What are the features of the eruption of “temporary” teeth?
Baby teething normally occurs at six months of age. The first sign of this process is the formation of a dental tubercle on the edge of the gum. This occurs as a result of pressure on the mucous membrane - it gradually stretches, becomes thinner and a breakthrough occurs. Then you can see the edge of the crown of the new tooth above the gum. As soon as the entire crown appears above the gum cavity, this is the eruption of the tooth.
In various sources you can find exact dates for teething, but they are arbitrary. Any discrepancies with them depend on the individual developmental characteristics of the baby. There is no need to worry if your child's first tooth appears later or earlier than his peers. Teething is a natural process that occurs on an individual schedule.
Did you know that baby teeth have roots? It’s just that by the time they begin to fall out, they resolve on their own. If sometimes a tooth has to be removed before its natural loss occurs, its root can be seen.
In erupted baby teeth, the formation of roots occurs according to the following scheme:
- The formation of the roots of the incisors occurs by the age of two.
- The roots of the molars will be fully formed by the age of 4 years.
- The formation of the roots of the fangs occurs by the age of 5 years.
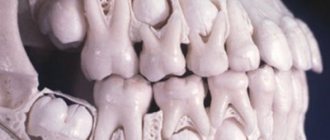
Eruption of baby teeth and their number
It is normal for the first tooth to appear at six months of age. A harbinger of this is the formation of a small bulge, a tubercle, on the surface of the child’s gum. After some time, the gum in this place will become thinner, and the growing tooth will appear through it. Full eruption occurs when the gum ruptures and the crown of the primary tooth emerges.
In accordance with the generally accepted standard, a baby’s teeth should appear at specific times and in a certain sequence. But these figures are very conditional, and small deviations in any direction are not critical.
It was previously believed that late teething was a sign of developmental delay. But it has now been established that children whose baby teeth began to appear late are in no way behind their “toothy” peers.
Late eruption of the first teeth can be determined at the genetic level, or be a consequence of an infectious disease or a lack of vitamins. The lower incisors most often appear earlier than expected. There are cases when a child was born with them.
Diagram of baby teeth eruption in children
In any case, by the age of 2.5 – 3 years, a person grows 20 milk teeth:
- 4 lower incisors;
- 4 upper incisors;
- 4 fangs;
- 8 molars.
This is their normal number. During the change to permanent teeth, the same amount falls out and is replaced by new, stronger teeth, plus another 8 to 12 teeth grow (including wisdom teeth). Thus, children change 20 teeth.
What is the approximate timing of teething in children?
The timing of teething is influenced by the child’s intrauterine development, because the process of their mineralization occurs even before the baby is born. The health of baby teeth, as well as permanent teeth, and the timing of their eruption depend on the course of pregnancy.
As teeth grow, mineral accumulation and root growth continue in their crowns. Their growth stops after they are fully formed. The duration of this dormant period lasts until approximately three years of age.
Important: If a baby tooth has been treated, very often slower resorption of its root occurs. Therefore, as soon as the time has come for it to fall out, it will continue to be in its original place. In such cases, it needs to be removed to make room for further growth of the permanent tooth.
Based on their numerous observations, the approximate timing of teething in children has been established:
At 6-8 months of age, the child begins to erupt the lower and upper central incisors.- From 8 to 14 months, the baby develops lateral incisors (2 upper and 2 lower).
- The eruption of the first molars occurs at 12-16 months. At the same time, gaps remain between them and the incisors for future fangs.
- The appearance of fangs occurs between 16 and 24 months.
- Eruption of the second molars occurs from 20 to 30 months.
At 2-2.5 years of age, a baby should have 20 teeth:
- 8 incisors;
- 8 molars;
- 4 fangs.
Sometimes teething may occur in the wrong direction. By the age of three, when the dentition is fully formed, the baby is actively chewing food, and they return to their normal position.
Important: The timing of teething is different for each child. There is no need to panic if by the age of three your child does not yet have a full set of teeth. But if the baby has no teeth at all by the age of one year, be sure to consult a pediatrician who will help you find out the possible reasons for the delay in teething.
Similar problems are possible due to some diseases:
- Disruption of metabolic processes in the body.
- Rickets.
- Endocrine diseases.
With such diseases, the following symptoms may occur:
- Late closure of fontanelles.
- Child growth retardation.
- Curvature of the legs.
