When discussing whether caries is dangerous during pregnancy, pregnant women most often have no doubt that the disease negatively affects the baby. However, expectant mothers consider medical intervention even more dangerous, so they often ignore unpleasant symptoms. If treatment is neglected, the disease can progress to an advanced stage, when it is no longer possible to save the teeth, and the entire body is affected by harmful bacteria. Let's look at which diagnostic methods are the safest, and figure out how dentists solve the issue.
Factors causing caries during pregnancy
Women bearing children encounter carious lesions primarily due to exposure to acids produced by pathogenic microorganisms. There is a common belief that oral diseases occur due to calcium and phosphorus deficiency, but this is not true.
The reasons that provoke the problem.
- Hormonal changes. The chemical composition of saliva changes, its protective properties decrease, and the processes of enamel remineralization slow down. She becomes most vulnerable to pathogenic bacteria.
- Poor hygienic care. Expectant mothers, faced with difficulties such as toxicosis or increased fatigue, push hygiene into the background, which leads to the accumulation of dense plaque.
- Poor nutrition. The body does not receive enough of the necessary minerals to maintain healthy teeth.
- Indulgence in high-carbohydrate foods (sweets, flour), sour, carbonated drinks containing sugar contributes to the destruction of the enamel layer.
- Frequent snacks between main meals. Because of this, the acid-base balance worsens.
- Rare visits to the dental clinic. Some women consider the period of bearing a child to be very risky; they are afraid of harming the fetus, so they avoid visiting the doctor. They believe that it is better to endure minor pain than to allow medical intervention. If you do not get rid of the pathology at the initial stage, serious consequences for the mother and baby in the womb are possible.
Effect of X-ray
X-rays are another factor that frightens not only pregnant women, but also ordinary people. There are a lot of myths about the negative impact of x-rays on the human body, and since a woman during pregnancy must take care not only of herself, but also of the new life within herself, it is often because of these myths that she refuses dental treatment, for fear of harming the baby.
Of course, the X-ray procedure must be approached with all seriousness, but in this case you should not be afraid of it. After all, we are talking about a targeted effect, which is strictly aimed at a small area in the oral cavity, while the woman’s chest, neck and stomach are reliably protected by a lead apron. Therefore, we can say that exposure to X-rays is minimized and cannot in any way harm either the baby or the expectant mother.
Why is caries dangerous in pregnant women?
The pathological process is caused by the active growth and reproduction of Actinomyces Naeslundii bacteria. If they are present on the surface of incisors, canines and molars, microorganisms often enter the gastrointestinal tract and blood along with food during meals. The risk of increased uterine tone, dilation of the cervical canal and destruction of the membranes increases.
Thus, any stage of the disease can lead to unplanned premature delivery or miscarriage in the first trimester if measures are not taken in time to eliminate the provoking factors and the teeth are not treated. It is important to stop the destructive activity of pathogens.
How does the process affect the woman and child?
Bacterial flora from the pathological area spreads throughout the body. Pathogens penetrate into the general bloodstream and lead to a deterioration in health. The effect of caries during pregnancy on the fetus is expressed in its abnormal growth and development, and the appearance of congenital anomalies. The baby may be born with various defects and lack of body weight.
Advanced forms of the disease provoke pulpitis and periodontitis. The expectant mother develops characteristic symptoms:
- increase in temperature indicators;
- disorders of the digestive system;
- the appearance or significant increase in the manifestations of toxicosis.
Toothache deserves special attention. This is a painful symptom that leads to psycho-emotional stress and, as a result, negatively affects the course of the gestational process in general and the well-being of the fetus in particular.
Possible complications
Uncomplicated and painless dental caries during early pregnancy does not have any effect on the expectant mother and child. However, in the presence of pain, a woman’s quality of life significantly deteriorates, her emotional state is disrupted, and irritability occurs.
Since hard tissues are destroyed quite quickly, pulpitis or periodontitis often develops. In the absence of timely medical intervention, periostitis of one or both jaws, abscesses, sepsis, phlegmon and other consequences cannot be ruled out.
