Navigation:
- What to look for during a self-examination
- Choosing a specialist depending on symptoms
Today, a problem such as pathology of the oral mucosa is often diagnosed.
The disease can affect the lips, tongue, and cheeks. What to do? You need to go to the doctor! The dentist will provide assistance to the patient. If the disease is associated with therapeutic problems, you should visit a therapist. If necessary, narrow specialists will be invited for consultation. Note! For any abnormalities of the oral cavity and its organs, you should consult a doctor promptly. Ignoring the disease can lead to serious complications. The sooner the patient gets to the doctor, the faster and easier the therapy will be.
Many ailments of the chewing organs and oral cavity can be treated by a dentist. The tongue is a mirror of the body. His condition allows us to judge:
- About the work of the heart;
- Spleen and liver;
- Kidney, when the pathology is detected from the side;
- Stomach or pancreas;
- Teeth, gums;
Based on the nature of the patient’s complaints, plaque, color, smell, and tests, the doctor determines the problems that have arisen. It is important not to delay going to the medical center. When the disease concerns the chewing organs or mucous tissues of the mouth, you need to consult a dentist. Dentistry in St. Petersburg is a department where they will provide professional assistance to any patient. Diseases are often caused by bacterial, viral, fungal infections, and improper functioning of internal organs.
- Go to the dentist if the burning sensation bothers you, the problem is related to the gum tissues, teeth. Inflammation can be caused by a denture, periodontal disease, or an unsuccessful filling.
- Visit an ENT specialist to rule out tonsillitis and tonsillitis.
- For no apparent reason, make an appointment with a therapist. The doctor will determine the provoking factor and refer you to the right specialist.
This could be an endocrinologist, a neurologist, an infectious disease specialist and other doctors.
Which doctor should I contact?
Almost all internal problems leave a mark on the tongue, especially if they are associated with microflora (this includes staphylococci, spirochetes, fungi, streptococci). In a painful condition, there is usually an infection in the form of fungi, viruses, and bacteria. Independent diseases of the tongue, independent of internal pathologies that cause the inflammatory process, do not appear often; they are mainly associated with other organs, which makes it possible to identify internal problems that have not yet manifested themselves.
- Dentist: the tongue may hurt, burn, and disturb the mucous membrane, in cases associated with teeth and gums. It can rub the denture, cause inflammation of a bad tooth, incorrect filling, periodontal disease, and so on.
- Otolaryngologist, or simply ENT doctor. He will examine the oral cavity and larynx for sore throat, tonsillitis and other inflammatory diseases.
- Therapist. If there are no obvious reasons, you can go to him first. The doctor will try to determine what the problem is and, if necessary, refer you to a specialist or for tests.
- Endocrinologist. Sometimes these diseases may well be the result of a malfunction of the endocrine system.
Dermatologist and oncologist
If a tumor appears on your tongue, you will be referred to an oncologist.
There is a separate group of tongue diseases that cause the growth of tumors on its surface or in the thickness of the tissue. Almost always, these tumors are initially benign, but the lack of treatment, as well as their injury, significantly increases the risk of malignancy - transition to a malignant state.
The most common is considered to be papilloma, caused by a similar virus, which looks like a small soft formation on a thin stalk that does not bring any discomfort to the patient (besides everyday inconveniences). Due to the fact that papillomas, as well as many other similar pathologies, most often arise not on the tongue, but in other areas of the body, the participation of a dermatologist becomes most obvious in making a diagnosis.
Its task is to determine the nature of the spot or tumor, as well as an initial guess as to the cause of its occurrence. In the future, the management of such a patient will be entrusted to an oncologist if one of the following diseases is diagnosed (in addition to papilloma):
- condyloma;
- fibroma;
- botryomycoma;
- lipoma;
- lymphangioma;
- hemangioma;
- cyst;
- adenoma of the sublingual salivary gland.
Swelling of the tongue and larynx is often a symptom of allergies.
Most of these diseases rarely affect the tongue, which is confirmed by statistics, but an experienced and careful doctor must consider all possible options. Treatment of such benign tumors is a combination of surgery and subsequent drug therapy.
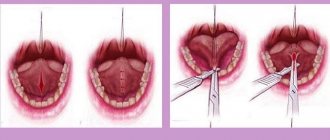
Resection of the tumor is strictly mandatory, since it is not possible to prevent its growth or the risk of malignancy. Today, there are many methods for removing formations from the tongue, and the choice of a specific method depends on the opinion of the doctor, the patient’s health status and his financial capabilities. Typically, you have to choose from the following options:
- excision;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryodestruction;
- sclerosing therapy;
- radio wave removal;
- laser removal;
- cauterization.