Carefully examine your baby's gums: they should be red and swollen. To help your baby speed up the teething process and relieve pain, you can buy special teething toys. They cool easily, and the coolness perfectly relieves pain and itching from the gums. Children chew such rings with great pleasure, thereby speeding up the eruption of their first teeth.
You should definitely show your baby to an endocrinologist in the following cases:
- The baby was born with teeth.
- The eruption of the first teeth occurred before the age of 3 months.
The order in which primary teeth appear is extremely important because it influences the formation of the bite. Heredity plays a primary role in this case. If mom or dad's teeth grew incorrectly, then there is a high probability that their child will experience the same thing.
Causes of missing teeth or late eruption
Main reasons:
- Deficiency of minerals (calcium, vitamin D).
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, rickets, thyroid diseases.
- Metabolic disease.
- The so-called congenital adentia, when the rudiments of teeth are absent
If teeth have not yet made themselves felt at 1 year of age, the doctor will take an x-ray. If rudiments (roots) are detected, he will most likely prescribe medications or a diet containing calcium and vitamin D, as well as phosphorus. If an x-ray shows the absence of tooth rudiments, then at the age of two years the child will have to have removable dentures, and at an older age - implants.
It is impossible to speed up teething, but it is quite possible to help the baby cope.
Problems that arise during teething in children
During the teething process you may encounter the following problems:
- Late or early appearance.
Most often, early teething can occur with the lower central incisors. Sometimes a child may already be born with them.
Late teething is possible due to poor nutrition of the child, as well as past illnesses and concomitant chronic pathologies.
- Violation of the order and pairing of teeth eruption.
It is also possible that one or more teeth are missing from the dentition. This situation is possible due to the death of the embryos during the prenatal period of the baby’s development.
- Increase in temperature during teething.
How to alleviate the baby’s condition and help him endure the pain?
Recommendations:
- Prepare teethers in the form of toys. The most popular are food-grade silicone, as well as items filled with water that need to be pre-cooled.
- Take care of the baby's environmental hygiene. Because he puts everything in his mouth, and his gums are inflamed, there is a risk of infection.
- Gum massage can be done using your fingers or wet gauze.
- Give older children cookies or fruit more often.
- Special gels (Kalgel, Kamistad, Doctorbaby) give a short-term effect. You need to smear them not according to schedule, but when it hurts. Consult your physician before purchasing. Also, there are painkillers specifically for children (Dentokind).
- Apply to the chest more often , provide attention, play and distract.
- Ventilate the room more often for the overall well-being of the child.
- As an antipyretic, paracetamol is allowed for young children.
Reasons to call a doctor:
- increased body temperature over 39 degrees;
- loose stools more than 6 times with abnormal green or bloody stools;
- frequent vomiting;
- yellow or green runny nose;
- continuous tearful state;
- hematomas on the gums;
Differences between baby and permanent teeth
The structure and shape of “temporary” and permanent teeth are very similar, but there are still some differences:
- The enamel of a baby tooth is much thinner compared to a permanent tooth.
- Smaller crown sizes.
- The pulp is larger in volume.
- The root canals are much wider.
- The divergence of the roots occurs because between them there are the rudiments of permanent teeth.
Parents are often interested in how many baby teeth a child should have, and worry if the baby doesn’t have a single incisor per year. The dentist will tell you whether this is normal or a sign of illness; you should not make a diagnosis yourself. There are children whose teeth appear even after one and a half years. Each child’s body is individual, and development does not always fit into generally accepted frameworks.
The process of teething is unpleasant for babies, and parents have more questions than answers. We will try to cover topics of interest, including the number of baby teeth at different ages and the timing when they begin to be replaced by permanent ones.
Milk teeth – what are they?
This name was given to milk teeth by Hippocrates. He justified this by the fact that the first teeth are formed from milk, because it is the main food of young children.
And in some ways he was right. Milk contains a large amount of calcium, which is necessary for the formation of teeth.
In addition, the first teeth are not strong and are easily destroyed if the baby does not eat properly.
The rudiments of baby teeth appear in babies in the womb, at about 10-12 weeks of the first trimester of pregnancy, and by the end of the second trimester the incisors are already fully formed.
Primary and permanent teeth are very similar, but there are still several differences between them:
- the crowns of the first teeth are smaller;
- baby teeth have thinner enamel (which is why they are destroyed very quickly, and by the age of 5-6 they fall out on their own, without causing any discomfort to the child);
- The roots diverge slightly and begin to dissolve before the permanent teeth grow.