When infectious and septic complications are observed, the risk of infecting the baby in utero increases significantly. Possible premature birth, endometritis, chorioamnionitis. Ignoring the problem leads to complete or partial destruction of the dental unit and requires its removal followed by prosthetics.
Indications for the procedure
We found out whether teeth are removed during pregnancy and whether it is even possible to carry out such a procedure at this time. Obviously, there needs to be a compelling reason for its appointment. This is a surgical operation, which in the situation under consideration is performed only if there are strict indications:
- infection of surrounding tissues: usually this phenomenon is observed with the rapid development of carious lesions and its complications - pulpitis, periodontitis. That is, when it is not possible to maintain one, and inflammation progresses very quickly,
- severe damage down to the root,
- malignant neoplasms or cysts: in this case, not only removal, but also surgical intervention to remove the tumor may be required,
- unexpected growth of wisdom teeth, which causes damage to its “neighbors” and leads to acute inflammatory processes,
- advanced gum disease: the presence of a serious pathology, which again progresses very quickly, while drug therapy does not produce positive results.
Pulpitis may be an indication for tooth extraction
. Due to painful sensations in the oral cavity, a pregnant woman begins to become very nervous and worried. In addition, this inevitably affects the diet of the expectant mother, which is why the baby involuntarily suffers. Therefore, the issue of dental treatment during pregnancy must be resolved.
Methods for diagnosing caries during pregnancy
If characteristic symptoms are present, the problem can be diagnosed without much difficulty. The main task of various studies is to search for hidden non-carious pathologies and early detection of severe forms of carious lesions that require urgent medical intervention.
The most informative are the following diagnostic techniques.
- Examination of the oral cavity. Contrasting spots and dark holes are observed on the white surface. The doctor uses a dental mirror and probe and may apply specialized chemical solutions.
- Electrodiagnostics. An excellent alternative to x-rays. Based on information about the strength of the electric current, the specialist calculates the depth of the hole.
- Transillumination. Hard tissues are illuminated with a cold light beam, which makes it possible to distinguish diseased structures from healthy ones.
- Laser diagnostics. The dentist looks at how the beam directed at the destroyed layers of enamel is reflected. A safe and informative method for viewing even the most difficult to reach areas.
At the initial stage, the pathology is differentiated from non-carious diseases. For example, with systemic hypoplasia, fluorosis, acid necrosis, chronic pulpitis. If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to a maxillofacial surgeon, periodontist and other specialized specialists.
How does pain relief affect the body of a pregnant woman?
Basically, the harm from local anesthesia during pregnancy comes down to the possible manifestation of allergies.
In dentistry, modern local anesthetics are used, which are practically not absorbed into the blood and do not cause systemic complications.
Those. if a woman is not allergic to a specific drug, then pain relief affects her in the same way as before pregnancy - it numbs the jaw and does not cause unwanted effects.
You should be wary of hypersensitivity. Pregnancy is accompanied by hormonal changes, which can cause allergies in cases where they were not previously observed.
To avoid unwanted reactions, the patient needs to remember what medicine was used to relieve pain before, and during treatment, inform the doctor about deterioration in well-being.
Can X-rays and anesthesia be used?
Does radiation affect pregnancy during caries, how to protect the baby in the womb from harmful effects? Sometimes this method cannot be avoided during therapy, but it is contraindicated during pregnancy. In rare cases, exceptions are possible, but doctors still try not to address them.
Modern equipment used in the Dentika clinic provides minimal radiation doses when using special sensors. If the dentist nevertheless decides to carry out the procedure, the pregnant woman is put on a special lead apron to protect the little person inside. And even with such protective measures, such diagnostics are categorically not recommended.
As for anesthesia, everything is more flexible here. During the gestational period, local agents (external gels and ointments, injections into the gums) are welcome. They are indicated no earlier than from the 14th week, that is, upon completion of the process of formation of the placenta, which protects the baby from external factors.
