back and lateral surfaces of the tongue. The alternation of lesions with restored and destroyed epithelium makes the surface of the tongue look like a geographical map. In addition to external changes, burning and pain in the tongue may occur. Therapy for desquamative glossitis is based on the treatment of the underlying disease that provoked the development of glossitis.
— rhomboid (median) glossitis Rhomboid glossitis is a congenital anomaly of the tongue as a result of disruption of fetal development processes.
- villous glossitis: this form of glossitis is characterized by the proliferation and keratinization of filiform papillae.
- folded glossitis: glossitis of this form is a congenital anomaly and is characterized by the formation of folds on the back of the tongue, the deepest of which runs longitudinally along the midline. Folded glossitis usually does not cause complaints and does not require treatment.
- Gunter's glossitis: this form of glossitis is one of the signs of anemia caused by a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid. It is characterized by the absence of papillae and a smooth (varnished) surface of the tongue.
— interstitial glossitis: a similar form of glossitis develops with syphilis in the tertiary period. The tongue becomes denser, its mobility is limited.
villous glossitis geographic language Glossitis Prevention of glossitis includes: oral and dental hygiene, regular visits to the dentist, reducing the consumption of aggressive and spicy foods, avoiding smoking and alcohol abuse.
Treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa
The basis of treatment for diseases of the oral mucosa is the elimination of the causes that provoked them. The oral cavity is subject to sanitation, the sharp edges of the teeth are processed, and the denture is correctly adjusted. The patient is advised to stop smoking and eating spicy and hot foods.
Tartar in case of stomatitis is removed, and the teeth are subject to treatment. It is necessary to rinse the oral mucosa with antiseptic agents. Folk remedies are also used: infusions and decoctions of chamomile and calendula. If signs of stomatitis persist after 5-10 days, most likely their cause is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract or helminthic infestation. Then local treatment is combined with general treatment.
The dental clinic diagnoses and treats a wide range of diseases of the oral mucosa. These diseases are diverse, variable and often cause a lot of suffering to patients, despite the fact that they cannot be correctly diagnosed and treated correctly everywhere. In addition, diagnostics using the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue helps to clarify the condition of internal organs and systems, which is important because it does not require additional complex laboratory methods.
Prevention
Preventive measures to help avoid the development of pathologies in the oral cavity include:
- high-quality hygiene procedures;
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- compliance with the basic rules of healthy lifestyle;
- Regular visits to medical examinations.
At the first signs of developing an oral cavity disease, you should immediately consult a doctor: timely diagnosis and adequate therapy will help stop the development of the disease at an early stage.
Preventive measures
By following simple rules, you can significantly reduce the risk of stomatitis:
- strengthening the immune system;
- personal hygiene and oral care;
- normalization of the gastrointestinal tract;
- proper nutrition, which includes all the necessary vitamins;
- rejection of bad habits;
- thorough washing of children's toys, bottles and other items;
- frequent trips to fresh air, active lifestyle;
- timely visits to the dentist and treatment of diseased teeth.
The oral mucosa is constantly exposed to a variety of irritants - chemical, mechanical, thermal, numerous microbial agents and toxins. In addition, the oral cavity is a sensitive indicator, showing the state of the internal organs and promptly signaling the presence of problems in one or another body system.
Symptoms of oral infections
The diseases in question are characterized by the presence of a number of common symptoms. Typically, when visiting a doctor, patients complain of dryness and discomfort in the mouth, which manifest themselves during communication with an interlocutor, while drinking or eating food.
Additional signs of the development of a pathological process include:
- prostration;
- decreased performance;
- insomnia;
- increased body temperature;
- violation of taste perception;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- an unpleasant aftertaste of a temporary or permanent nature.
Inflammation of the tongue is accompanied by swelling of the affected organ and a feeling of numbness. The presence of infectious diseases of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is indicated by pain at the site of the disease, the appearance of ulcers, wounds, ulcers, a dense film and cheesy white coating, and difficulty in salivation.
Symptoms of stomatitis
Stomatitis can be recognized by a number of symptoms, the most common of which are:
- Redness with swelling and pain.
- Subsequent formation of ulcers with a smooth edge under a thin film (with bacterial stomatitis).
