Plaque research
intensity, color and thickness
If the plaque is sticky and difficult to remove from the surface, then there is a reason to take care of examining the patient for gastroenteritis; the presence of a putrid odor promises confirmation of the diagnosis. A thin whitish layer, easily removed, with a metallic taste in the mouth, indicates damage to the stomach and intestines.
A greasy deposit like sludge indicates stagnation of food in the intestines, accumulation of excess mucus, and poor digestion of food. A whitish layer at the base of the tongue indicates enterocolitis, the same at the edges and on the front, not reaching the tip, shows pulmonary problems. If the latter type of deposits turns into a foam-like layer, it means that the patient has chronic bronchitis.
A yellowish coating indicates problems with the gallbladder and ducts, and if it is located in the lower region of the organ, then jaundice begins. If the entire tongue is covered with yellowness, the liver is not working properly, there is excess bile, cholecystitis and problems with the digestive system develop.
The brown color of the layer indicates serious problems with the lungs and stomach; the same sign evenly in the middle part of the tongue, symmetrically with respect to the middle groove, indicates bilateral pneumonia. A black-brown coating, difficult to remove, resembling a chessboard, occurs with pellagra, namely, a deficiency of B vitamins and nicotinic acid. At a late stage of the disease, the organ turns red, and the surface resembles a varnished coating.
Diagnosis of diseases of internal organs by language has been worked out over decades of medical practice. But it is the doctor, seeing the first signs of the disease, who will prescribe an examination and determine the true cause of the appearance of changes on the surface of the tongue. The patient can only raise the alarm on his own; all other actions remain the prerogative of the specialist.
Tongue diseases
A lacquered tongue is observed when
Changes in the condition of the mucous membrane of the tongue are an indicator of pathogenic processes in the body
A special symptom of the mucous membrane of the tongue is the so-called “lacquered tongue”. It occurs when the taste buds atrophy.
The tongue becomes smooth, which causes the shine characteristic of other mucous surfaces of the mouth to appear. A lacquered tongue occurs with loss of the ability to absorb vitamin B2, chronic colitis and stomach cancer.
Due to the first reason, there is a deficiency of vitamins PP and B2 - pellagra, the second symptom of which is a brown, hard-to-remove plaque covered with cracks in a checkerboard pattern. Advanced pellagra causes the return of the symptom of a varnished tongue and its severe redness. The bright red lacquered tongue is called "cardinal tongue".
A varnished tongue is a sign of anemia
Another cause of a lacquered tongue is anemia. This disease in most cases occurs due to a lack of vitamins B9 and B12, as well as iron, in the body. With anemia, the tongue, in addition to redness, acquires a glossy shine. The appearance of shine is explained by the fact that during anemia the papillae of the tongue atrophy and their smoothing is observed.
The main symptoms of anemia are:
- drying and peeling of the skin;
- deterioration of hair and nails;
- redness of the tongue;
- in severe cases of the disease, cracks may appear on the palms and soles;
- weakened immunity, which can, in parallel with anemia, lead to colds, flu, bronchitis and other similar ailments;
- lethargy; mood swings;
- dizziness, sometimes even fainting;
- vomit; constipation or diarrhea.
Condition of the mucous membrane of the tongue
Changes in the condition of the mucous membrane of the tongue are an indicator of pathogenic processes in the body, and therefore in medicine the characteristics of the tongue are used to diagnose diseases.
An excessively dry surface of the mucous membrane of the tongue indicates, first of all, dehydration. It can also be caused by peritonitis, intestinal obstruction, hyperthermia in infectious diseases, as well as a long stay in a coma. With prolonged constant dryness, the appearance of cracks in the tongue is possible. A dry tongue with numerous cracks is also characteristic of diabetes mellitus, and if left untreated in a diabetic coma, the speech organ becomes brownish-brown.
Inflammation
The most common reason leading to a change in the color of the mucous surface of the tongue is its inflammation. The etiology of the process includes a complex of probable factors, so all types of inflammation of the tongue were combined into a common group of diseases called glossitis. All types of glossitis cause the tongue to become discolored, but not all cases are red.
In addition, hyperemia is not the only symptom of inflammation, although a red tongue may indicate the onset of the disease. Types of glossitis that can lead to redness of the mucous membrane of the tongue are as follows:
- desquamative;
- Gunter's;
- diamond-shaped;
- catarrhal;
- atrophic;
- allergic.
All types of glossitis cause the tongue to become discolored, but not all cases are red.
Depending on the type of glossitis, the features of redness of the tongue (partial or complete) and the shade of red may vary. To make a preliminary diagnosis, it will be necessary to analyze the remaining symptoms, some of which are characteristic only of one type of disease, and the other part relates to the general clinical picture.
One of the most common signs is swelling of the tongue, as well as plaque on its surface and impaired salivation. In addition, small ulcers or erosions may appear in the mouth and tongue, causing an unpleasant odor, and the patient may experience a slight increase in temperature.
Important! Treatment of glossitis is primarily symptomatic and is based on the use of antiseptics, anti-inflammatory and anesthetic agents. If the inflammation is the result of some internal disease, then this cause will need to be eliminated, otherwise glossitis will recur
Treatment of glossitis
After diagnosing glossitis based on the general clinical picture and data from the patient’s blood test, the doctor prescribes a treatment procedure. Treatment is primarily aimed at the main cause of the disease, and if it lies in the general condition of the body, then also at its improvement. Firstly, during treatment, too hot, sour and sweet foods are excluded from the diet. Secondly, to strengthen the immune system, it is prescribed to use a complex of vitamins (vitamin B, vitamin E).