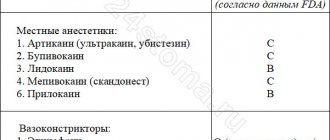
Safe anesthesia for pregnant women
Local anesthetics are used that do not cross the placental barrier. Another requirement for painkillers is a low degree of impact on blood vessels.
Lidocaine is not suitable for expectant mothers, as this drug can cause muscle weakness, cramps and a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
The best option is anesthetics based on anticaine:
- Ubistezin;
- Ultracaine;
- Alfacaine;
- Artifrin.
These drugs do not harm the baby because they act locally. They also have a reduced concentration of vasoconstrictor components (adrenaline, etc.), which is safe for the mother.
Treatment at different times
Having figured out the dangers of caries during pregnancy in mild and severe stages, it becomes obvious that it is impossible to do without high-quality and timely therapy. Most dentists advise urgent treatment of teeth when primary symptoms appear.
Unfortunately, in an “interesting situation” the use of not all medications is permissible. For this reason, the therapeutic regimen should be developed exclusively by a doctor, taking into account the clinical picture, the patient’s condition, her medical history and other prerequisites.
How is caries treated in the first trimester?
This is the most unfavorable time for any medical procedures. The embryo is still very small, it is not protected by the placenta, and is vulnerable to external factors, including diseases of the mother. Obstetricians-gynecologists distinguish 2 main stages:
- From the moment of fertilization to the 3rd gestational week. The baby is sensitive to chemicals and toxins; any treatment can cause a miscarriage.
- Three weeks or later. Human internal organs and systems are formed. The woman suffers from toxicosis, heartburn, and problems with digestive function. Medicines have a bad effect on the development of embryonic structures.
It is better to postpone all events for several months. However, if the process is advanced, severe inflammation has occurred, a steady increase in body temperature and pain is observed, the dentist makes a decision on urgent treatment using the most gentle methods possible, weighing the benefits and possible risks.
How is caries treated in the second trimester?
The likelihood of negative effects on pregnancy is reduced. The expectant mother should closely monitor the condition of her oral cavity, practice daily hygiene and follow preventive measures.
If carious darkening is detected in the initial stages, experts recommend remineralizing therapy. The affected tissues are cleaned of plaque and other deposits, and then covered with special compounds. There is no drill involved, no need to use local anesthesia, and the woman does not experience any discomfort. Subsequently, it is necessary to pay special attention to care procedures and prevent the growth of the affected area.
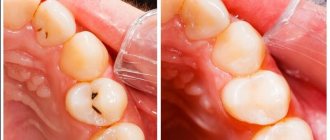
In advanced cases, filling is performed. Pathological areas are removed, the hole is sealed with composite, ceramic and other materials.
When choosing anesthetics, antibiotics and analgesics, their toxicity is taken into account. In general, the so-called equator of pregnancy is considered the safest time for intervention.
How to treat caries in the third trimester
At the final stage of the gestational process, the baby gains weight very quickly. It puts pressure on the mother's vena cava, which leads to surges in blood pressure, fainting and changes in heart rate.
Before giving birth, a woman should not take a semi-recumbent position for a long time, which also makes therapy almost impossible. Dental diseases themselves do not affect the fetus in any way, but the use of certain medications has an irritating effect on the mucous membranes and the entire body as a whole, and can lead to premature birth.
When the doctor performs certain manipulations, the expectant mother becomes very tired, overtired, and feels fear. This often provokes increased uterine contractions and organ tone.
Treatment cannot be avoided if:
- inflammatory process;
- large affected area;
- pain that cannot be eliminated by rinsing with herbal decoctions and other gentle methods;
- steady increase in temperature.
This condition does not have the best effect on the health of the patient and the fetus. The clinic must ensure the most comfortable position of the woman’s body so that the baby does not put its weight on the vessels (aorta and vena cava) of the expectant mother.
Radical measures (extraction, implantation, prosthetics) are taken after the birth of children. The presence of dental diseases is not an obstacle to natural childbirth. Caesarean section is indicated for obstetric indications not related to the oral cavity.
Features of dental treatment for pregnant women
Pregnancy is not an absolute contraindication to any dental procedures. However, the patient must warn the doctor about her situation, and also indicate the exact duration of pregnancy.
