What is a consultation with a doctor and how is it different from a simple conversation about my health problems? What exactly do I pay for when I pay for a doctor’s consultation?
When any illness overtakes us, we get injured, or face any other health problem, we face the need to consult a doctor as a professional to solve these problems. Finding a good doctor is a separate serious task. But now a specialist to whom you are ready to entrust the most precious thing you have - your health - has been found and you go to him for a consultation. You have previously found out the cost of this consultation and asked yourself: “What do I have to pay for? I’m going to the doctor first just to talk.”
You should be very clear that any conversation with a professional, in particular with a doctor, involves a detailed clarification of what is unusual with you, what worries you, what prevents you from living a normal life for you. In addition, it is necessary to carefully study the materials of previously conducted examinations, methods and results of previous treatment. In other words, the doctor, using his professional knowledge, clarifies the symptoms or manifestations of a possible disease, clarifies when and as a result of which these symptoms appeared, whether the diagnosis of the disease was correctly established by the specialist to whom the patient previously contacted, how correctly and effectively the treatment was carried out, etc. d. Thus, it becomes possible to get a general idea of the medical problem that forces you to seek medical help, outline subsequent medical measures, and give adequate recommendations to the patient who has applied.
In order to properly conduct a conversation with the patient and FIND OUT THE MOST VALUABLE INFORMATION FOR SOLVING THE PATIENT’S PROBLEMS AND GIVE BASED ADVICE, the doctor uses his professional knowledge, which was acquired in the process of intense, long-term, EXPENSIVE and ongoing study. Well, using any professional knowledge to solve other people’s problems is called WORK, and any work must be paid depending on its intensity and duration. The work of returning and restoring the most precious thing a person has, his health, should be paid especially well.
What is the difference between a doctor's appointment and a consultation? Why does it cost more?
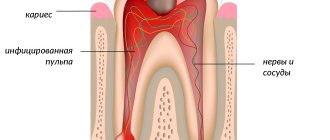
A doctor's appointment is, in fact, a logical continuation of a consultation. Once the physician has a general understanding of the patient's problems, he or she usually needs additional information, primarily from a physical examination, to accurately determine the disease or medical problem (diagnosis). During such a study, the doctor must carefully examine the patient and identify the external manifestations of the disease: changes in the shape and color of the skin and mucous membranes, the presence of pathological rashes and any abnormal formations or tumors, the presence of pathological discharge from natural orifices, disruption of the normal functions of organs accessible for examination and systems, etc.
Through palpation (feeling), percussion (tapping) and auscultation (listening), the doctor can determine the presence of pathological enlargements of the lymph nodes and internal organs, pain in certain parts of the body, assess the function of the heart, lungs, intestines, etc. Sometimes, only on the basis of consultation and physical examination can a diagnosis of the disease be made. However, in most cases, the path to diagnosis lies through laboratory, functional, ultrasound, x-ray and other special studies. So, an appointment with a doctor necessarily includes a consultation and physical examination and, if indicated, other examinations aimed at establishing a diagnosis of the disease and prescribing its treatment. It is an accurate diagnosis and the prescription of the correct treatment that is the actual purpose of seeking medical help.
Specialization of doctors
Most often, men turn to a urologist with their intimate problems. Although he cannot be called an exclusively male doctor, because representatives of the fair sex can also turn to him. A urologist specializes in diseases of the urinary tract and reproductive system. Women turn to him most often with kidney ailments and a problematic bladder, and for other intimate issues they go to a gynecologist. But since in men the urinary and reproductive systems are closely connected, a urologist deals with both. This doctor is responsible for both systems of the male body.
An andrologist is already considered a more specialized specialist, because he treats exclusively men. This specialty appeared relatively recently. Andrologists treat a huge range of diseases and serve as a urologist, sexologist, endocrinologist, urologist and even a psychologist for men. It is these doctors that both very young boys and older men go to for treatment. The andrologist simultaneously specializes in the following medical fields:
- Neurology
- Venereology
- Sexology
- Urology
What is the doctor's job when making a diagnosis?