To restore the mucous membrane of the tongue after such a procedure, it will take some time and the use of healing drugs, antiseptics and painkillers.
Particular attention is paid to plaque on the tongue.
Additional Information . Removing the tumor from the tongue is sometimes the only way to biopsy it, since partial tissue sampling in this case carries the risk of bleeding. Biopsy is a mandatory research method when diagnosing cancer.
Symptoms
Very often, symptoms can tell you which doctor you need to see if you first pay attention to the condition of the tongue. For example:
- Pallor may be caused by taking a course of antibiotics or vitamin deficiency;
- Trembling may indicate multiple sclerosis and stroke;
- When cultured, a curdled coating will indicate candidal stomatitis;
- Purple color signals disorders of the circulatory system;
- Swelling of the back of the tongue on the right is characteristic of liver dysfunction, on the left - the work of the spleen;
- Dry cracks appear in diseases of the stomach;
- Yellow-green color signals an exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease;
- The tongue has become less mobile;
- Worried about irritation and itching;
- There is an unpleasant odor;
- Weeping erosions have occurred;
- Cracks, swelling, spots appeared.
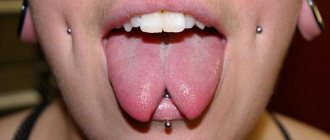
Tongue diseases can be caused by injuries, enlarged lymph nodes, inflammation due to infection, malignant formations, allergic reactions, anemia, viral ulcers, glossitis, lichen, smoking, alcohol, etc. A separate conversation about the fashionable piercing today, the consequences of which can bring a lot of concern . For example, during the procedure, nerve endings may be damaged; when the puncture is not performed correctly, pathogenic microbes may enter the wound, which will lead to inflammation and suppuration. An allergic reaction to the metal may also occur.
Acute glossitis
Here you need to explain in more detail which symptoms require urgent medical attention. There are many types of glossitis, and often their symptoms are similar.
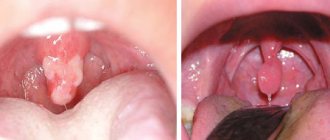
- Catarrhal glossitis is manifested by inflammation of the mucous membrane with swelling and redness. Caused by bacteria, a complication of candidal stomatitis, smoking, acute respiratory infections, influenza, alcohol, caries, and can signal gastrointestinal diseases.
- Ulcerative: It can be recognized by a dark gray plaque, bleeding ulcers and an unpleasant odor from the mouth. It signals ulcerative necrotic stomatitis and especially develops with decreased immunity.
- Abscess: develops in case of injury to the tongue, it swells, turns red, becomes painful, breathing may be difficult, and swelling increases.
- Mycotic: if a white cheesy coating appears on the back of the organ, this indicates mycotic glossitis; it appears when immunity is reduced.
- Desquamative: signals problems with the circulatory/digestive system, kidney disease, dysbacteriosis, metabolic disorders. It manifests itself as itching and burning, mild soreness, and red polishing spots.
- Herpetic glossitis: against the background of acute respiratory infections, hypothermia and stress, it is visually manifested in the appearance of bubbles on the mucous membrane, which, when bursting, turn into painful ulcers. The temperature rises, the head hurts, joint pain torments.
With glossitis, the tongue hurts and burns, tissues swell, speech becomes difficult, salivation is impaired, and it becomes difficult to chew food.
Chronic glossitis
It also manifests itself in several forms:
- Folded: it is characterized by multidirectional folds and is often hereditary.
- Rhomboid: Appears as a diamond-shaped area of inflammation protruding at the base, with a smooth, red texture.
- “Geographical”: starting with a small gray spot, it grows over time, the spots partially merge, foci appear among them, the surface looks like a map, there is almost no pain.
- “Black hairy” tongue: causes sensations of a foreign body in the mouth due to the proliferation of filiform papillae, their appearance darkens to black. Smoking, alcohol, and germs can cause the problem.
- Leukoplakia: thickening of the mucosa, predominantly affects men over 50 years of age. It can be caused by smoking, injury, inflammation, and can be hereditary. People infected with HIV develop a special, “hairy” leukoplakia, recognized as an early symptom of AIDS.
If glossitis is suspected, bacterial culture is usually performed, after confirmation of the diagnosis, rinsing with antiseptics is prescribed, anesthetics are used for pain, and herbal rinsing is used for mild inflammation. When it comes to phlegmon of the tongue, they resort to the help of a surgeon when the necrotic tissue is removed.
Common causes of tongue pain
There are common diseases that cause pain in the oral muscle organ. Knowledge about them will help you figure out which doctor to go to if your tongue hurts.
- Injuries, cracks caused by friction against a plate or denture in the mouth. Burns from hot food or chemicals.