Oral rinses and baths are very effective in treating glossitis. Solutions of furatsilin, chlorhexidine, and anesthetic solutions are used.
If ulcers are present, the tongue is treated daily. For treatment, a cotton swab is used, after which rinsing with antiseptic agents is carried out.
The doctor may also prescribe applications using a special gel rich in vitamins, carotoline, and rosehip oil, which has a healing effect.
It is very important during treatment and during prevention to monitor the general state of health and prevent the occurrence of diseases that contribute to the appearance of glossitis of the tongue.
Lacquered tongue
When examining the tongue, the doctor determines its color, shape, swelling, thickness, moisture, teeth marks, the severity of the vessels under the tongue, the color and nature of plaque. A healthy person's tongue is pink, clean and shiny; plaque indicates the presence of some disease. An equally important indicator is the violation of the relief of the tongue, the appearance of various grooves. This often indicates a violation of vitamin metabolism.
The organ appears varnished as a result of atrophy of its papillae. With some pathologies, the number of papillae decreases, sometimes they disappear altogether. As a result, it looks smooth, shiny, as if varnished. This condition is typical for malignant tumors of the stomach, vitamin B12 deficiency, and chronic colitis.
The smooth surface of the tongue, the so-called varnished tongue, often appears with iron deficiency and B12 deficiency anemia
A type of “varnished” tongue includes the so-called “chessboard” tongue, which is covered with a difficult-to-remove coating of black-brown color, with cracks resembling a chessboard.
This happens with pellagra (deficiency of nicotinic acid and vitamin B). In the late stage of pellagra, the tongue acquires a red tint with a varnished surface - “cardinal tongue”.
A disease that causes a varnished tongue
A smooth surface of the tongue, the so-called “polished” or “varnished” tongue, often appears with iron deficiency and B12 deficiency (pernicious) anemia, as well as with a deficiency of vitamins B2 and PP. The factors that lead to such changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue also affect the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines: the same changes occur there - atrophy of the gastric mucosa.
Vitamin B12 is necessary for normal hematopoiesis, the formation of epithelial cells, the functioning of the nervous system (participates in the formation of myelin), growth and regeneration processes.
The lacquered tongue is observed:
- megaloblastic anemia (pernicious anemia, pernicious anemia, Addison-Biermer anemia);
- lesions of the digestive tract (the tongue becomes bright red, smooth, highly sensitive to chemical irritants, atrophy of the gastric mucosa and achylia are noted);
- disorders of the nervous system (paresthesia, pain, gait disturbances).
The crimson lacquered tongue is characteristic
The reasons for changes in the color and tongue to raspberry color in adults may be gastritis, pneumonia, poisoning, lack of vitamin B12
The reasons for the change in the color of the tongue to crimson in adults may be gastritis; pneumonia; poisoning; lack of vitamin B12. A raspberry tongue may be associated with chronic liver disease.
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract, in particular gastritis, will be indicated by a bright crimson tongue coated. At the same time, the intensity of plaque accumulation will be uneven: there will be less of it along the edges and at the tip, and more in the center. At the same time, the appearance of a burning sensation on the tongue indicates a decrease in stomach acidity.
With a lack of vitamin B12, a severe form of anemia may occur. It develops against the background of poor absorption of vitamin B12 in the body or its insufficient intake from food. Nerve cells and bone marrow especially suffer from vitamin B12 deficiency. One of the signs of anemia is a raspberry lacquered tongue.
Red lacquered tongue
“Red lacquered” tongue, or atrophic glossitis (the surface of the tongue is bright red, shiny, smooth due to atrophy (death) of the taste buds) - stomach cancer (a malignant tumor arising from the epithelium (surface cells of the stomach)), chronic colitis (inflammation colon), malabsorption of nutrients in the intestine, vitamin B12 deficiency, xerostomia (dry mouth), candidiasis.
- https://si-yanie.com/smartblog/308_diagnostika-po-yazyku.html
- https://www.remedium.ru/doctor/detail.php?ID=2993
- https://buzovanovosti.ru/aksessuary/raspberry-tongue-in-adult-causes-diagnosis-of-diseases-by-language.html
Post Views: 448
LiveInternetLiveInternet
When thinking about oral hygiene, one should not forget about such an important organ as the tongue. It performs many functions in the body. A clean tongue without plaque is a sign of a healthy digestive system. Diagnosing diseases by language is a fairly common phenomenon and for some reason is becoming a thing of the past now. After all, it has long been known that the tongue, in addition to numerous functions, performs one more - it serves as a mirror of the body.
Diagnosis by language:
- shows not only the general condition of the body, but can also give specific details: imbalance, lack of vitamins and an allergic reaction to the food you eat. Is the tongue wet or dry, is it coated, what color is it, are there marks from the teeth, etc. - all these are important signs.
- Diagnosis by language is based on the premise that the language reflects the state of the entire organism; and since the heart meridian and the spleen-pancreas meridian, kidney and liver meridians are connected with the tongue, the state of the tongue is directly related to these organs, especially the heart, being the key to identifying its function. Based on this, it is believed that the language reflects the states of “emptiness and fullness” of these organs, blood, body juices and Chi. Thus, by the appearance of the tongue it is possible to determine the severity of the pathological condition and predict the outcome in the absence of treatment.
