Progeny is a deviation from the norm in the structure of the dentition. It is expressed in enlargement and protrusion of the lower jaw. Such pathological deformation occurs statistically in the range of 1.4 - 30% of patients.
External signs:
In addition to a protruding lower jaw, patients with pathology experience:
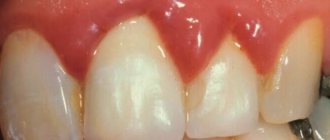
- recession of the face in the middle part;
- thickening of the lower lip relative to the upper, its protrusion, and sometimes inversion;
- deepened nasolabial folds;
- increased angle between the lower and upper jaw.
Mesial occlusion or progenia: what is it?
Several centuries ago, people with mesial occlusion were considered mentally retarded.
A similar defect was present in the composer Richard Wagner and Emperor Charles V, but such great people could not achieve great success with mental disabilities, so the theory was not confirmed. Since with a mesial bite the lower jaw is pushed forward, the face takes on a menacing and angry appearance.
That is why pathology contributes to the formation of not only aesthetic, but also psychological problems: a person feels uncomfortable with such a defect. Problems of the dental system also develop. Incomplete closure of the teeth and the resulting gap between the jaws contribute to the accelerated proliferation of pathogenic microflora, which leads to various diseases of the oral cavity. Treatment of mesial occlusion is important not only for restoring facial aesthetics, but also for preventing various dental diseases.
Correction Methods
Progeny detected in adulthood also requires correction, just like a problem in children. A peculiarity of the treatment of mesial occlusion is that after installation of corrective systems, patients may be bothered by pain symptoms.
The choice of therapy for adults is limited, since their bone structures are already formed and less elastic than those of children and adolescent patients. Correcting progeny by restraining the growth of the lower jaw will be ineffective.
Methods for correcting anomalies in mature patients include:
- Application of fixed orthodontic structures.
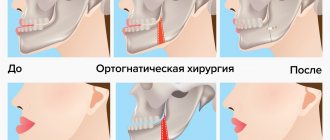
- Surgical intervention. The operation may include the removal of some teeth or correction of the lower jaw bones followed by plastic surgery.
A conservative way to deal with the defect involves wearing braces or other removable structures to correct the bite. This treatment takes a long time, but produces positive effects when the structures are worn correctly. Braces are used to treat any form of the disease: false, true and combined progeny.
Recently, the edgewise method has been used to eliminate the defect. The essence of the operation is to use a device equipped with rings and locks, shaped like tubes.
The elements of the device are fixed on the supporting teeth, and braces are installed on the front incisors. Round arches or special orthodontic structures are attached to the grooves of the corrective systems:
- twist-fles;
- nitinol archwires;
- tetrahedral arcs.
All about myotherapy in orthodontics
Not in all cases, mesial occlusion can be corrected using conservative treatment methods. The installation of orthodontic structures in this situation will be considered only as a component of complex therapy.
If the defect is simultaneously combined with a shortened frenulum of the tongue, then the patient is offered surgery. During the procedure, adults sometimes have their bottom row of teeth removed.
If you are inattentive to the problem and lack of treatment, a defective bite becomes the cause of various complications, among which are:
- premature destruction and abrasion of dental elements;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal due to inadequate chewing of food;
- difficulty swallowing;
- migraine;
- extraneous sounds in the hearing organs.
Causes of mesial bite
There are three main factors associated with malocclusion that cause its development: genetic, congenital, acquired. According to statistics, in 13 people with mesial bite the cause is a genetic predisposition. The anomaly can form during fetal development as a result of various maternal diseases provoked by viral infections. Also, mesial bite can result from:
- birth injuries;
- adenoids, which interfere with nasal breathing;
- incomplete upper dentition;
- adentia (partial or multiple);
- enlarged tonsils, cleft palate;
- rickets, bone hypoplasia, osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- microdentia, macroglossia;
- short frenulum of the tongue.