Many parents think that there are no nerves in baby teeth, but this is absolutely not true. In many children, the nerve endings are destroyed very early, so children do not feel pain in the area of a tooth that is already completely destroyed.
Why are baby teeth needed, their difference from permanent teeth
Temporary teeth - canines, molars, lateral and central incisors, which are replaced by molars. Their appearance is a painful process, which is accompanied by a decrease in immunity. But they are also important for the baby. The purpose of temporary incisors, canines and molars is to:
- ability to chew food;
- proper speech development;
- formation of the facial skeleton and bite;
- acquiring chewing skills;
- aesthetics of the oral cavity.
The main difference from permanent ones is their ability to quickly break down. If an adult loses a tooth, he will experience pain in its place for a long time. When baby incisors begin to change, this does not happen: during the period of loss, they become loose, and therefore children do not notice their loss. Parents have the incorrect opinion that incisors do not have nerves or roots. This myth is based on the fact that temporary teeth fall out painlessly. However, from a dental point of view, these two facts are in no way related to each other.
Although temporary incisors fall out, they need to be cared for after the first one appears. You should not think that they do not need cleaning and care, since they are not permanent anyway. The condition of the temporary incisors will also determine the condition of the molars. If dental diseases appear, you should consult a doctor, as they provoke an incorrect bite or jaw structure.
If you look at the outside of a child’s mouth, you will notice that permanent teeth are not much different from temporary teeth. But there is a difference. Primary canines, molars and incisors have the following features:
- thin enamel;
- the crown is smaller;
- the pulp is larger;
- milky shade;
- they are susceptible to caries;
- located vertically;
- divergence of roots due to molars;
- wide channels.
The number of baby teeth in children is also excellent: there are only 20 of them, and 32 permanent ones. They make up the chewing row.
Possible problems with deviations from the norm
Complete edentia is a case when teeth are completely absent.
Regardless of the fact that the molars have just appeared or are about to erupt in the mouth of their beloved child, parents should be vigilant, because there are many dental problems. The main issue is the delay in the growth of permanent teeth (a baby tooth has fallen out, but a new one has not appeared).
The reason may lie in a genetic predisposition or edentia, which arose due to a violation of the formation of rudiments during intrauterine development. If there is no way to influence the situation, the child is indicated for prosthetics.
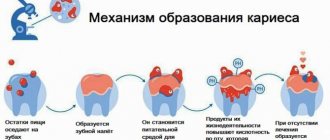
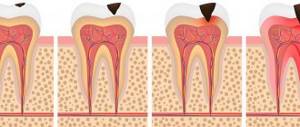
When permanent teeth erupt, another problem may arise – pain. This is most often due to thin, not fully formed enamel, which does not have sufficient mineralization. It is at this stage that the tooth is susceptible to various diseases, in particular caries.
With deep destruction of dental tissues, even more serious diseases develop: pulpitis, periodontitis. Therefore, you cannot ignore a child’s toothache; you need to make an appointment with a pediatric dentist as soon as possible.
At the very beginning of the growth of permanent teeth, other problems can occur:
- loss of a root unit is a signal of serious problems with the child’s health;
- an increase in the level of trauma - the active lifestyle of children during the period of maturation of molars often leads to injury to the incisors and canines, and attempts to chew hard objects end in the breakage of molars and premolars.
Each case requires the intervention of a specialist to eliminate the negative consequences.
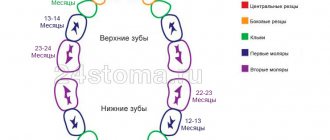
Sequence and timing of teething
Typically, incisors appear by 6 months, and by three years the process is completed. Their sequence follows a special schedule. But small deviations are the norm, as children develop individually. If the order of appearance with the pattern differs significantly, it is recommended to see a doctor.
Tip: You should visit the pediatric dentist once a year to prevent abnormal jaw structure and other diseases.
It is normal if the child has at least one incisor out before he is one year old. Deviations up and down are acceptable for 4-6 months. According to the eruption pattern, they appear in the following sequence:
- central incisors – 6-9 months;
- lateral teeth – 9-13 months;
- first molars – a year and a half;
- fangs – 18-20 months;
- second upper and lower molars – 20-30 months.