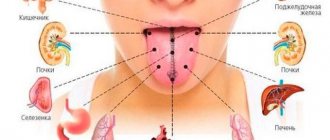
- There are four zones in the tongue that correspond to certain organs (meridians). Thus, in the area of the tip of the tongue the pathology of the heart and lungs is manifested, in the area of the middle part of the tongue the pathology of the spleen - pancreas and stomach is reflected, the area of the root of the tongue determines the condition of the kidneys, and the area of the lateral sections - the condition of the liver (and gallbladder). In case of illness, it is necessary to separately evaluate changes in the body of the tongue and separately - changes in the nature of plaque. It is believed that the body of the tongue mainly reflects the state of “emptiness or fullness” of the function of the internal organs, and the nature of the plaque indicates a superficial or internal syndrome, as well as the relationship between the forces of the pathogen and the body’s defenses.
- Increased sensitivity and discoloration of certain areas of the tongue reflect disorders in those organs that are associated with these areas.
Eastern approach
- From the point of view of ancient Eastern medicine, it was believed that the appearance of a healthy person’s tongue is subject to changes depending on the time of year. So, in summer the papillae of the tongue are slightly enlarged, and in autumn they have a lighter or yellowish tint.
- The moisture or dryness of plaque indicates the amount of “juice” in the body.
- The appearance or disappearance of plaque on the tongue is a sign of worsening or improvement of the disease. If during the course of the disease there is no plaque on the tongue, but then appears, then this indicates the development of disorders in the stomach or is a heat syndrome. If at the beginning of the disease there is a plaque and it soon disappears, then this indicates an “emptiness of the stomach chi,” accompanied by a weakening of the body’s defenses. If the thick plaque becomes thinner, this indicates an improvement in the patient's condition.
- The assessment of plaque on the tongue is made by color, thickness, shape, appearance (wet - dry), as well as the ability of the plaque to separate.
- A thin coating indicates an incipient disease, a thick coating indicates a chronic one. White plaque, gradually thickening and acquiring a yellow, and then gray and dark tint, means the progression of the disease, and, conversely, clearing and thinning of the plaque indicates an improvement in the condition.
The topographical arrangement of internal organs on the tongue in classical Ayurveda, as indicated by R. Steuernagel (an Ayurvedic therapist who teaches diagnostics in Europe and also works in Chinese traditional medicine), is not recorded in manuscripts. In Chinese medicine, there are three Heaters (Sanjiao):
the first is located above the diaphragm and warms the heart and lungs,
the middle one is between the diaphragm and the navel,
lower – heats the lower abdomen.
Anyone familiar with the doshas will see parallels with the location of vata (lower abdomen), pitta (middle abdomen) and kapha (chest and upper stomach).
The Chinese identified the organs of the three Warmers in the language:
for example, the back third of the tongue or its root reflects the lower Heater, i.e. cotton wool (organs such as the kidneys, bladder, large intestine are located there),
the middle part (stomach, liver and gall bladder) belongs to pitta
and the upper (lungs and heart) refers to the upper Heater or kapha.
The arrangement of organs in these three parts of the tongue is not influenced by the qualities and functions of the three doshas, i.e. dryness of vata in the front of the tongue and also the kapha zone or accumulation of mucus from kapha in the lower third of the tongue where vata is located.
- Excitation of the body (thickened, smooth median fold);
- Radicular pain, curvature of the spine in the lumbar region (curvature of the fold at the root of the tongue);
- Radicular pain, curvature of the spine in the thoracic region (curvature of the fold in the center of the tongue);
- Radicular pain, curvature of the spine in the cervical region (curvature of the line at the tip of the tongue);
- Chronic enterocolitis, dyspeptic conditions (dental marks on the lateral surfaces of the tongue);
- Trembling of the tongue (thyrotoxicosis, neurasthenic conditions, alcoholism, hidden fear or anxiety);
- Chronic disorders in the large intestine (multiple intertwined small folds of the tongue);
- Renal dysfunction;
- Colon dysfunction;
- Intoxication of the large intestine;
- Intoxication of the gastrointestinal tract (duodenum and small intestine);
- Weakness of the heart, various forms of cardiovascular failure);
- Chronic bronchitis (foamy plaque);
- Bilateral pneumonia (brown plaque);
- Hypofunction of the lungs (most likely emphysema).
How can you learn about malfunctions in the spine, stomach, and liver using your tongue and prevent them?
- CURVATION OF THE FOLD AT THE TIP OF THE TONGUE signals cervical osteochondrosis. Most likely, this is the result of a sedentary lifestyle, working for a long time with a computer or at a desk.
- BENDING OF THE FOLD IN THE MIDDLE OF THE TONGUE - lumbar osteochondrosis, it usually affects professional drivers and people who spend a lot of time behind the wheel. To avoid osteochondrosis, you need to regularly warm up: several squats, head rotation - simple but very useful exercises.
- REDdening of the tip of the tongue is a sign of weak cardiac activity, beginning of coronary artery disease. Diseases of the pulmonary system can be judged by changes at the edges of the tongue, closer to the tip. Heart and lung diseases most often affect smokers, so such changes in the tongue are a serious reason to quit smoking.
- YELLOWSHIP ON THE TONGUE AND PALATE indicates liver disease and chronic cholecystitis.
- BY THE PLAQUE AT THE BASE OF THE TONGUE, disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys are judged.
- TEETH PRINTS ON THE TONGUE are a sign of dysbacteriosis, slagging in the body. In this case, it is worth changing your diet, eating less fatty and fried foods.
- TRIMING OF THE TONGUE is a manifestation of neurasthenic syndrome. The advice here is this: try to improve the psychological situation at home, at work, and change your lifestyle.
- CRACKS IN THE TONGUE can indicate various diseases of the blood, endocrine system, and kidney pathology. This is where we need to check most seriously. A sign of problems in the body is a decrease in taste sensations. There are zones on the tongue that are responsible for the reaction to sweet, sour, salty, and bitter. If a person stops feeling any of these tastes, then we can talk about diseases of the nervous and endocrine systems.