Malocclusion is caused by artificial feeding, a deviated nasal septum, untimely teething, and uneven wear of milk teeth. Bad oral habits of children also influence the formation of malocclusions.
Content:
- Features of mesial occlusion
- Why does curvature occur?
- How to correct a mesial bite in a child
- Elimination of progeny in adults 4.1. How long does mesial bite correction last?
- Consolidation of the results obtained
- Why does protrusion of the lower jaw need to be treated?
One of the most complex dental anomalies is mesial occlusion.
It leads to the advancement of the lower jaw forward, which causes the aesthetics of the face to deteriorate and the proportions to be disrupted. Let's look at how to correct this disorder in adults and children, which includes modern treatment for this type of curvature.
Classification of mesial occlusion
Progeny is of the following types:
- True. With this type of bite, an increase in most parameters of the lower jaw is observed. The pathology is characterized by severe symptoms and an overdeveloped lower jaw. This mesial bite is facilitated by a genetic factor and problems with bearing a fetus. The pathology of this form is noticeable from early childhood, so treatment should begin at the age of 3-4 years.
- False. The mesial bite of this type is characterized by normal dimensions of the lower jaw. Pathology is formed as a result of underdevelopment of the upper jaw or its incorrect position. It can also be caused by chronic ENT diseases, problems with nasal breathing, early change of teeth, short frenulum of the tongue. Also associated with a false mesial bite is the habit of thumb sucking or prolonged pacifier sucking.
- Combined. Combines signs of true and false progeny. Such malocclusion requires a long period of treatment. It is compiled individually, most often requiring both surgical intervention and the subsequent use of orthodontic structures.
Each of the listed abnormal bites can be of three degrees of severity. They are determined by the size of the gap that is formed between the incisors of both jaws and the angle of the lower jaw.
Causes, clinical picture of pathology
The main reasons causing the defect are:
- genetic factors;
- congenital disorders, incorrect formation of tooth germs;
- illnesses of the expectant mother during pregnancy or pathologies of fetal development;
- trauma in childhood, earlier removal of temporary units;
- increased abrasion of enamel;
- hormonal imbalances;
- excessive increase in the size of the tongue, which begins to affect the frontal area;
- respiratory tract diseases;
- bad habits in a child;
- long-term breastfeeding;
- lack of phosphorus, calcium in the body, poor diet.
During a visual examination, the doctor conducts a survey to find out what your diet is like and your general health. Diagnostics are required to assess the degree of pathology and draw up a correction plan. The Patient’s appearance and facial symmetry are also analyzed. If the angle of the lower jaw increases or the chin protrudes excessively, a preliminary diagnosis can be made immediately. This type of defect is also indicated by deepened nasolabial folds and flattened chin. It is necessary to evaluate the functionality of the muscles around the mouth and the position of the articular heads. Additionally, radiography and photometry are performed, which may be required to obtain more information.
Forms of mesial occlusion
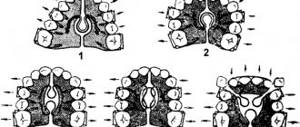
When diagnosing malocclusions, three main forms are distinguished: dentoalveolar, gnathic (skeletal), and mixed. The first includes progeny, characterized by incorrect position of the teeth. For therapy, you can use a brace system. The second type of abnormal bites is accompanied by a violation of the size of the jaw bones. This is a complex form that often requires surgery to treat. With a mesial occlusion of a mixed form, a combination of skeletal and dentoalveolar signs is observed - abnormal jaw sizes and incorrectly formed dentition.
Correction of pathology
Treatment of progenic bite depends on the etiology, severity, age and individual characteristics of the patient. The main means of correction is hardware. If necessary, other methods can be used - surgical, orthopedic, myogymnastics.
The fastest treatment is that begins at the end of the primary occlusion. The slowest is in adolescents over 15 years of age, after the growth of the jaw bones has completed. Gnathic (jaw) anomalies are more difficult to correct than dentoalveolar ones.