When teething, the genetic factor is important: if one of the baby’s parents began to have teeth at 7-8 months, then the child’s teeth will begin to grow at the same age. If their chewing row was formed incorrectly, then the same thing awaits the child.
The order of eruption of all baby teeth
We have already established which teeth come out per year. Ideally, there should be 8 of them, and these are incisors. By the age of one and a half years, 4 first molars (two each on the upper and lower jaw) and 4 canines are added to them. A total of 16 pieces.
Between the ages of 2 and 3 years, 4 more second molars erupt. In total, there should be 20 units in the milk bite.
Read about the timing of the eruption of permanent teeth in the feature article on the website.
How many baby teeth should children have?
There are 20 teeth in total, but the proper order of appearance is excellent. There are newborns who have two lower incisors. This is not a pathology, but a phenomenon indicating the normal development of the baby. But such cases are rare in practice.
The rate at which incisors appear depends on many factors, including the course of pregnancy. After all, at 7-13 weeks their formation begins, and by the last trimester mineralization occurs. To maintain strength, doctors prescribe calcium to women. Dentists recommend following this calculation formula: subtract 6 from the baby’s age in months, and you will get the number of baby teeth needed.
Number of teeth in 1-3 years
The process of their appearance is individual. By the age of one year, the baby has incisors (8 pieces). Do not exclude that some babies do not have a single tooth by 12 months. It is not uncommon for a baby to have no incisors until he is one year old, and then after three months all of them appear at once.
By the age of two, the baby acquires molars (8 pieces). That is, by this time there should be 16 of them. 4 fangs with normal development appear by 1.5-2 years. Typically, a child’s dentition is formed at 2-2.5 years. Parents have noticed that children have goals between their teeth, but after three years they begin to align and fit closer to each other.
Number of teeth at 4-6 years
In order to determine how many teeth a child has at 4 years old, you need to go to the doctor, since it is not easy to count them yourself. By this age, all teeth appear. There are 20 of them in total:
- 8 incisors;
- 8 molars;
- 4 fangs.
If at the age of four there are not even incisors or they have not all erupted, you need to consult a doctor, as this indicates pathology. Their late appearance indicates frequent illnesses of the baby or poor nutrition.
Reasons for late eruption:
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- genetics;
- rickets;
- developmental delay;
- bowed legs;
- metabolic disorder;
- damage to the pituitary gland.
The process of teething is individual for each baby. It is impossible to say exactly how many baby teeth children should grow in the first year of life: some may have 10 of them, while others may not have any. And any of these indicators is considered the norm. In total, by the age of 3, the baby should have 20 baby teeth.
How many teeth should a child have at 3 years old?
All twenty baby teeth appear by about 2-2.5 years. It includes eight incisors and molars, as well as four canines. By this time, they are erupting, including in the wrong direction, but by the age of three, in most cases they occupy a normal position, since the child is actively chewing food.
If by the age of three a boy or girl does not have a full set, do not panic. This may be an individual characteristic of the child. To be sure, it is advisable to consult a pediatrician and dentist to clarify the cause of the delay and rule out rickets, metabolic disorders or endocrine diseases.
Much depends on heredity
When and how many baby teeth a child will have depends on many factors, but mainly on heredity. If one of the parents got their first tooth after 6 months, then most likely the baby should not wait for the early appearance of teeth. Much depends on how the baby’s mother ate throughout pregnancy. The formation of teeth occurs in the first trimester. It is during this period that it is necessary to saturate the body with calcium and potassium, if this is not done the child will take his own from the mother’s body. It often happens that after pregnancy and childbirth, a woman’s teeth deteriorate greatly - this is a sign that she has a lack of important microelements for the formation of the child’s teeth and skeletal system. The expectant mother should eat fish, cottage cheese, hard cheese, sour cream, and drink kefir.
In any case, the baby's first milk tooth will definitely appear in due time. This is always a joyful and touching moment that will forever remain in the memory of the child’s parents. It often happens that already at 3-4 months the baby’s first central incisor appears. And in some children it appears only after a year.
As pediatricians explain, in most cases a child should have 8 teeth per year. Baby teeth appear according to the following average statistical schedule:
- 6 -7 months - lower incisors - 2 pcs.;
- 8-9 months - upper incisors - 2 pcs.;
- 10-12 months - 2 upper lateral incisors;
- 11-13 months - 2 lower lateral incisors;
- 12-15 months - there should be 4 more teeth - the first molars appear;
- 18-20 months - 2 upper and lower canines erupt;
- 20-30 months - 4 more teeth appear - 2 upper and lower molars.