It is best to diagnose the disease if the tongue is clean. To do this, it should be brushed just like teeth. It is better to do this with a special tongue massager or at least with a regular soft toothbrush. This is very useful, because by massaging the area of the tongue, we thereby influence the internal organs that are projected in one place or another, and thereby bring their functions back to normal.
Source: AiF Health
The state of health can be judged by the color of the tongue, the coating on it and the surface. Plaque on the tongue is the first sign of decreased immunity, and the thicker it is, the longer the chronic disease of a particular system lasts. By the color of the tongue you can determine: 1. Infectious diseases (flu, measles), in which the color becomes burgundy. 2. Too pale tongue indicates anemia, heart failure. 3. Purple color signals diseases of the blood and respiratory system. 4. A red and shiny tongue indicates atrophy of the gastrointestinal mucosa or cirrhosis.
When assessing plaque on the tongue, you need to pay attention to its location: 1. White plaque in the middle of the tongue (usually with cracks) indicates gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers. 2. White plaque at the root of the tongue most likely corresponds to enterocolitis. 3. White plaque along the edges in front indicates lung disease, and brown plaque indicates pneumonia. 4. White plaque on the back at the edges - the kidneys are suffering. 5. Plaque covers the tongue due to dysbacteriosis, stomatitis, or fungal infection. 6. Taking on a yellow color, plaque indicates problems with the pancreas, cholecystitis. 7. If the plaque has a brown tint, there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract. 8. Blue plaque - typhus, dysentery.
The shape and other features of the tongue also have diagnostic value: 1. Any cracks indicate problems with the stomach (gastritis). 2. Dryness occurs not only with fever, but also with diabetes and anemia. 3. A burning sensation on the tongue (of course, not after eating spicy food) indicates stress, cervical osteochondrosis.
The mucous membrane of the tongue is the beginning of the gastrointestinal tract, therefore its swelling indicates the need for diagnosis by a gastroenterologist.
Alarm signals of the tongue include: - redness of the right side - disruption of the liver; - redness on the left side - problems with the spleen; - thickening of the tongue - dysbacteriosis, thyroid disease, mental disorder; - white plaques - thrush (candidiasis).
Sometimes ulcerations, cracks, and erosions appear on the tongue, which, depending on the location, also reflect the condition of the body according to V. Lad: - a semicircular coating at the root of the tongue indicates the sensitivity of the colon, and a white spot indicates toxins in it; - a white spot in the middle of the tongue - disruption of the entire gastrointestinal tract; - cracked tongue - chronic intestinal diseases; — tooth marks are characteristic of enterocolitis; - a trembling tongue indicates thyrotoxicosis, neurasthenia; - a line in the middle of the tongue for problems with the spine; - a line curved at the root - for lower back pain; - a line curved in the middle - for problems in the middle part of the back; - the line bends at the tip for neck pain. How to care for your tongue? It has already been said that the tongue is a kind of filter for food that can enter the respiratory tract. However, in addition to everything else, it prevents unwanted microorganisms from entering the gastrointestinal tract, because the root of the tongue is always covered with epithelial growths.
The tongue needs to be helped to cleanse itself because: - it is a collection of bacteria; — along with food, bacteria can enter the stomach and blood.
Cleaning your tongue should be done after brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth, but before eating. Nowadays, brushes have been created that allow you to move on to tongue hygiene after cleaning your teeth.
However, the procedure can be carried out: - with your fingers (takes 1 minute), after each movement of the pads from the base of the tongue, you need to rinse both your fingers and your mouth; - use a spoon to scrape your tongue, also rinsing the spoon and mouth.
The oral cavity is also cleansed with vegetable oil, for which you need to take a tablespoon of any of them in your mouth and rinse for 15-20 minutes. The oil will become watery at the end of the procedure: its white color indicates cleansing, yellow indicates the need to repeat rinsing.
https://vkurse.ua/health/ukazyvaet-yazyk.html
(From the book “The Art of Diagnosis by Face” by E.I. Gonikman)
“The tongue during illness is a true imprint of the internal state of the body, the state of not only the digestive instruments, but also other organs. The tongue is grooved with thick edges in case of simultaneous pathology of the spleen and liver, convex in case of abdominal dropsy, pointed in case of tabes. In general, the outlines of the tongue correspond to the outlines of the bones of the face.” M. Nechaev
According to Chinese traditional medicine, the tongue is connected to the heart. The condition of the tongue and speech reflect heart problems. However, the body functions as a single whole and the connection of the heart with other organs is also reflected in the tongue.
Reading the tongue provides valuable information about the energy balance of internal organs and allows you to make an accurate diagnosis if they are disturbed.
When examining the tongue, you should pay attention to:
1. Color
2. The nature of plaque in different areas of the tongue.
3. Shape and character of the surface. The surface can be: dense, smooth, loose, striated, etc.
4. Various formations on the tongue - papillomas, blisters, aphthae. Their location indicates the organ in distress.
The damage to the tongue is, as a rule, homologous in nature, depending on the damage to the internal organs. M. Nechaev, a famous Russian doctor, wrote: “Impairments can cause curvature of the tongue: when the organs of a certain half of the body are diseased, the corresponding side of the tongue changes in volume, its tip deviates.”
The great wisdom of the Creator when creating man lies in the presence of correspondence systems that promptly signal organs in distress, reflecting at the same time a change in fate.
Let's briefly look at some of the most important details of language diagnostics.
Normally, the color of the tongue is pink, its surface is smooth, with evenly spaced papillae.