In a milky bite
In the primary dentition, attention is paid to the normal development of the alveolar ridges and jaws. If the HF is underdeveloped, massage of its anterior segment is indicated to stimulate growth .
It is necessary to control the eruption of the upper “threes” and their bite with the lower incisors. If the frenulum of the mouth is shortened, its plastic surgery is performed.
The most important task in temporary occlusion is to prevent bad habits in the form of sucking foreign objects, lips, fingers. For this purpose, a vestibulo-orural plate with a lingual stop .
To normalize chewing, hard foods are introduced into the child’s diet.
Weaning off mouth breathing and ensuring lip closure is achieved with the help of vestibular plates and training the orbicularis oris muscles.
Make sure that when sleeping the child’s chin does not rest on the chest.
At 3-4 years of age, with a progenic bite and a small (up to 1.0 mm) reverse overlap of the incisors, the edges of the maxillary and mandibular incisors and the cusps of the canines are ground to ensure marginal closure of the incisors. This promotes proper growth of the dental arches.
In the morning and evening, a two-minute massage is performed for the vestibular deviation of the maxillary anterior teeth.
To correct the bite, myogymnastics is used - training of the oral muscles. The choice of exercises depends on the type of anomaly.
In particular, to correct non-closure of the lips and normalize the work of the orbicularis oris muscle, alternating forward extensions and stretching of the lips are performed. With an open bite, the jaws are alternately clenched and unclenched.
To limit the growth of the lower jaw, a chin sling (extraoral sling) is used, which is a plastic or fabric mouth guard that covers the chin and is connected to a neck sling or head cap. The kappa pulls the lower jaw back, inhibiting its growth.
To change the position of the upper “ones” and “twos”, with deep incisal overlap, use the Bruckle apparatus complete with an extraoral bandage.
Treatment lasts about 1-2 months. It is recommended to wear the Brückl apparatus constantly, without removing it even during meals (with mandatory cleaning and washing before bed and after each meal). Treatment is completed once multiple contacts between the maxillary and mandibular teeth are achieved.
If the child’s body is weakened, it is necessary to normalize his diet and take general strengthening medications.
Causes of congenital absence of upper incisors and methods of correcting the defect. In this publication we will tell you how to use the Kois deprogrammer.
Follow the link https://dentist-pro.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/naskolko-effektivna-miogimnastika.html if you are interested in myogymnastics exercises for children.
In a mixed bite
In the initial stages of progenic occlusion, formed due to bad habits, vestibular plates are used, installed during sleep. Adjacent to the lower anterior incisors, they cause their retrusion.
Important. The vestibular plate prevents mouth breathing. If a child is used to mouth breathing, he may begin to choke and refuse the plate.
In this case, holes of up to 7 mm are made in it, located at the level of the closure of the lips. As the child gets used to nasal breathing, the holes are gradually closed with a quick-hardening polymer.
Reduction or elimination of the sagittal gap is achieved using shield devices.
To eliminate the habit of pushing the bass forward, use a cap with a chin guard. It works more effectively if used simultaneously with the Bruckle device.
In case of significant (more than 3.0 mm) reverse overlap of the anterior teeth, the Brückle apparatus is used. The device is made in the form of a plate equipped with clasps for “sevens” and a vestibular arch for the correction of lower frontal teeth (retrusion). There is also an inclined platform for deflecting the upper “ones” and “twos” in the vestibular direction.
To correct severe dentoalveolar progenia, various orthodontic appliances with similar effects are used. Double Schwarz plate, Frenkel, Wunderer, Hoffmann, Andresen-Goipl activators, Balters bionator. The Frenkel activator, in particular, is a plate for HF and LF, with a vestibular arch and polymer overlays on the chewing teeth.
For the first 1-2 months, function regulators should be worn only 1-2 hours a day. This is necessary for the child to gradually get used to them. Wearing time increases gradually. Subsequently, the devices are worn constantly, removed only during meals.
The period of treatment in children depends on their age, the severity of the anomalies, the device used, and ranges from 1 to 8-10 months.