Dependence of the number of teeth on the baby’s age
The difference in the period of eruption of each pair of teeth in different children can reach 4–6 months. Therefore, the conditional schedule of their appearance does not contain the specific age of the child, but certain intervals.
So, how many teeth will a child have depending on age:
- At ten months , a child has at least 2 teeth. Usually these are the lower central incisors, but exceptions are not uncommon. If the first milk teeth appear late, they do not always erupt in the correct order. So, for example, one lower and one upper incisor or 2 central upper incisors may appear first. By the age of 10 months, most children already have 2 teeth above and 2 below, and some have already erupted 4 upper and 4 lower incisors by this time.
- By the time a child turns one year old , he already has 6–8 teeth. For some, the upper primary molars begin to erupt by this time. But most often, a one-year-old child has fully erupted 4 upper incisors and 2 lower ones.
- It is believed that normally, by the time a child turns 2 years old, all 20 baby teeth should have erupted. But as mentioned earlier, the development of each child is individual. And if the baby’s first teeth appeared not at 6 months, but later, then it is likely that by the age of two, instead of 20 teeth, he will have only 16.
- By the age of three, the child has probably already erupted all of his baby teeth. If previously there was a fairly large distance between them or they grew at an angle, now the teeth are aligned, occupy the correct position, and are more closely adjacent to each other.
- By age 4, children usually have a full set of baby teeth. After the 20th tooth has erupted, their number does not change until replacement with molars begins.
- At the age of five, some children already begin to replace their baby teeth with molars. This happens in the same order in which they erupted. That is, first the baby incisors fall out and permanent teeth grow in their place. In addition, at the age of 5, the 21st and 22nd teeth – molars – may begin to appear. This means that the number of teeth at this age can be different for different children: from 19 (if baby teeth have begun to fall out) to 22 or 24.
The missing teeth will certainly erupt. As a last resort, you can visit the dentist and make sure that everything is fine with the baby and his teeth.
Baby teeth begin to form in the womb.
They begin to erupt in young children aged 4 months and older.
Every parent should know how many baby teeth a little person should have, and what is the monthly schedule for their eruption.
- Milk teeth – what are they?
- How many baby teeth should children have?
- Teething schedule
- How to help your baby when he is teething?
- Do baby teeth need to be treated?
- Video on the topic
We calculate using the formula
Teething symptoms:
- temperature;
- general weakness and lethargy;
- tearfulness;
- increased salivation;
- The baby puts everything in his mouth and wants to scratch his gums.
Often, to calm the baby, the pediatrician prescribes homeopathic tablets, the use of special cooling gels for the gums, and rubber teethers. If the body temperature rises to 38°C, you can give the child an antipyretic drug. But in any case, the best way to calm the baby during this period is to pick it up or put it on your chest. The appearance of the first tooth is stressful for a little person; it is important to calm him down, hug him, and be attentive and loving parents.
It’s only for the first six months that parents wait for the teeth to appear, then they will grow so quickly that you won’t notice it. What you should pay attention to is the severe delay in the eruption of baby teeth. If after 10 months the baby does not show signs of their appearance, you should contact your pediatrician or pediatric dentist to rule out causes of delayed development such as rickets or a lack of a certain group of vitamins.
To do this, you need to subtract 4 from the number of months the baby has lived. The result means the number of teeth placed. For example, the baby is 11 months old. You need to subtract 4 from 11, you get 7. This means that at 11 months the baby should have 7 teeth: 4 central incisors, 2 upper laterals and 1 lower lateral. The main thing is not to take such calculations too seriously. Naturally, this formula corresponds to the norm, calculates the average number of teeth, and each child is individual.
Symptoms indicating the imminent appearance of baby teeth
Main symptoms:
- Redness and swollen gums.
- Heavy salivation.
- Increased excitability.
- Intestinal disorders.
- Fever, runny nose, cough.
- The child aggressively chews toys or bites the breast during feeding.
Some signs can be confused with an incipient viral or other disease, so you need to pay attention to all the symptoms and see a pediatrician if in doubt.