- Glossalgia is pain in a muscle organ in the presence of systemic diseases (gastrointestinal tract, endocrine and nervous systems).
- Glossitis is an inflammation of the superficial or deep tissues of an organ caused by the presence of systemic diseases or the tongue’s own disease.
- An infectious lesion caused by a violation of the microflora of the oral cavity, sore throat, caries (infectious lesions of the teeth), periodontitis (inflammation of the gums).
- Anemia - a decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin, a reduced supply of oxygen to the organs. The tongue becomes blue and painful.
- Leukoplakia is the appearance of foreign formations on the surface (plaques), which can become keratinized (the organ tissue becomes coarser) and degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
- Stomatitis is a disease of a fungal and infectious nature, accompanied by pain, plaque and rashes on the organ.
- Blockage of the salivary glands - causes pain under the tongue, accompanied by dry mouth.
- Oncological diseases.
- Allergies.
Treatment
All of the above diseases of our speech organ have similar symptoms, characterized by plaque, redness, swelling, changes in color, shape and erosion. And only a specialist can determine what kind of disease has affected this organ, after conducting a series of studies. Therefore, based only on the described symptoms, you should never self-medicate, which can significantly worsen the condition and complicate the recovery process.
Usually, ointments (painkillers, antifungals), antiseptic solutions, and wound healing agents are used. For viral diseases, general treatment is added to local treatment.
Diseases of the tongue can indicate to a specialist internal diseases that have not yet discovered themselves. Find out which doctor treats tongue and seek help for any of the above symptoms.
Consultations with a doctor online Taking care of your health is a life priority for everyone.
Communicate with doctors online and receive qualified assistance without leaving your home. Try it Please note! The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.
Features of the structure of the tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ, which is covered on the outside with mucous membrane and papillae that perceive taste (sweet, salty, spicy, bitter), nerve fibers in the thickness of the organ - tactile sensations. After food enters the oral cavity, receptors transmit information through nerve endings located deep in the organ to the brain. Its tip and sides are adjacent to the teeth. The root is located at the entrance to the pharynx.
The mucous membrane does not have a submucosal layer, therefore it is firmly attached to the muscle base and does not fold into folds like skin. The muscular organ is penetrated by vessels and lymphatic formations (lingual tonsil), which nourish it and protect it from pathogenic microorganisms.
Under the tongue and near its root there are salivary glands that secrete secretions. It protects the oral cavity from drying out and exposure to microbes and fungi.
Candidal stomatitis
This pathology of the tongue is provoked by Candida fungi from the yeast category, which can be classified as a conditionally pathogenic microflora. In small quantities they live on the mucous membranes of a healthy person, without contributing to the development of any diseases. Most often, children and elderly people who have decreased immunity are susceptible to this disease.
The main factors that provoke thrush in the mouth and tongue are:
- immune system diseases;
- long-term use of antibacterial medications;
- infection of the child by the mother during childbirth;
- insufficient or lack of oral hygiene;
- intestinal diseases;
- changes in hormonal balance.
For young children, switching to artificial formula with a large amount of sugar, as well as parents’ failure to comply with the requirements for cleaning feeding supplies, pose some danger.
Among adult patients, the risk group includes people with impaired immune systems due to HIV, cancer, and diabetes. Candidal stomatitis is often provoked by smoking and frequent rinsing of the mouth with lotions, which contributes to drying of the mucous surface of the tongue and the creation of a favorable environment for the colonization of Candida fungi.
Leukoplakia
This tongue disease in most cases occurs in mature men and is usually associated with metabolic disorders or pathologies of the digestive organs. Leukoplakia does not cause pain, but the patient may experience discomfort when eating spicy foods. Usually this causes the tongue to tingle. The symptoms of this disease are characterized by the fact that the mucous membrane of the organ begins to become covered with whitish plaques, spreading to other parts of the oral cavity. Spots can even appear in the corners of the mouth. With the development of leukoplakia, therapy for the disease that provokes it is necessary. The affected parts of the tongue are cleaned with:
- radio waves;
- laser therapy;
- electroexcision;
- diathermocoagulation.
If a specialist suspects the cells have degenerated into cancer cells, surgical treatment is performed.
Infectious glossitis
Infectious diseases of the tongue can be recognized by its appearance, as well as by the symptoms caused by the pathology. Additionally, symptoms that accompany the inflammatory process are treated, for example, antipyretics are used for fever, and analgesics are used for severe pain.
Infectious type glossitis is an inflammatory process that affects the tissues of the tongue and is caused by infection. This disease very rarely occurs on its own. In most cases, this is a manifestation of a certain inflammatory process, for example, stomatitis. In this case, the tongue stings greatly.