In permanent bite
Correction of progenia over the age of 12-13 years is difficult, since malocclusion becomes stable by this time.
With a strong dentoalveolar elongation of the anterior segment of the lower dental arch , accompanied by a forward displacement of the lower teeth and deep (to the height of the coronal part or even more) overlap of the anterior teeth, achieving complete success in treatment is doubtful.
Moderate dentoalveolar form is treated with the same orthodontic devices as during the period of mixed dentition. Preference is given to permanent edgewise technology (braces). If necessary, removable devices are connected - plates, mouthguards.
After using the Bruckle apparatus or the Yangel device in combination with the Bruckle activator or extraoral traction (the choice of option is determined by the severity of the anomaly), normal overlapping of the incisors is usually achieved. However, a gap of up to 10 mm can form between the chewing teeth, which is difficult to eliminate.
To facilitate changes in the size of the jaw bones, individual teeth are removed on the LF, and a compactosteotomy is performed on the HF. In some cases, surgical treatment must be used.
The duration of retention after correction depends on the type and severity of the anomaly.
In the video, see the principle of operation of a face mask in the treatment of progenic bite.
Symptoms of mesial occlusion
The most clearly degenerate sign of malocclusion is a strongly protruded jaw. Symptoms can be facial and intraoral and are associated with the following disorders:
- gaping of the mouth;
- angry face in profile;
- chin pushed forward;
- development of speech defects, problems with chewing;
- in some cases, dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint develops;
- reverse incisal overlap;
development of periodontal disease due to improper distribution of load on the teeth.
If, due to an incorrect bite, the teeth have a twisted position, gingivitis, caries, and tartar can form. The patient has a violation of chewing function, and difficulties with prosthetics arise. Also, with mesial occlusion, a characteristic clicking of the jaw often occurs during meals.
Why does curvature occur?
Among the main causes of progeny:
Genetic predisposition. If one of the parents has this problem, then there is a very high probability that the child will also have it.- Anomalies of intrauterine development. Often the disease occurs due to failures that occur at any stage of pregnancy.
- Enlarged tonsils, adenoids. With these problems, a person gets used to breathing through his mouth. Constant improper breathing can cause the lower teeth to move forward.
- Untimely loss/removal of baby teeth, long-term absence of permanent units.
- The habit of biting the upper lip, pathological abrasion of teeth.
- The presence of a cleft palatine, a short hyoid frenulum.
- Facial injuries, jaw fractures, tumor growths.
Complications without treatment
In case of malocclusion, treatment is always necessary, since the pathology is not only accompanied by cosmetic defects, but can also cause various complications, which include:
- improper chewing load leads to rapid wear of tooth enamel, which causes increased sensitivity and the risk of premature loss;
- development of periodontal disease against the background of increased periodontal wear;
- problems with the digestive system due to poorly chewed food;
- underdevelopment of individual facial muscles and the appearance of painful sensations in them;
- premature tooth loss;
- difficulties associated with treatment - prosthetics and implantation.
Also, with an abnormal bite, problems with diction, jaw joints, and the rapid occurrence of infections in the oral cavity may occur. With timely and proper treatment, such complications can be completely eliminated.
Diagnostics
Not all types of progeny are physiological deviations, but the very possibility of effective treatment will depend on the subtleties of their definition. After all, the true form of this process in its final stages is practically impossible to correct.
To clarify the diagnosis:
- anthropometric indicators are taken;
- occlusion of the oral cavity and dentition is assessed;
- They do a functional test that will reveal whether the patient has true or false progeny.
After such clarification, it is revealed how far the deviation occurred from what is considered the norm. They do this with:
- Special rollers.
- Teleradiography.
- Orthopantomography is a panoramic tomography of the dentition, which allows one to obtain a detailed image of all teeth, jaws, and the adjacent part of the facial skeleton.
- Additionally, electromyography of the muscles - masticatory and temporal - is performed to assess involvement in the process and functional disorders in the surrounding tissues.