- Burning and pain at the site of the lesion.
- Increased salivation, characteristic odor from the mouth.
- Bleeding gums.
- Increased temperature, local or throughout the body.
- The appearance of ulcers is often concentrated on the inside of the lips; it is also possible to affect the area under the tongue, the tongue and gums, and the inner surface of the cheeks.
Traumatic factor
The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is extremely resistant to injury, because throughout life a person eats food, hot or cold, peppery, sour or spicy, chews and swallows it. However, excessive exposure to traumatic factors can cause damage to the mucosa. It could be:
- Mechanical - caused by any object. Most often it occurs when there is a blow, a fall, accidental biting with teeth, gnawing on nuts or seeds, or when the mucous membrane is touched by a poor-quality filling or the edge of a denture.
As a result, erosion, ulcer or wound occurs, a person experiences pain, and bleeding is possible when large vessels are touched.
- Thermal - when eating too hot food. A short-term noticeable pain occurs, later the affected area acquires a whitish tint, and the mucous membrane begins to peel off.
- Chemical - when eating too sour, peppery, spicy food. In this case, a chemical burn occurs, the symptoms of which are the same as those of a thermal burn.
Minor injuries to the mucous membrane of any nature usually heal on their own within 5-7 days, and do not require special treatment or a visit to the dentist. Injuries with bleeding or deep burns require qualified action; it is impossible to cure them at home alone.
How to treat at home
When inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth begins, you need to consult a doctor. Gum disease can be eliminated when its cause is identified. Home therapy is carried out in case of minor pathologies when the provoking factors are known.
- For irritation, you can use antiseptic rinses.
- Pharmacy antimicrobial agents or decoctions of medicinal herbs help well.
- Dentists recommend light massage movements with a medium-hard brush. The massage is performed carefully to avoid injury.
- It is necessary to exclude too cold and hot foods from the diet to avoid unpleasant sensations.
- Stress damages the health of gum tissue. After all, the body actively produces cortisol, which causes inflammatory processes.
Inflammation of the oral mucosa
The oral cavity often suffers from inflammation and ulcers.
Lesions vary in size, appearance, and localization area. Pathologies can occur in any area, including the palate, lips, and tongue. In such a situation, a person complains of pain, the tissue turns red and swells. When the top layer of tissue is destroyed, ulcerative holes form. They may be whitish, take the form of a blister, and fill with liquid. Inflammation of the oral mucosa is primarily manifested by a burning sensation. Therefore, you should consult a doctor in time. Periodontology in St. Petersburg uses complex technologies to treat the tissues that surround the chewing organs. Thanks to modern equipment and advanced techniques, the loss of units is reduced to zero. The main task of the dentist is to maintain reliable fixation of teeth in the gums and jaw bones. To do this, bleeding, discomfort, bad breath, and receding gum tissue are eliminated.
Causes of inflammation
The inflammatory process often begins when the rules of oral hygiene are ignored. The risk of disease increases with the following factors:
- Poor nutrition, when the body is deficient in microelements and vitamins, overeating fatty and sweet foods.
- A decrease in the body's defenses appears as a result of excessive loads and stress.
- Colds, chronic diseases, gastrointestinal pathologies, and blood diseases have a negative effect on the oral cavity. Patients note that under such circumstances the mucous membranes in the mouth and tongue hurt.
- Passion for alcoholic beverages and smoking.
- Taking medications that have a negative effect on periodontal tissue.
- Anomalies of the jaw bone that prevent the complete cleaning of accumulated plaque.
In older patients, gingival tissue dystrophy may be diagnosed, which provokes periodontal pathologies. In addition, abnormal phenomena are caused by infections, chemical and physical irritants, allergies, herpes, and systemic disorders. If normal salivation is disrupted, the risk of disease increases, as the mucous membranes dry out. Learn more about the most common provoking factors.