We start cleaning in a year
From 3 to 7 years old, a child’s mouth should have 20 baby teeth. Around the first grade of school, and maybe a little earlier, baby teeth begin to fall out and are replaced by molars.
Many parents believe that if their child’s teeth change, then they don’t need to take care of their baby teeth at all. This is a misconception. In addition to regular brushing, these teeth need to be treated. So, if a child has a toothache, it is necessary to contact a dentist who will cure it and put a filling. It’s even better for your child to go to the dentist at least once a year so that the doctor examines the oral cavity, evaluates the location of the teeth, and determines whether there are any problems with the frenulum. You should definitely visit a doctor and during the period of changing teeth, your child may need to wear leveling braces. All details can be found out from the dentist.
It is important to monitor compliance with the following rules:
- be sure to ensure that your baby’s diet contains foods rich in potassium and calcium - dairy products, cottage cheese, fish and fresh vegetables;
- brush your teeth regularly;
- do not give sweets to your child under 3 years of age;
- be sure to offer to chew an apple or carrot to strengthen the enamel;
- Do not give sweet drinks at night.
You need to take care of your baby’s oral cavity from the time the first tooth appears. You can wipe it with gauze, and when there are more teeth, buy a special baby brush at the pharmacy that you can put on mom’s finger and brush your teeth thoroughly. After a year, you need to buy your child his own toothbrush and toothpaste and show him how to brush his teeth. At any age, if your child has a toothache, take him to the dentist immediately. The main thing that young parents should be concerned about is not the timing of their child’s teeth and how many teeth they will have, but that they grow up strong and healthy.
A child's first teeth appear around the sixth month of his life. By the age of three, an almost complete set is already “observed” in the baby’s mouth. How many baby teeth do children have? When does the shift start? What time period does the whole process take and how to care for the oral cavity during this period? These are the questions that concern mothers of many first-born children.
What does missing teeth in a year mean?
If a child does not grow a single tooth in a year, this may indicate congenital adentia, that is, milk units may not appear at all. This is a rare anomaly, but it cannot be completely ruled out. You can find out about this only by taking an x-ray. The absence of milk units before the age of one year may indicate such deviations as retention or dystopia, when the rudiments of teeth in the jaw bone occupy an incorrect location and do not break out.
If the process of teething is very slow, and the number of teeth per year is significantly less than eight, then this indicates anomalies in the development of the baby in the prenatal period or the presence of internal diseases of the body. The pathology is often associated with disorders of mineral metabolism and dysfunction of the endocrine system.
How many baby teeth should children have?
By the age of three, the mother can see quite a lot of teeth in the baby’s mouth. This is a milk kit, which will later be replaced with a permanent one. If we talk about exactly how many baby teeth the baby has at this moment, then there are twenty of them.
In both the top and bottom rows, the child should already have (location from the “edge”):
- two molars;
- fang;
- lateral incisor;
- pair of central incisors;
- lateral incisor;
- fang;
- two molars.
They are located symmetrically relative to each other. And on each jaw there are ten “instances”.
In very rare cases, the milk kit turns out to be incomplete, i.e. the number of teeth does not reach the “required” twenty. If the baby is already one year and three months old, and there is a lot of free space left on the gums, then it needs to be shown to the dentist. It is likely that the baby does not have the rudiments of some representatives of the dairy family. Only a specialist can confirm or refute the mother’s guesses.
Do baby teeth need to be treated?
Baby teeth need to be given special attention, because without proper care they quickly deteriorate.
If you notice that a black spot has appeared on your child's tooth, contact your dentist.
The appearance of baby teeth is a big event in the family, and it should be given special attention. Make notes about which tooth appeared and at what age, and if there are any deviations from the norm, consult your dentist and pediatrician. Teach your child to take care of his teeth from early childhood.
Replacing the milk kit with a permanent one
It is important to know that the “sixes” are the first to grow out of the permanent set. “Fours” and “fives” from the dairy series are not indigenous and in any case will have to be replaced. Therefore, there should be no concern about loosening of the molars. This is the norm.
For children, the entire temporary set must be replaced. To avoid mistakes, you can save all the “pearls” that fall out. And when all twenty dairy representatives are “on hand”, then we can talk about the completion of the process.
In principle, an adult should not have baby teeth in his mouth, but there are exceptions. The reason here is the absence of a permanent tooth germ, which automatically preserves the milk one.