Main nuances of therapy:
- while carrying a child, caries, pulpitis, periodontitis and inflammatory gum diseases (gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis) can be treated;
- To fill a tooth, you can use both chemically curing materials and light-curing composites; photopolymer lamps are safe for the fetus;
- enamel bleaching is prohibited;
- Dental treatment is carried out under local anesthesia (injection of Ultracaine, Articaine), the expectant mother must not be allowed to endure terrible pain in the dentist’s office;
- General anesthesia is strictly contraindicated.
How to relieve toothache
If pain suddenly appears due to caries during pregnancy, it is important to visit the clinic as soon as possible. When this cannot be done immediately, it is worth eliminating or at least alleviating the unpleasant symptoms in safe ways. Several effective home methods:
- rinsing the mouth with soda or saline solution, herbal decoctions;
- applying garlic paste wrapped in gauze to the wrists;
- holding a small piece of lard behind the cheek on the side of the diseased unit;
- aloe leaf applied to the site of inflammation;
- plantain juice applied to soft tissues.
From the second trimester, the use of pharmaceutical drugs is permissible. For example, Paracetamol, Kalgel, No-shpa (Drotaverine), Tempalgin show high effectiveness.
But before taking any kind of remedy (including folk remedies), you should consult your doctor. Dentika specialists will compare the benefits and possible harms of using medications, calculate the exact dosages that are safe for the expectant mother and baby, and give other advice on how to prevent negative consequences.
How pregnancy duration affects – choosing a safe period for the procedure
Often, the harm from inaction is much more serious than from a standard dental procedure, which is an extraction. If, during a routine examination, a specialist discovered obvious indications for this procedure, then before removing a diseased tooth, it is necessary to obtain appropriate permission from a gynecologist and therapist.
So, let's talk in more detail about the difficulties and nuances associated with the extraction procedure during different periods of pregnancy:
- first trimester: the first ten weeks are especially important for the healthy development of the fetus. Strong worries about the upcoming treatment, anesthesia and x-ray examination - all this together may not have the most positive effect on the process of development and formation of the child’s basic body systems. On the other hand, severe pain can provoke uterine contractions and hypertonicity, and besides, the risk of spreading infection and developing complications increases too much. In dental practice, it is not uncommon for patients to undergo treatment in the early stages, not knowing about their pregnancy. If the situation is urgent, the doctor will perform the procedure. However, dentists agree that it is better to do everything possible to postpone the removal at least until the last month of the trimester,
- second trimester: at this time the embryo transforms into a full-fledged fetus with sufficiently developed internal organs, including the heart. Now the mother’s stress will not affect the child so much, so this trimester is the optimal time to schedule extraction of the diseased element,
- third trimester: at such a long period, such treatment methods are extremely undesirable, which is mainly due to the risk of uterine contractions and the onset of premature labor.
The second trimester is the optimal time to prescribe extraction of the diseased element.
The first trimester involves the formation of the internal organs of the fetus and the placental barrier, so it is better to postpone medical procedures. In the third trimester, the risk of premature birth increases too much.
“When I was pregnant, I had a tooth removed, though not a wisdom tooth, but still. I think it was week 17. But my dentist is real gold! He also managed to clean three channels so that nothing hurt at all afterwards. After removal, the hole ached for about an hour, and then everything went away. I don’t want to force my opinion on anyone, this is just my personal experience. I always adhere to the principle that the most important thing is the doctor, his experience and professional skills. I was very lucky in this!”
Irishka, 28 years old, fragment from correspondence on the forum
“And it just so happened that in the fifth month my teeth literally began to crumble. Then I was very scared, I kept putting off going to the dentist - I was afraid for the child. In short, I delayed it out of my stupidity. As a result, there was a need for tooth extraction, but I was forbidden to perform the operation. In short, I suffered then. As a result, the dentist in a private clinic was already removing the remaining teeth and was very angry that I had not come earlier. By the way, they gave me good anesthesia; nothing hurt at all, neither during the removal nor afterwards. The temperature did not rise, and everything was fine with the baby.”