Stomatitis
The symptom of stomatitis is an inflammatory process; patients have pain in the oral mucosa. More often a child may get it, although adults are not immune from this pathology either. In fact, this disease refers to defensive reactions to irritation factors. Pathology actively develops when:
- decreased immunity;
- the body is affected by viruses;
- an excessive amount of pathogenic bacteria has appeared;
- mouth tissues are injured;
- hygiene rules are not observed;
Adults more often suffer from herpetic pathology with the formation of multiple blisters that turn into ulcers. In addition to this form there are:
- allergic form, which is characterized by swelling, tissue hyperemia;
- Vincent's disease with ulcerative-necrotic anomalies of the gingival papillae;
- thrush, which is caused by yeast-like fungi that create cheesy layers;
- aphthous form, which often indicates diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
Also, Koplik spots may appear on the mucous membrane in measles, exudative erythema, lesions in scurvy, a “crimson” tongue in scarlet fever, tissue hyperemia in Kawasaki disease.
Gingivitis
The initial stage of periodontitis in medicine is called gingivitis. This is inflammation of the gums. The most common causative agents of the disease are gram-negative anaerobic bacteria. Sticky deposits are located along the edges of the gums, as well as in areas that are difficult to clean. Then the soft coating compacts, forming stones. The disease also develops:
- for malocclusions;
- with incorrectly placed filling material;
- for pathologies of oral breathing;
- with endocrine changes;
- for diabetes mellitus;
The disease is diagnosed in pregnant women because their hormonal levels have changed. The swollen tissues bleed and pyogenic granulomas form. Pathology often appears during menopause, because at this time an insufficient number of special epithelial cells are formed. They are very vulnerable, they bleed and hurt. Without treatment, gingivitis gives rise to periodontitis, gum pockets deepen, persistent bad breath appears, the supporting apparatus of the masticatory organs weakens, and bone destruction begins. All this leads to thinning of the bone tissue, loosening of the units, and atrophy of the gum mucosa. In the later stages of the disease, teeth fall out.
Oral injuries
If the oral cavity became inflamed, most often the patient had injury and damage to the mucous membranes. Scratches and accidental bites from uneven or broken crowns or poorly ground dentures first cause the appearance of blisters, and after their ruptures, ulcers. A number of products, as well as chemicals, cause irritation and allergies. Ulcerations form in these places. Fruit acids, flavorings, astringents, some toothpastes, sweets, and mouthwashes are especially irritating to mucous tissues.
How to treat at home
When inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth begins, you need to consult a doctor. Gum disease can be eliminated when its cause is identified. Home therapy is carried out in case of minor pathologies when the provoking factors are known.
- For irritation, you can use antiseptic rinses.
- Pharmacy antimicrobial agents or decoctions of medicinal herbs help well.
- Dentists recommend light massage movements with a medium-hard brush. The massage is performed carefully to avoid injury.
- It is necessary to exclude too cold and hot foods from the diet to avoid unpleasant sensations.
- Stress damages the health of gum tissue. After all, the body actively produces cortisol, which causes inflammatory processes.
When and which doctor to contact
If the pathology does not go away after 3-5 days, such patients require consultation with a periodontist. Treatment begins with a medical history and examination of the oral cavity. Tests are prescribed according to indications. Blood tests, x-rays, and bacteriological studies may be required. After identifying the cause, a treatment plan for the pathology is drawn up. Local treatment includes:
- Anesthetic solutions;
- Applying protective applications;
- Use of corticosteroids;
- Cauterization with laser beams;
- Use of chemicals;
Anesthetic liquids can be used. Pain is relieved by applications of sucralfate. Many dentists add lidocaine. An alternative option is to use paste. Some types of ulcers are treated with low-power laser, which prevents relapses.
Prevention of inflammatory processes in the mouth
Inflammation of the oral cavity is easier to prevent than to cure. You should visit your dentist regularly so that he can detect the disease at an early stage.
- If there are bite defects, they must be corrected.
- You should properly care for your oral cavity, clean your tongue, crowns, and clean soft tissues.
- There should be a balanced diet with all the necessary microelements and vitamins.
- It is imperative to treat chronic diseases.
Visits to the dentist for preventive examinations are carried out twice a year. If necessary, professional cleaning is performed. Visits to a periodontist should be scheduled at the first periodontal problems.
+7 St. Petersburg, Maly Prospekt V.O., building 4
You can ask any questions you may have and find out the available time for making an appointment with the administrators of the ARTES clinic! Call and come for an appointment!