Sometimes consultation with specialists from related fields of medicine is required. An otolaryngologist or speech therapist may be invited to attend: deviations at certain stages of progeny directly affect the speech apparatus. After all, speech sounds are formed not only by the vocal cords located deep in the larynx, but also with the help of the teeth and tongue.
Treatment of mesial occlusion
Before you begin to correct mesial progeny, it is important to correctly determine its degree and shape. The specifics of treatment also depend on the age of the patient. In children, bite correction is carried out according to a scheme that differs from the method used for adults. Their correction process takes less time. If you or your child is experiencing mesial malocclusion, contact iOrtho Clinic. The clinic uses innovative Invisalign aligners to cope with malocclusions.
Methods of treating pathology in adults
Correction of incorrect jaw position in adults is performed in a comprehensive manner. The most commonly used braces are systems that can be used to change the position of teeth. For severe mesial malocclusion, braces are used in combination with other treatment methods or as a final stage. An alternative to braces can be veneers or aligners.
Also, as a method of correcting a forward jaw, myogymnastics is used, which consists of a set of therapeutic and preventive exercises. They are performed to correct disorders of the dental system. This method is used in adults in combination with other treatment options, and in children it can be used as an independent method when it comes to correcting a primary malocclusion.
As practice shows, mesial occlusion often requires surgical intervention, which involves increasing or decreasing the area of the lower jaw bone. After its completion, rehabilitation is required for a month, compliance with the rules established by a specialist. After surgery, the patient is required to wear braces.
Methods for correcting bites in children
If a child has a mesial bite, the cause of its development must be determined. If the pathology is not congenital, it can be corrected by straightening the length of baby teeth. In other cases, the use of the following orthodontic structures is required:
- double-jaw devices - removable structures that consist of upper and lower plates connected by wires or base material;
- Dilyar's face mask is a device consisting of a metal frame, two supporting pads of soft material, a transverse frame and palatal beams that provide fixation of the jaw;
- twin-block - a device with two removable orthodontic plates, which allows you to change the relationship of the jaws and the shape of the dental arches;
- extraoral devices – tight pressure bandage on the upper lip, face arches, chin sling;
- cervical traction is a type of face bow that affects the dentition.
For malocclusion in children, surgical intervention is extremely rarely required.
Varieties of progeny
Progeny can manifest itself in two forms:
- true;
- false.
True progeny
True progeny is a disorder in which both lateral and anterior teeth are in the reverse bite, and in the case of central occlusion, a space is formed between the front teeth of both dentitions. In this case, the main causes of pathology are developmental anomalies of the lower jaw.
Persons suffering from true progeny face serious disturbances in the functioning of the jaw apparatus. In particular, the unnatural arrangement of antagonist teeth deprives patients of the opportunity to bite off and chew food thoroughly, and excessive protrusion of the lower jaw causes them to experience significant psychological discomfort.
False progeny
False progeny is a malocclusion in which only some front teeth are in reverse relationship. The relative position of the remaining teeth on both jaws remains correct. Examples of false progeny include senile progeny or incomplete fusion of the alveolar processes and palate after surgery.
Prognosis and prevention
The most effective results in correcting malocclusion are achieved during the mixed or primary dentition. If you choose the right treatment method, it is possible to achieve high-quality jaw alignment in adulthood, but it will take more time.
The formation of the bite in infancy plays an important role. It is important to monitor the correctness of breastfeeding, the position of the child during sleep, and prevent the formation of bad oral habits. Timely treatment of disorders that slow down or impair the growth of jaw bones and dental correction is also required.
Consolidation of the results obtained
After treatment, the person must wear permanent retainers. They are thin wires. They are fixed on the back surface of the row so that the teeth do not “creep” into their usual places.
Removable transparent aligners also help to consolidate the achieved results. They need to be worn almost around the clock or put on only at night - the doctor develops the exact scheme for each patient.
As soon as the closure of the rows becomes correct, the client should begin to engage in special gymnastics. It helps strengthen the facial muscles.