A yellowish coating on the tongue indicates existing problems with the gallbladder. Yellow plaque increases with seasonal exacerbations of the liver and gallbladder. One of the signs of developing jaundice is yellowness in the lower part of the tongue, which is detected when it is raised to the palate.
A coated tongue with a thick, often different type and color coating occurs in infectious diseases, as well as in disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition, with pathology of the digestive organs, the following changes in the surface of the tongue may be observed:
— white coating, indicates increased dryness (Metal) of the digestive organs;
- a geographical tongue, characterized by the presence on its surface of areas of different color and size with deep grooves and reliefs.
Geographic tongue occurs with chronic damage to the gastrointestinal tract, as well as with some forms of mental disorders.
The general characteristic changes in the tongue indicated above indicate a close connection between the digestive organs: stomach, spleen, pancreas with the structures of the brain and psyche.
- A tongue with a black coating is an ominous indication of a disorder of the digestive system, especially the gallbladder and pancreas.
— Black plaque also indicates a violation of blood pH towards acidosis (acid-base balance), due to dehydration of the body.
— The varnished tongue has a shiny, smooth, bright red surface due to atrophy of the taste buds. Occurs in stomach cancer, the body’s inability to absorb vitamin B2, and chronic colitis. The so-called “chess” tongue is a type of “varnished” tongue. With this pathology - pellagra (deficiency of nicotinic acid and vitamin B) - the tongue is covered with a difficult-to-remove black-brown coating, with cracks resembling a chessboard. In the late stage of pellagra, the tongue acquires a red tint with a varnished surface - “cardinal tongue”.
- With Birmer's anemia, a smooth, as if scraped tongue, devoid of the papillary layer, is observed. Clinical patients experience burning and tingling in the tongue area.
— Deep imprints of teeth on the lateral surface and front of the tongue characterize meridional disorders, hidden neuroses, and the more pronounced the neurosis, the clearer the imprints.
- In case of severe infectious diseases, poisoning, accompanied by high fever, severe pneumonia, the tongue becomes red (crimson) in color.
- In case of severe renal, toxic disorders, the tongue has a dark red color.
— A pale, bloodless tongue indicates anemia and severe exhaustion of the body.
- In advanced cases of cardiovascular disorders, a bluish tint of the tongue is observed. At the same time, a sharply cyanotic tongue is an ominous sign of imminent death.
— In case of dysfunction of the cerebellum, cerebral circulation, hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, the tongue is bent or deviated to the side.
- A tongue with deep transverse fissures also indicates a predisposition to vascular disorders of the brain.
- Flat ulcers on the tongue indicate a tuberculosis process.
- A black tongue may indicate cholera infection.
— A whitish coating on the tongue indicates a pathology of the large intestine (the back third of the tongue), problems with the duodenum are manifested by a whitish coating on the tongue, localized in the middle third of the tongue.
- If there is plaque on the middle part of the tongue and a light red coloring of its tip and edges, one can think of a violation of the acid-forming function of the stomach.
- Streaks of foam on both sides of the tongue indicate the presence of rheumatism.
- With scarlet fever, the tongue resembles strawberries with sour cream - alternating white and red spots.
- tongue trembling indicates a brain disease or a deep neurotic disorder.
— With anemia due to iron deficiency in the body, a burning sensation of the tongue is noted.
- Diabetes is characterized by a dry tongue, the surface of which has numerous cracks.
— If the underside of the tongue is bluish, a circulatory disorder with cardiopulmonary insufficiency can be assumed.
— Pale coloring of the underside of the tongue indicates pathology of the liver and gallbladder.
https://valeo-puls.narod.ru/Yasik.htm
Diet
With any changes in the language, it is first necessary to normalize the diet. Excluded from the menu:
- Fast food;
- Fatty meat (pork, lamb, duck);
- Salty and spicy foods;
- Smoked meats and marinades;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Alcohol;
- Bakery and sweets;
- Mushrooms.
Pathological diseases of the oral cavity are very diverse and do not always have characteristic symptoms.
Some diseases develop gradually, unnoticed by the patient, and only a doctor can detect them during the next examination.
This happens with, or more precisely, its variety - Gunter's glossitis.
Glossitis is an inflammatory disease that develops on the mucous membrane of the tongue.
In this case, pathological changes in the mucous membrane occur, it takes on an unusual appearance, and sometimes this process is accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
Discomfort in the oral cavity is the first sign of the development of glossitis
As a rule, glossitis is not an independent disease, but one of the signs of serious disorders in the body. If we talk about Gunter's glossitis, it is one of the symptoms of anemia that occurs due to a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid in the patient's body.
Changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue during the development of Gunter's glossitis acquire the following features:
- the surface of the tongue becomes very smooth, as if polished;
- the color of the mucous membrane becomes very bright, crimson;
- There may be a slight burning sensation in the mouth.
The papillae of the tongue, mainly in the root zone, become atrophic and smoothed. The mucous membrane of the tongue becomes covered with reddish areas of inflammation, located mainly along the edges and at the tip; aphthous rashes and cracks may appear. Similar changes can occur in the mucous membrane of the gums, cheeks, pharynx, soft palate, and even the esophagus.
In parallel, atrophy of the gastric mucosa is observed, which is most pronounced in the fundus area; the folds of this mucosa become smooth or not defined at all, the walls of the stomach become thinner, and polypous growths may appear on them.
Development occurs gradually; first, symptoms similar to the inflammatory process appear, the tongue becomes scalded or inflamed. Then atrophic processes occur on it, leading to changes in the mucosa, which can subsequently “spread” to the gums, cheeks and other mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus.