Dr. E. O. Komarovsky reminds us that the “wrong” sequence when a permanent set appears is not a pathology!
Helping your baby when his first teeth are cutting
The most difficult period in a baby's life is when his first incisors come out. For most children, this happens before they turn one. At 4–6 months, the baby’s behavior and mood can change dramatically due to the fact that the gums in the area of the erupting units become inflamed, painful and itchy. The baby becomes too capricious, refuses to eat, sleeps poorly, and his mouth is watering. Many attentive parents also notice that the baby begins to cough, has diarrhea and a runny nose. What to do in this situation? A number of rules must be followed.
Rule #1: Don't be nervous.
Children sense a change in the mood of their parents, especially their mother, and begin to be even more capricious. Give your baby maximum attention, do not show aggression or irritation.
Rule #2: Ease Teething Signs
Special cooling and anti-inflammatory gels (for example, “Kamistad Baby”) and teethers will help with this. Instead of teethers from the pharmacy, pieces of hard vegetables and fruits wrapped in a special mesh or gauze are suitable.
Rule No. 3. Closely monitor the child’s condition
Diarrhea, fever, runny nose and cough may well be signs of teething. But these symptoms may also indicate various viral and infectious diseases. If you suspect an acute respiratory viral infection or an intestinal infection, it is better to call an ambulance.
Reasons to call a doctor: fever, vomiting, loose stools more than 5-6 times a day (or if blood is found in the stool), frequent and opaque nasal discharge, a “barking” choking cough.
Rule No. 4. Carefully monitor personal and general hygiene
Wash your hands before applying gel to your baby's gums to relieve teething symptoms. Disinfect all objects that surround the baby, because he puts everything in his mouth. If hygiene is not observed, there is a risk of infection and the child may develop stomatitis.
Oral care while changing teeth
Every child should be able to take care of their oral cavity. But from the moment the teeth become loose, this process must be treated with special care:
- It is advisable to use a toothbrush after every meal;
- the oral cavity should be rinsed with herbal infusions;
- Tooth enamel must be monitored more carefully and treated if caries appears.
- if the parents’ teeth began to fall out late, then there is a high probability that the baby’s milk set will begin to loosen later than usual;
- caries must be treated even on baby teeth;
- There is no need to worry if the change in the milk series goes in the wrong order (for example, instead of the incisors, the fangs will fall out first).
It is very important to provide adequate nutrition during this period; in particular, the child’s diet should contain foods containing a lot of calcium, vitamin D and phosphorus. In order to stimulate the resorption of the roots of the milk set, it is necessary to give the child fresh vegetables and fruits.
Dangerous consequences of the problem when there are no teeth on time
For different children, the number of teeth at 1 year can vary from 4 to 8. If there are fewer of them, and they erupt significantly later than the dates indicated by WHO, then, most likely, the remaining units (molars and canines) will also be delayed.
The lack of milk elements by the time the baby begins to eat food, which must be chewed thoroughly, leads to problems: food is not chewed fully, individual units of the series are subject to excessive load, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint (temporomandibular joint) occur.
The defect can cause problems with speech and pronunciation of various sounds. If the order and timing of teething is violated, the child’s bite may be disturbed, and disproportion and asymmetry of the face may occur.
When do baby teeth fall out?
At about five to six years of age, teeth change. For some kindergarten children, this occurs earlier, at 4 years old. But this process also proceeds in its own way, and therefore the time periods are indicated arbitrarily. The process does not cause pain and does not bother the baby. But sometimes a situation happens when the incisor cannot fall out, and the permanent one is in a hurry to take its place. Then you need to consult a dentist.
Fact: if a baby tooth has been treated, it will fall out for a long time. Sometimes the incisors are removed using an anesthetic.
The change of the chewing row occurs in the same order as eruption. Before the age of 14, a teenager must change his entire row. From 6 to 9 years, 8 incisors fall out, from 9 to 11 - the first molars and canines, the second molars appear up to 14 years.
Humans have 32 molars. The remaining 12 erupt at the time of replacement of incisors, canines and molars. The first 4 of them appear at 5-6 years of age, before the temporary incisors have time to fall out. The last third pair (wisdom teeth) appears late in a person and can erupt until the age of 30. Their appearance provokes painful sensations.
The article touched upon interesting questions that concern parents of newborns: how many baby teeth should children have when they erupt and gradually fall out.