Marina A., Tula, fragment from correspondence on the forum
Read our article about how to properly care for your oral cavity after tooth extraction >>>
Preventive measures
The risk of developing caries during pregnancy is significantly reduced if you follow simple rules.
- Even during the planning period, cure all diseases of the oral cavity. Holes in teeth must be properly filled.
- Clean at least twice a day. It is better to do this after each meal (you can use a special rinse aid).
- Pay special attention to removing food debris in the interdental spaces using floss, irrigator, or an ordinary toothpick.
- If you are vomiting from early toxicosis in the first trimester, you do not need to immediately run for a brush. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with clean water, wait about half an hour and only then brush your teeth. Otherwise, abrasion of the enamel will occur.
- Try to eat properly so that the body receives a sufficient amount of vitamins, minerals and other valuable components, without which it is impossible to maintain oral health. Deficiency of essential elements also leads to pathologies of fetal growth and development.
- Avoid snacking. It is better to eat a hearty meal, rinse out the food particles, or clean them out in any convenient way.
- Visit the dentist in a timely manner. Treatment of caries during pregnancy at the spot stage is quite quick and painless. If you start a pathological process, you will have to resort to serious methods that pose a danger to the child in the womb.
Means for healing the hole, approved for pregnant women
It is recommended to refrain from eating for about 3 hours. Immediately after treatment, you should not heat the sore spot - this can only intensify postoperative symptoms and even provoke inflammation. Rinsing your mouth is also contraindicated, since this can damage the blood clot, which is a kind of barrier that protects the open wound from infection.
As for medications, pregnant patients are usually prescribed Paracetamol for pain (0.5 g is the maximum single dosage) and the antiseptic Amoxiclav. A chamomile decoction for mouth rinsing will help relieve signs of inflammation and provide additional disinfection. Before using it, be sure to consult a specialist.
Patients are often prescribed Amoxiclav
Let's sum it up
If a carious lesion is detected during pregnancy, you should not be afraid of dental intervention. Ignoring the problem often leads to the destruction of teeth and their loss. The risk of negative effects on the fetus, premature birth and miscarriage increases. However, not everything is so scary if you consult a specialist at the initial uncomplicated stages of the pathology.
When asked whether caries during pregnancy can be treated for pregnant women both in the early and late stages, doctors give a clear answer - this is a necessary measure to prevent serious complications. Therapeutic and diagnostic methods used in different trimesters may differ slightly.
Wisdom tooth removal during pregnancy: risks and complications
Surgery on the third molar is the most difficult. The procedure itself has a high probability of developing complications, especially in the lower jaw. Extracting the root of a lower extreme molar requires cutting into the gum and removing part of the bone, which is a more traumatic surgical procedure than a simple procedure.
After extirpation of the figure eight, body temperature may rise, severe pain in the jaws, head, neck, throat, swelling of the face and other negative phenomena may occur. The recovery period is long and painful. For these reasons, surgery is performed only in extreme cases: if there is a risk of infection spreading, or if there is severe, ongoing pain.
If it is possible to wait until childbirth or at least until the 2nd trimester, then the extraction of the figure eight is postponed.
Recommendations to help avoid problems
In order not to become one of the pregnant women suffering from gingivitis (and, according to statistics, there are more than 60%), you must adhere to simple rules.
- Carry out the necessary hygiene procedures regularly: brush your teeth using a toothbrush with soft bristles, and do this as thoroughly as possible, use floss and antiseptic rinses.
- Avoid excessive amounts of sweets and consume sweets, chocolate and cakes in moderation. It is strongly recommended to refrain from chewing toffee and caramel, since the remains of viscous delicacies can accumulate in the periodontal space of swollen gums, provoking particularly active proliferation of microorganisms.
- Eat more vegetables and fruits, paying special attention to foods containing vitamin C.
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women cannot be postponed until later. Occurring due to changes in hormonal status and the growth of microbial microflora, it provokes even more active proliferation of bacteria, which in the most severe cases can cause intrauterine infection of the fetus.