Treatment of pathology
Therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the symptoms of glossitis and treating the underlying diseases that provoke the development of the inflammatory process in the tissues of the tongue.
A special diet, including pureed soups, slimy porridges and purees, helps reduce the intensity of pain when eating food. Rinsing the mouth with a solution of furatsilin or potassium permanganate is designed to reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process and eliminate foci of active growth of pathogenic microflora. In case of severe pain, the patient is prescribed anesthetic applications to the tongue.
Diagnosis of diseases by language
Most people wonder how to determine a disease by the tongue, because its changes in color and “texture” indicate not only the condition of the oral cavity, but also malfunctions in the body; it can effectively tell which doctor to contact in case of a tongue disease.
First of all, you need to create a correspondence diagram:
- part of the tip carries information about the condition of the heart and lungs;
- the middle “monitors” the pancreas, liver and spleen;
- the root is responsible for the digestive organ;
- lateral zones (closer to the root) - buds.
The placement of the sections schematically follows the arrangement of organs in the human body.
Self-diagnosis can be carried out
To do this, you need to examine the oral cavity in daylight in the morning, on an empty stomach, and pay attention to:
- an unpleasant companion to some ailments is a characteristic bad breath;
- shade and appearance of the tongue;
- presence of plaque, its features;
- structural changes in the surface (ulcers, cracks).
Prevention of tongue diseases
To reduce the risk of diseases of the tongue itself and other organs, you need to monitor your diet, daily routine, and have less contact with infectious patients. Caring for the tongue itself should be no less thorough than caring for your teeth.
Accumulating plaque, especially in sick people, is a place for mass reproduction of bacteria and fungi. If it is not removed in time, it will become a source of infectious pathogens that can penetrate any part of the body.
When cleaning the oral cavity, it is useful to use toothbrushes with a ribbed back surface to clean the tongue from plaque, or special spoons and scrapers. But they must be used carefully so as not to damage the taste buds and mucous membrane. After cleaning, it is advisable to use pharmaceutical rinsing solutions or prepare homemade herbal decoctions.
Why is my tongue red and stinging?
The causes of these unpleasant symptoms can be both external factors and various diseases of the oral cavity. In each specific case, it is necessary to identify the exact cause of the burning sensation and select the appropriate treatment if necessary.
External provoking factors
Specific food
A common non-dental cause of tongue tingling is eating pineapple. This fruit, if not ripe enough, contains more acids that corrode the sensitive oral mucosa.
Bromelain is one of the causes of burning and redness of the tongue and palate. There is especially a lot of it in unripe pineapple. This is an enzyme capable of breaking down protein. If we take into account that a person consists of protein, then the pineapple “eats” us while we eat it.
Also, any other overly salty, spicy or sour food can cause discomfort in the oral cavity. Especially if your food contains a lot of pepper. This occurs due to severe irritation of the sensitive receptors of the tongue.
Cigarettes
Another burning sensation is smoking. The reason lies in the burn of the mucous membrane. Hot tobacco smoke can be very harmful, and if you add to all this the influence of nicotine, tar and other dubious substances released when smoking, then a burning tongue is the least unpleasant thing you can get.
Tongue tip injuries
Various mechanical impacts can easily cause injury to the tongue. The cause may be an incorrect bite, haste while eating and talking. An incorrectly installed prosthesis or if it is not the right size increases the likelihood of biting your tongue when closing your jaw.
Trying to chew nuts with your teeth doesn't do any good either. In addition to breaking teeth, the sharp edges of the shell severely injure the mucous membrane.
Taking a certain group of drugs
Medicines containing chemical and some herbal components, when taken orally, can irritate the mucous membranes, cause inflammation and affect the surface of the tongue. The first reaction becomes noticeable at its tip - itching, tingling and redness occur.
Allergic reactions
If the body is hypersensitive to certain substances from the outside, not only the skin, but also the tongue can react. Tongue tingling may occur if you are intolerant to any component of the toothpaste, mouthwash, or have a reaction to food.
Oral diseases as a cause of discomfort
Tartar
His education is related to dental disorders.
Tartar consists of a large number of pathogenic microorganisms that produce toxins.
Frequent contact of the tongue with the affected surface can lead to almost imperceptible inflammation of the mucous membrane.
This causes symptoms such as: the tongue stings and the tip turns red.
Stomatitis and herpes
These are two completely different diseases in origin, but they have similar symptoms. During exacerbation, redness and tingling of the tongue are observed.
Candidiasis
The fungus affects the entire mucous membrane of the oral cavity, but it is the tongue that suffers the most. A white coating forms on it and it swells slightly. Its walls may become thinner, which will cause an increased reaction in the form of a burning sensation.
Dry mouth
A common disease that involves the tongue itself, and especially its edges. It reacts sharply to lack of moisture. Due to the occurrence of many small cracks, sensations appear in the form of burning and redness.
Bruxism
Possible cause of tongue pain. Uncontrolled clenching of the jaw and grinding of teeth can easily lead to accidental injury to a muscular organ.
Glossitis
Infectious disease. A characteristic symptom is redness and swelling of the tongue. In the future, the discomfort only intensifies and can lead to difficulty speaking.
Also, a burning sensation and redness of the tongue can be caused by a number of diseases of internal organs and systems.
Among them, the most notable are:
- Gastritis. With increased acidity, due to the high concentration of gastric juice, a malfunction of the stomach occurs. As a result of reflux, contents from the stomach are thrown back into the esophagus and throat. When it enters the oral cavity, hydrochloric acid irritates the mucous membranes, including the tongue. This is where the tingling begins.