The doctor must not only comprehensively know all the symptoms and signs of the disease, be able to correctly perform and evaluate the results of certain diagnostic methods, but also do a tremendous amount of analytical work in the course of making a diagnosis. During the examination of the patient, the doctor identifies the most characteristic and important symptoms and manifestations of the disease and, based on his knowledge, identifies this disease, i.e. establishes his diagnosis. To do this, every modern doctor needs not only a good education received at a higher medical school and appropriate specialization. A modern doctor cannot stop constantly learning and improving until the end of his medical career, i.e. While the doctor is working, he is learning and accumulating both a constantly growing body of theoretical knowledge and invaluable practical experience, which, in turn, is also constantly analyzed. This is the extreme complexity of medical work, and this is also why the medical profession is one of the highest paid in the civilized world.
Is it possible to do without a face-to-face consultation with a doctor and receive comprehensive recommendations for solving a medical problem in absentia (for example, through an online consultation)?
The answer to this question can only be negative in all cases, because any correspondence consultations (including via the Internet) can only be of a general and indicative nature. Without seeing the patient, the doctor can never make the correct diagnosis, and, consequently, prescribe adequate, reasonable and effective treatment. The fact is that based on the symptoms described by the patient or the manifestations of the disease that are important in his opinion, it is impossible to form a true impression of the existing problem. There are many more reasons why in all cases you should seek real medical help ONLY IN PERSON. Let's list the main reasons.
Firstly, a person who does not have special medical education often does not know what the most important symptoms should be described when presenting his problem. Secondly, the same symptoms can have completely different diseases. Thirdly, it is often impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on symptoms alone; additional research is required. Fourthly, the same disease can develop differently in different people, which may require different approaches to diagnosis and treatment methods. Fifthly, the treatment requires proper monitoring, including the use of objective diagnostic parameters. Finally, not everywhere in Russia there are high-quality laboratories; not all medical institutions have all the necessary equipment and specialists to diagnose various diseases and monitor the quality of their treatment.
The specialists of the Andros clinic are constantly working to maintain and improve their professionalism, and our institution annually spends large amounts of money for these purposes. The clinic’s doctors undergo training cycles in the best specialized institutions in Russia, the USA, France, Germany, Denmark and Italy, and attend congresses and symposia under the auspices of the leading urological and gynecological associations of the world, of which they are members. The Andros Clinic has its own library of the best foreign medical literature; we receive 4 of the world's most prestigious journals on urology and gynecology. The doctors at the Andros Clinic have extensive practical experience (we serve up to 800 patients monthly), which is constantly subject to careful critical analysis.
Meaning of the word doctor
(Latin: Doctor, actually means teacher, teacher). Initially among the Romans, and then in the Middle Ages, the word D. generally meant a teacher and in this sense was identical with the words magister, scholasticus, etc. Only from the 12th century. it became an honorary title for scientists. Some jurists, and especially scholastics of the 13th century. began to receive the title D. with the addition of various distinctive epithets; Thus, Thomas Aquinas was called D. angelicus and communis, Gerson - D. christianissimus, Wyclif - D. evangelicus, Bacon - D. mirabilis, etc. At large church meetings, the title Doctores concilii was received by scientists who had an advisory voice. The Church Fathers (Catholic) bore the title Doctores ecclesiae. Jewish scientists were called Doctores thalmudiaci, dividing them into D. gema rici and mischnaici. As an academic degree, the title of D. was first given by the University of Bologna, around 1130, after which the emperors granted universities the right to award the degree of D. legum to persons who had studied Roman law. The popes granted the univ. the privilege of giving the title to D. canonum et decretalium. Later, when both rights - Roman and canonical - began to be studied together, both degrees merged into one: D. utriusque juris (both rights). The first D. of theology (theologiae) was created, it is believed, by the University of Paris in 1231, after which D-res medicinae, physicae, logicae, grammaticae, notariae (notarial art), etc. became common. The title of D. acquired character the highest scientific degree, and it could be obtained only after previously achieving the bachelor's and licentiate degrees. The D. and Master's degrees were initially completely equivalent; only from the 16th century. in the faculties of law, medicine and theology, the doctoral title was preferred, while philosophers preferred the master's degree. From the end of the 18th century. and the faculty of philosophy in most states accepted the doctorate as the highest academic degree. Having granted universities the privilege of raising the degree of D., the emperors themselves distributed, through their court palatines, diplomas for the degree of D. From the seal attached to them in the capsule (bulla), the persons who received them were called Doctores bullati, in contrast to Doctores rite promoti , awarded the degree of D. at universities. According to previous Imperial German laws, persons who received a doctorate were treated as nobles. Requiring a preliminary test to obtain the academic degree D., Univ. (including Russians) sometimes give honorary (honoris causa) doctoral diplomas for special merits. The distribution of an honorary doctorate, per diploma, is carried out (especially often in Western universities) at the choice of the university. councils, during major academic holidays, anniversaries, etc. In modern times, the degree of D. began to be received in Western countries. Univ. and women. In France, the doctoral title is rare. In England, which has retained the lower scientific degrees of bachelor and licentiate, the designations of the D. degree are written immediately after the name: DD.-Doctor of Divinity (theology); D. (s.) L. - D. of (civil or canon) Law; LLD - D. juris; MD—Medicinae D.; DM - D. of Music. Requirements imposed by the univ. for raising to the power of D., different in different states, and sometimes in the same state, for example. England, every university on various grounds gives the degree D. Often achieving a doctoral degree is associated with large costs for printing a dissertation, for an exam, etc. In most parts of the university. the examination consists of a written essay on a given topic (Klausur), an oral conversation (Colloquium) - usually about the written essay, and a test in various subjects (examen rigorosum), after which the person seeking the degree of D. and bearing the title of doctoral student ( doctorandus), must submit a dissertation, which in some universities. still needs to be publicly defended. In the theological faculty, the degree of D. is usually given only honoris causa, while in others, in most cases, a test is required. Until recently, promotio in absentia was practiced in Germany, without an exam, only on the basis of a submitted dissertation, often not even printed; but on the initiative of prof. Momsen had this resolved. In Russian univ. The degree of D. is given only upon preliminary achievement of a master's degree, excluding the Faculty of Medicine; to obtain it, a doctoral dissertation is required, in which some new scientific question must be developed and which must be publicly defended. For doctors of medicine and surgery, see Medicine. In our dormitory, the title of Doctor of Medicine is given mainly to doctors, even if they do not have an academic degree of Doctor of Medicine.
Diseases treated by an andrologist
This specialist is primarily consulted for lesions of the genital organ. The symptoms are quite different. This may include severe pain in the groin and perineum, burning during urination, pain in the lower abdomen and testicles, redness and the appearance of growths on the skin in the intimate area. It is also worth contacting an andrologist if there is discomfort when urinating, incomplete emptying of the bladder, or difficulty urinating. In addition, the doctor is responsible for issues of premature ejaculation, weak or absent erection, hypogonadism, scrotal pathology, prostatitis, and male menopause. A consultation with an andrologist will be required for the following symptoms:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Pathologies of reproductive function
- Impaired secretion of male sex hormones
- Micropenis and other deviations from normal sizes
- All kinds of anomalies in which the testicles, prostate gland, scrotum and other appendages are absent
- Pathologies in which the testicle does not descend correctly or does not descend into the scrotum at all
- Gynecomastia
- Ejaculation and libido disorders
- Increased prolactin levels
- Male menopause, which is manifested by lower testosterone production, erectile dysfunction, severe exhaustion of the body
- Endocrine pathologies
- Cancers of the pelvis
- Inflammation of the head of the penis and foreskin
- Inflammation of the tissues of the testicles and their appendages
- Urethritis of various origins
- Prostate diseases
- A man’s stable and long-term definition of himself as a woman without mental reasons or sexual dysfunctions