- Anemia. With a deficiency of iron and folic acid, a burning sensation of the tongue and the entire oral cavity often develops.
Also, this symptomatology is characteristic of liver disease, kidney failure, diabetes, pinched occipital nerve, menopause, certain heart diseases and lichen planus.
Causes of the red surface of the tongue and the appearance of plaque
Here we will look at the reasons why a person’s red tongue is covered with a characteristic overlay.
- You must have noticed that with a sharp increase in temperature, heat and fever, the entire face and skin may become red and swollen. The same applies to the oral cavity.
- Dry scarlet deposits are caused by inflammation of the gray matter of the brain, as well as its outer layers. The same symptoms are caused by inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal mucosa and even lungs.
- The cause of the shiny, glossy sediment is a critical level of body temperature and multiple burns to the body.
Scarlet fever
- A change in color to a red-crimson hue can indicate severe systemic diseases of a viral or infectious nature. As a rule, the therapist diagnoses a sore throat, pneumonia or scarlet fever based on this color of the tongue. If we are talking about the latter, then another symptom for diagnosis can be considered inflammation of the papillae on the tip and back of the tongue. If the red color of the muscle darkens, then you should look for kidney diseases and infections, or suspect intoxication of the body. The cherry hue also speaks of infectious and viral diseases such as measles and influenza.
- Allergies to cosmetics and food elements manifest themselves in the form of uneven scarlet spots appearing on the mucous membrane.
- Burns and injuries to the organ also lead to swelling and redness of its surface.
- The specific disease Kaposi's sarcoma manifests itself in the form of characteristic spots on the muscle with a dense blue coating on them.
- Anemia (anemia) leads to a painful and pale color of the oral cavity, while the muscle remains unnaturally red.
- Red and slightly brownish sediment on the surface is left by bad habits, such as drinking wine, overusing coffee and tea products, and smoking.
- Also, characteristic overlays are caused by parasites in the body.
- Let’s not forget about the tongue disease glossitis, which is always accompanied by redness.
- Surprisingly, even an ordinary dark stone, as well as advanced caries, can contribute to unnatural deposits on the mucous membrane.
- Patients often notice a red tongue after taking courses of antibiotics.
Causes of tongue inflammation
The inflammatory process in the tissues of the tongue can develop as an independent disease against the background of a bacterial infection or manifest itself as a symptom of a systemic pathology. Local glossitis often results from viral infections.
A burn to the oral cavity provokes the development of inflammatory processes that can affect the tongue. In a similar way, mechanical injuries act on organ tissue, becoming a favorable environment for the active growth of bacteria. The risk group includes patients prone to systematic alcohol consumption and smoking.
Glossitis is one of the main symptoms of poisoning with heavy metal salts. An acute reaction can develop when using someone else's toothbrushes or frequent use of mouth rinses.
Symptoms of glossitis often develop against the background of damage to the tongue from the sharp edges of decayed teeth, elements of dentures or braces. Chemical irritants contribute to the development of oral dysbiosis. An imbalance in the microflora causes glossitis to progress to the chronic stage.
Causes of pimples on the tongue
The main causes of rashes:
- Traumatic injuries, burns. It is not uncommon for the tip or side surface of the tongue to be damaged by cutlery, excessively hot food, or one’s own teeth.
- Weakened immunity. When pimples appear on the tongue closer to the throat, at its base or near the frenulum, this may indicate reduced immunity. A variety of pimples and bumps are localized here: condylomas and warts, candidal bumps.
- Development of benign and malignant tumors.
- Poor nutrition, bad habits. If you violate the rules of nutrition, excessive consumption of spicy, hot, rough foods, an irritating and traumatic effect on the mucous membrane occurs, which provokes the appearance of pimples. Excessive smoking and alcoholic libations also cause diseases of the mucous membranes in adults.
- The causes of lumps at the end and root of the tongue may be allergic. Allergic disease manifests itself not only on the skin, but also on mucous membranes.
Large bumps located close to the pharynx make it difficult to swallow food and can lead to breathing blockage.
- If pimples appear on the tongue closer to the larynx, they could be caused by various diseases of a chronic, viral and infectious nature.
- Neglect of hygiene rules. Eating unwashed foods and irregular oral hygiene not only in children, but also in adults, causes irritation of the mucous membrane and, as a result, the appearance of inflamed pimples.
In most cases, bumps at the base of the tongue, pimples on the side, growths on the tip of the tongue are manifestations of the following diseases:
Diseases of the mucous membrane of an inflammatory nature (glossitis) are accompanied by the formation of painful red rashes on the mucous membrane, in severe form - abscesses, phlegmons.
- Metabolic disorders, vitamin deficiency. Such conditions are characterized by redness and enlargement of the taste buds, which often become inflamed and acquire a red-white color.
- Herpes, characterized by the appearance of painful red pimples and blisters.
If red bumps or nodules appear on the base of the tongue, this may be a symptom of pyogenic granuloma. The formations consist of blood vessels and are localized in the wounded area. Pathology occurs due to injuries and damage to the mucous membrane. When touching the formations, a person feels a sharp pain.
- Digestive disorders (malabsorption). Pimples on the root, all over the surface of the tongue, are one of the symptoms of this pathology.
- Candidiasis (thrush). A disease that often affects newborns. The child's tongue becomes covered with red bumps and a cheesy coating forms. The baby behaves restlessly, cries, and has difficulty swallowing; these symptoms are caused by itchy red-white pimples and dry mouth.
- HPV – human papillomavirus. Formations are localized in any area of the tongue: at the tip, root, side. The bumps on the tongue closer to the larynx cause particular discomfort, as they interfere with swallowing and create the sensation of a foreign object in the mouth.
- Allergic diseases. The rashes do not hurt, but they interfere with swallowing and speaking.
- Diseases common to children: chickenpox, measles.
Prognosis and prevention
Timely treatment of glossitis and the underlying disease allows you to count on the patient’s complete recovery. An unfavorable prognosis occurs when the pathology is complicated by phlegmon, abscesses or malignant neoplasms.
Prevention of glossitis involves compliance with hygiene standards. Patients at risk are advised to visit the dentist regularly. Excessively spicy foods should be excluded from the diet. Quitting smoking and drinking strong alcohol reduces the likelihood of glossitis.
Diseases that our tongue can tell about.
The appearance of plaque on the tongue may indicate various diseases, but sometimes it is observed in a minor form in a healthy person. In particular, in adolescents during puberty, plaque may form due to a hormonal surge. A light, white and odorless coating through which the pink color of the tongue can be seen is considered acceptable.
By the way, in summer the plaque is more pronounced, but the papillae of the mucous membrane are clearly visible, in the fall the plaque is drier and lighter, and in winter it has a yellowish tint
It is also important to maintain oral hygiene: use special toothbrushes with a ribbed back surface for the tongue
Common manifestations of glossitis
The first symptom of glossitis is a feeling of burning, discomfort and the presence of a foreign body in the mouth. The tongue becomes bright red or burgundy and swells. In a patient with edema, salivation increases. In this case, the taste sensations are dulled, or completely lost, or the taste is distorted. With glossitis, eating causes difficulty and pain. Pronunciation becomes slurred. If the patient does not resort to treatment for a long time, then glossitis becomes chronic, which is manifested by persistent and dense swelling and changes in the structure of the tongue, sometimes mushroom-shaped growths form.
In the case when glossitis is caused by pathogenic microflora, the patient exhibits symptoms of acute inflammation, namely:
- swelling;
- hyperemia;
- painful sensations;
- temperature increase;
- bubbles that, when opened, leave pathogenic erosions.
If the patient has an immunodeficiency, the inflammatory process spreads to the oral mucosa.
Candidal glossitis manifests itself as a white coating on the tongue, which can be loose or dense and fixed; hyperplastic changes in the tongue are also noted.
If glossitis is advanced, it is complicated by abscesses. At the beginning of this stage of the disease, the patient experiences symptoms such as:
- sharp throbbing pain;
- slurred speech;
- uneven enlargement of the tongue;
- swelling;
- increased salivation.
If glossitis is complicated by phlegmon, then the resulting swelling and area of purulent tissue melting move to the bottom of the mouth and neck. During this period, the patient feels severe, pronounced pain, while the process of chewing food is disrupted. The patient has difficulty speaking and breathing, and sometimes has attacks of suffocation. The patient may also experience symptoms of intoxication, or more precisely:
- weakness;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- heat.
WHAT TO DO WHEN A CHILD HAS A CARRIBON TONGUE?
A crimson tongue can be a symptom of a disease, but the procedure largely depends on its cause. If you have alarming symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment of scarlet fever will be based on the use of an appropriate antibiotic
For Kawasaki disease, it is important to start treatment as early as possible. It involves the use of infusions of immunoglobulins, acetylsalicylic acid, and sometimes steroids
Vitamin deficiencies may require their use, changes in diet or treatment of diseases that result (for example, nonspecific intestinal inflammation). Large amounts of vitamin B12 are found in animal products such as meat, milk, fish, and eggs. Vegetables and fruits rich in folic acid include spinach, broccoli, legumes, kiwi, and oranges. The source of iron for the body can be, for example, liver, red meat, legumes, nuts, cocoa. If the cause of glossitis is a fungal infection, it requires treatment with appropriate antifungal drugs.
Secondary medical education
- General midwife
- Dental assistant
- Dentist
- Dentist
- Dental Technician
- General expert research laboratory assistant
- Blood service laboratory technician
- AIDS service laboratory technician
- Laboratory assistant of forensic biological departments
- Laboratory assistant of forensic histology departments
- Laboratory assistant of physical and technical departments
- Laboratory assistant at chemical and toxicological departments
- Gynecological nurse
- Neonatology nurse
- General practice nurse
- Nurse of the intensive care and anesthesiology departments
- Ophthalmic nurse
- Pediatric nurse
- Physical therapy nurse
- Nutritional Nurse
- Massage nurse
- Care nurse
- Healthy lifestyle nurse
- Tuberculosis service nurse
- Psychoneurological nurse
- Blood service nurse
- AIDS service nurse
- Dental nurse
- Therapeutic nurse
- Physiotherapeutic nurse
- Surgical nurse
- Medical statistician
- Laboratory assistant doctor
- Nurse's assistant
- X-ray technician
- Paramedic laboratory assistant
- Narcology paramedic
- General practitioner
- Paramedic of the public education system
Category: Medicine / FindHow.org
Information on the topic
- Online testing for certification of medical specialists
- Free treatment according to the guaranteed volume of medical care in Kazakhstan
- List of clinical stations for medical category
- How are healthcare professionals certified?
- How to attach to a clinic in Kazakhstan
- Online testing of energy specialists
- Register of medical organizations
- Trial online testing UNT
- Trial online testing for the civil service of the Republic of Kazakhstan
- How to find a job without experience in Kazakhstan
- Laws for civil service tests in Kazakhstan
- Frequently asked questions about online testing (law enforcement)
- Rules for admission to universities in Kazakhstan
- How to enter the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Republic of Kazakhstan
- Compulsory social health insurance (OSHI) in Kazakhstan
- Online testing of engineers in the field of construction and architecture